1. 引言
动脉粥样硬化(Atherosclerosis, AS)是心肌梗死、中风、心绞痛等心脑血管疾病发生、发展的重要病理基础。泡沫细胞是AS中的特征性病理改变,出现于AS形成早期,贯穿于AS的发生发展过程中。泡沫细胞主要是由血液中的巨噬细胞迁移到血管内皮吞噬脂质形成,形成的泡沫细胞大量聚集于血管壁受损处,进而形成动脉粥样硬化斑块,由于炎症反应,造成斑块破裂、脱落造成血栓引发心血管疾病[1] 。正常情况下,巨噬细胞通过低密度脂蛋白(low density lipoprotein, LDL)受体摄取LDL,此摄取受细胞内胆固醇浓度的负反馈调节,不会导致泡沫细胞形成。当LDL氧化成氧化型低密度脂蛋白(oxidized low density lipoprotein, ox-LDL)时,其受体识别位点发生了变化,ox-LDL主要被巨噬细胞上的凝集素样氧化型低密度脂蛋白受体-1(LOX-1)[2] [3] 和清道夫受体快速识别,并且大量摄取, 此吞噬无负反馈调控机制,且ox-LDL可抵抗溶酶体酶及组织蛋白酶对它的降解,最终导致细胞内胆固醇代谢失衡,抑制胞内胆固醇流出,胆固醇脂合成增加,分解减少,最终以脂滴的形式聚集在细胞内,形成泡沫细胞[4] [5] 。
巨噬细胞吞噬ox-LDL,形成泡沫细胞,是目前常见且应用最广的体外培养模型。LDL主要由甘油三酯和胆固醇脂组成其核心成分,载脂蛋白、游离胆固醇和磷脂组成其表面成分,含有多种丰富不饱和脂肪酸,易被氧化修饰成ox-LDL[6] [7] 。ox-LDL的制备操作复杂,所需仪器价格昂贵,一般实验室无法完成。并且ox-LDL的化学性质不稳定、难保存[8] [9] 。血清是由血浆去除纤维蛋白原而形成的一种复杂的混合物,它主要由水和各种化学成分组成,这些化学成分包括白蛋白、α1、α2、β、γ-球蛋白,甘油三酯,总胆固醇,谷丙转氨酶等。本研究通过建立巨噬细胞培养体系,拟用血清替代低密度脂蛋白,诱导巨噬细胞转化为泡沫细胞,该方法的建立为动脉粥样硬化病理机制研究以及降血脂药物筛选提供了一种快速、便捷、经济的方法。
2. 材料和方法
2.1. 材料
2.1.1. 实验动物
清洁级昆明小鼠,8~12周,体重22~25 g雌雄兼用,购于承德医学院动物实验中心。
2.1.2. 试剂和仪器
RPMI-1640培养液购于Gibco;胎牛血清(100607)购于杭州四季青生物工程研究所;氧化型低密度脂蛋白购自北京欣源佳和生物科技有限公司;油红O购自Sigma;异丙醇购自天津市福晨化学试剂厂;24孔细胞培养板购于CORNING-COSTAR;总胆固醇(TC)和游离胆固醇(FC)检测试剂盒购于普利莱基因有限公司。
2.1.3. 仪器
CO2培养箱购于日本Taibai;光学显微镜购自日本Olympus公司。
2.2. 方法
2.2.1. 小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞分离培养
用碘酒及75%酒精分别消毒小鼠腹部后,倒立小鼠,从下腹部一侧注射不含胎牛血清的RPMI-1640培养液5 mL,轻柔小鼠腹部2 min,静置5 min后将其颈椎脱臼处死,置于75%的乙醇中浸泡5 min,随后放于超净台上,无菌条件下打开腹腔,抽取腹腔液,离心10 min (3000 r/min),弃上清,用RPMI-1640洗涤1遍,调整细胞密度至1 × 108 L−1,接种于放有无菌玻片的24孔细胞培养板内,置37℃、5% CO2培养箱无血清RPMI-1640培养4 h后换液。
2.2.2. 实验分组
4 h换液后,将细胞分为以下3组,无血清RPMI-1640组,无血清2 × 10−2 g/L ox-LDL的RPMI-1640组,5%,10%,20%血清RPMI-1640组,每组设6个复孔。
2.2.3. 细胞吞噬功能检测
细胞培养4 h后换液,进行墨汁吞噬实验,在培养体系中加入墨汁(10%)每孔1 × 10−4 L,放回培养箱中孵育,3 h后取出玻片,去离子水冲洗,中性树胶封片。镜下计数,计算吞噬墨汁细胞占总细胞的比例。
2.2.4. 分离培养的活细胞观察
细胞培养24 h后,取出玻片,弃细胞培养液,PBS清洗,苏木素染核3 min,盐酸乙醇分色返蓝后,中性树胶封片,显微镜观察。
2.2.5. 泡沫细胞油红O染色
取油红饱和液与蒸馏水以3:2的比例稀释,静置10 min后过滤使用。弃细胞培养液,用PBS清洗3遍,每次5 min,随后用体积分数为50%的异丙醇固定1 min,油红O染色10 min,去离子水清洗,苏木素染核3 min,盐酸乙醇分色返蓝后,取出玻片,中性树胶封片,显微镜观察。
2.2.6. 总胆固醇和游离胆固醇的含量测定
裂解前,细胞用PBS洗涤2次。按比例每1 × 106细胞加0.1 ml裂解液,混匀裂解工作液。室温2000 g离心5 min留上清液用于酶学测定。取190 μL工作液加入微板,加入10 μL待测样品﹑或标准品﹑空白对照溶液。37℃反应20 min然后在470 nm进行测定。用BCA法测定细胞蛋白。
3. 结果
3.1. 分离培养的巨噬细胞观察
培养24 h,苏木素染色,于镜下观察,可见细胞贴壁,核蓝染,细胞形态不规则,呈圆形、三角形、不规则形,伪足和突起伸出,胞浆丰富,核大为肾形、卵圆形、马蹄形或不规则核,居于细胞内一端,见图1。
3.2. 培养巨噬细胞的鉴定
将培养2 h的细胞做3 h的吞噬试验,3 h后取出玻片,去离子水冲洗,中性树胶封片。镜下计数,计算其吞噬率,发现所培养的细胞对墨汁颗粒有很强的吞噬能力,吞噬率为96.43%,见图2。
3.3. 不同浓度血清对巨噬细胞内脂质蓄积的影响
巨噬细胞与不同浓度的血清(体积分数5%,10%和20%)孵育7 h后,油红O染色封片,显微镜观察,
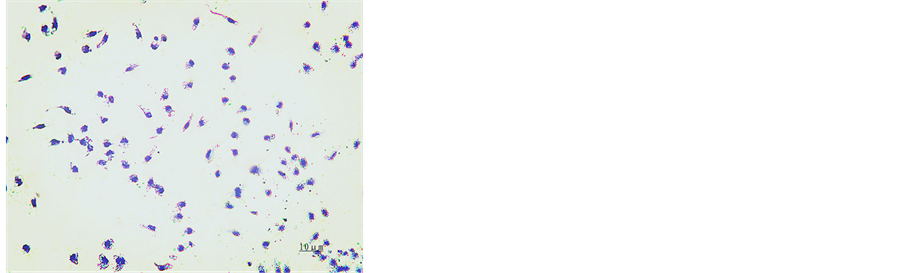
Figure 1. Hematoxylin staining for macrophages after 24 h cultivation (×200)
图1. 培养24 h后巨噬细胞苏木素染色(×200)
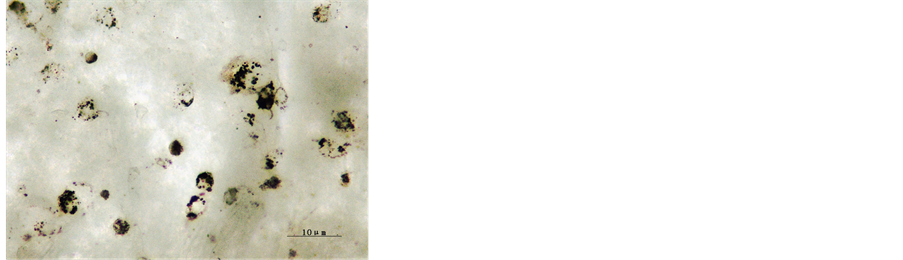
Figure 2. Ink phagocytosis test of macrophages after 2 h cultivation (×400)
图2. 培养2 h后细胞墨汁吞噬(×400)
细胞内脂质被染红,细胞核蓝色。与无血清RPMI-1640组组相比,可见细胞内脂滴增多,且随着浓度的增大,脂滴增大变多,部分融合成大脂滴。与无血清20 mg/L ox-LDL的RPMI-1640组相比,体积分数为10%的血清与ox-LDL 2 × 10−2 g/L的染色效果较接近。但随着血清浓度的增加,体积分数为20%血清诱导的巨噬细胞有部分细胞破裂、脂滴丢失、细胞减少的现象,见图3。
3.4. 不同作用时间血清对巨噬细胞内脂质蓄积的影响
巨噬细胞与10%的血清孵育不同时间(4 h,8 h和12 h)后,油红O染色封片,显微镜观察,细胞内脂质被染红,细胞核蓝色。与无血清RPMI-1640组相比,可见细胞内脂滴增多,且随着时间的增加,脂滴增大变多,部分融合成大脂滴。与无血清2 × 10−2 g/L ox-LDL的RPMI-1640组相比,血清作用8 h与ox-LDL 2 × 10−2 g/L作用24 h的染色效果较接近。当作用时间多于8 h时,巨噬细胞有部分破裂、脂滴丢失、细胞减少、缩小的现象,且时间越长,这种现象的越明显,见图4。
图3. 不同浓度血清对巨噬细胞内脂质蓄积的影响
3.5. 细胞内总胆固醇和游离胆固醇含量测定
巨噬细胞与10%的血清孵育7 h,与无血清RPMI-1640组相比,细胞内总胆固醇和游离胆固醇含量都明显增加(P < 0.01);细胞内胆固醇酯比重较与无血清RPMI-1640组明显增加(P < 0.01)。结果见表1。
4. 讨论
小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞的提取方法多为灌洗法[10] ,本实验采用成熟的小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞培养方法,通过
图4. 不同作用时间血清对巨噬细胞内脂质蓄积的影响

Table 1. Cholesterol and cholesteryl ester content within the Cells (x̅ ± s, n = 6)
表1. 细胞内胆固醇和胆固醇酯的含量(x̅ ± s, n = 6)
细胞形态学观察以及墨汁染色两方面鉴定所培养的细胞为巨噬细胞,且纯度较高。
巨噬细胞是重要的免疫细胞,具有免疫调节、抗肿瘤等重要的作用,以及多种功能特点,如吞噬功能、富含溶酶体等,吞噬功能是其典型的功能,在泡沫细胞的形成过程中,巨噬细胞内胆固醇代谢稳态失衡[11] ,巨噬细胞可摄取ox-LDL和富含甘油三脂的脂蛋白而转化成泡沫细胞,吞噬后的ox-LDL对巨噬细胞的功能有影响作用,可表达炎性细胞因子、抑制诱导型一氧化氮合酶的表达、增加细胞毒性、促进细胞内脂质的蓄积,诱导泡沫细胞的形成等[12] [13] 。泡沫细胞内的脂质来源于被吞噬的血液中的修饰脂蛋白,这些修饰脂蛋白以脂滴的形式储存于胞浆,脂滴外周被蛋白不完全包裹[14] 。而泡沫细胞的鉴定多用油红 O染色[15] ,油红-O属于偶氮染料,是很强的脂溶剂、染脂剂,能溶于细胞中的脂类,与甘油三酯等中性脂肪结合呈小脂滴状,它在脂类中的溶解度比在溶剂中大。当玻片浸入染液时,染料则离开溶剂而溶于细胞内的脂质中,特异性的使细胞内的脂滴呈红色,通过这一特性对血清诱导形成的细胞进行鉴定是否为泡沫细胞。
根据文献报道[16] -[18] 本实验室曾使用ox-LDL对巨噬细胞进行诱导,但在作用过程中发现用含10%血清的RPMI 1640培养液培养的巨噬细胞,在油红O染色时,出现无ox-LDL含10%血清的RPMI1640组内细胞脂质被染红的现象,并且加入ox-LDL诱导的部分细胞丢失破碎,故推测血清中的脂质亦被巨噬细胞所吞噬,造成无ox-LDL含10%血清的RPMI1640组内的巨噬细胞被诱导,加入ox-LDL诱导的细胞由于同时过度吞噬血清中的脂质,引起细胞丢失破碎,故设计拟通过血清诱导巨噬细胞转化为泡沫细胞的实验,采用国产四季青胎牛血清对巨噬细胞进行诱导。由于血清内含有多种复杂的化学成分,血清本身存在动物个体、来源、产地不同的差异,各个批次脂类含量亦有差异,使用血清对巨噬细胞进行诱导存在不稳定性[19] 。但在相同作用时间下,与无血清RPMI1640组相比,不同浓度的血清(体积分数5%,10%和20%)孵育7 h后,均产生了诱导效应,随着浓度的增大,脂滴增大变多,部分融合成大脂滴。10%的血清与ox-LDL 2 × 10−2 g/L的染色效果较接近。但当血清浓度达到20%的高浓度时巨噬细胞有部分破裂、脂滴丢失、细胞减少的现象。若用10%血清对巨噬细胞作用不同时间(4 h,8 h和12 h),随作用时间的延长,巨噬细胞内脂滴增多变大,10%血清作用8 h与ox-LDL 20 mg/L作用24h的染色效果较接近。但当作用时间多于8 h时,部分巨噬细胞有破碎缩小、脂滴丢失的现象,且时间越长,细胞破裂、数量丢失越严重。因而可采用血清高浓度短时间、或低浓度长时间作用细胞来诱导泡沫细胞生成,本实验结果发现10%血清作用巨噬细胞7 h诱导泡沫细胞可以作为体外泡沫细胞模型的建立。该方法建立的泡沫细胞的模型,细胞内的总胆固醇和游离胆固醇含量均较无血清组显著升高。动物血清能改变巨噬细胞内的胆固醇酯代谢平衡,使胆固醇酯在巨噬细胞内大量堆积,增加脂滴的形成。动物血清作为泡沫细胞的诱导物质,来源于动物血液中全部的脂类,较ox-LDL诱导泡沫细胞的产生更为接近人类的动脉硬化的发病机理,但本实验动物血清是否是高血脂动物,血脂组成与高脂动物血脂组成是否一致,对泡沫细胞模型的建立是否有影响还有待于今后进一步的工作。
综上所述,10%四季青胎牛血清作用于小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞7 h诱导泡沫细胞 是一种快速、便捷、经济的体外模型建立方法。

NOTES
*通讯作者。