1. 引言
煤制烯烃项目是近几年来国内煤化工企业重点开发建设、投入运营的项目[1] 。煤制烯烃过程工艺复杂,需要大量水资源,并产生大量废水,该废水水质特点复杂,含有大量有毒物质[2] ,导致生化处理中活性污泥微生物受多因素影响,抗冲击能力较差,硝化菌属不易生长富集,氨氮去除率低。而出水氨氮值过高,会显著提高后续深度处理难度并降低膜的使用寿命。因此,开发煤制烯烃废水硝化菌属的富集培养技术,培养抗冲击能力强、高脱氨率的活性污泥,在此类废水处理中具有重要的意义。
硝化菌属是一类具有硝化作用的化能自养细菌,包括亚硝化菌和硝化菌两个生理菌群。硝化作用必须由亚硝化菌和硝化菌协同完成,至今还没有发现能够把氨直接氧化成硝酸的微生物,氨和亚硝酸盐分别是亚硝酸细菌和硝酸细菌进行自养生长的唯一能源[3] 。硝化反应反应式[4] 为:



硝化细菌硝化作用能有效将氨氮转化为硝酸盐氮,降低水中氨氮含量。硝化反应有如下特征[4] :1)氨氮的生物氧化需要大量的O2,每去除1 g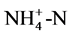 需4.2 g O2;2) 硝化过程细胞产率非常低,难以维持较高浓度;3) 硝化过程产生大量质子(H+),消耗碱度,理论上大约每氧化1 g
需4.2 g O2;2) 硝化过程细胞产率非常低,难以维持较高浓度;3) 硝化过程产生大量质子(H+),消耗碱度,理论上大约每氧化1 g 需要碱度7.14 g。研究表明,污水中硝化细菌的浓度与硝化速率成正比[5] ,但硝化细菌对溶解氧、温度、pH、碱度等外界因素的变化反应灵敏,易受外界环境的影响,能否高效富集驯化硝化细菌,将直接影响硝化效果和生物脱氮的效率。本研究以宁夏某化工厂煤制烯烃废水为研究对象,考察硝化菌属对该废水的适应性,通过培养驯化得到富集硝化菌属的活性污泥,服务于煤制烯烃类废水处理,在除碳同时达到高效脱氨的目的。
需要碱度7.14 g。研究表明,污水中硝化细菌的浓度与硝化速率成正比[5] ,但硝化细菌对溶解氧、温度、pH、碱度等外界因素的变化反应灵敏,易受外界环境的影响,能否高效富集驯化硝化细菌,将直接影响硝化效果和生物脱氮的效率。本研究以宁夏某化工厂煤制烯烃废水为研究对象,考察硝化菌属对该废水的适应性,通过培养驯化得到富集硝化菌属的活性污泥,服务于煤制烯烃类废水处理,在除碳同时达到高效脱氨的目的。
2. 实验装置及方法
2.1. 实验装置
本实验装置采用圆柱形容器,有效容积20 L,内设曝气头,采用鼓风机曝气。采用间歇性进水运行方式,通过控制进水成分、培养装置内的温度和pH值等为硝化细菌的生长提供最佳条件,以达到富集硝化细菌的目的。实验装置如图1。
2.2. 实验材料及仪器
实验用水:本实验用水取自宁夏某化工厂煤制烯烃废水调节池,用自制纱布滤筛去除浮渣。水质指标如表1。
供试污泥:实验活性污泥取自宁夏某甲醇厂SBR系统。
主要实验器材:玻璃培养器,鼓风机,5B-3C型化学耗氧量仪(COD仪),PHS-3C型pH计,哈希溶解氧仪,分光光度计。
2.3. 实验方法及步骤
实验运行周期设为12 h,每天运行两周期,运行模式为:进水2 h→曝气8 h(含进水2 h)→沉淀3.5 h→出水0.5 h。(夜间不取样,下文每周期数据皆为白天取样数据)。每周期进出水量为4 L,通过不断控制优化各个参数,逐步增加进水氨氮质量浓度的培养方式进行实验。根据相关研究[6] 及现场实验条件,相关实验参数控制为:温度:26℃~30℃;DO:2~4 mg/L;pH:7.5~8.5;HRT:12 h;MLSS:3000 mg/L左右。
2.4. 主要测试项目及方法
COD:重铬酸钾法;DO:溶氧仪;pH:pH计;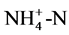 :纳氏试剂法。
:纳氏试剂法。
3. 实验结果与讨论
全周期硝化细菌培养情况如图2所示。从硝化菌属培养驯化过程来看,可将硝化细菌的富集培养分为三个阶段。前15周期为第一阶段。此阶段第2周期氨氮去除量达到9.58 mg/L,硝化速率为0.27 × 10−3 mg (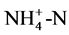 )/(mg MLSS·h),第6周期氨氮去除量为0.2 mg/L,硝化速率仅有0.0055 × 10−3 mg (
)/(mg MLSS·h),第6周期氨氮去除量为0.2 mg/L,硝化速率仅有0.0055 × 10−3 mg ( )/ (mg MLSS·h),第12周期氨氮去除量为9.56 mg/L,硝化速率又达到0.27 × 10−3 mg (
)/ (mg MLSS·h),第12周期氨氮去除量为9.56 mg/L,硝化速率又达到0.27 × 10−3 mg ( )/(mg MLSS·h),硝化速率先变小后变大,硝化作用波动大。经分析认为,由于底泥取自某甲醇厂SBR池,系统活性污泥
)/(mg MLSS·h),硝化速率先变小后变大,硝化作用波动大。经分析认为,由于底泥取自某甲醇厂SBR池,系统活性污泥
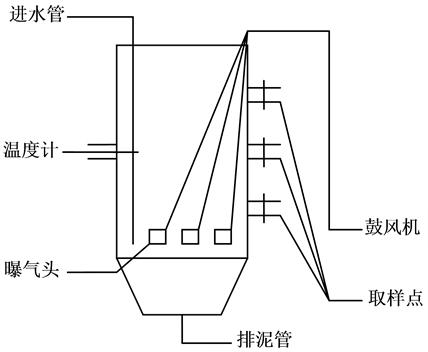
Figure 1. Experimetal setup
图1. 实验装置图

Table 1. Coal to olefin wastewater quality indexsp
表1. 煤制烯烃废水水质指标
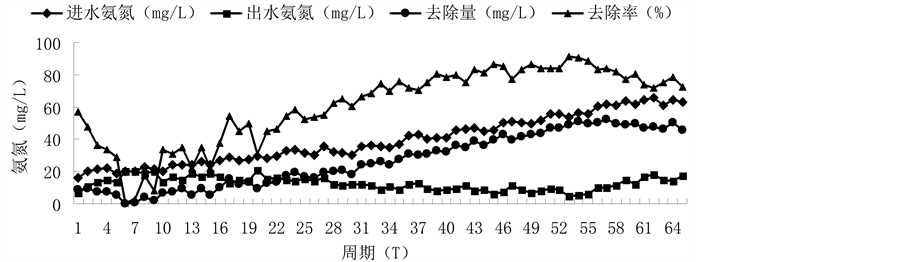
Figure 2. Full cycle nitrifying bacteria culture conditions
图2. 全周期硝化细菌培养情况
中含有硝化细菌,因此在第1、2周期表现出很好的硝化活性;又由于该活性污泥硝化菌属对煤制烯烃废水的不适应性,硝化细菌受到该废水的冲击,6~9周期硝化作用较弱;经过10~15周期的培养驯化,硝化细菌活性有所恢复,硝化速率提高。在这一时期,氨氮转化率不高,去除率在30%左右,说明硝化细菌还没有成为优势菌,由于提供碳源有限,异养好氧细菌数量逐渐下降,可称为硝化细菌富集培养的纯化期[6] 。第16~55周期为第二阶段。随着进水氨氮浓度的不断增大(25 mg/L到55 mg/L),氨氮去除量亦不断增大,从第16周期10.24 mg/L增加到第55周期49.64 mg/L,呈直线增长。氨氮出水值最低仅为4.76 mg/L,去除率最高达到91.2%,硝化速率最高达到1.4 × 10−3 mg ( )/(mg MLSS·h)。这一阶段硝化细菌活性强、数量急剧增加,成为系统中优势菌,可称为硝化细菌富集培养的剧增期[7] 。第56~60周期,进水氨氮浓度继续增大到60 mg/L,但氨氮去除量变化不大,维持在50 mg/L左右。此时系统氨氮去除效果趋于稳定,说明此阶段硝化细菌的数量基本已达顶峰,可认为系统处于富集培养的稳定期。当进水氨氮浓度达到65 mg/L时,氨氮去除量有所下降,去除率降低到72%,出水氨氮值升高,达到18.42 mg/L。
)/(mg MLSS·h)。这一阶段硝化细菌活性强、数量急剧增加,成为系统中优势菌,可称为硝化细菌富集培养的剧增期[7] 。第56~60周期,进水氨氮浓度继续增大到60 mg/L,但氨氮去除量变化不大,维持在50 mg/L左右。此时系统氨氮去除效果趋于稳定,说明此阶段硝化细菌的数量基本已达顶峰,可认为系统处于富集培养的稳定期。当进水氨氮浓度达到65 mg/L时,氨氮去除量有所下降,去除率降低到72%,出水氨氮值升高,达到18.42 mg/L。
3.1. 氨氮容积负荷对硝化细菌的影响
图3、图4分别为氨氮容积负荷与氨氮去除率和氨氮出水值的关系。结合图3、4可以看出,从硝化细菌培养驯化的剧增期开始,随着氨氮容积负荷逐渐增大,氨氮去除率升高,出水氨氮值降低;在氨氮容积负荷为110 g·m−3·d−1时,氨氮去除率最高达到87.57%,此时出水氨氮值降到最低,仅为6.92 mg/L;当氨氮容积负荷继续增大到120 mg/L、130 mg/L时,氨氮去除率降低,出水氨氮质量浓度升高。经分析,当氨氮容积负荷过高时,反应器中游离氨浓度相应增高,而硝化细菌对游离氨极为敏感,过高游离氨使硝化作用减弱[8] 。并且较高的氨氮容积负荷导致DO不足,硝化不完全,亚硝酸盐得以积累;而游离亚硝酸(FNA)是硝酸细菌的真正基质, 也是亚硝酸细菌和硝酸细菌的真正抑制剂[9] 。因此由实验结果可得,氨氮容积负荷为110 g·m−3·d−1左右时,氨氮转化率高,氨氮的出水质量浓度较低,对硝化细菌的富集较为有利。
3.2. C/N比对硝化细菌的影响
污水中的碳源会影响硝化细菌的新陈代谢及氨氮转化效率[10] ,但也有研究表明当温度和pH值适合,DO和氨供给充足,有机物浓度对硝化作用不造成影响[11] 。取处于培养驯化剧增期活性污泥0.6 L置于2 L反应器内,进水COD、氨氮分别为300.3 mg/L、31.76 mg/L,每3小时添加葡萄糖一次,使系统COD维持在300 mg/L左右,其他影响因素不变。出水水质指标如表2。
通过表2可以看出,经过4个周期,氨氮值由31.76 mg/L降到10.88 mg/L,硝化速率仅为0.15 × 10−3 mg ( )/(mg MLSS·h)说明在持续高有机物浓度下,硝化细菌受到抑制,硝化效果不明显。高有机物
)/(mg MLSS·h)说明在持续高有机物浓度下,硝化细菌受到抑制,硝化效果不明显。高有机物
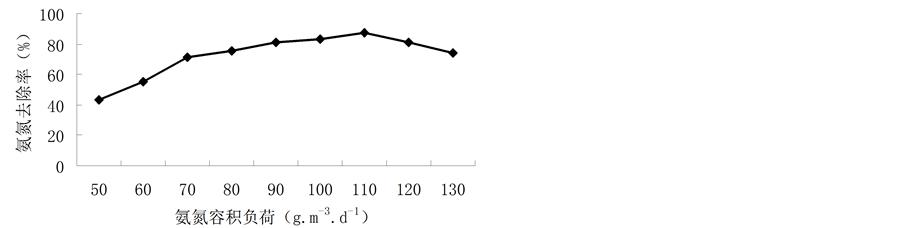
Figure 3. Relation between ammonia nitrogen volumetric loading and ammonia removal rate
图3. 氨氮容积负荷与氨氮去除率的关系

Figure 4. Relation between ammonia effluent value and ammonia nitrogen volumetric loading
图4. 氨氮容积负荷与氨氮出水值的关系

Table 2. Ammonia effluent value under high organic concentration
表2. 高有机物浓度下出水氨氮值
浓度条件下,好养异养菌在竞争DO时具有优势,抢夺系统中的DO,导致硝化细菌硝化作用减弱。
本试验中,系统处于硝化细菌富集培养稳定期时,将进水C/N比控制在8:1,进水氨氮值约为55 mg/L时,经过6 h分解代谢,系统内COD仅为50 mg/L左右,氨氮值为25 mg/L左右,此时系统内C/N比仅为2:1左右;12 h后系统内氨氮值降到6.92 mg/L左右。说明系统在C/N比为2:1时,硝化反应依旧进行,且其硝化速率达到1 × 10−3 mg (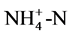 )/(mg MLSS·h)。由于试验中采用的水力停留时间较长,当好养异养菌充分分解代谢C源有机物后,不再与硝化细菌竞争DO,系统硝化速率加快。此时系统内活性污泥能有效脱氨除碳,出水COD值能达到30 mg/L以下,去除率达到90%以上,氨氮平均去除率达到87.57%,出水氨氮值降到10 mg/L以下。说明合适的C/N比能保证硝化细菌和好氧异养伴生菌协同生长,达到脱氮除碳的目的。
)/(mg MLSS·h)。由于试验中采用的水力停留时间较长,当好养异养菌充分分解代谢C源有机物后,不再与硝化细菌竞争DO,系统硝化速率加快。此时系统内活性污泥能有效脱氨除碳,出水COD值能达到30 mg/L以下,去除率达到90%以上,氨氮平均去除率达到87.57%,出水氨氮值降到10 mg/L以下。说明合适的C/N比能保证硝化细菌和好氧异养伴生菌协同生长,达到脱氮除碳的目的。
4. 结论
1) 将温度控制为26℃~30℃,DO为2~4 mg/L,pH为7.5~8.5,实验HRT为12 h,MLSS控制为大约3000 mg/L左右时,经过65个周期培养驯化,能够得到富集硝化菌属的活性污泥,服务于煤制烯烃废水的治理,出水COD 30 mg/L以下,出水氨氮10 mg/L以下,达到国家《污水综合排放标准》GB8978-1996一级标准。
2) 氨氮容积负荷在110 g·m−3·d−1左右时,硝化细菌活性强,硝化速率达到1.4 × 10−3 mg ( )/(mg MLSS·h),对硝化细菌的富集较为有利。随着容积负荷的增大,出水氨氮质量浓度逐渐升高,但氨氮的去除量基本维持不变。在培养富集硝化细菌过程中,氨氮容积负荷应采取逐步加大的方式。
)/(mg MLSS·h),对硝化细菌的富集较为有利。随着容积负荷的增大,出水氨氮质量浓度逐渐升高,但氨氮的去除量基本维持不变。在培养富集硝化细菌过程中,氨氮容积负荷应采取逐步加大的方式。
3) 碳氮比对氨氮的去除有重要的影响。碳氮比控制为8:1时,COD、氨氮去除率能分别达到93%和91.2%。在C/N比仅为2:1时,硝化作用依然进行,且硝化速率达到1 × 10−3 mg ( )/(mg MLSS·h)。适当的C源不仅刺激了少量的伴生菌的生长,而且为硝化细菌的生长提供了碳源,促进硝化作用的进行。
)/(mg MLSS·h)。适当的C源不仅刺激了少量的伴生菌的生长,而且为硝化细菌的生长提供了碳源,促进硝化作用的进行。