1. 引言
空间物体包括工作正常的卫星和失效卫星,同时也包括各种空间碎片。以太阳光辐射为主的光照环境是空间物体经历的主要外部环境之一,对空间物体的探测控制、工作性能和效率、寿命等具有重要影响。根据各自任务需要,研究者对空间光照环境和条件进行了大量研究[1] [2] ,得出了一些有意义的结论。空间物体光照特性不仅考虑地球周围的空间光照情况,还要考虑空间物体轨道运动带来的影响,在更精细的应用中甚至还要考虑目标的形状、姿态、材质、平整度和反射率等复杂因素的影响。本文从空间物体光照问题的理论分析出发,构建该问题的数学模型,对空间物体光照的影响参数进行详细分析,并进一步探讨空间物体光照特性在空间活动中的主要应用。
2. 空间物体光照问题的数学建模
2.1. 地影与受晒因子
由于地球的遮挡,使太阳不能直射的阴影区称为地影。由于太阳的大小以及太阳与地球之间的距离,使得地影包括本影区和半影区两部分。本影区是阳光全部被地球遮蔽的区域,半影区是阳光部分被地球遮掩的区域,如图1所示。rES为日地距,rS为太阳半径,rE为地球半径,δu(≈15.8′)和δρ(≈16.2′)分别为本影角和半影角。本影区为圆锥体,其半顶角为δu,高度约为217rE。由于δu和δρ为小角,对于近地空间物体可将地影近似看作为半径等于rE的圆柱体本影,阳光近似看作平行光,地影无本影与半影之分[3] 。
当空间物体受阳光照射时,称为受晒;反之,当空间物体处于地影内时,称为星蚀。设空间物体轨道周期为T0,其在轨道上运行一圈的受晒时间为Ts,定义受晒因子Ks为
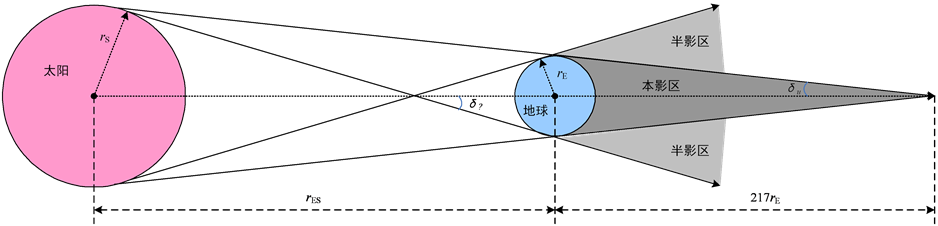
Figure 1. The earth’s umbra and penumbra area
图1. 地球的本影区和半影区
 (1)
(1)
可知,当空间物体全轨道受晒时,Ks = 1;反之,当全轨道星蚀时,Ks = 0。
2.2. 地影方程的解
假定地影为圆柱体,如图2所示。令地心至太阳中心的矢量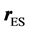 与地心至空间物体的矢量
与地心至空间物体的矢量 之间的夹角为ψ。则空间物体在地影内所满足的条件为[4]
之间的夹角为ψ。则空间物体在地影内所满足的条件为[4]
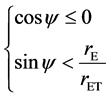 (2)
(2)
设太阳的黄经为λS,黄赤交角为εS,a、e、i、Ω、f、ω分别是空间物体轨道的长半轴、偏心率、轨道倾角、升交点赤经、真近点角和近地点幅角。经推导可得空间物体地影方程的表达形式为
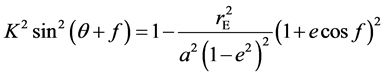 (3)
(3)
式中:
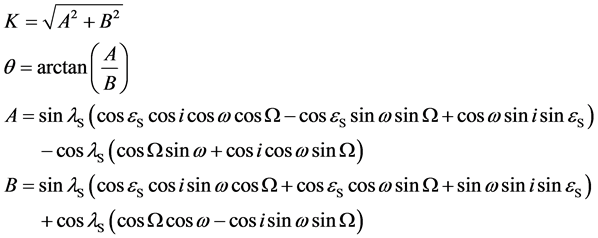
由该方程可解出空间物体进、出地影的“位置”fI和fO。
方程(3)可用迭代法求解,其迭代过程:首先令e=0,有
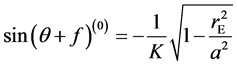 (4)
(4)
解出fI和fO的初值 和
和 ,然后分别代入方程(3)的右端进行迭代,直到满足一定精度为止,即给出空间物体进、出地影的“位置”fI和fO。
,然后分别代入方程(3)的右端进行迭代,直到满足一定精度为止,即给出空间物体进、出地影的“位置”fI和fO。
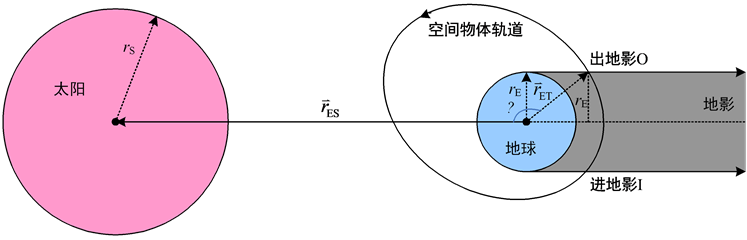
Figure 2. The relationship between earth’s cylinder shadow and space object
图2. 圆柱地影与空间物体的关系
迭代计算过程中,有两种情况需要注意:
1) 根据(θ + fI)在第三象限和(θ + fO)在第四象限,确定fI和fO。
2) 如果sin(θ + f)(0) ≤ ‒1,表示接近无地影(指空间物体不进入地影区)状态或就是无地影的情况,此时可令(θ + f)(0) = 270˚代入方程(3)右端开始迭代;如果再出现sin(θ + f)(0) ≤ ‒1,就当作无地影处理,相应地令fI = 0、fO = 0即可。
2.3. 太阳的黄经
太阳的黄经是指太阳在黄道春分点坐标系中的经角λS,由春分点γ开始沿逆时针方向(即太阳周年视运动的方向)度量,范围为0˚~360˚。
当计算精度要求不高(低于0.01˚),计算太阳位置时可假设地球运动是一个纯椭圆,即忽略月球及行星摄动。设T为J2000起算的儒略世纪数,则
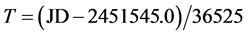 (5)
(5)
式中:JD是儒略日数(含小数部分),与公历之间的转换关系见文献[4] 。由于T的单位较大,所以计算时要注意保留足够的小数位数。
再由太阳几何平黄经(当日平分点起算)
 (6)
(6)
太阳平近点角
 (7)
(7)
太阳中间方程
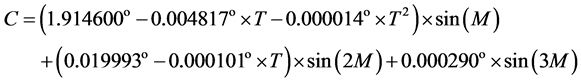 (8)
(8)
求得太阳的真黄经是
 (9)
(9)
通过以上方法可以获得太阳在当日黄道春分点坐标中的真几何黄经。如果需要把太阳黄经转到J2000坐标中,在1900年~2100年范围内可利用下式进行:
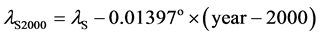 (10)
(10)
2.4. 黄赤交角
黄道面与赤道面的夹角是黄赤交角。黄赤交角存在缓慢的变化,变化范围22˚00′~24˚30′,变化周期约为4.1 × 104年。上次黄赤交角最小值距今约2.8万年。近期计算黄赤交角可用以下公式:
 (11)
(11)
式中,τ是1900年起算的儒略年数。
3. 空间物体光照的影响参数分析
3.1. 影响参数集合
由式(3)可知,空间物体进、出地影的位置fI、fO与参数λS、εS、a、e、i、Ω、f、ω有关,这些参数又都是时变的,与时间t有关。再考虑式(1)知,空间物体的受晒因子Ks还与轨道周期T0有关,而椭圆轨道的T0只与a有关。因此,空间物体的受晒因子Ks与参数λS、εS、a、e、i、Ω、f、ω、t有关,即有如下函数表达式
 (12)
(12)
3.2. 圆轨道的参数条件设定
为了分析问题的方便,设空间物体轨道为常用的(近)圆轨道,即令e = 0,则有
 (13)
(13)
其中,fI和fO可由式(4)求解,而其差值与f、ω无关。在求解fI和fO时,由于地球自转和其它摄动因素的存在,Ω等影响参数是随时间变化的,使得精确的求解过程仍然比较复杂。考虑fI和fO之间的时间间隔(即空间物体一次飞越地影的时间)比较小,因此可以利用fI时的参数近似求解fO,即忽略空间物体飞越地影时t变化的影响。这样,由式(4)和式(13)可得
 (14)
(14)
带入式(13)得
 (15)
(15)
式中:
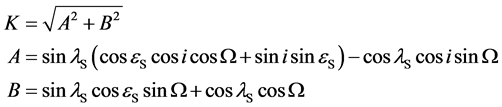
计算时,如果出现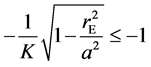 ,则取
,则取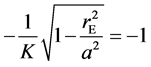 。
。
此外:
1) 黄赤交角εS是一个变化十分缓慢的参量,变化周期远超过空间物体的轨道寿命,最近数十年内可近似取恒值23˚26′。
2) 太阳黄经λS的变化也比较慢,变化周期为一年,在[0˚, 360˚]范围内近似均匀变化。
3) 长半轴a=rE+h,与轨道高度h线性相关。对于常用的LEO轨道,可以认为h在[200 km, 2000 km]范围内自由选择。
4) 轨道倾角iÎ [0˚, 180˚]、升交点赤经ΩÎ[‒180˚, 180˚]均可认为自由选择变量。
3.3. 圆轨道长半轴(高度)对受晒因子的影响
根据式(15),如果只改变空间物体的轨道长半轴a,则K为一不变的正数,随着a的增大,受晒因子Ks逐渐变大,直到等于1(即全轨道受晒)为止。
作为例子,设λS = 0˚、I = 90˚、Ω = 120˚,计算受晒因子Ks随轨道长半轴a变化的典型曲线如图3所示。
3.4. 圆轨道的全轨道受晒分析
根据式(15),如果空间物体全轨道受晒,则需要
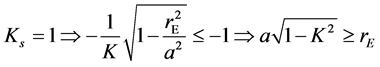 (16)
(16)
上式即为圆轨道情况下的全轨道受晒方程。
4. 空间物体光照特性在空间活动中的应用
光照条件是空间物体正常工作的基础和保障,空间物体光照特性在航天活动中有着多种重要的应用。应用方向包括空间目标光学探测与跟踪、太阳敏感器、太阳光压作用、空间太阳能发电、航天器温度控制、天基红外遥感等,下面选取几种主要应用进行讨论。
4.1. 空间目标光学探测与跟踪
空间物体探测与跟踪是发现目标、管理目标、避免空间碰撞威胁、引导武器攻击目标的前提和基础,目前实现这一需求的主要手段是雷达和光电望远镜。由于雷达属于主动探测,其探测能力与作用距离的4次方成反比,而光电系统的探测能力与距离的平方成反比,且定位跟踪精度更高。因此,光学探测是空间物体探测的重要手段之一,而且在某些情况下(如高精度跟踪与引导,探测1~30 cm [5] 的小尺寸目标等)是目前空间物体探测的唯一手段。
以美国空间目标监视系统为例,其对10 cm以上的低轨目标主要依赖地基雷达,中高轨目标则依赖光电系统。对于1~10 cm的低轨目标,美国国防部(DOD)和宇航局(NASA)均提出了探测与跟踪要求,其采用的手段是地基大口径、大视场搜索望远镜。其中,美国NASA与美国空军研究实验室(AFRL)于2010年研制了1.25 m级搜索跟踪望远镜(Meter Class Autonomous Telescope, MCAT)[6] ,以期实现低轨l~10 cm碎片的搜索发现与跟踪测量;美国国防部先进项目局(DARPA)正在研制口径为3.5 m,视场为3.5˚的大口径地基搜索望远镜,用于低轨暗弱目标的搜索,甚至采用了曲面CCD[7] ;美国空军的3 m旋转水银搜索望远镜,也正用于低轨目标的搜索发现[8] 。另外,美国天文界正在研制的用于小行星搜索发现的2~8 m
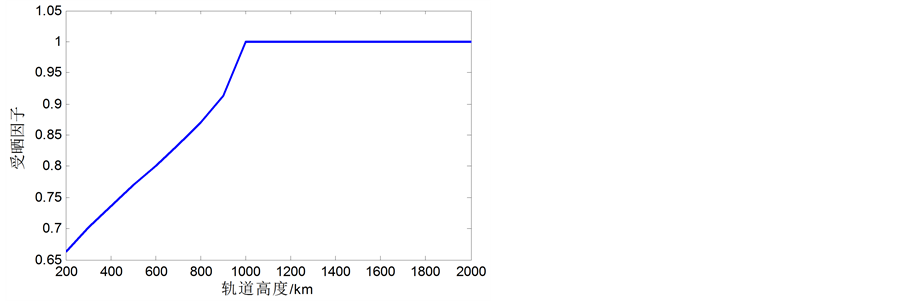
Figure 3. Curve: sunshine factor Ks changing with orbital semimajor axis a
图3. 受晒因子Ks随轨道长半轴a的变化曲线
级地基望远镜[7] ,也规划用于低轨小目标的搜索发现,如8.4 m口径、3˚视场的LLST望远镜,4个1.8 m口径、3˚视场的PAN STARRS望远镜阵。
为了能够利用光学探测系统对空间物体进行探测与跟踪,需要符合空间物体光学可探测条件,即要求目标不在地球阴影区,不在太阳的视圆面上及其附近区域,不在月亮视圆面上,探测系统和目标之间的传播路径没有被遮挡,目标能够反射光辐射,且探测系统可以接收到。简单而言,空间物体经过光照区的时间范围[9] 、空间物体到光学探测系统方向与太阳到光学探测系统(太阳光)方向的夹角γ(见图4)是影响空间物体可见光探测的基本要素。无论光学探测系统是地基还是天基,都是如此。
在计算时,空间物体经过光照区的时间范围可以由式(3)求得,而空间物体到光学探测系统方向与太阳到光学探测系统(太阳光)方向的夹角γ可由下式求解:
 (17)
(17)
式中, 、
、 分别是光学探测系统到太阳的矢距和光学探测系统到空间物体的矢距。对于地球轨道目标,可近似认为
分别是光学探测系统到太阳的矢距和光学探测系统到空间物体的矢距。对于地球轨道目标,可近似认为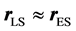 。
。
由此可见:
1) 空间物体在光照区是可见光探测的必要条件,但并非充分条件,即在光照区时不一定都能被探测。实际上,白天对空间物体进行高精度跟踪测量是目前空间目标探测领域的一项重要课题,由于白天天空背景较亮,背景噪声较强,采用传统光电探测方法探测跟踪空间物体十分困难[10] 。
2) 存在空间物体在光照区,而光学探测系统在地影的情况,此时对光学探测系统的工作是有利的。有利方面主要体现为:一是有利于光学探测系统稳定探测跟踪空间物体;二是在空间物体是可见光侦察卫星的情况下,卫星对光学探测系统是单向可视的,具有侦察不对称性。
4.2. 太阳敏感器
太阳敏感器(sun sensor)是航天领域广泛应用的一类敏感器,几乎在所有航天器上都会配备。它通过在光照区敏感太阳矢量的方位来确定太阳矢量在星体坐标中的方位信息,结合太阳历获取卫星的姿态。太阳敏感器的设计和姿态确定算法都比较简单、敏感精度高,而且太阳的高亮度、高信噪比使得检测比较容易实现,因此,它可以提供星上姿态控制基准信号,适用于对航天器的姿态和轨道控制。但是太阳敏感器必须在光照区才能工作,航天器一旦进入地影后它只能停止工作,所以它需要与其它姿态测量装置组合工作。
例如,微小卫星经常用磁强计作为姿态测量的主要部件,但磁强计的测量精度是影响微小卫星定姿性能的重要指标。为提高磁场估计精度,文献[11] 采用太阳敏感器和陀螺对磁强计误差进行辅助测量与修

Figure 4. The relationship among space object, optical detection system and the sun
图4. 空间物体、光学探测系统与太阳之间的关系
正。仿真表明该方法简单易行,姿态角精度提高了1˚左右,角速度精度最高提高了0.003˚/s左右,并增强了卫星稳定性,有利于成像等任务的完成,有效提高了微小卫星导航系统性能。
4.3. 太阳光压作用
当空间物体处于光照区时,太阳光照射在目标表面会产生一种压力,这种现象称为太阳光压作用。当光照到物体上并被物体吸收时,物体会得到一定大小的推力;如果光在物体表面进行反射,那么物体可得到两倍大小的推力。设太阳光与物体表平面的夹角为α,物体受光照的表平面面积为A,则可以算出全反射情况下作用在物体表平面上的推力为
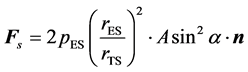 (18)
(18)
式中, 是地球到太阳的距离,一般可取平均值
是地球到太阳的距离,一般可取平均值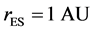 (1个天文单位,地球到太阳的平均距离);
(1个天文单位,地球到太阳的平均距离); 是物体到太阳的距离;
是物体到太阳的距离;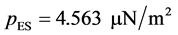 ,是1 AU处的太阳辐射压力;
,是1 AU处的太阳辐射压力; 表示在理想情况下,推力总是沿着物体表平面的法向方向。实际中并非全反射情况,要引入一个小于1的推力修正系数。
表示在理想情况下,推力总是沿着物体表平面的法向方向。实际中并非全反射情况,要引入一个小于1的推力修正系数。
太阳光压在航天活动中有重要作用,主要包括:
1) 引起空间物体轨道摄动和姿态扰动。太阳光压是空间物体轨道摄动和姿态扰动的重要因素[12] ,尤其对于高地球轨道和深空轨道。因此,在航天任务分析设计、航天器轨道和姿态控制时,需要重点考虑。
2) 太阳帆推进,实现太阳系飞行。太阳帆依靠反射太阳系中广泛存在的太阳光光子产生推力,通过持续累积推力形成大的速度增量,而不需要消耗任何推进剂,具有其它推进系统无法替代的优点,可广泛应用于低成本大速度增量的太阳系飞行任务,是一种很有前景的新型空间推进方式[13] 。
3) 进行Halo轨道编队控制[14] 。该编队需要的控制力量级小,常规的推进方式难以实现,太阳帆能产生微小的连续光压力,可以用于Halo轨道附近的编队控制。
4) 用于空间碎片的离轨清除。在地球轨道上的空间碎片(如失效卫星),如果装载或附着太阳帆,则可以利用太阳帆指向太阳产生辐射压力,经过连续不断工作,迫使碎片离开原有轨道,抬升或降低到新的轨道,实现离轨。例如,英国曾计划2011年发射一颗3 kg重的纳卫星——“立方体太阳帆”(CubeSail),试验太阳帆清除空间碎片的技术可行性。CubeSail可附着在空间碎片上,并携带碎片坠入大气层[15] 。
4.4. 空间太阳能发电
利用太阳能帆板把接收到的太阳能转化成电能,是航天器最常用的能源供应方式。
此外,随着地球能源供需矛盾和环境保护问题日益突出,空间太阳能电站(Solar Power Satellite, SPS)成为大规模利用绿色太阳能的重要研究方向,受到世界各国的广泛重视。空间太阳能电站是指在空间将太阳能转化为电能,再通过无线方式传输到地面的电力系统[16] 。早在1968年,美国的彼得·格拉赛博士首次提出空间太阳能电站的构想。美国在20世纪70年代,投入约5000万美元进行空间太阳能电站和关键技术研究,并且提出5 GW的“1979 SPS基准方案”。1999年,NASA在2年内投资2200万美元,开展了“空间太阳能探索性研究和技术”的计划,提出SPS未来发展的技术路线图,计划于2020年实现10 MW系统的空间验证[17] 。2007年,美国国防部组织专家完成了《空间太阳能电站作为战略安全的机遇》中期评估报告[18] 。国际无线电联盟于2005年底发表了《空间太阳能电站白皮书》[19] 。空间太阳能电站相对于地面太阳能电站,主要优势体现在不受昼夜和天气的影响,可以连续工作,太阳能利用效率高,对于太阳定向装置和能量存储装置要求低,而且地面天线对于环境的影响较小。但其研制、维护成本高昂,具有明显的劣势,而且目前还面临很多关键技术的挑战,如空间大功率无线电力传输技术、高效太阳能发电技术、巨型空间系统装配和控制技术、空间电站的热和电管理技术等。
5. 结论
空间物体光照特性受太阳、地球及空间物体自身位置、形状、姿态、材质、平整度和反射率等多种因素的影响,其中“太阳–地球–空间物体”的轨道位置关系是最基本的一组关系,是其它关系成立和研究应用的基础。文中通过分析这一基本关系,构建了空间物体光照问题的一般数学模型,并对相关的影响参数及影响程度进行了详细分析,获得的一些结论可用于空间物体受光照情况的任务分析与设计,或用于空间物体运行管控、对抗中的任务分析和规划。在此理论基础上,结合现实和潜在的应用方向,探讨了与空间物体光照特性密切有关的多种典型应用,可为深入开展这些相关研究提供参考和借鉴。