1. 引言
猪繁殖与呼吸综合征(Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome, PRRS)俗称蓝耳病,是由猪繁殖与呼吸综合征病毒(PRRSV)引起的一种接触性的传染病,主要引起母猪流产及仔猪呼吸系统障碍[1] 。该病1986年首次发生于美国[2] ,次年研究者从流产胎儿的体内分离得到病原PRRSV [3] 。我国于1995年在北京养猪场首次爆发此病,1996年由郭宝清分离出病原,命名为Ch-1α [4] 。2006年,我国江西、浙江、湖南、湖北、江苏等地发爆发高热病,此后该病在我国呈现不断蔓延的趋势,对养猪业造成了严重的危害和巨大的经济损失。
PRRSV属于套式病毒目,动脉炎病毒科,有囊膜,囊膜表面有纤突,是单股正链RNA病毒。整个基因组长15 Kb,含有8个开放性的阅读框[5] 。ORF1编码RNA复制酶和转录相关蛋白[5] ,其中NSP2蛋白是最容易变异的一个蛋白,很多学者都认为,近几年出现的高致病性变异毒株就是由NSP2基因的不连续缺失造成的[6] 。ORF2-7编码病毒的结构蛋白,其中M蛋白最保守,其次N蛋白,GP5蛋白变异最显著,又由于GP5蛋白是病毒最重要的保护性蛋白[7] ,故其成为基因疫苗和亚单位疫苗研究的主要对象。由于PRRSV高度变异性,我们从重庆某发病猪场进行了病毒的分离鉴定和基因分析,对PRRS流行病学的研究和疫苗的研制具有重要意义。
2. 材料和方法
2.1. 病料来源
重庆市某猪场送检的5份病死猪的心、肝、脾、肺、肾、淋巴结。该猪场2014年4月出现病猪体温41℃以上,新生仔猪呼吸困难,发病率和死亡率都很高;剖检可见:猪的肺脏有点状出血。
2.2. 主要试剂
Ex Taq酶、小量胶回收试剂盒、逆转录试剂盒均购自TaKaRa公司;病毒RNA提取试剂盒购自TIANGEN公司;新生牛血清、DMEM,胰蛋白酶,0.2 μm过滤器购自北京鼎国生物试剂公司。
2.3. 毒株的分离
2.3.1. 病料处理
采集病猪的肺脏用灭菌的生理盐水进行研磨,−80℃反复冻融3次,1000 rmp离心5 min,取上清,用0.2 μm的过滤器进行过滤,收集滤液于灭菌的青霉素瓶里,按5%的比例加入双抗,−80℃保存备用。
2.3.2. 病毒分离和细胞鉴定
将已长成单层的Marc-145细胞,弃去培养液,用PBS缓冲液清洗一次,接种1 mL已融化的滤液,同时设正常Marc-145细胞为阴性对照,置培养箱中吸附30 min,之后取出培养瓶弃滤液,加8 mL含10%胎牛血清的DMEM维持液,于37℃,5% CO2培养箱中培养3天,每天观察细胞的状态,及时收集病变细胞。
2.3.3. 病毒TCID50的测定
将Marc-145细胞铺于96孔组织培养板中(105细胞/孔),培养过夜待细胞铺满时开始试验;第四代毒液用无血清DMEM细胞培养液作连续的10倍稀释至10−9;将96孔组织培养板中的培养液弃去,用1xPBS洗2遍;将稀释好的病毒液加入96孔组织培养板中,100 μL/每孔,每个稀释度做6个重复,37℃恒温生化培养箱中作用1 h;弃去96孔组织培养板的病毒液,用1xPBS洗2遍;于96孔组织培养板加入含10%胎牛血清的DMEM维持液100 μL每孔,置于37℃ CO2培养箱中培养,72 h后观察并记录细胞病变孔数,按世界卫生组织规定的方法计算组织细胞培养半数感染剂量(50% tissue culture infective dose, TCID50)。
2.4. 毒株的鉴定
2.4.1. 引物的设计与合成
参考GenBank已发表的中国大陆地区PRRSV毒株的基因序列,设计针对PRRSV引物的设计NSP2,GP5的特异性引物,产物大小分别为168 bp,750 bp。NSP2上游引物:5'-CTGTCGGTGGTCCCCTCAA-3',下游引物:5'-GGTGCGTCAGCGTTGTTG-3'。GP5上游引物:5'-GTTTACCCAACGCTCCTTA-3',下游引物:5'-ACTGGCGTGTAGGTAATGG-3'。
2.4.2. RT-PCR检测
按照TIANGEN病毒RNA提取试剂盒说明书提取RNA,并按照TaKaRa逆转录试剂盒说明书将其逆转录成cDNA,用基因的特异性引物进行扩增。扩增条件为:NSP2:95℃ 5 min;94℃ 30 s,53℃ 30 s,72℃ 30 s,共35个循环;72℃ 10 min。GP5:95℃ 5 min;94℃ 30 s,56℃ 45 s,72℃ 30 s,共35个循环;72℃ 10 min。扩增结束后取5 μL PCR产物进行琼脂糖电泳检测。
2.4.3. 基因序列分析
将鉴定为阳性的PCR产物送苏州金维智公司测序,将测序结果与经典毒株及其他变异株的基因序列用DNAMAN生物学软件在亲缘关系方面进行比较。
3. 结果
3.1. 病毒分离结果
将处理后的滤液接种于Marc-145细胞中,培养至第二代开始出现明显的病变,细胞变圆,膨大,聚集成团,最后慢慢脱落(如图1、图2所示)。
3.2. 毒株TCID50检测结果
经检测,结果如表1所示。
按照Reed-Muench法计算,该分离株的病毒滴度为10−5.67 TCID50/0.1mL。
3.3. 基因RT-PCR扩增结果
将处理后的样品做RT-PCR检测,扩增产物通过1.0%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳在紫外凝胶成像系统下可见特异性片段条带,大小符合预期结果(如图3所示)。
3.4. 序列分析结果
将NSP2和GP5的测序结果分别与已发表的国内分离株及欧洲型、美洲型标准毒株进行核苷酸同源性分析,经过序列比对发现所分离的毒株NSP2基因与经典美洲型毒株VR-2332的核苷酸同源性为66.7%,与近年来流行的高致病性毒株SD,JXA1同源性达到98.8% (如表2所示)。经DNAMAN软件建立的进化树显示,该分离株与HUB1类聚同一分支上,与其亲缘关系最近(如图4所示)。而GP5基因在个别碱

Figure 1. Normal Marc-145 cell
图1. 正常的Marc-145细胞(10×)

Figure 2. Marc-145 cells infected after 72 h
图2. 感染72 h后的Marc-145细胞(10×)

Figure 3. The result of PCR. M: DL-2000 DNA Marker; 1: purpose strip of GP5; 2: purpose strip of NSP2; 3: Negative control
图3. 毒株PCR鉴定结果。M:DL-2000 DNA Marker;1:GP5基因PCR产物;2:NSP2基因PCR产物;3:阴性对照
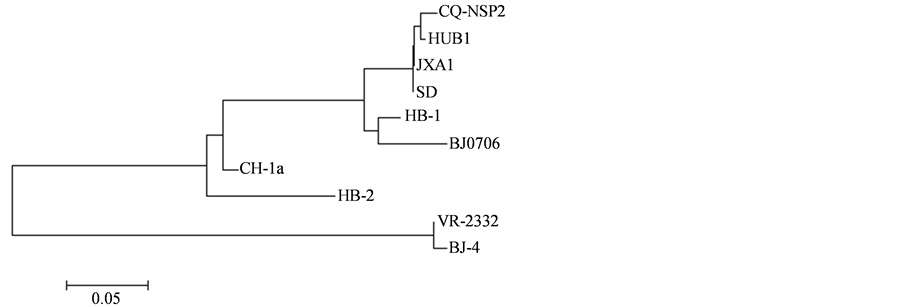
Figure 4. The systemic cladogram analysis of the genomes between PRRSV strains
图4. 分离株NSP2基因与国内其他毒株的遗传进化树
表1. 毒株CPE观察结果

Table 2. The nucleotides homologies between different PRRSV strains
表2. 分离株与10株PRRSV毒株核苷酸序列同源性比对结果(%)
基上也存在变异。
4. 讨论
本研究从重庆某猪场成功分离到一株HP-PRRSV病毒,并对其进行鉴定。该病毒感染Marc-145细胞,使细胞出现明显病变,按照Reed-Muench的方法计算第四代病毒的滴度为10−5.67 TCID50/0.1mL。用RT-PCR从处理过的滤液中扩增出PRRSV的NSP2和GP5基因片段,序列分析表明该毒株的NSP2基因与经典型的VR-2332核苷酸同源性为66.7%,与高致病性变异毒株SD,JAX1核苷酸同源性可达到98.8%,本实验结果表明从重庆某猪场发病猪中分离得到的毒株为高致病性蓝耳病变异株。
虽然不同的PRRSV分离株在形态学和生物学特性上十分相似,但其基因型和抗原性明显属于两个亚型,一种是以VR-2332为代表的美洲型,一种是以LV代表的欧洲型,二者的核苷酸同源性很低仅有60% [8] 。无论是美洲型的毒株还是欧洲型的毒株,都有一个显著的特点,病毒本身具有高度变异性。其中变异最为显著的就是NSP2、GP5、GP3蛋白。
PRRSV的非结构蛋白NSP2由ORF1a编码,参与病毒的复制过程并与对细胞或组织的嗜性有关[9] 。从2006年分离到PRRSV起,HP-PRRSV基因组上均显示NSP2基因存在不连续氨基酸的缺失[6] ,成为高致病性变异株的标志。通过对NSP2序列分析发现,该毒株的NSP2序列与JXA1,BJ0706,SD毒株的同源性最高,遗传进化方面与HUB1关系最近,同时显示该蛋白存在30个不连续氨基酸的缺失,由此可以推测该毒株可能由JXA1,BJ0706或SD变异而来,且为高致病性变异毒株。
GP5属结构蛋白,基因位于ORF5上,全长603 bp,是病毒主要的保护性抗原,在结构蛋白中突变率最高。同型毒株间,GP5氨基酸序列相似性在88%~99%之间[10] 。测序结果显示,该毒株的GP5基因与JXA1的同源性最高,在基因的第135、201、300、456及600位发生突变。
2006年11月28日,重庆市首次爆发蓝耳病,2007年该病的发病率和死亡率分别达到6.11%和2.06% [11] ,随着疫苗的使用以及养殖户防范意识的增强,该病的发病率有所下降,但其仍是危害我市猪场的主要疾病之一。该病流行范围广,病原污染严重,一年四季均可发病,以5~7月多发。临床表现和病理变化不典型,同时主要以混合感染为主[12] ,这就使临床诊断困难加大。目前,该病无有效的特效药治疗,仍以预防免疫为主。实际应用中主要免疫灭活疫苗和弱毒疫苗,但其存在免疫效果差和返毒等潜在缺点,均不是理想的疫苗。因此开发安全有效的新型疫苗势在必行。
5. 展望
近年来,随着基因工程和细胞工程技术的发展,通过基因敲除或外源表达蛋白等技术,研制更加安全高效的疫苗已成为可能。目前已有研究表明基因缺失疫苗散毒水平低,返强机率小,而且效力不减[13] ;病毒样颗粒疫苗不含核酸物质,安全性高,且能引发机体强效的免疫反应[14] 等疫苗成为了新型疫苗的研究方向。总之,猪繁殖与呼吸综合征的新型疫苗研究取得了很大的进步,对PRRS的防控奠定了基础。
基金项目
重庆市科技攻关计划项目(cstc2012gg-yyjs80014),重庆市科技人才培养计划项目(cstc2013kjrc- 1jrcpy80001)。