1. 引言
自三里岛事故和切尔诺贝利事故后,核工业界开始关注被认为发生概率极低的严重事故,之后很多国家要求核电厂制定相应的严重事故管理指南(SAMG)。严重事故管理成为整个安全保障体系中纵深防御的组成部分之一。尽管如此,直到福岛事故发生之前,仍有很大一部分人认为随着三里岛后的核电厂技术改进,严重事故只是假想事故,严重事故管理对核电厂只是锦上添花,SAMG对于核电厂可有可无。日本政府在递交国际原子能机构(IAEA)核安全部长级大会的报告中认为已在福岛核电站采用的严重事故管理措施,最大限度减少了事故演变为严重事故的可能性,并在发生严重事故的情况下减轻事故后果。但是,审视事故后处理的情景就会发现,尽管部分措施(例如利用消防水系统向反应堆注水)发挥了作用,但在各种响应行动中还有相当一部分措施并未发挥作用,包括旨在恢复电力供应和反应堆冷却功能的措施,还有一些措施已证明是不够充分的。事故管理措施基本上被视为是操作员的自愿行动,而不是法定要求,因此,相关措施的建立和实施缺乏严密性。此外,有关事故管理的导则自1992年发布以来就未再接受评审,也一直未得到加强或改进。
福岛事故之后,人们才更加清醒和深刻的认识到,严重事故绝不仅仅是所谓的假想事故,离我们并不遥远。日本监管当局认为应把事故管理措施从操作员自愿的安全努力转变为法定要求,并使用概率安全评估方法来建立事故管理措施,以防止严重事故,包括评审设计要求。其他世界各国内包括核安全当局、核电业主、各核能研究单位以及普通民众,对核电厂严重事故的关注也都提高到了一个前所未有的程度,针对严重事故的管理也作为核电业主及核安全监管当局一项重点工作。
本文对国内外严重事故管理情况以及严重事故管理发展的趋势进行了介绍,并对国内严重事故管理指南发展提出建议。
2. 国内外严重事故管理发展状况
2.1. 国外严重事故管理发展情况
1988年,美国开始执行核电厂逐个严重事故评价计划(IPE)[1] ,并在1993年完成了所有核电厂的评价。1992年,美国电力研究院(EPRI)出版了严重事故管理的技术基础报告TR-101869。1993~1995年间,将注重地震和火灾风险的评估纳入了IPE外部事件(IPEEE)分析[2] 。1994年11月4日,美国核管会(NRC)批准通过了关于核电站的严重事故管理要求的正式立场,采用NEI 91-04修订版1第5部分“严重事故问题终结导则”来评估电站响应严重事故的能力。根据评估结果,在现有人员和硬件条件下实施恰当的改进方案,每个执照者自己制订改进计划并通报NRC,最迟不能超过1998年11月31日。随后,美国三大能源集团,Westinghouse,Combustion Engineering和Babcock & Wilcox分别为其用户研制出了通用SAMG,即WOG、CEOG和B&WOG。其中,WOG SAMG[3] 框架后来成为世界范围内应用最为广泛的SAMG。WOG SAMG在1991年发布第一版后,后来又不断对其进行升版。最初的WOG只能覆盖功率工况下的严重事故,目前WOG已经在世界范围内的一些电厂(如南非Koeberg、瑞士Beznau、斯洛伐克Mochovce)覆盖了停堆工况和(或)乏燃料水池工况。
2001年的“9·11”恐怖袭击事件之后,NRC发布了安全公告、命令和许可条件,最终形成了新的法规10CFR50.54 (hh)。该法规要求执照持有者在火灾或爆炸导致核电厂大面积损坏的时候,发展和应用导则及策略以保持或者恢复堆芯冷却、安全壳和乏燃料水池的冷却能力。这些要求,经过业界不断的探索,使得美国所有核动力厂最后发展并形成了EDMG (Extensive Damage Mitigation Guidelines)。EDMG的要求是考虑那些远远超过那些历史上被认为是设计基准以及已经由经验反馈而被实施了适当防护的事件。
至此,美国在核电站事故管理方面,已经形成了EOP、SAMG、EDMG系列,基本可以应付可以想象的核事故情况。
法国在1980年代开始严重事故研究和严重事故管理工作,并改进了应急运行规程(EOP)并于80年代末开始制定法国体系的严重事故事故导则(EDF GIAG)。在对比世界上主要的SAMG优缺点的基础上,法国AREVA公司专门针对EPR堆型研制出了新的严重事故管理导则OSSA。该导则可以覆盖功率工况和停堆工况,并专门考虑了全场断电叠加丧失所有应急柴油机的工况。EPR OSSA中应用到的严重事故专设缓解系统和仪表设备都按一定原则进行了分类,对其中有严重事故鉴定要求的系统和仪表设备均进行了试验鉴定[4] 。
2.2. 国内严重事故管理发展情况
从2000年起至今,随着国际上针对核电厂应对严重事故的研究不断深入,国家核安全局密切注意国际上关于严重事故管理的一些新动态,采取了相应的行动。
2002年,国家核安全局发布了政策声明《新建核电厂设计中几个安全重要问题的技术政策》,对新建核电厂几个影响安全的重要方面提出了一系列指导性的政策。其中要求采用概率论、确定论和工程判断相结合的方法确定可能导致严重事故的重要事件序列,并评价可能的设计或规程修改来降低这些序列的风险。
2004年国家核安全局发布了新版《核动力厂设计安全规定》[5] 和《核动力厂运行安全规定》[6] ,明确要求我国所有新建核电厂在执照申请阶段要考虑应对严重事故应采取的合理可行的预防和缓解措施,例如严重事故工况下的可燃气体控制措施、防止高压熔融物喷射的措施、防止安全壳旁路的措施等,并开发严重事故管理指南等。
日本福岛事故后,由环境保护部(国家核安全局),国家发展改革委,财政部,国家能源局,国防科技工业局共同颁布的《核安全与放射性污染防治“十二五”规划及2020年远景目标》[7] ,对严重事故管理提出了进一步要求,明确要求新建核电机组具备较完善的严重事故预防和缓解措施,运行电厂在2013 年底前要制定并实施严重事故管理导则,在建电厂首次装料前要制定并实施严重事故管理导则,并考虑各类事故工况和多堆厂址共因失效工况,分析评估严重事故下重要设备、监测仪表的可用性和可达性。
事实上,我国大亚湾核电站于1999年就开始严重事故可行性研究,并随后提出了严重事故管理计划,并于2001年底正式开展了SAMG研发。大亚湾SAMG于2005年开始正式实施,这是我国首个实施的SAMG。2009年,秦山三期的SAMG也开始实施。
国内在建核电厂从岭澳核电厂二期和秦山二期扩建工程之后,所有的在建核电厂都承诺开展SAMG制定工作。目前国内在建核电厂都按承诺向国家核安全局提交了SMAG,但由于国内SAMG的研究起步较晚,目前已提交的SAMG只包括了功率运行工况。
福岛核电厂事故之后,覆盖乏燃料水池和停堆工况的SAMG的研究变得更加重要。除此之外,极端的自然条件和群堆厂址下的严重事故管理在福岛事故后也开始成为人们关注的问题,但无论国内、国外,这方面的研究还有待开展。
2.3. 相关法规导则
目前,国际上比较权威的严重事故管理方面的指南是2008年国际原子能机构(IAEA)发布的导则“No. NS-G-2.15”“Severe Accident Management Programmes For Nuclear Power Plants”[8] 。该导则是IAEA聘请各国专家在总结各核电先进国家严重事故管理经验的基础上制定的,其内容完整、系统、严谨,在严重事故预防、缓解、核动力厂薄弱环节的识别、核动力厂能力的识别、事故管理策略的制定、规程和指南的制定、事故管理的硬件规定、仪器仪表和控制的作用、管理的职责和路线、验证和确认、教育和培训、新信息的处理、支持分析和管理体系等14个方面对严重事故管理指南的编制给出了指导性的建议。
国内目前涉及严重事故管理的法规包括国家核安全局发布的新版《核动力厂设计安全规定》(HAF102)和《核动力厂运行安全规定》(HAF103)。HAF102明确了严重事故的定义以及针对严重事故预防和缓解必须的措施,HAF103则要求核动力厂必须制定严重事故管理指南并对指南相关信息进行了规定。
为了落实《核动力厂设计安全规定》(HAF102)和《核动力厂运行安全规定》(HAF103)中严重事故管理相关内容,2010年底,我国核安全当局编制发布了核安全导则《核动力厂严重事故管理》(征求意见稿)[9] 。该导则以IAEA严重事故管理导则“No. NS-G-2.15”“Severe Accident Management Programmes For Nuclear Power Plants”为参考蓝本编写而成,基本反映了目前世界上对严重事故管理最先进的要求。
3. 严重事故管理的发展趋势
根据福岛经验反馈以及国内外严重事故管理调研情况,笔者认为,未来核电厂严重事故管理发展可以从以下四个方面来看:
(1) 指南涵盖的工况
早期严重事故管理指南的编制主要覆盖功率工况下的严重事故,以WOG SAMG框架最具代表性,该指南假设严重事故的始发事件在满功率运行工况下发生。后来,随着低功率、停堆工况下PSA分析的发展,Surry电厂停堆PSA、Beznau电厂的BERA停堆PSA和EPRI/Westinghouse ORAM方法都表明,在低功率运行和停堆工况下的堆芯损伤频率与满功率工况下的具有同样量级。因此,西屋在后来的WOG中将SAMG拓展至停堆工况(含乏燃料水池事故)。福岛事故的事实也证明,停堆工况下的严重事故(含乏燃料水池事故)需要更多关注。南非Koeberg核电厂是第一个将SAMG扩展至停堆工况(含乏燃料水池工况)的核电厂。其指南框架图如图1。
南非Koeberg核电厂严重事故管理指南包括主控室(MCR)使用部分和技术支持中心(TSC)使用两个部分。根据技术支持中心(TSC)的状态不同,严重事故控制室导则可分为两部分,若技术支持中心尚未成立,且核电厂处于功率运行工况,则进入SACRG-1 (主控室严重事故初始响应导则);若技术支持中心尚未成立,且核电厂处于停堆工况,则进入SACRG-3 (主控室余排系统接入后严重事故初始响应导则);若技术支持中心已成立,则执行严重事故管理导则,则进入SACRG-2 (TSC正常运作后主控室严重事故导则)。
TSC人员是SAMG的主要使用者。TSC相关的导则分为以下三个主要部分:诊断导则(DFC、SCST)、严重事故导则(SAG-1至SAG-8)、和严重威胁导则(SCG-1至SCG-4)。其余的TSC导则包括严重事故缓解后的长期监督(SAEG-1)和出口导则(SAEG-2),以及一些计算辅助曲线(CA-1至CA-7)。CA曲线可以帮助TSC得到一些重要参数或判断电厂的状态。
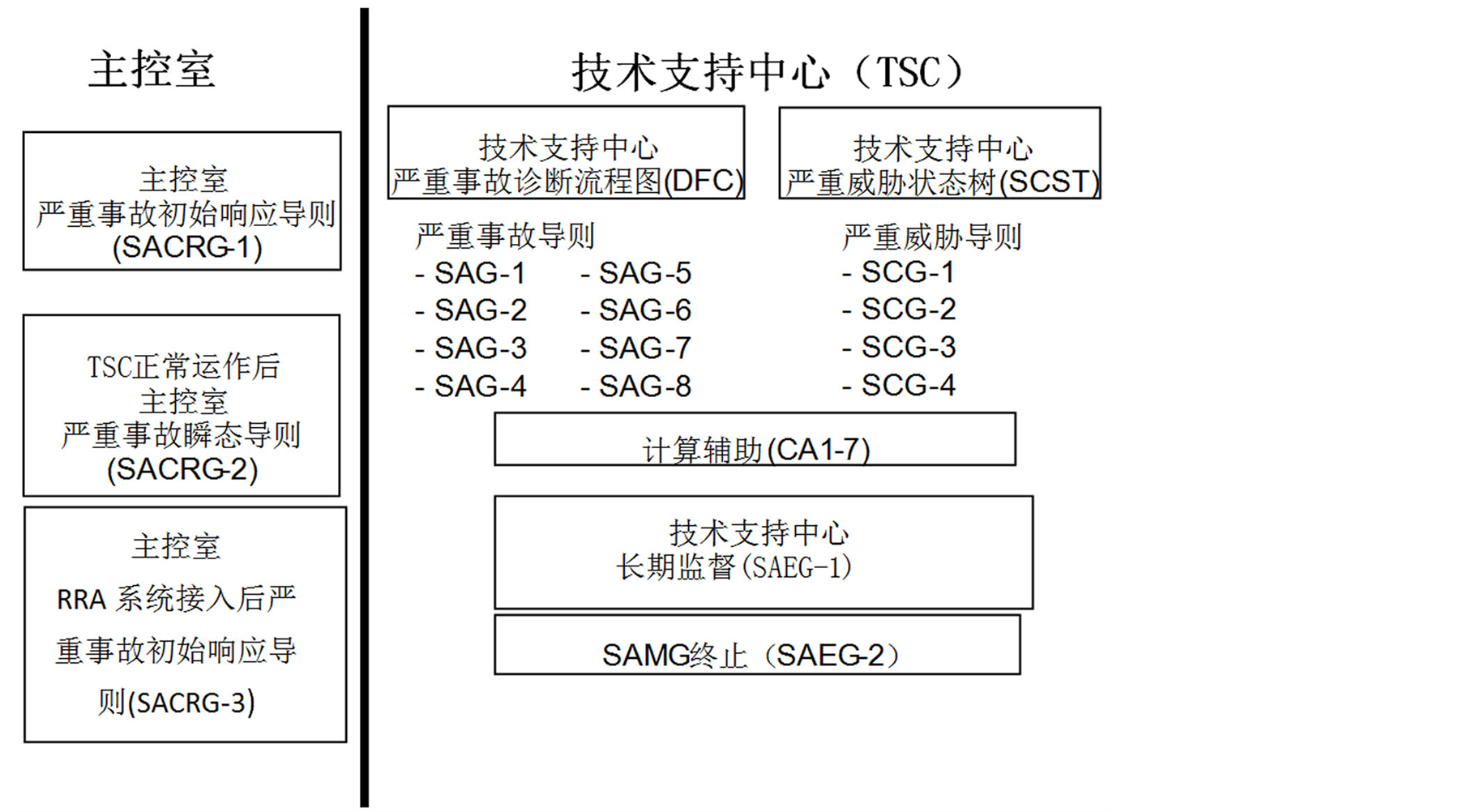
Figure 1. SAMG of Koeberg nuclear power plant in South Africa
图1. 南非Koeberg核电厂严重事故管理指南框架图
(2) 极端自然灾害
极端自然灾害,如火灾、水淹、地震等,可能造成大范围的共模失效,使得电厂完全丧失动力源和/或冷源。福岛事故即属于此种情况。为应对类似福岛事故的这种由于极端自然灾害引起的严重事故,一方面,需要增强电厂的硬件能力,如提高抗震和防水淹等级、配备更大容量的蓄电池、缩短外部电源和设备的接入时间、增强严重事故监测设备和缓解系统的多样性功能、更多考虑非能动设备等;另一方面,需要增强SAMG的覆盖范围。需要考虑的问题包括:(a) 增加严重事故初始工况(极端自然灾害类),重新分析严重事故进程和现象;(b) 丧失仪表和控制动力之后SAMG的应用方法;(c) 在SAMG中增加对注入海水和非含硼水的考虑;(d) 增加对电厂外部设备接入的管理。
(3) 群堆厂址
在福岛事故中,多座反应堆同时发生事故,分散了应对事故所必需的资源。此外,因为两座反应堆共同使用一些公用设施,而两座反应堆之间的实体间距很小,一座反应堆事故的发展过程必然影响邻接反应堆的应急响应。
在《核动力厂严重事故管理》(征求意见稿)导则中要求在SAMG中要考虑群堆厂址的特殊性(相互支持及影响)。但目前国内外SAMG均未考虑到这一点。
经过此事福岛事故的教训,日本已经表示,将采取措施,确保在一座反应堆发生事故进行事故处理的同时,其他反应堆仍然能够独立运行。日本也将确保设计时就考虑每座反应堆的独立性,防止一座反应堆的事故影响到相邻的反应堆。另外,日本将推进并完善“挑选确保每台机组核安全的责任人员,以保证每台机组能独立应对事故”这种体制。
(4) 超出SAMG范围的工况
SAMG的编制基于这么一个假设,即主控室(MCR)和技术支持中心(TSC)之间的命令和控制是可用的。但是,当核电站出现相当大的毁坏时(如大范围爆炸,MCR不可居留),电厂的事故管理将超出SAMG的范围。此时,需要应用类似美国EDMG (Extensive Damage Mitigation Guidelines,大范围损伤缓解导则)的导则来管理电厂。
EDMG的主要思路是应用电厂外部的移动设备给电厂补水(如RWST补水、SG补水、ASG补水、乏燃料水池补水、安全壳淹没、放射性喷淋沉降等),并考虑一些可能的手动缓解操作(如纯手动的SG排放手段、现场手动控制汽动辅助给水泵等)。此外,需要对现场的通讯设备进行改造,使其不依赖现有的电源系统。
4. 建议和讨论
国内SAMG研制起步较晚,目前为止,已实施及研制中的SAMG也基本以早期的西屋WOG SAMG为蓝本,只包括了功率运行工况,对乏燃料水池和停堆工况研究还不够,也未考虑核电厂应对极端自然灾害和群堆厂址下的严重事故管理,与核安全当局核安全导则《核动力厂严重事故管理》(征求意见稿)的相关要求还有一定距离。
基于目前国内外SAMG的研制现状,并考虑福岛事故后国内核电厂可能开展的相关改进和严重事故发展的趋势,笔者建议国内SAMG发展规划如下:
(1) 短期(1~2年)
(a) 基于核电厂的设计特点,结合短期内实施完成的设计改进(基于福岛事故经验教训),各在运及在建核电厂完成功率工况SAMG编制及实施;
(b) 结合SAMG编制及福岛事故经验教训,开展严重事故下设备可用性分析论证工作;
(c) 对制定的SAMG,广泛开展同行评审工作,进一步完善和提升国内SAMG研制水平;
(d) 由国家核安全局对主控室和技术支持中心执行SAMG的人员资质采用考试等方式进行认证;
(e) 完善核电厂应急演习方案,考虑可能出现的严重事故场景,充分识别可能的危险因素并制定相应的应对措施。
(2) 中期(3~5年)
(a) 结合福岛事故经验反馈及概率风险分析结果,完成涵盖停堆工况、乏燃料水池工况以及外部事件SAMG,形成全范围的SAMG;
(b) 针对全范围的SAMG,与国际同行开展广泛的交流,开展国际及国内的同行评审工作,修改完善后在各核电厂正式实施;
(c) 开发全范围严重事故模拟仿真系统,开展全面的SAMG培训和验证工作。
(3) 长期(5~8年)
(a) 参考美国EDMG研制经验,完成应对极端工况、群堆的管理导则编制相关工作;
(b) 密切跟踪国际上SAMG相关研究动向并开展相关工作,保持国内SAMG研究在国际处于领先地位。
严重事故的预防和环节措施是应对核电厂各类威胁的最后一道屏障,因此必须作为核电厂以及核安全当局一项常抓不懈的重点工作来做。在国内同行的共同努力下,相信未来我国必将形成一套完整的核电厂事故管理体系,确保核电安全健康发展,保障人民群众人身财产安全。