1. 引言
学习是学生最重要的生活内容,但是日益凸显的学习倦怠现象越来越引起人们的关注。相当一部分学生厌倦学业,迟到、逃课甚至逃离学校,更让人们吃惊的是校园暴力事件接二连三地发生,学习倦怠所带来的消极影响已不容忽视。本研究以师范类大学生为研究对象,在研究其学习倦怠整体情况的同时,引入学校归属感这一变量,进一步探析师范类大学生学习倦怠的心理原因,深入探究学习倦怠的形成机制。
1.1. 学习倦怠的界定
对学习倦怠(Learning Burnout)的研究起源于职业倦怠(Job Burnout)现象。国外研究者较多认可Freudenberger(1974)和Maslach(1982)的研究成果,并参考其在“职业倦怠”中使用的定义,认为学习倦怠是学生对学校的课程学业学习持负面消极态度,并且表现出对所学专业和学校活动热情消减,对同学、朋友态度冷漠和关系疏远。国内学者所下定义也不尽相同,台湾学者认为学习倦怠是由于学业压力或其他个人心理层次上的因素,导致学生出现情绪低落、个人成就感低下等现象。杨丽娴等(2004)发现当学生对学习缺少兴趣或缺乏动力却被迫为之时,就会感到厌烦,并对学习产生消极态度,导致学生出现一种身心疲惫的心理状态,称为学习倦怠。
1.2. 学校归属感的定义
学校归属感(School Belonging)是指学生对自己所就读的学校在思想上、感情上和心理上的认同和投入,愿意承担作为学校一员的各项责任和义务,及乐于参与学校活动(包克冰,徐琴美,2006)。根据国外学者 De Vos & Dijkstra的观点,将学校归属感定义为学生感到自己是班级或学校中重要的一员、被他人接受、被他人认为有价值及与他人成为一个整体的一种情感,并把学校归属感划分为:班级归属感和学校归属感(Goodenow & Grady, 1993)两个层次,这种观点更加注重个人与周围他人的比较和联系。
1.3. 研究现状及理论来源
目前,人们对大学生“学习倦怠”的现象越来越重视,导致大学生学习倦怠的原因主要有:传统重成绩轻能力的教育问题、严峻的就业环境问题、家庭的贫富差距问题。学生的学习倦怠产生原因是多方面的,但最主要还是因为较长时间来自学校课程等方面压力(戴春林, 2006)。
连榕、杨丽娴等(2006)采用Maslach的倦怠理论,切合依据我国大学生的实际情况,编制出《大学生学习倦怠调查量表》,并将大学生学习倦怠分为三个维度,即情绪低落、行为不当和成就感低。
关于归属感问题上,马斯洛需要层次理论指出:人的基本需要有5种,它们由低到高依次为生理需要、安全需要、归属和爱的需要、尊重的需要和自我实现的需要。其中归属与爱的需要也被称为社会需要、社交需要。若这些需要得不到满足,就会对人的精神和生活产生影响,导致其工作学习效率降低并伴随情绪低落。同理,学校归属感的缺乏也会影响在校学生的情绪情感,而消极情绪必将抑制其学习,使其学习动力和效率降低。近几年来,国外已有学者把学校归属感作为研究学生心理健康层面的重要变量。相关研究结果显示,对学校有较高认同感的学生拥有较高的学校归属感,这会有助于其学业成绩表现和提高出席率,相反学校归属感较低的学生则可能出现较多的辍学行为(Ridley & Walther, 2002)。Anderman (2002)的研究发现,郊区学校学生比市区学校学生有较高的学校归属感;女生的学校归属感比男生高。李靖环、陈洪霞等(2007)等针对高校学生进行了学校归属感的调查,研究表明学校归属感较低或无归属感的大学生表现出更多的不良行为,他们大多对学习没有兴趣或缺乏学习动力、敌视学校、对社会抱以消极的信念、常常以自我为中心、性格孤僻冷淡、情感冷漠等。
以往研究表明,学生的学习倦怠和学校归属感可能存在某种联系,本研究试通过科学合理的方法明确大学生学校归属感与学习倦怠的关系,希望能够在理论和实践上对降低大学生学习倦怠提供指导。
2. 方法
2.1. 被试
本研究选取某师范大学学生为被试,采取随机抽样的方法,共发放问卷380份,回收360份,其中有效问卷为334份,有效率为87.89%(被试情况如表1所示)。

Table 1. The distribution of subjects
表1. 被试分布情况
2.2. 测量工具
2.2.1. 大学生学习倦怠量表
本研究采用连榕等人编制的《大学生学习倦怠量表》,其中量表内部一致性系数为0.865,分半信度为0.880,量表分为3部分:情绪低落、行为不当、成就感低三个分量表。采用5点法记分,从“完全不符合”至“完全符合”为“1-5”记分,反向计分项目反向计分。
2.2.2. 学校归属感
学校归属感问卷采用郝佳(2008)自编问卷,共34个题目,其中包括学校认可、自我角色认可、校园同伴关系认可、个人地位认可、责任感和安全感六个维度,问卷采用5点计分,无反向计分题。该问卷具有较好的区分度、信效度良好,适合本研究的问卷要求。
2.3. 施测过程和数据采集分析
采用集体施测方式,以指导语指导被试填答问卷。所有数据录入在SPSS数据库上进行,采用SPSS11.0和AMOS18进行数据分析,研究采用方差分析,相关分析及回归分析等统计方法。
3. 结果
3.1. 师范类大学生学习倦怠和学校归属感的状况
表2中数据显示,学习倦怠总分的平均项目得分为2.81,属于中等程度范围,说明师范类大学生普遍存在中等程度的倦怠。由此可见,师范类大学生学习倦怠虽然不至于非常严重,但也不容乐观。而学习倦怠三个维度上,行为不当得分最高,其次为情感低落和成就感低。学校归属感总分的平均项目得分为2.94,也属于中等偏下程度范围,表明师范类大学生处于较低归属感水平。
表3说明,师范类大学生学习倦怠在性别、年级上均存在显著的主效应。经多重比较分析:1) 在行为不当上,女生显著高于男生(p < .05);2) 在情感低落上,大三,大一学生显著高于大二学生。
表4说明,师范类大学生学校归属感在性别、年级、学科类别上均存在显著的主效应。经多重比较分析:1) 在责任感上,文科学生显著高于理工科学生(p < .05);男生显著高于女生(p < .01)。2) 在自我角

Table 2. Descriptive statistics of learning burnout and school belonging
表2. 学习倦怠和学校归属感的描述统计

Table 3. MANOVA analysis of learning burnout on total score and its dimensions of subjects with different characteristics
表3. 不同被试特征在学习倦怠各维度及总分上的MANOVA分析
注:*p < .05,**p < .01,***p < .001,下同。

Table 4. MANOVA analysis of school belonging on total score and its dimensions of subjects with different characteristics
表4. 不同被试特征在学校归属感各维度及总分上的MANOVA分析
色认可上,大二年级学生显著好于大一年级学生,大一年级学生显著好于大三年级学生(p < .05)。3) 在学校认可上,男生显著好于女生(p < .01)。
3.2. 师范类大学生学习倦怠和学校归属感的关系
表5表明学习倦怠各维度及总分与学校归属感各维度呈极其显著负向相关,说明师范类大学生学校归属感越低,学习倦怠水平越高。
为进一步了解各因素之间的关系,以学习倦怠各因子为因变量,以学校归属感各因子为预测变量,进行逐步回归(结果见表6)。对回归系数的显著性检验表明回归系数显著,说明学校归属感能较好的预测大学生学习倦怠的程度。
其中,个人地位认可和自我角色认可是情感低落的有效预测变量,联合解释率为14.9%;个人地位认可、自我角色认可、学校同伴关系认可以及责任感是成就感低的有效预测变量,联合解释率为27.1%;个人地位认可是行为不当的有效预测变量,其直接解释率为18.2%;个人地位认可、自我角色认可以及责任感是学习倦怠的有效预测变量,联合解释率为26.6%。

Table 5. Correlation analysis between learning burnout and school belonging
表5. 学习倦怠与学校归属感的相关分析

Table 6. Multiple regression analysis of learning burnout and each dimension of school belonging
表6. 学校归属感和学习倦怠各维度的多元回归分析
说明当前师范类大学生个人地位认可是学习倦怠最重要的预测变量。图1是师范类大学生学习倦怠与归属感各维度模型验证路径图,其中各拟合指数为χ2 = 6.778,df = 6,p = .342,GFI = .994,NFI = .991,IFI = .999,FMIN = .020,RMSEA = .020。从图1可以进一步看出,个人地位认可维度的重要预测地位。
4. 讨论
4.1. 师范类大学生学习倦怠和学校归属感的总体状况
从学习倦怠和学校归属感总分的均值来看,当前师范类大学生普遍处于中等程度的倦怠水平,这与以往的研究一致(李晓军,周宗奎,游志麒,2008;孙晓莉,2009;张传月,黄宗海,莫华善,2007)。这可能是由于激烈的竞争和严峻的就业压力等因素的影响,使大学生产生自我认同失调、缺乏自信、消极逃避挫折等行为。师范类大学生学习倦怠的总体情况虽不是特别严重,其得分处于中等水平,但这个分
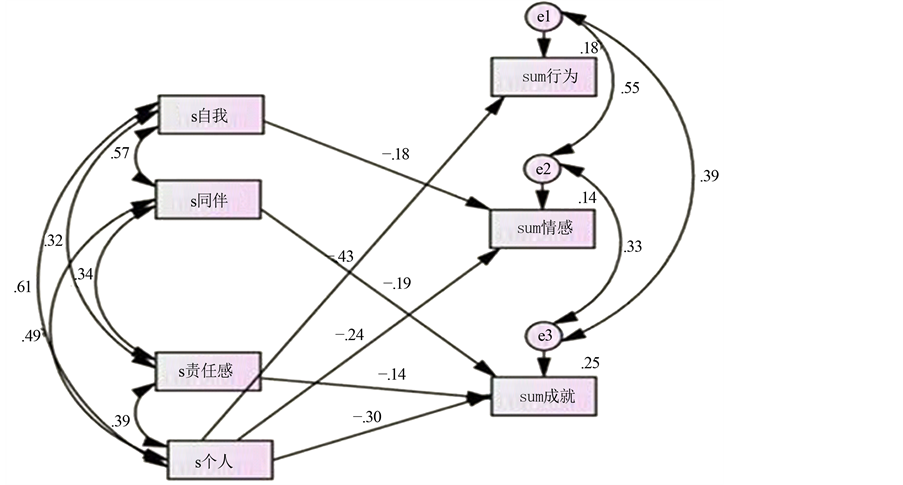
Figure 1. The validation model path diagram of learning burnout and school belonging
图1. 学习倦怠与学校归属感验证模型路径图
数并不容乐观,应该承认还是有一部分学生有学习倦怠的心理状态。出现这种情况也就能够解释为什么大学生中的确存在学习倦怠现象,但却容易被忽略的问题。而在学习倦怠的三个层面中,大学生在行为不当这一层面上得分高于其它两个层面。因而可知,有相当部分的学生表现出迟到、早退、缺席、逃课等一系列不当的学习行为,这也验证了当代大学生中存在学习问题。也许迟到、早退等类似现象在一些老师眼里是习以为常、屡见不鲜的现象,因而就很少有教育者会去深究个中原因。在他们看来,一节课中缺席一两位学生是非常平常的事,听不听课是学生自己的事情。当然也有一些教育者试图对这些现象做出努力,然而他们采取的对策无非就是课前点名、课中提问、期末考评,很少有教师会考虑到学生到底喜不喜欢这门课,自己的这种教学方式是否适合学生,这也让教育工作者反思自己的不恰当教学方法和轻视态度对学生的影响。学习倦怠现象普遍存在,直接影响了大学生的学习和成才(连榕,杨丽娴,吴兰花,2006;杨丽娴,连榕,2005)。因此,提高大学生应压能力和树立正确的价值观是促进大学生形成积极的学习心理,减少其消极心理的重要问题。
从学校归属感各分量表的得分分布看,师范类大学生在自我角色认可、学校同伴关系认可、个人地位认可、安全感这几个维度上得分都比较高,而在校园认可和责任感的得分处于中等水平。剖析上述差异产生的原因:一方面,大学生正处在成年早期阶段,已具备成年人的心理特质,虽然并没有完全发展成熟,但其自我意识、自我认识和评价相比高中时期更稳定和成熟。另外,大学不同于高中,大学生活与学习方式也发生了改变,大学生在大学期间独立面对和承担离开父母生活的压力和困难,这也使得大学生的自我意识得以快速的发展,因而他们在自我角色认可维度上表现较高得分。另一方面,大学生在自我意识发展、趋于成熟的过程中,自我定位、自我评价等相对不稳定,与同伴的关系、老师的评价等都会对其自我评价造成影响。亲密的同伴关系有利于大学生对自我认识形成积极良性的评价、有助于他们对学校和集体产生信赖和依恋的态度,反之,则会影响他们其他方面的发展。
4.2. 师范类大学生学校归属感和学习倦怠的性别状况
学习倦怠方面,在行为不当上,女生得分高于男生。说明男生与女生的学习心理状况不同。经高考进入大学学习的女生可能其继续成长的动力减弱,对自己的要求降低,也不再严于律己,加之女生更易受情感情绪的影响,表现出更多的倦怠行为。学校归属感方面,在责任感和学校认可维度上男生得分均高于女生,这可能是男生作为师范类大学中的少数群体,在很多方面都会显示他们作为男生的优势以及强者的形象,所以男生可能会不自觉的充当保护者的角色,更多的表现出高责任感;同样在学校认可上,男生得分好于女生。由此看来,关注师范类女大学生的学习情绪,提高女生的学习积极性应成为师范类院校学生工作的一个重要内容。
4.3. 师范类大学生学校归属感和学习倦怠的年级状况
在学习倦怠的情感低落维度上,大三、大一年级高于大二年级学生,在学校归属感的自我角色认可维度上,大二年级学生好于大一年级学生,大一年级学生好于大三年级学生。这可能是由于:对于大一年级学生来说,刚刚摆脱学业繁重的高中生活,进入新鲜而宽松的大学校园,作为新生,还没能真正融入大学生活,遇到的各种的不适应又无法自己排解,所以会感到情感低落;而大三年级的学生要面对考研、就业等人生规划的难题,各种压力使他们表现出学习倦怠现象,作为高年级学生,自我意识更加深刻,遇到困难不愿去寻求帮助,也很少倾诉,所以常感觉到低落;大二年级学生经过一年的适应,能更好的融入校园和学习,加之没有就业,学业等负担,所以在学习上表现出更多的兴趣和热情,在自我角色认可维度上要好于大一、大三年级学生。
4.4. 师范类大学生学校归属感和学习倦怠的学科类别状况
学校归属感得分上,责任感维度上表现为文科学生高于理工科学生。本研究选取师范类大学生为研究对象,师范生本身对师范院校的有较高的认同感和归属感。师范院校相对更重视基础学科的教学,作为基础学科的主力学科,文科偏重于知识的传授,文科生的习惯、教育环境等因素造成了他们更善于表达自己的感情和感受,更看重自己在所属团体中的认同感和归属感。所以以传授理论知识为主要教学目标的师范院校中,可能会出现文科生有更高的归属感,他们也会表现出相对理工科而言,更多的责任感。
4.5. 师范类大学生学校归属感和学习倦怠的关系
研究表明师范类大学生学校归属感和学习倦怠呈极其显著负向相关,进一步回归分析得出回归方程模型,其中个人地位认可是学习倦怠最重要的预测变量。研究引入学校归属感这一变量,其设想的合理性得到证实。希望在以后的大学生学习倦怠的辅导和干预中,学校能够加入学校归属感这一影响因素,及时关注和矫正大学生的倦怠行为。
5. 结论
1) 师范类大学生的学习倦怠状况虽然不至于非常严重,但也不容乐观,其中行为不当得分最高,其次为情绪低落和成就感低;学校归属感处于相对较低的水平。
2) 学习倦怠方面,在行为不当上,女生得分高于男生。学校归属感方面,在责任感和学校认可维度上,男生得分均高于女生。
3) 在学习倦怠的情感低落维度上,大三、大一年级高于大二年级学生,在学校归属感的自我角色认可维度上,大二年级学生好于大一年级学生,大一年级学生好于大三年级学生。
4) 学校归属感得分上,责任感维度上表现为文科学生高于理工科学生。
5) 师范类大学生学校归属感和学习倦怠呈极其显著负向相关,其中个人地位认可是学习倦怠最重要的预测变量。

NOTES
*通讯作者。