1. 引言
太阳能集热热水器拥有很长的应用和研究历史,然而能同时产生电能和热能的太阳能光伏/光热复合集热系统(简称PV/T系统)直到近30年[1] 才被提出并引起诸多研究者的关注 [2] - [4] 。太阳能光伏/光热复合集热器(简称PV/T集热器)为PV/T系统的核心部件,它将太阳能集热组件与光伏组件合二为一,能同时产生电能和热能并提高太阳能的利用率。目前国内外对PV/T热水系统的经济性研究主要包括:文献 [5] 采用电子表格的方法分析太阳能热水系统的寿命周期、寿命周期成本。文献 [6] 根据印度的气象数据对主动式和被动式PV/T太阳能蒸发器进行经济性分析。文献 [7] 根据希腊的气象数据对PV/T系统的单位面积投资成本、投资回收期等方面进行分析,得出多晶硅PV/T系统的投资回收期小于10 a。文献 [8] 运用SimaPro 5.1软件,用生命周期法分析不同温度下的投资回收期,得出PV/T系统的投资成本效益高。以上的经济性研究不足之处均是对集热器的年产热量或者发电量进行估算,以此计算太阳能集热器年收益值。本文在动态系统模拟软件TRNSYS (Transient System Simulation Program) [9] 的平台上建立太阳能光伏/光热复合家用热水系统模型,对全年发电和产热量进行全年逐时模拟,并进行经济性评价,为我国太阳能光伏/光热复合家用热水系统的应用提供参考。
2. 系统模型
本文建立的太阳能光伏/光热复合家用热水系统为典型的家庭热水系统,如图1所示,包括PV/T复合集热器(光伏电池组、管板式热水通道)、保温水箱、上/下循环管,蓄电池、控制器和逆变器等部件。用热水人数为4人,24小时供生活热水,生活热水的使用水温为40℃ [10] ,日热水用水量小时变化与家庭成员结构、作息规律、生活习惯等因素有关,热水用水量小时变化曲线如图2所示 [11] ,若生活热水的出水温度达不到使用要求,则开启辅助电加热器进行补偿。光伏组件发电不并网,光伏组件的采光面积依据满足热水需求的设计采光面积而定,配备蓄电池,用于日常家用电器供电,不足部分由市电供给。根据中国标准气象数据 [12] ,以长沙地区为例经过计算 [10] ,太阳能集热器采光面积取2 m2,外形尺寸为
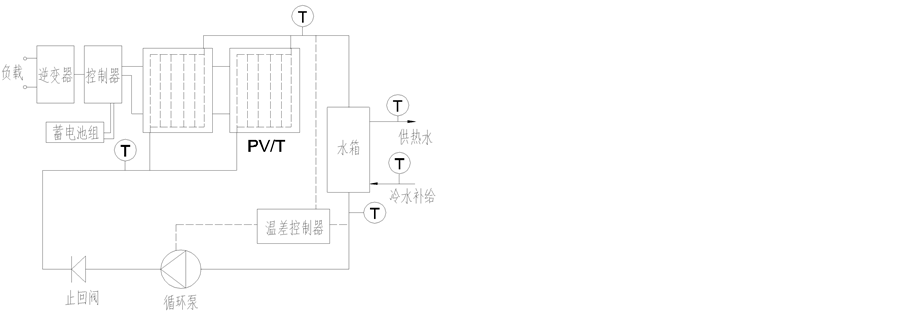
Figure 1. Schematic of PV/T hybrid domestic hot water system
图1. PV/T复合家用热水系统示意图

Figure 2. Daily change curve of hot water consumption
图2. 日热水用水量小时变化曲线
2000 × 1000 mm2,2台集热器并联。光伏组件采用多晶硅电池片,单片面积为156 × 156 mm2,72片(6 × 12),单台集热器的电池有效采光面积为1.752 m2,最大功率为250 w。水箱容积取200 L,辅助电功率为1500 W。
PV/T复合家用热水系统模型在TRNSYS中的模块连接示意图如图3,主要包括PV/T复合集热器模块、气象数据处理模块Type15-3、用于参数计算的运算器、能量计算的积分模块Type24、保温水箱Type4c、温控分流及合流三通Type11、控制模块Type2b、循环泵模块Type3b和用水模式Type14b,其中PV/T复合集热器模块为TRNSYS自编模块,其数学模型及其计算流程见文献 [13] 所示。气象数据处理模块Type15-3采用的气象数据来自于EnergyPlus [14] 根据中国标准气象数据 [12] 整理成的数据格式,输出长沙地区冷水月平均温度和月总辐射分布如图4。
3. 经济性分析
3.1. 系统能耗分析
太阳能光伏/光热复合家用热水系统的能耗主要包括全年辅助电加热能耗和循环泵能耗,能量收益包括全年热水产热量和发电量。通过模拟计算,系统运行1 a的热水产热量为1296 KWh,电辅助加热耗热

Figure 3. TRNSYS information flow diagram for the PV/T hybrid domestic hot water system
图3. PV/T复合家用热水系统的TRNSYS模块连接示意图

Figure 4. Mean monthly temperature of cold water and total radiation
图4. 冷水月平均温度和月总辐射
量为1361 KWh,发电量为292 KWh,循环水泵功耗为24 KWh,热水需热量为2411 KWh。图5为产热量、电辅助耗热量、发电量和热水需热量的月平均值。由图5得出,系统热水产热量月均值最大值出现在7月份,热水需热量最小值的月份同时也是7月,7月电辅助能耗值最小,12月至3月电辅助能耗相对较大,系统全年使用热水的太阳能保证率约为0.44。
3.2. 综合能源价格现值
综合能源价格是一个将初投资考虑在内的全面反映经济分析对象相对于提供单位能量所需费用的参数。基于李军 [15] 提出的太阳能热水器综合能源价格现值的表达式,本文研究的太阳能光伏/光热复合家
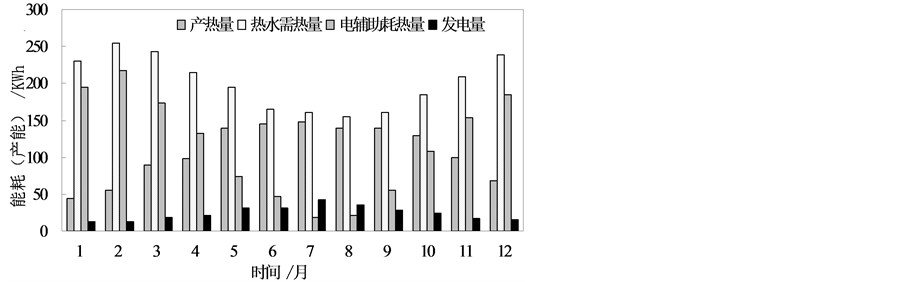
Figure 5. Monthly average energy consumption and power generation of the system
图5. 系统各项能耗及发电量月平均值
用热水系统的寿命周期内综合能源价格现值可以表示为:
 (1)
(1)
式中,M——综合能源价格现值,元/KWh;V——将安装等费用计入的热水系统初投资,元/台;t——计算年数,a;n——热水器寿命周期,a;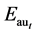 、
、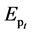 和
和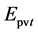 ——第t年电辅助加热耗热量、循环泵功耗和发电量,KWh/a;
——第t年电辅助加热耗热量、循环泵功耗和发电量,KWh/a;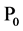 ——第0年电价,元/KWh;i——基准折现率。
——第0年电价,元/KWh;i——基准折现率。
系统的寿命取值为20 a,系统设备投资成本如表1所示,其中蓄电池寿命为5 a,每年用于与太阳能热水系统有关的维修费用(包括太阳集热器维护、集热系统管道维护和保温等费用)占总增投资的百分率取0.5%,安装费用约占设备费用的4.5%,基准折现率取10%。电价年上涨率分别取1%和3%,不考虑阶梯电价,假设第0年电价为市电价格0.6元/KWh。
图6为光伏/光热复合家用热水系统全生命周期的初投资费用现值,可得出当电价年上涨率分别取1%和3%时,系统运行20 a的投资费用现值分别为1.316万元和1.413万元,由TRNSYS模拟计算所得系统运行20 a所需热水加热量为48,223 KWh,由此得出系统的寿命周期内综合能源价格现值分别为0.273元/KWh和0.293元/KWh。
3.3. 动态投资回收期
太阳能光伏/光热复合家用热水系统设计使用寿命为20 a,为了克服静态投资回收期未考虑资金时间价值的缺点,PV/T系统的动态投资回收期方程为:
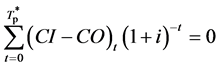 (2)
(2)
式中,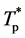 ——动态投资回收期;
——动态投资回收期; 、
、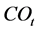 ——第
——第 年的现金流入、流出额;i——基准折现率;t——计算年数,a;n——热水器有效使用年限,a。
年的现金流入、流出额;i——基准折现率;t——计算年数,a;n——热水器有效使用年限,a。
以电价增长率d = 3%为例,动态投资回收期计算表如表2所示,寿命周期内各年净现金累积折现值如图7,可得出当电价年上涨率分别取1%和3%时,动态投资回收期分别为13.2 a和11.06 a。
3.4. 内部收益率
内部收益率为净现值为零时的折现率,是所有的经济评价指标中最重要的评价指标之一,被认为是项目投资的盈利率, PV/T系统的内部收益率为:
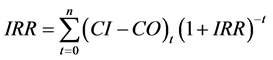 (3)
(3)
式中, ——内部收益率;其他符号同式(2)。
——内部收益率;其他符号同式(2)。
根据现金流量计算表,可得出当电价年上涨率分别取1%和3%时,寿命周期内太阳能光伏/光热复合家用热水系统的内部收益率分别12.8%和15.4%。
3.5. 敏感性分析
通过改变电价的年增长率和基准折现率,对太阳能光伏/光热复合家用热水系统进行全生命周期内综合能源价格、动态回周期和内部收益率进行敏感性分析,结果如表3所示。表3结果表明,当电价增长率变化范围为0%~10%,电价增长率对太阳能光伏/光热复合家用热水系统的经济性影响较大,当能源紧张,电价持续上涨时,电价增长率对内部收益率影响很大,内部收益率与电价上涨率正相关,随着电价上涨率增加而趋于上涨,同时,项目的动态投资回收期随着电价增长率增加而缩短,使项目取得较好的收益。基准折现率不影响内部收益率,但是会对投资回收期影响较大,当基准折现率变化范围为0%~15%,项目的投资动态回收期变化范围为7.69~16.04 a,在项目的寿命周期之内。综合能源价格现值在寿命周期内随基准折现率与电价增长率变化比较小,在分析范围之内均保持较低,小于0.3元/KWh。
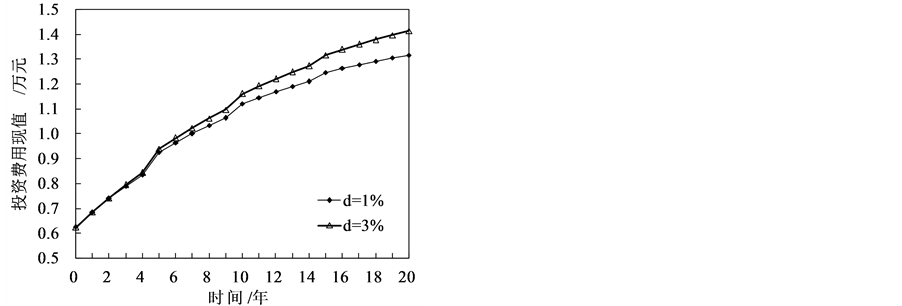
Figure 6. Present value of life cycle investment cost
图6. 寿命周期内投资费用现值

Figure 7. Cumulative discounted values of life cycle net cash flow
图7. 寿命周期内净现金流量累积折现值

Table 1. System equipment investment cost
表1. 系统设备投资成本

Table 2. Calculation table for dynamic payback period of investment
表2. 动态投资回收期计算表
表3. 敏感性分析
4. 结论
1) 太阳能光伏/光热复合家用热水系统运用于长沙地区典型4人家庭热水模式时,当基准折现率为10%时,分别考虑电价年上涨率为1%和3%,寿命周期内综合能源价格现值分别为0.273元/KWh和0.293元/KWh,动态投资回收期分别为13.2 a和11.06 a,内部收益率分别为12.8%和15.4%。
2) 全年逐时能耗模拟表明,太阳能光伏/光热复合家用热水系统热水产热量和发电量月均值最大值出现在7月份,热水需热量最小值的月份出现在7月,因此电辅助能耗值最小,12月至3月电辅助能耗相对较大,全年太阳能保证率约为0.44。
3) 敏感性分析表明,电价的年增长率和基准折现率对系统的经济性能影响很大。当基准折现率变化范围为0%~15%,系统的投资动态回收期变化范围为7.69~16.04 a,在系统的寿命周期可接受范围之内,综合能源价格小于0.3元/KWh。当电价增长率变化范围为0%~10%,电价格年增长率上涨时,内部收益率显著提高,取得较好的项目收益,同时系统的动态投资回收期随着电价增长率增加而缩短,因此当能源紧缺导致电价上涨时,经济性优势更显著,具有广阔的应用前景。
基金项目
湖南省科技厅计划项目(2013FJ3003)。