1. 引言
建立精确可靠的年代是研究过去环境变化的基础[1] -[4] 。放射性碳法(14C法)是100 a B.P.~50 ka B.P.时间范围内的主要定年方法[5] 。其基本假设是:大气中宇宙射线产生的14C通过光合作用进入植物体内并与大气中的14C含量达到平衡,即生物体存活期间具有与大气相近的14C含量,一旦生物体死亡之后,其体内14C含量便按其半衰期衰减(14C半衰期是5730 a):N = N0e−lt,其中,N0是14C的初始含量,是已知的,l是衰变参数,这样可以根据样品中的N含量测定样品的年代t。
但由于碳库效应的影响,样品的14C年龄往往与真实年龄存在差距[6] 。就湖泊沉积物而言,由于流域老碳和湖水硬水效应的共同作用,沉积物14C年龄一般都比实际偏老。如张家富[7] 等通过对固城湖沉积物全样有机质的14C年龄和石英的光释光年龄的对比研究发现,14C年龄总体上要老于光释光年龄约2000 a,并将之归结为碳库效应的影响。为消除碳库效应的干扰,大多研究者都是采用线性回归的方法获得碳库效应年龄,即将深度为零的14C年龄回归值作为碳库效应年龄。研究表明,碳库效应年龄在空间上有明显的差别,如我国环渤海海岸带全新世沉积物碳库效应年龄为400 a[8] ,青海湖为1039 a[9] (还有700 a[10] 和1500 a[11] 之说),岱海表层沉积物为2000 a[12] ,青藏高原错鄂是3470 a[13] ,而青藏高原班公错更高达6670 a[14] 。近来,吴艳宏[12] 、汪勇[15] 等研究认为,湖泊沉积物14C年龄偏老的程度在湖泊水文状况和大气14C浓度等因素影响下会随着时间推移而发生变化,即在时间序列上碳库效应也并非恒定。
本文拟通过对东平湖沉积物14C年龄数据,结合137Cs、210Pb测年数据以及湖泊发育过程与洪水事件等综合分析与探讨东平湖沉积物的碳库效应及其层序变化,为进一步精确解读该区环境变迁信息提供参考。
2. 研究区概况
东平湖(35˚43'N~36˚07'N, 116˚02'E~116˚18'E),位于山东省西部东平县境内(图1),是黄河下游仅存的天然湖泊,也是古梁山泊唯一遗存水域。东平湖目前面积627 km2(包括老湖与新湖),常年水面209 km2,平均水深2~4 m [16] 。湖区为暖温带大陆性半湿润季风气候区,四季分明,多年平均气温13.4℃,平均降水量为640 mm,多集中在夏季,无霜期约200 d。主要水源来自湖东南部的大清河(大汶河下游河段),向北经小清河泄湖水入黄河。该区地质构造上位于鲁中隆断区域徐州凹陷带的交界处,在不同方向的动力作用下,产生了较大断裂带,形成了构造洼地,加上黄河与大汶河流经此地,便成为地表径流和地下径流汇集的地区,积水成湖[17] -[19] 。
东平湖形成历史较为复杂,以土山岛为中心地带的一片水域最早见于唐代记载[18] [20] ,由于水景清美,誉称“小洞庭”(土山岛上至今留有唐朝诗人东平太守苏源明建的“洄源亭”遗址),又由于临近小安山,也叫安山湖。北宋时期,梁山泊因黄河泛滥扩大,合并安山湖于其中。公元1351年黄河改道南流,失去了黄河水补给的梁山泊逐步淤浅收缩,到金末多涸为陆地,但安山湖仍存于小安山以北。公元1411年,明朝利用安山湖蓄水济运,使安山湖成为重要的水柜留存于古运河南岸。1855年,黄河改道夺大清河入海,淹没了包括安山湖在内的黄河与大汶河交汇地带的一大片洼地,时称积水洼,民国年间定名为东平湖。1958年改建为东平湖水库,成为黄河蓄滞洪区。
3. 材料与方法
2008年4月在东平湖湖心(35˚59'11.6''N, 116˚11'35.3''E)水深3.85 m处,用水上平台钻取157 cm长的
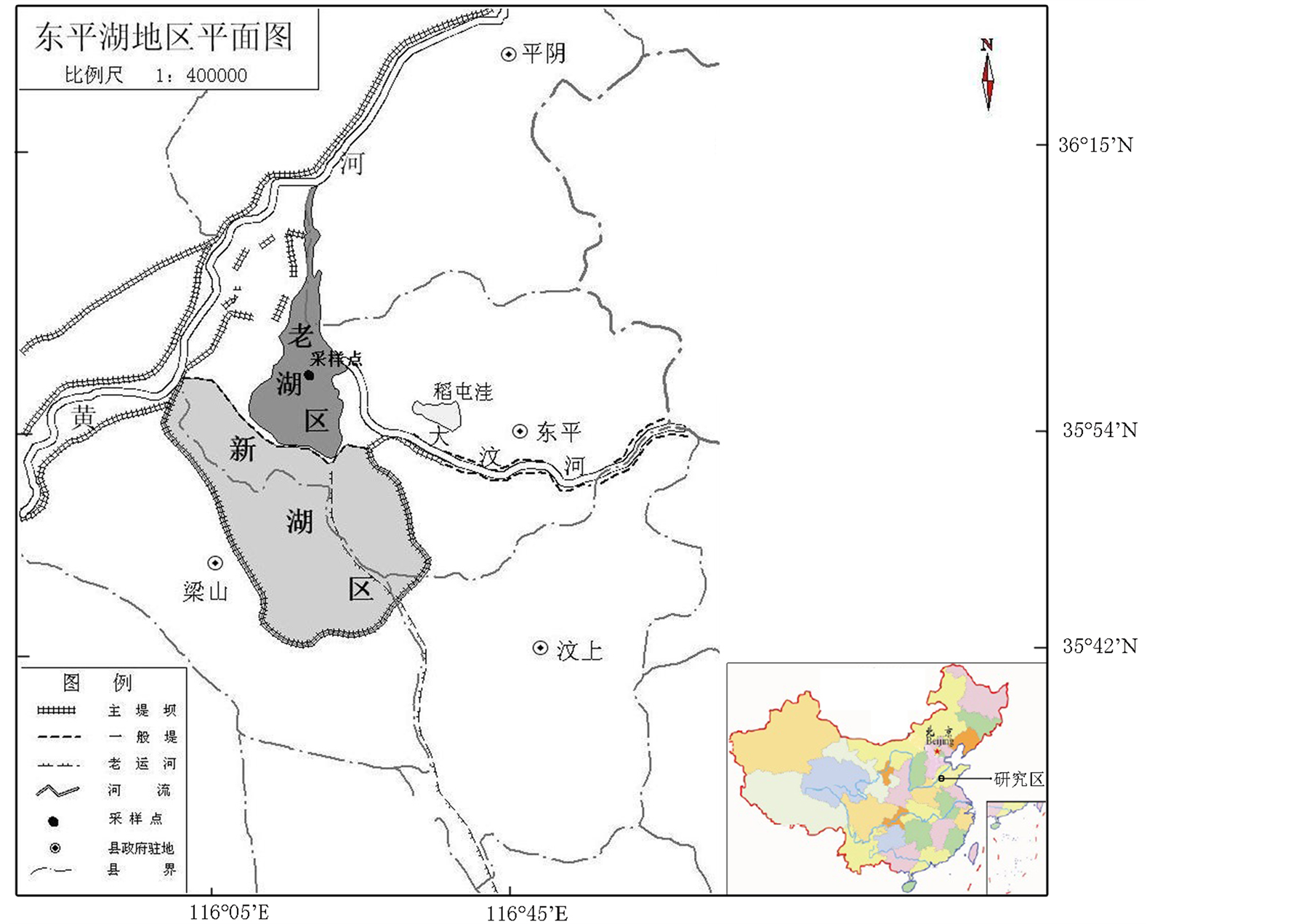
Figure 1. Sketch map of Lake Dongping and the sampling site
图1. 东平湖及采样点位置示意图
沉积岩芯柱,用于常规分析;另用重力采样器在附近采得长为60 cm的短岩芯柱,密封保存,用于210Pb和137Cs测年。2011年4月在湖心处采集了沉水植物马来眼子菜,用于14C测年以确定湖水多年的平均年龄。同时利用自制采水器采集湖水样品和表层沉积物样品,湖水采自水深1 m处,点位与表层沉积物样位置相近。所采湖水带回实验室后加CaCl2,蒸发获得结晶CaCO3用于14C年代测定。表层沉积物样品是利用重力采样器在湖心获得。
210Pb和137Cs测年是在中国科学院南京地理与湖泊研究所湖泊沉积与环境国家重点实验室进行用美国EG&GOrtec公司生产的高纯锗井型探测器和IBM微机构成的16K多道分析器所进行的。
水草的14C年代分析是由新西兰National Isotope Centre, Institute of GNS science of New Zealand完成的。湖水和表层沉积物样品在中国科学院地球环境研究所黄土与第四纪国家重点实验室利用加速器质谱仪(AMS)测定。岩芯柱72 cm、119 cm、144 cm处的14C年龄在波兰Poznań Radiocarbon Laboratory of the A. Mickiewicz University完成,其余(13 cm、28 cm、38 cm)14C年龄在中国科学院南京地理南京地理与湖泊研究所利用液体闪烁计数仪(LSC)测定。
沉积岩芯柱粒度指标是在中国科学院南京地理与湖泊研究所湖泊沉积与环境国家重点实验室用英国Mastersizer2000激光粒度仪(分析范围0.02 μm~2 mm)分析的。
4. 结果
4.1. 沉积物岩性与粒度特征
东平湖湖心157 cm长的沉积岩芯其岩性特征明显分为两部分(图2),120 cm以下为灰黄色粉砂夹淡黄色粘土,属河流相沉积;120 cm以上为湖相沉积,其中120~10 cm段主要为黄色或淡黄色粘土,10 cm以下为淡黄色或灰黑色淤泥。
总体来看,沉积物粒度特征在120 cm处发生明显变化,120 cm以下粒度较粗,中值粒径在20 µm以上,平均约30 µm,<4 µm的粘土含量在20%以下,平均15%。反映该段沉积环境不稳定,水动力比较强。120 cm以上沉积物粒度总体较细,中值粒径大多在10 µm以下,平均约8.9 µm,<4 µm的粘土含
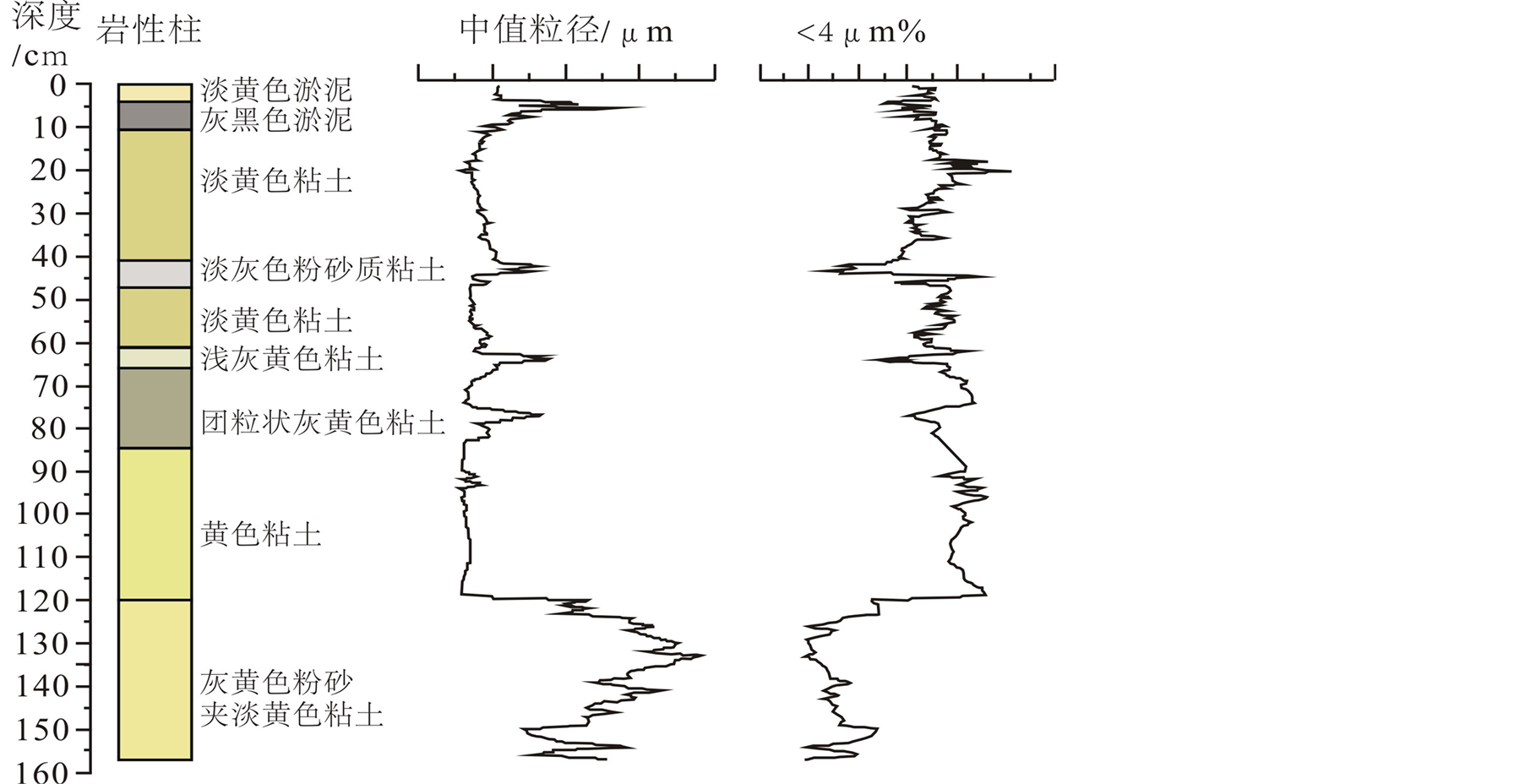
Figure 2. Lithological property and grain size in core of Lake Dongping
图2. 东平湖沉积岩性与粒度特征
量在30%以上,平均35.8%。反映该段沉积环境较稳定,水动力较弱,为相对静水沉积环境,这也响应于沉积孢粉的记录[21] 。
4.2. 年代结果
利用东平湖沉水植物马来眼子菜、湖水和沉积岩芯样品共获得了9个14C年龄(表1),湖心沉水植物马来眼子菜、湖水和表层沉积物的14C年龄分别为484 ± 20 a B.P.、2345 ± 28 a B.P和1284 ± 49 a B.P.,沉积岩芯柱的14C年龄从上到下依次为980 ± 70 a B.P.、1300 ± 50 a B.P.、1900 ± 120 a B.P.、2820 ± 35 a B.P.、5220 ± 40 a B.P.、5115 ± 35 a B.P.,除了底部样品外,总体上14C年龄随着深度增加而增加,没有出现明显的年龄倒转现象,说明沉积层序是比较稳定的。
东平湖沉积物137Cs的蓄积峰位置在12 cm处,对应于1963年人工核试验高峰,利用1963年137Cs核素蓄积峰进行校正,采用210Pb计年的CRS模式建立东平湖现代沉积年代序列,具体结果见文献[22] 。根据CRS模式建立的年代序列,岩芯柱13 cm、28 cm、38 cm分别对应于1962年、1935年、1905年,进一步可推测47 cm处约为1855年(表1)。
5. 讨论
马来眼子菜(Potamogeton malaianus)是一种多年生沉水草本植物,其光合作用所需的CO2主要来自于水体中的溶解碳,因此所测得的其14C年龄反映了湖水多年的平均年龄。从14C测年结果来看,东平湖湖水多年的硬水效应约为484 a。
湖水的14C年龄为2345 ± 28 a B.P.,明显高于沉水植物的14C年龄。据监测,东平湖湖心4月份的湖水pH值为9.11,明显大于8月份的8.05,10月份的7.91和12月份的7.83[23] ,这是因为东平湖区春季干旱降水少,湖水以地下水补给为主,致使湖水的14C年龄偏高。表层沉积物碳库效应年龄与组成沉积物有机碳来源的综合信息有关[13] ,从14C年龄结果来看,表层沉积物碳库效应约为1284 a,高于多年沉水植物、低于湖水的碳库效应。
东平湖近现代沉积物(47 cm以上)的14C年代与210Pb测年结果对比可明显看出碳库效应的存在。且随着深度增加碳库效应有增大的趋势(表1),如果考虑误差的话,深度13 cm、28 cm、38 cm处的沉积物碳库效应年龄分别约为980 a、1300 a、1900 a。这种碳库效应的变化可能与黄河泛滥以及人类活动有关。

Table 1. 14C and 210Pb dating results of Lake Dongping
表1. 东平湖14C测年与210Pb年代
1855年黄河在兰考铜瓦厢决口夺大清河北流入海,安山湖所在的汶河下游淤塞而成的东平湖常在黄河大汛时河水倒灌入湖,也带来了“老碳”沉积物。1935年黄河在鄄城和范县决口,河水南泛经淮河入海,1938年国民党又在花园口炸堤,河水南流入洪泽湖10 a,东平湖失去黄河水源及其沉积物,碳库效应也相应减弱。1958年东平湖滞洪区改建为东平湖水库,黄河水一般不再能够进入东平湖,只有在黄河下游发生大洪水时才作为滞洪区使用,这样人为断绝了黄河水源的东平湖沉积物碳库效应进一步减小。
从东平湖历史时期(47 cm以下)形成的沉积物的14C年代来看,其碳库效应也非常显著。导致沉积物碳库效应变化的原因更为复杂,黄河、古济水、流域“老碳”、湖泊硬水效应以及人类活动等都可能是引起碳库效应变化的重要因素,尤以黄河泛滥为最。据研究,东平湖始见于唐代记载[18] 。考虑到东汉王景治河以后黄河安流千年,后世学者一般就认为东平湖形成于唐代。笔者倒以为东平湖形成时代可能在唐朝以前,因为唐代初有东平湖记载时其面积已经很大,号称“小洞庭”了,而这么大一块湖面的形成必与重大的气候水文事件相关,不可能无故出现。但为什么史书不见任何记载呢?这可能与唐以前朝代的社会分裂有关。清代著名学者胡渭认为“魏晋南北朝,河之利害不可得闻,唐自长寿以来,时有决溢,见之于史,而无大变迁,故不志《河渠》”;虽强调“王景之功不可误”,但又明确指出:“肃、代以后,强藩跋扈,并帝制自为,次道云“纵有河事,不闻朝廷”是也。而愚更有说焉。河灾羡溢,首尾亘千里之外,非一方可治,当四分五裂之际,尔诈我虞,唯魏、滑同患,故田弘正从薛平之请,协力共治,否则动多掣肘,纵有溢决,亦迁城邑以避之而巳。此河功所以罕纪也。据史所书谓唐少河患,亦未为笃论。”北大学者辛德勇[24] (2012)最近也撰文指出,王景治河后黄河下游河道千年安流并非事实,期间黄河也经常发生洪水,只是洪水并未导致河道变迁而已。北魏孝明帝时期就有崔楷治河议的记载:北魏孝明帝熙平三年(公元516年),黄河连年泛滥,弥漫冀、定等数州,崔楷特向皇帝提出治河的建议并被采纳,虽最后半途而废,但表明南北朝时期黄河洪水还是很频繁的。频繁泛滥的洪水导致东平湖地区的水系改变,并形成湖泊也是很有可能的。如是,则东平湖大约形成于公元516年左右。据此计算,119 m处的沉积物碳库效应可达3700 a左右。
公元944年,黄河在滑州决口,河水东漫梁山,形成梁山泊。公元1077至1168年,黄河数次决入梁山泊,使梁山泊进一步扩大并绵延数百里,安山湖并入其中。84~73 cm段沉积岩性与粒度值与其前有较大差别(图2),对应于该时期的黄河泛滥沉积。但其上72 cm处的14C年龄为2820 ± 35 a B.P.,显然是受碳库效应的影响。若以公元1168年计,其碳库效应约为2038 a。
从沉积岩性来看,120 cm以下主要为河流相沉积,可能是古济水流经时的沉积物。《尚书·禹贡》有云:大野既潴,东原厎平。表明大禹治水(古济水)以后,大野泽已经停聚深水,东原(东平古称东原)一带也获得治理。也可推知大禹时代东平湖地区就发育有古济水(济水发源于河南济源王屋山,是中国古代独流入海的一条大河,与黄河、长江、淮河并称为“四渎”。其经河南荥阳荥泽后分南济和北济流入大野泽,再从大野泽东北方梁山、东平一带流出,经泰山西南绕至泰山西北,然后北流入渤海),形成有河流沉积。这与岩性及粒度值反映也是相符的(图2)。144 cm处的河流沉积物14C年代为5115 ± 35 a B.P.,由于河流沉积为动水环境,碳库效应年龄难以确定。
总的来看,利用14C-AMS测年建立精确可靠的沉积物年代有一定的困难。就东平湖而言,由于东平湖的形成和演化与黄河和大汶河等水系密切相关,如东平湖就是历史上由大野泽、梁山泊和安山湖在黄河泛滥的作用下演变而来,并最终于1855年黄河在兰考铜瓦厢决口改道最终形成。黄河改道决溢的影响,带来的大量冲积物对沉积物层位真实年龄的测定带来困难,甚至出现年龄倒转;东平湖沉积物有机质含量相对较低[25] ,对14C-AMS测年也带来一定误差;一般来说,当新形成的有机质含量占98%以上时,可以获得较为可靠的年代结果,而当受到较老有机质含量较大影响,由于“老碳效应”,测年的14C年龄并不能代表样品最后沉积时的年代,造成测年结果偏老,而且沉积物碳库效应在时间序列上也并非恒定。可见,运用多种测年手段与方法对沉积物定年具有重要意义。
6. 结论
1) 公元516年前后,频繁泛滥的洪水导致东平湖地区的水系改变致东平湖成湖。
2) 由于历史时期黄河泛滥、古济水、流域老碳以及人类活动等多重因素的影响,东平湖沉积物碳库效应随着深度有明显变化,深度0 cm、13 cm、28 cm、38 cm、72 cm、119 cm处的沉积物碳库效应年龄分别约为1284、980 a、1300 a、1900 a、2045 a、3700 a,湖泊的多年硬水效应是484 a。
3) 14C测年技术是目前非常成熟的一个测年方法,但碳库效应的存在影响了沉积物14C测年的准确性,尤其是碳库效应在时间序列上也并非恒定,因此利用14C定年需要非常小心。采用简单线性回归技术获得的碳库效应年龄可能并不一定反映沉积物真实年龄,运用多种可能的方法测定沉积物年龄,并相互比较验证,来确定不同沉积时段的碳库效应年龄,以建立准确的年代框架,为古环境变迁信息解读提供可靠的年代基础。
致谢
中国科学院南京地理与湖泊研究所王苏民研究员、羊向东研究员、吴艳宏研究员、张恩楼研究员、潘红玺副研究员、王荣博士参加了野外采样工作,室内分析得到了夏威岚副研究员、刘恩峰博士等的帮助,特此感谢。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金项目(41072258, 40772209)。

NOTES
*通讯作者。