摘要:
目的: 对辣螺中的糖蛋白进行分离纯化,并分析其理化性质。方法: 采用缓冲溶液低温提取辣螺中的糖蛋白,以硫酸铵对糖蛋白粗提液进行梯度分级沉淀,各级组分经DEAE-52阴离子交换柱分离、纯化,得到的糖蛋白命名为LGP-1, LGP-2, LGP-3, LGP-4,再经Sephadex G-100层析纯化,得到的糖蛋白命名为LGP-Ⅰ, LGP-Ⅱ, LGP-Ⅲ, LGP-Ⅳ, LGP-Ⅴ, LGP-Ⅵ, LGP-Ⅶ。结果: 40%级硫酸铵沉淀得到3种糖蛋白组分(LGP-Ⅰ, LGP-Ⅱ, LGP-Ⅲ)。60%级酸铵沉淀得到3个糖蛋白组分(LGP-Ⅳ, LGP-Ⅴ, LGP-Ⅵ)。总糖含量17.86%、20.00%、13.14%、21.57%,蛋白质含量56.72%、62.58%、71.86%、60.86%。结论: IR分析表明,各组分均含有多糖的−OH、−COO−、−NH、−C−O−C等特征基团。
Abstract:
Purpose: This paper studied on extraction, isolation and purification as well as physical chemistry properties of the Glycoprotein from Thais clavigera Kuster. Method: The crude extract was then fractionated with 3 concentrations of ammonium sulfate solution. LGP-1, LGP-2, LGP-3, LGP-4 were prepared from the crude through DEAE-cellulose. LGP-I, LGP-II, LGP-III, LGP-IV, LGP-V, LGP-VI, LGP-VII were prepared through Sephadex G-100 chromatography. Result: The results showed that three glycoprotein components were carried out from 40% grade ammonium sulphate precipitation, named LGP-I, LGP-II, LGP-III. Three peaks appeared for 60%s, named LGP-IV, LGP-V and LGP-VI. The sugar were 17.86%, 20.00%, 13.14%, 21.57%, and the contents of protein were 56.72%, 62.58%, 71.86%, 60.86%. The IR indicated glycoprotein groups contained −OH, −COO−, −NH, −C−O−C characteristics.
1. 引言
辣螺,学名疣荔枝螺(Thais clavigera Kuster),含有丰富的糖蛋白,在我国南北沿岸及舟山各岛屿沿岸均有分布,为岩相潮间带最习见螺类之一。目前已有研究证实海洋软体动物——海兔、虾夷扇贝和文蛤中的糖蛋白具有明显的抑瘤作用[1] -[3]。关于牡蛎提取液具有抗氧化作用[4] [5] ,栉孔扇贝[6] 和管角螺[7] 等中提取的糖蛋白具有显著的抗肿瘤与增强免疫力的活性之类的研究更是引起了广泛的关注。糖蛋白是指由比较短,往往带分支的寡糖链上的羟基与多肽某些特殊部位的羟基或酰基形成肽键的一类有侧链的复杂大分子物质,在自然界广泛存在于动物、植物和某些微生物中,在生物体内它以不同的形式存在而发挥作用,是细胞膜、细胞间基质、血浆、粘液、激素等的重要构成成分[8] -[10] 。现在对海洋软体动物中提取糖蛋白的生物活性研究较多,但对辣螺糖蛋白的研究较少。本研究只要利用阴离子交换柱、凝胶层析柱分析辣螺糖蛋白的组成,以分离纯化辣螺糖蛋白。
2. 实验部分
2.1. 材料与仪器
2.1.1. 材料与试剂
新鲜辣螺(图1),购于舟山市南珍菜市场;透析袋(34, MW:3000),天津市纽森科技有限公司;DEAE- 52纤维素,Whatman公司;Sephadex G-100,Pharmacia公司;考马斯亮蓝R250,美国Fluka公司;磷酸氢二钠,磷酸二氢钠,硫酸铵,氯化钠(分析纯),国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
2.1.2. 仪器
日本日立CR21G冷冻离心机;BT1-100恒流泵,上海琪特分析仪器有限公司;FD-1000冷冻干燥机,上海爱朗仪器有限公司(东京理化器械(株)独资工厂);JJ-2组织捣碎机,上海梅香仪器有限公司;华凌BCD-199HC,中国雪櫃實業有限公司;BSA323S电子天平,赛多利斯科学仪器(北京)有限公司;UV-1100

Figure 1. Thais clavigera Kuster
图1. 辣螺
紫外可见分光光度计,上海美谱达仪器有限公司;Nicolet-6700付立叶红外光谱分析仪,森井电机株式会社(香港);YP-2固体压片机,上海山岳科学仪器有限公司;WS70-1红外线快速干燥器,上海锦屏仪器有限公司通州分公。
2.2. 实验方法
2.2.1. 辣螺糖蛋白的提取
辣螺螺肉匀浆→冷冻保藏→解冻→加缓冲溶液浸提→4℃离心→过滤→糖蛋白粗提液→硫酸铵分级沉淀,使浸提液中硫酸铵浓度分别达到30%,60%,100%三个级别→4℃离心→收集清夜透析→冷冻干燥→DEAE-52阴离子交换层析→收集洗脱液冷冻干燥→Sephadex G-100凝胶过滤层析→收集洗脱液冷冻干燥
2.2.2. 辣螺糖蛋白的分离
DEAE-52离子交换层析柱,分别用蒸馏水、0.1 mol/L、0.5 mol/L的NaCl溶液洗脱,流速为1.7 mL/min。分管收集,逐管分别用苯酚–硫酸法和紫外分光光度法检测糖和蛋白的紫外吸收情况。收集单一峰组分(合并糖和蛋白洗脱曲线的重合峰位),冷冻干燥。
2.2.3. 辣螺糖蛋白的纯化(改法同上)
Sephadex G-100凝胶过滤层析柱(25 mm × 100 cm),用蒸馏水洗脱,流速为1.7 mL/min,每管收集5 ml,逐管分别用苯酚-硫酸法和紫外分光光度法检测糖和蛋白的紫外吸收情况。收集单一峰组分(合并糖和蛋白洗脱曲线的重合峰位),冷冻干燥。
2.2.4. 总糖含量的测定
采用苯酚-硫酸法,以蒸馏水做空白对照,以干燥后的葡萄糖在0~140 μg/ml范围内作准标准曲线,测其总糖含量。
2.2.5. 蛋白质含量的测定
采用考马斯亮蓝法,用抗体作为标准蛋白,在20 ug~150 ug/100 ul之间绘制标准曲线。根据标准曲线计算待测样本的浓度。
2.2.6. 辣螺糖蛋白的红外光谱测定
取样品1 mg,用KBr压片,测定红外光谱,扫描范围4000~400 cm−1。
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 辣螺糖蛋白的提取分离及其纯化
辣螺匀浆200 g经缓冲溶液浸提、硫酸铵分级沉淀、透析、冷冻干燥得到3组不同的粗糖蛋白,命分别名为LGP-a,LGP-b,LGP-c,分别为15.78 g,7.83 g,0.23 g。
3.2. DEAE-52阴离子交换柱层析分离辣螺糖蛋白
经过翻阅大量的参考文献,本实验选择蒸馏水、0.1 mol/L、0.5 mol/L的NaCl溶液进行连续梯度洗脱,每个浓度洗脱30支试管。将辣螺糖蛋白LGP-a,LGP-b,LGP-c按上述方法分别进行洗脱,洗脱结果如图2~图4所示:
透析后的3个级别硫酸铵沉淀辣螺粗糖蛋白液经阴离子交换柱DEAE-52,用蒸馏水(试管号1-30)、0.1 mol/L(试管号31~60)、0.5 mol/L(试管号61~90)的NaCl溶液进行连续梯度洗脱,辣螺糖蛋白得到较好的分离。分离的糖蛋白组成结果由图1~图3所示,280 nm蛋白质吸收峰主要有5个,其中40%级硫酸铵沉淀粗糖蛋白有2个峰,分别是LGP-1和LGP-2;60%级硫酸铵沉淀粗糖蛋白有2个峰,分别是LGP-3和LGP-4,LGP-3所得量极少;100%级硫酸铵沉淀粗糖蛋白有1个峰,为LGP-5(该组糖蛋白所得量极少),用苯酚-硫酸法在490 nm下和考马斯亮蓝法在280 nm下检测,其总糖含量为14.74%,蛋白质含量为
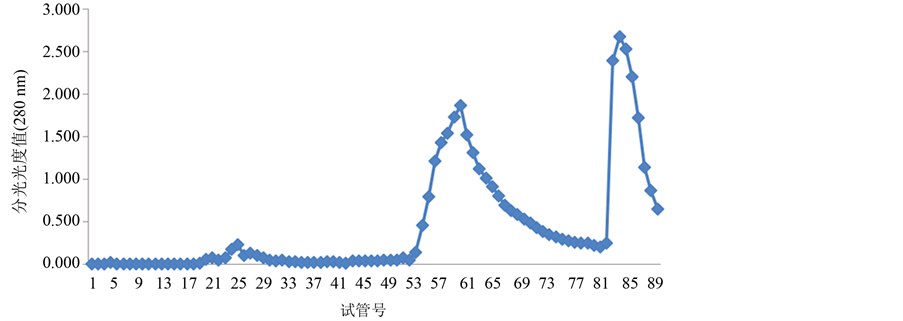
Figure 2. The separated results of LGP-a from Thais clavigera Kuster DEAE-52-ceUulose
图2. 辣螺糖蛋白LGP-a在DEAE-52上的洗脱
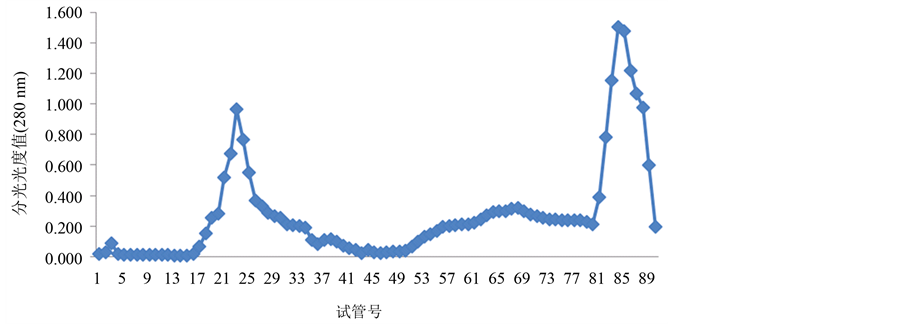
Figure 3. The separated results of LGP-b from Thais clavigera Kuster DEAE-52-ceUulose
图3. 辣螺糖LGP-b在DEAE-52上的洗脱
62.99%。峰LGP-3和LGP-5为未经洗脱液洗脱而透过的峰,可能为糖蛋白的凝聚体。
3.3. Sephadex G-100凝胶过滤层析分离辣螺糖蛋白
分别收集糖蛋白LGP-1和LGP-2,LGP-4的洗脱液,然后冷冻干燥,用Sephadex G-100凝胶过滤层析柱分离糖蛋白LGP-1,LGP-2,LGP-4,以蒸馏水为洗脱液洗脱,结果如图5~图7:
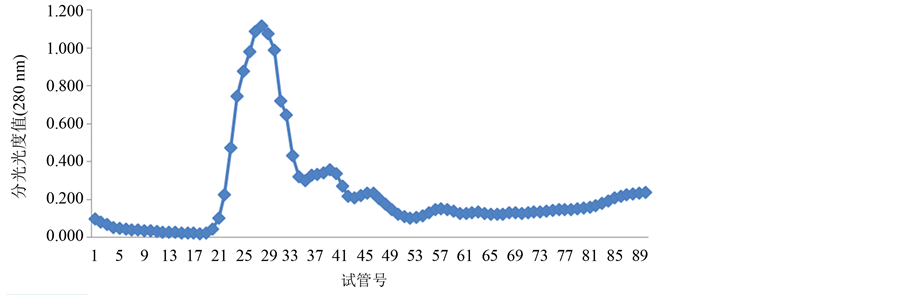
Figure 4. The separated results of LGP-c from Thais clavigera Kuster DEAE-52-ceUulose
图4. 辣螺糖LGP-c在DEAE-52上的洗脱
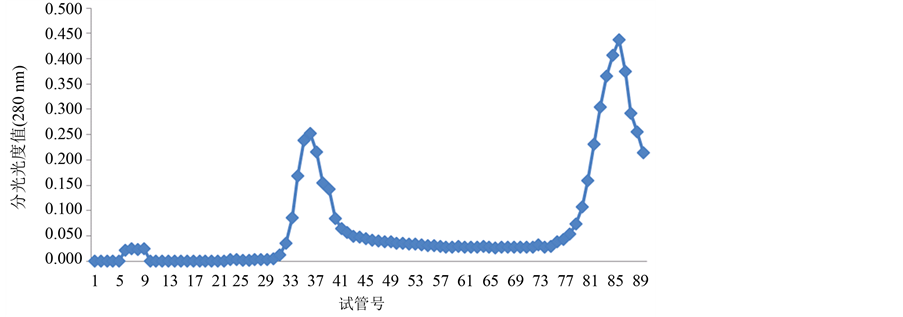
Figure 5. The separated results of LGP-1 on Sephadex G-100 gel
图5. LGP-1在Sephadex G-100上的洗脱
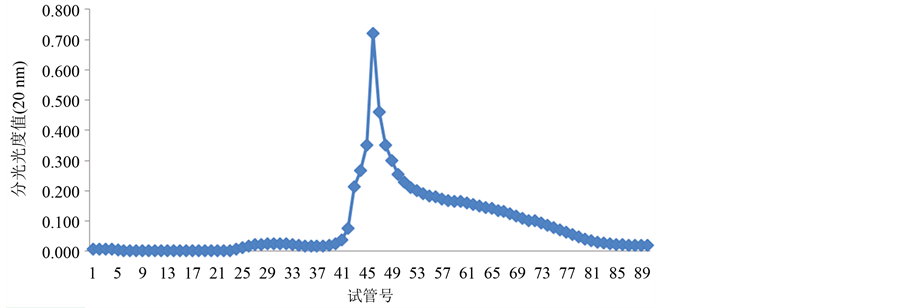
Figure 6. The separated results of LGP-2 on Sephadex G-100 gel
图6. LGP-2在Sephadex G-100上的洗脱
由图4~图6所示,糖蛋白LGP-1,LGP-2和LGP-4在洗脱后得到5个峰。LGP-1在洗脱后得到2个峰,分别是LGP-Ⅰ和LGP-Ⅱ,其中LGP-Ⅰ所得量极少。LGP-2在洗脱后得到1个峰LGP-Ⅲ。LGP-4在洗脱后得到2个峰,分别是LGP-Ⅴ和LGP-Ⅵ。用苯酚-硫酸法在490 nm下和考马斯亮蓝法在280 nm下检测,其总糖含量和蛋白质含量分别是13.14%、21.57%、71.86%、60.86%。
3.4. 辣螺糖蛋白的红外光谱分析
分别收集LGP-Ⅰ和LGP-Ⅱ,LGP-Ⅲ,LGP-Ⅴ和LGP-Ⅵ的洗脱液,冷冻干燥,得到不同组分的糖蛋白白色粉末与LGP-Ⅶ粉末一起进行红外光谱分析,结果如图8~图12:
如图8~图12所示,从红外数据分析来看,辣螺糖蛋白LGP-c、LGP-Ⅱ、LGP-Ⅲ、LGP-Ⅴ和LGP-Ⅵ的特征吸收峰:3500~3200 cm−1为糖的O-H伸缩振动区域;3300-2800cm−1区域为糖的C-H伸缩振动区域;都含有-NH(1409.73 cm−1,1400.01 cm−1,1402.02 cm−1,1409.73 cm−1)、C-O-C(1068.38 cm−1,1124.31 cm−1,1240.02 cm−1,1105.03 cm−1,1133.96 cm−1)等糖链基团。都含有1670~1570 cm−1区域的酰胺键(肽键)的特征吸收峰。同时还都具有明显的糖的特征吸收峰(898~1089 cm−1)。
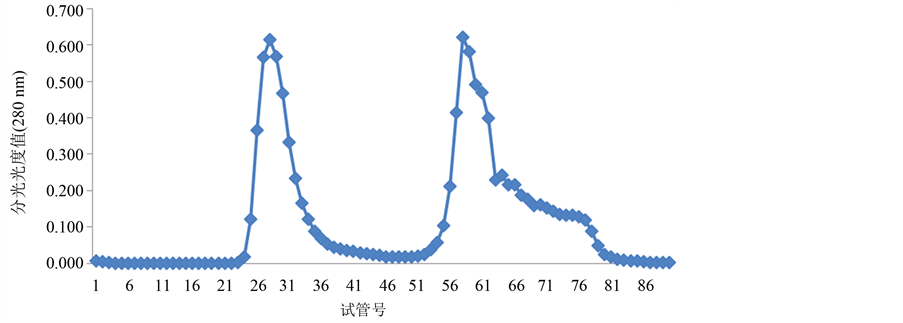
Figure 7. The separated results of LGP-4 on Sephadex G-100 gel
图7. LGP-4在Sephadex G-100上的洗脱

Figure 8. Infrared absorption spectra of LGP-Ⅶ in F22
图8. LGP-Ⅶ的红外光谱

Figure 9. Infrared absorption spectra of LGP-Ⅱ in F22
图9. LGP-Ⅱ的红外光谱

Figure 10. Infrared absorption spectra of LGP-Ⅲ in F22
图10. LGP-Ⅲ的红外光谱

Figure 11. Infrared absorption spectra of LGP-Ⅴ in F22
图11. LGP-Ⅴ的红外光谱

Figure 12. Infrared absorption spectra of LGP-Ⅵ in F22
图12. LGP-Ⅵ的红外光谱
4. 结论
本实验将辣螺糖蛋白经硫酸铵分级沉淀,DEAE-52阴离子交换层析和Sephadex G-100凝胶过滤层析分离纯化得到5个糖蛋白组分,分别是LGP-Ⅰ,LGP-Ⅱ,LGP-Ⅲ,LGP-Ⅳ,LGP-Ⅴ,LGP-Ⅵ,LGP-Ⅶ。其中LGP-Ⅶ,LGP-Ⅰ,LGP-Ⅳ所获得的量极少。其他组分的总糖含量分别是17.86%、20.00%、13.14%、21.57%,蛋白质含量分别是56.72%、62.58%、71.86%、60.86%。各组分蛋白都含有酰胺键,糖的O-H,C-H伸缩振动的特征吸收峰及-NH、C-O-C等糖链基团。

NOTES
*通讯作者。