1. 引言
影视、网络等媒体中的暴力内容,对儿童攻击性的影响日益受到关注(郭俊伟等,2007)。属于媒体内容之一的动画片具有对比强烈、色彩鲜明、纯度较高等特点,这些特点增强了作品中暴力的震撼力,这样恰好满足孩子生理和思维发展的感官刺激,受到了儿童的大力追捧(肖伟,宗传玉,2008)。另一媒体内容“真人视频”贴切现实生活,能客观实在的表现我们生活的真实环境,也受到儿童的欢迎。
关于媒体暴力和攻击性行为的关系,Huesmann L.等人的一项从1977到1992年的纵向研究发现,儿童时期过多接触媒体暴力和对攻击性媒体角色的理想化认知与其成年后的攻击性存在一定的关联。华盛顿大学的一项调查发现,在因暴力入狱的男性犯人中,有1/4到1/3的人承认他们在犯罪时有意识地模仿电视中的暴力犯罪手段。然而,Mark Griffiths(1999)对攻击性媒介提高个体攻击性的结论提出质疑,认为已有关于攻击性媒介影响的研究大都存在研究方法的问题。最终,2000年7月,美国心理学会、医学会等六大专业团体签署了一份联合声明,声明指出“在一些儿童身上确实存在媒体暴力与攻击行为之间的因果关系”。
一直以来,广电总局只对真人暴力视频的播放有所限制,对动画片几乎是完全开放的。虽然我国对进口动画片要经过审查,但是审查更为注重政治倾向,而对暴力倾向的关注明显不够。因此,我们希望通过此次实验能得出一个比较确定的结论,让家长们有一个明确的认识。
2. 研究方法
2.1. 被试
研究选取85名被试进行了实验,被试年龄在7到9岁之间,所有被试均智力健全,视力或矫正视力正常,无色盲,听觉正常,无精神方面过往病史。
2.2. 实验材料
2.2.1. 视频选择
在视频的选择上, 采用以下标准:时间段(10分钟以内),内容以打斗为主(含血腥场面和特技表现)、画面清晰细腻,含少量的人物对白。真人与动画视频的人物,情节,语种等内容基本相同,两种视频呈现时间相同。综合上述标准,实验组节选动画版和真人版的《明日之杖》作为实验材料。对照组的实验材料为非暴力形象的中性情绪视频《看鱼》的片段。
2.2.2. 内隐认知任务文字材料
IAT测试材料包括两种维度:类别维度和属性维度,在本研究中,考虑到7~8岁儿童的特殊性,类别维度由3个自我/非我词组成,其中自我词包括:我、自己、我们;非我词包括:他、他人、他们。属性维度为攻击性/非攻击性词汇,其中攻击性词汇包括:消灭、袭击、攻击;非攻击性词汇包括:拥抱、握手、微笑。
2.2.3. 其它材料
苦瓜汁(纯天然压榨,不含任何香料和糖精)、番茄汁、辣椒酱、一次性纸杯若干。
2.3. 实验设计
①被试分组:将被试随机分为A,B,C,3组,然后随机匹配到不同的视频条件下进行实验。②视频观看阶段:A组只看动画形象视频,B组只看真人形象视频,C组观看非暴力形象的中性情绪视频。③看完视频后,完成实验一:攻击性行为测验。④继续看与之前相同的视频5分钟,完成实验二:内隐攻击性测验。⑤实验结束后,看5到6分钟亲社会行为的视频,并对被试进行情绪抚慰。⑥感谢被试,赠送礼品。
2.3.1. 攻击性行为实验
实验目的:研究在不同视频条件的影响下,被试在行为上所表现出来的攻击性的差异情况。
实验设计:该实验采用单因素组间设计。其中,自变量为视频中的人物形象:动画暴力形象vs真人暴力形象vs非暴力形象。因变量为视频中形象对儿童攻击性行为的影响。为避免被试因“社会期许效应”影响实验结果,本实验采取单盲设计(盲被试)。
实验过程:让被试在正常无疲劳且情绪稳定的情况下认真观看视频。A组观看动画形象视频,B组观看真人形象视频,C组观看非暴力形象的中性情绪视频。被试在看完视频后立即进行攻击性行为测验。此阶段采用Lieberman,Solomon,Greenberg和McGregor(1999)提出了“辣椒酱”范式。实验中,被试首先会受到伪被试的激惹,(比如,给被试倒一杯很难喝的果汁)。然后,要求被试为伪被试倒辣椒酱,可混在番茄汁中让伪被试饮用,(事先向被试表明伪被试不喜欢吃辣)。将所倒辣酱的数量作为被试攻击行为的指标。
2.3.2. 攻击性内隐认知实验
实验目的:研究在不同视频条件的影响下,被试的内隐攻击性的差异情况。
实验设计:该实验依旧采用单因素组间设计。其中,自变量为视频中的人物形象:动画形象vs真人形象vs非暴力形象。因变量为视频中形象对儿童内隐攻击性的影响。为避免被试因“社会期许效应”影响实验结果,本实验采取单盲设计(盲被试)。
实验过程:让被试继续观看实验一阶段的视频材料5分钟,A组观看动画形象视频,B组观看真人形象视频,C组观看非暴力形象的中性情绪视频。被试在看完视频后立即进行内隐攻击性测验。内隐攻击性IAT程序采用汉化了的美国Inquisit专业软件,实验均采用个别施测,每个被试单独完成两个测验。程序记录被试的每一次按键反应的时间及正误。内隐攻击性测试IAT包括5个步骤:第一步骤,练习类别维度词分类;第二步骤,练习属性维度词分类;第三步骤,测试相容组(自我与攻击)的分类;第四步骤,练习换位后类别维度词分类;第五步骤,测试不相容组(自我与非攻击)的分类。在整个过程中,被试只知道所做的是一项组词测试,并不清楚实验的真实目的。由主试说明具体要求,首先进行练习,然后开始正式实验。
3. 研究结果
研究共对85名被试进行了实验,被试年龄在7到9岁之间,其中2个被试中途因设备故障退出实验。利用SPSS 19对收集到的83个数据进行分析,计算出收集到的83个数据的攻击性量表的分数,并据此排除量表极端得分的被试的数据(排除样本攻击性量表得分的均分加减两个标准差以外的数据)。最终得到的有效数据为79个(其中动画视频组26个,真人视频组28个,控制组25个),其中男生40人,女生39人;年龄最小的被试是7岁,年龄最大的是9岁(M = 8.025, SD = 0.698)。
3.1. 攻击性行为实验结果
我们采用79名被试在行为实验中放的辣椒的勺数表示被试在行为实验中的外显攻击性程度。对3组被试在行为实验中放入的辣椒勺数进行单因素方差分析,结果发现分组主效应显著(F(2,76) = 4.281,p < 0.05)(如表1所示),事后检验(如图1所示)发现动画组与控制组总勺数存在显著差异(p < 0.01),动画组与真人组、真人组与控制组的总勺数均不存在显著差异,此结果说明动画视频导致被试的外显攻击性显著增加,而真人视频则未导致被试的外显攻击性显著增加。
3.2. 攻击性内隐认知实验结果
对3组被试在内隐联想测验(IAT)中所得的D值进行单因素方差分析,结果发现分组主效应不显著(F(2,76) = 0.200, p > 0.05)(如表1所示),说明动画与真人视频都未导致被试的内隐攻击性显著增加。
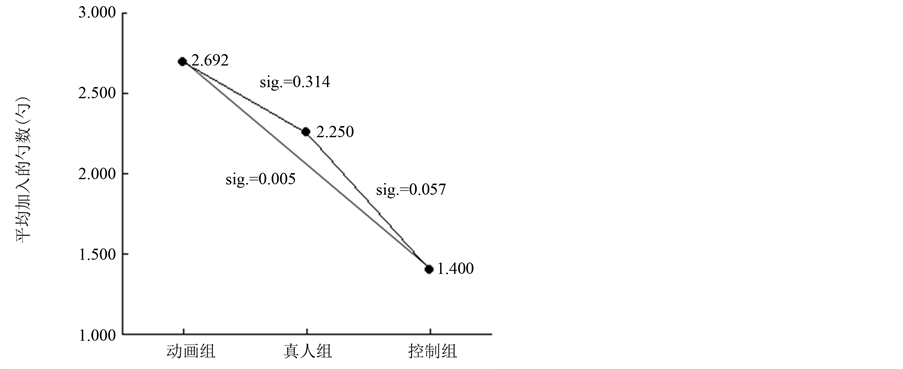
Figure 1. The average of chili sauce tablespoons of subjects and the results of their post-hoc test
图1. 各组被试加入辣椒酱勺数均值及其事后检验结果

Table 1. The effect of interclass variables to both explicit aggression and implicit aggression
表1. 组间变量对外显、内隐攻击性的影响
注:*p < 0.05。
3.3. 《动画片观看习惯调查表》结果
我们使用自编《动画片观看习惯调查表》对79名被试观看动画片的频率、类型以及暴力血腥程度进行了调查。
接受调查的79名被试中,有29.1%的被试(23名)表示他们每天都会看动画片,有29.1%的被试(23名)表示他们每隔两三天会看一次动画片,有41.8%的被试(33名)表示他们大约每周看一次动画片。
接受调查的79名被试中,有64.6%的被试(51名)表示他们喜爱看奇幻类的动画片,有8.9%的被试(7名)表示他们喜爱看教育类的动画片,有11.4%的被试(9名)表示他们喜爱看科教类的动画片,有15.2%的被试(12名)表示他们喜爱看武打类的动画片。
我们对79名被试经常观看的动画片的暴力、血腥程度进行3级评分(1到3分)。以性别作为自变量对他们所观看的动画片的暴力和血腥程度进行T检验。结果表明性别对于其所观看的动画的暴力程度影响不显著,t(77) = 1.378,p > 0.05;而在他们所观看的动画的血腥程度上,性别变量出现了显著性差异,t(77) = 2.242,p < 0.05,且男生观看的动画血腥程度(M = 1.55)显著的比女生观看的动画血腥程度(M = 1.23)高。
3.4. 《实验视频材料调查问卷》结果分析
实验结束后,被试对视频材料的难度、清晰度、理解度、观看后的感受进行评定。动画组有26名被试,真人组有27位被试对我们的实验材料进行了评定。视频材料的评定结果如图2所示。有评定结果可验证我们的研究在材料选择上是较为合理的。
4. 讨论
4.1. 动画与真人形象对儿童攻击性的影响
从实验结果来看,动画视频导致被试的外显攻击性显著增加,而真人视频则未导致被试的外显攻击性显著增加。这一结果验证了研究假设,也可作为解释近期诸多儿童因模仿动画片中情节而导致自身或同伴受伤害的社会事件的依据。
传统社会中,帮助儿童实现社会化进程的主要因素是家庭、学校以及伙伴,而电视的普及几乎从根本上改变了这种传统的格局,通过直观明了的视频材料获得信息来学习知识的儿童的比例明显上升(夏旭
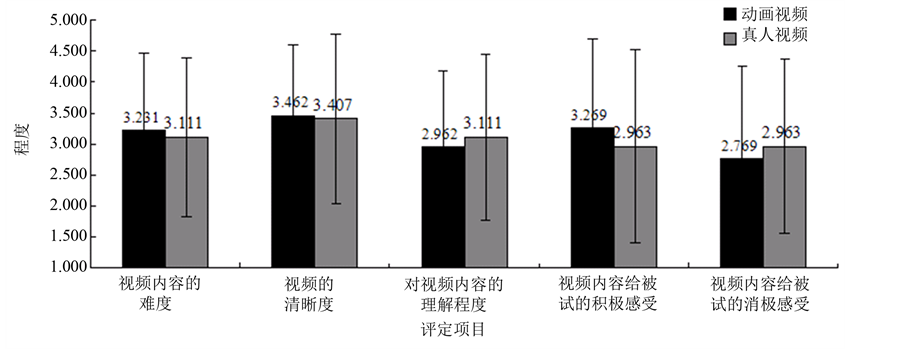
Figure 2. Evaluation result of video material
图2. 视频材料评定结果
光,王海华,2008)。与此同时,媒体渐渐成为青少年最主要的社会化来源,在青少年成长中起着重要的作用,从而使得影视、网络等媒体中的暴力内容,对青少年暴力行为的影响日益受到关注,并取得了一定的研究成果(郭俊伟等,2007)。近年以来,中国内地尤其是城市儿童和青少年的犯罪率和越轨行为的出现率不断上升,大多数人将其归结为孩子学业上的压力,社会治安环境的恶化和儿童交往对象的不当,极少有人注意到媒介暴力与儿童越轨行为间的关系(任频捷,2002)。
本研究攻击性行为实验中,观看动画视频的儿童与观看真人视频的儿童相比,在知道伪被试不喜欢吃辣的情况下,向伪被试的“饮料”中添加了更多的辣椒酱,以此表现其对伪被试更高的攻击性。同样的故事情节,同样的打斗场景,动画形象对儿童攻击性的影响更为明显。近年来热播的国产动画片中,《喜羊羊与灰太狼》、《熊出没》、《铠甲勇士拿瓦》等均含有很浓厚的暴力色彩。这些动画片中频繁出现打斗、焚烧、捆绑、屠杀等具有较强攻击性的情节和场景。试想,儿童在观看这些动画片的时候心理和生理受到了多大的影响。
4.2. 从攻击性伤害到动画片分级
动画片中的特技以及光和画面的表现力增强了作品中暴力的震撼力,这种震撼力甚至可以停留在其阅读人的心理从而形成或强或弱的心理影响力(夏旭光,王海华,2008)。很多家长及老师认为卡通节目对孩子的影响是比较积极、正面的,然而西方学者的研究早已表明,电视卡通片上的暴力镜头,远超过一般成人观看的电视片,大量的卡通节目中以暴力对付坏人,假维护正义之名行暴力血腥之实。以前在不同的国家,动画片的所属群体略有差别,可随着动画产业的不断扩大,动画片的受众年龄层普遍扩大,绝大多数动画片并没有进行严格的性质区分,儿童也在不同程度的受成人视频的影响(高超,2007)。
心理学家韦斯特曾进行了长达14年的追踪研究,结果发现70%的暴力少年犯在13岁就被确认有攻击性行为,有48%少年犯在9岁时就被确认有攻击性行为。从某种意义上讲,儿童的攻击性行为是导致今后各种行为问题的先兆。Bushman和Huesmann(2006)的研究也指出,媒体暴力的长时效应在儿童身上相对与成年人要更加明显。儿童的成长关系到国家的未来,他们的健康发展应该受到极大地重视。
在暴力不可避免的情况下,实行动画片分级制度,是减少对未成人不良影响的最好途径。在动漫较为发达的国家,譬如日本和韩国,早已实行了动画片分级制。像《蜡笔小新》这样的动画片,在日本就属于限制级,12岁以下儿童在没有家长陪同的情况下是不能单独观看的,但在我国,这样品动画片任何人都可以随意观看。2013年4月6日,因模仿《喜羊羊与灰太狼》动画片情节,江苏两个孩子被同伴绑在树上点火烧成重伤。这样血淋淋的事实向社会敲响了警钟,对于儿童所观看动画片进行分级限制是很有必要的。
5. 局限和展望
虽然本研究使用实证研究的方法得出了较为理想的结果,但是由于研究者自身能力水平的限制和时间和资源的制约,仍有很多不足之处。首先,由于被试年龄的特殊性,实验设计偏向于简易操作,在内隐认知试验中减少了词语数量,可能会对研究结果有一定的影响;其次,本研究的被试取样于武汉地区,研究结果的推广可能存在局限性;最后,由于被试资源的难获取和不稳定性,没能进行纵向研究已取得更有意义的实验数据。
未来的研究未来的研究可以使用多重方法如直接观察、间接报告和自述等相结合的方法来探讨动画与真人暴力形象对儿童攻击性的影响。Huesmann和Miller(1994)认为,对于观看电视暴力和攻击性之间关系的最合理假设是对于电视暴力的习惯性接触,使孩子养成了攻击性的习惯,并且这种习惯可以很好地保持到成年。因此,该领域的纵向研究将会取得较为科学和可靠的结果。
致 谢
感谢大学生科研项目资金支持。