1. 引言
近年来,全球气候特别是极端气候变化已成为人们关注的焦点,不少学者对极端低温频数和强度变化特征进行大量研究[1] -[5] ,并试图从不同方面探讨其形成机制[6] -[13] 。研究表明,东北春、夏季极端低温事件受极涡和阻塞高压的位置和配置的影响[9] -[11] 。北极涛动(AO)作为大气环流的主模态,在年代际和年际尺度上对我国极端低温事件都有影响[12] 。刘蕾[13] 则指出冬季瞬变波强度与极端低温频次呈明显的正相关关系。还有研究指出,中北大西洋海温异常可通过激发欧亚波列影响中国东北春季极端低温事件[9] 。
Hoskins and Pearce [14] 指出直接的非绝热加热异常强迫(如海冰和积雪异常、表层海温异常等)会引起气候异常事件。海洋学家指出在全球变暖的背景下,太平洋–印度洋对全球变暖的响应在空间上表现为非均匀性[15] ,这种非均匀响应使得海洋热状况如海洋温盐环流发生改变,进一步导致大气环流发生变化,即通过“大气桥”的作用影响到中高纬地区,对东亚气候变化有重要的调节和控制作用。研究表明,冬季黑潮区,赤道印度洋海表温度与我国东部冬季温度呈正相关关系,北太平洋中纬度中部海温异常与冬季温度负相关关系[16] 。在年际变化尺度上,赤道中东太平洋的海温异常与中国冬季气温呈正相关,而北太平洋海温异常则对中国冬季气温南北反位相振荡有一定的影响[17] ;在年代际尺度上,冬季北大西洋正异常,北太平洋除中部(30~40˚N)外均为正异常,这一海温分布与冬季长江中游及河套以南地区的气温呈显著正相关关系[18] 。赵永平等[19] 、许武成等[20] 研究了ENSO事件对中国南方冬春季气温的影响。
北极海冰作为极地冷源,与赤道地区海温(热源)对大气环流和区域以及全球气候有着同样重要的影响[21] 。研究表明,在年代际变化尺度上,冬季喀拉海、巴伦支海海冰面积异常与东亚冬季风和西伯利亚高压强度反位相变化[22] ,在年际变化尺度上,冬季喀拉海、巴伦支海海冰异常偏多可以激发500 hPa上欧亚型正位相的遥相关,使得西伯利亚高压偏弱,2月份入侵我国的冷空气次数减少[23] 。北极海冰异常对中国冬季气温也有影响,研究表明:冬季巴伦支海、格陵兰海、戴维斯海峡、白令海和鄂霍茨克海海冰异常对中国同期冬季平均气温、最低气温和最高气温都有显著影响[24] [25] 。黄菲和高聪晖[26] 也指出在年际变化尺度上,前期东西伯利亚海-波弗特海海冰异常对冬季东亚气温有显著影响。
前人从大气环流和海温等方面研究极端低温事件的机制,但极端低温事件具有明显的区域性,另外,研究表明海温和海冰对中国冬季气温有重要的影响,那么海温和海冰与中国冬季不同区域极端低温事件之间的关系是怎样呢?因此本文将参考黄菲和胡蓓蓓等[27] 关于南、北方区域的划分和极端低温事件的定义,以35˚N为界分南、北方区域,从海温和海冰的热源强迫异常来寻求各尺度下中国冬季极端低温事件的成因。
2. 资料和方法
本文采用中国大陆487个台站逐日气温资料数据集[27] 。海温和海冰资料采用哈德莱中心的观测数据集(Hadley Centre observations datasets),空间分辨率为1˚ × 1˚。本文资料时间时段取在1961.1~2010.12,文中冬季指前一年12月~当年2月,得到1962~2010共49个冬季,为了便于计算,去掉闰年的2月29日,故每个冬季共90天。参考黄菲等[27] 关于极端低温阈值和频数的定义,将每个测站1962~2010年共49年冬季逐日最低气温资料按照升序排列,取每一个测站共90 × 49个数中的第1个百分位的值定义为该测站冬季的极端低温阈值。如果该测站某日最低气温低于该阈值,则认为该测站该日发生了极端低温事件。每站每年冬季发生极端低温事件的日数称为该站该年冬季极端低温频数。
本文采用的客观分析方法主要有谐波分析方法、线性回归和相关分析方法。线性趋势的计算采用最小二乘法,相关系数和趋势统计显著性检验采用T分布检验方法。
2.1. 线性估计与气候倾向率
气象要素x存在长期趋势变化,气象要素的估计量 与自然数序列t的一元线性回归方程可以表示为:
与自然数序列t的一元线性回归方程可以表示为:
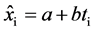 ,
, ,
,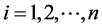
式中a为回归常数,b为回归系数, 称为气象倾向率,单位为某要素单位/10a。
称为气象倾向率,单位为某要素单位/10a。
采用最小二乘法可以求得
 (2-1)
(2-1)
(2-1)式中 ,
,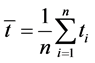
2.2. 气候趋势系数
气象要素与自然数序列的一元线性回归系数反映气象要素的长期趋势变化,但考虑到不同气象要素的均方差和单位对回归系数之值的影响,参考 [28] 的方法,将气象要素x与自然数序列t之间的相关系数定义为趋势系数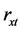 ,公式如下所示:
,公式如下所示:
 (2-2)
(2-2)
(2-2)式中n为气象要素的样本长度,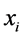 为气象要素的第i年值,
为气象要素的第i年值,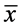 为气象要素的平均值,
为气象要素的平均值,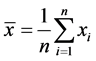 ,自然数序列
,自然数序列 ,
,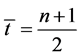 。按照(2-2)定义的趋势系数
。按照(2-2)定义的趋势系数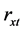 是相关系数的一种,是无量纲的,在[−1,1]之间变化,可以在不同变量和地点之间比较。
是相关系数的一种,是无量纲的,在[−1,1]之间变化,可以在不同变量和地点之间比较。 值为正(负)值表示气象要素在计算时间段的n年内存在线性增加(减少)的趋势,数值的绝对值越大表示长期趋势变化越快。
值为正(负)值表示气象要素在计算时间段的n年内存在线性增加(减少)的趋势,数值的绝对值越大表示长期趋势变化越快。
3. 极端低温事件的时间特征
黄菲等 [27] 文中给出极端低温频数的距平时间序列,本文参考其中的方法,首先,对极端低温频数标准化时间序列做线性趋势分析(图1(a)、图1(d)中的红实线),若通过95%的置信度检验则认为其显著,并计算线性趋势占原时间序列的方差贡献;其次,若线性趋势显著(不显著),对标准化时间序列去趋势后(标准化时间序列)采用谐波滤波,将周期大于8a的变化作为年代际变化分量(图1(b)、图1(e)),而周期小于8a的作为年际变化分量(图1(c)、图1(f))。由图1可以发现,南、北方区域极端低温频数均呈显著下降趋势,南方区域下降的更迅速,北方区域年代际变化分量与年际变化分量强度相当,南方区域则以年际变化为主。
4. 极端低温频数与海温的关系
4.1. 线性趋势
图2给出了与冬季北方地区极端低温频数标准化时间序列的线性趋势相联系的全球海温分布,由图2(c)可以看出,在长期变化趋势上,冬季北方地区极端低温频数变化与西北大西洋和北太平洋中部黑潮延伸体附近海域海温异常是正相关关系,与其他海区海温呈显著负相关。为了进一步研究冬季北方地区极端低温频数与海温的关系,我们将冬季北方地区极端低温频数线性趋势与海温做了超前滞后的回归,可以发现北太平洋中部的信号可追溯至前夏,前秋稍有减弱,同期冬季加强,至后期春季最强;前期北大西洋海温异常对冬季北方地区极端低温频数距平有负相关关系。南方地区与海温的关系(图略)与北方地区极为相似,强度偏弱。分析表明,极端低温频数长期变化趋势与全球变暖有关,特别是印度洋和北大西洋海区海温的增暖。
4.2. 年代际变化分量
图3是年代际变化尺度上北方区域极端低温频数与海温的超前滞后回归分析,从图3(c)可以看出,北方区域极端低温事件偏多时,同期冬季北太平洋呈现出北负南正的海温分布,在大西洋海区,格陵兰海和巴伦支海海温异常偏低,北大西洋北部偏暖,墨西哥湾和湾流海区异常偏冷。进一步分析表明,前夏北太平洋中部出现显著正异常,最大异常位于夏威夷东北部海区(图3(a)),前秋正异常最大区移至日本以东海域,在阿拉斯加湾海温负异常信号范围增加(图3(b)),冬季从鄂霍茨克海至阿拉斯加湾的北太平洋北部均为显著负异常信号,与北太平洋中部的显著正异常信号反位相振荡,至后期春季,海温正异常进一步加强。大西洋海温北负南正的分布在前夏和前秋已经存在,冬季形成东北–西南走向的负–正–负的分布,并一直持续至后期春季。另外,前期赤道以南的太平洋和大西洋海温异常与冬季北方区域极端低温频数呈显著负相关。
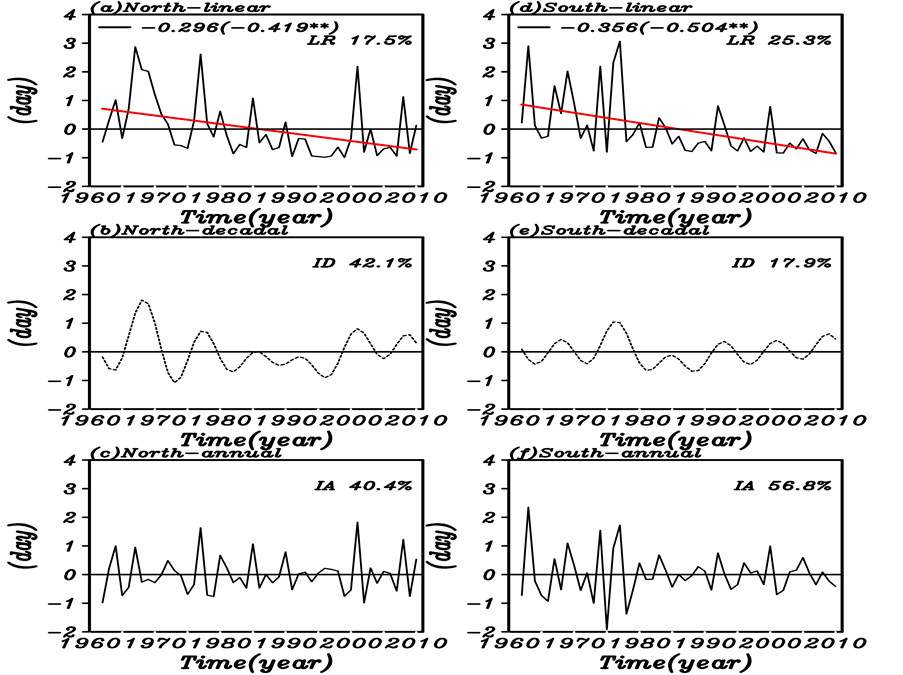
Figure 1. Time series of winter EMT frequency normalized in China ((a)-(c)the north of China, (d)-(f)the south of China. black solid lines and red solid lines are normalized time series and linear trends in figure (a) and (d), The numbers outside (inside) the parentheses denote dip ratio (trend coefficients), one star denotes trend coefficients are statistically significant over 95% significance level, two stars denote trend coefficients are statistically significant over 99% significance level. (b), (e) and (c), (f) are for inter-decadal component and inter-annual component of detrend normalized time series, respectively. Numbers in the upper right corner are for variances of normalized time series explained by linear component, ID component and IA component, respectively.)
图1. 中国冬季极端低温频数的标准化时间序列((a)~(c)为北方区域;(d)~(f)为南方区域;(a)、(d)中黑色实线和红色实线分别为标准化时间序列和趋势线,括号外的数字为气候倾向率,括号内数字为趋势系数,*:过95%信度检验,**:过99%信度检验;(b)、(e)为标准化时间序列去趋势后的年代际变化分量;(c)、(f)为标准化时间序列去趋势后的年际变化分量;右上角数字为各分量所占的方差贡献)
图4给出了与南方区域冬季极端低温频数年代际变化分量相联系的海温分布。从图4(e)可以看出,冬季太平洋海温呈现出北太平洋中西部海温与热带中东太平洋和南、北美洲西岸海温异常的反位相振荡,南方极端低温偏多时,北太平洋中西部海温显著正异常,北太平洋北部、北美西部沿岸至南美洲西岸与热带中东太平洋连成一片,海温呈现出负异常,这一空间分布型与太平洋年代际振荡(PDO)冷位相极为一致[29] 。进一步分析表明,PDO冷位相可追溯至前一年冬季,一直持续至后期春季,前冬南、北太平洋中部均为显著正异常,变化最大的负异常区域位于赤道以北的热带太平洋海区,前春北太平洋中部海温正异常进一步发展,负异常最大区位于北美西岸,在北太平洋组成马蹄状的空间分布型。研究还发现PDO冷位相在冬春季较强,夏秋季较弱。另外前期北大西洋海温异常与南方区域极端低温频数变化呈正相关。
以上分析表明,在年代际变化尺度上,冬季北太平洋海温北负南正的信号使得阿留申低压偏北偏弱,格陵兰海–巴伦支海海温负异常激发EU型大气遥相关正位相,影响中国北方区域。PDO冷位相的海温异常分布,使得冬季南方区域极端低温事件偏多,而朱益民和杨修群[30] 的研究则指出PDO冷位相时冬

Figure 2. The preceding summer (a), preceding autumn (b), simultaneous winter (c), and following spring (d) sea surface temperature anomalies regressed by linear trend component of the EMT frequency in the north China (significant values at the 90% confidence level are represented by black dots)
图2. 冬季北方区域极端低温频数的线性趋势分量对海表面温度的回归场(黑点过90%的显著性检验,(a) 前夏,(b) 前秋,(c) 同期冬季,(d) 后春)

Figure 3. The preceding summer (a), preceding autumn (b), simultaneous winter (c), and following spring (d) sea surface temperature anomalies regressed by inter- decadal component of the EMT frequency in the north China (significant values at the 90% confidence level are represented by black dots)
图3. 冬季北方区域极端低温频数的年代际变化分量对海表面温度的回归场(黑点过90%的显著性检验,(a) 前夏,(b) 前秋,(c) 同期冬季,(d) 后春)
季华南和西南地区气温偏暖,这可能是与研究的时间段不同有关,其影响机制要进一步分析。
4.3. 年际变化分量
从图5可以看出,年际变化尺度上,与北方区域极端低温频数变化相联系的海温分布:冬季北太平

Figure 4. Sea surface temperature anomalies regressed by inter- decadal component of the EMT frequency in the south China (Significant values at the 90% confidence level are represented by black dots, (a) the preceding winter, (b) the preceding spring, (c) the preceding summer, (d) the preceding autumn, (e) the simultaneous winter, (f) the following spring, (g) the following summer, (h) the following autumn)
图4. 冬季南方区域极端低温频数的年代际变化分量对海表面温度的回归场(黑点过90%的显著性检验,(a)~(h) 依次从前冬至后秋)
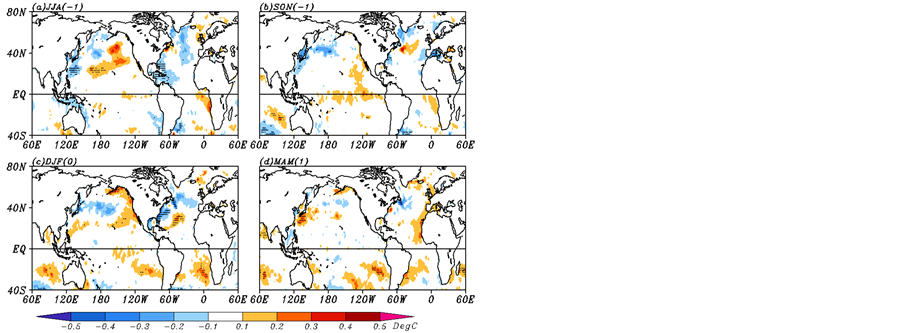
Figure 5. The preceding summer (a), preceding autumn (b), simultaneous winter (c), and following spring (d), sea surface temperature anomalies regressed by inter-annual component of the EMT frequency in the north China (Significant values at the 90% confidence level are represented by black dots)
图5. 冬季北方区域极端低温频数的年际变化分量对海表面温度的回归场(黑点过90%的显著性检验,(a) 前夏,(b) 前秋,(c) 同期冬季,(d) 后春)
洋中部与北美西岸海域海温异常的反位相振荡,进一步看与海温的超前滞后关系可以发现,前夏北太平洋中西部海温出现冷信号,前秋有所加强,至冬季达到最强盛,对应着冬季北方地区极端低温频数偏多,至后期春季基本消失。另外,前期中国北部近海和北大西洋中西部的海温异常与北方区域极端低温频数变化呈负相关。
图6给出了与南方区域极端低温频数年际变化分量相联系的海温分布,分析表明,南方区域极端低温事件主要受太平洋海温影响,前期阿拉斯加湾和白令海海区异常偏冷,对应冬季南方区域极端低温事件偏多,南方极端低温频数的正异常又影响后期春季赤道太平洋海温异常偏暖。另外,冬季在中国沿海出现海温的负信号,且一直持续到后期春季,这一分布表明中国近海的海温变化是随着我国极端低温变化的,进一步验证了康丽华等[17] 和Chen et al. [31] 的结论。
5. 极端低温频数与海冰的关系
北极海冰异常与冬季气温存在显著关系[25] [26] 。那么极端低温事件与北极哪些区域的海冰有关呢?北极海冰又是如何影响中国冬季极端低温事件的?为了清晰地分析南、北方区域极端低温频数与北极海冰异常的关系,本文将从线性趋势、年际变化分量和年代际变化分量三个方面对海冰进行回归分析。
5.1. 线性趋势
图7给出北极海冰与北方区域冬季极端低温频数线性趋势的超前滞后回归分析,冬季格陵兰海–巴伦支海的海冰异常与北方区域冬季极端低温频数的变化有显著正相关关系(图7(c)),前期夏季、秋季格陵兰海–巴伦支海的海冰异常增加(减少),使得北方地区冬季极端低温频数偏多(偏少),进而又反过来影响春季格陵兰海–巴伦支海的海冰异常增多(减少)(图7(a)~(d))。另外,前夏喀拉海、拉普捷夫海和东西伯利亚海及前秋拉普捷夫海、东西伯利亚、海楚科奇海和波弗特海海冰异常对北方区域冬季极端低温频数也有一定的预报意义。北方区域冬季极端低温偏多(偏少)时,除白令海和鄂霍茨克海之外的太平洋扇区各

Figure 6. The preceding summer (a), preceding autumn (b), simultaneous winter (c), and following spring (d), sea surface temperature anomalies regressed by inter-annual component of the EMT frequency in the south China (Significant values at the 90% confidence level are represented by black dots)
图6. 冬季南方区域极端低温频数的年际变化分量对海表面温度的回归场(黑点过90%的显著性检验,(a) 前夏,(b) 前秋,(c) 同期冬季,(d) 后春)
边缘海海冰异常融化(图7(c)),且持续至春季。与南方区域极端低温频数线性趋势相联系的北极海冰异常(图略)较北方区域的弱,但分布基本一致。
5.2. 年代际变化分量
在年代际变化尺度上,对冬季北方区域极端低温频数有显著影响的主要是格陵兰海海冰异常,两者有显著正相关关系(图8(A)-(c)),分析前期夏、秋季和后期春季的海冰异常可以发现,前期夏季格陵兰海海冰异常信号已经存在,且一直持续至后期春季,此外,巴伦支海部分海区海冰异常对冬季北方区域极端低温频数也有一定的预报意义。冬季北方区域极端低温事件反过来影响后春波弗特海和巴芬海海冰异
Figure 7. The Arctic sea-ice concentration (shadings; above the 90% confidence levels) anomalies regressed by linear trend component of the EMT frequency in the north China ((a) the preceding summer, (b) the preceding autumn, (c) the simultaneous winter, and (d) the following spring)
图7. 冬季北方区域极端低温频数的线性趋势分量对北极海冰的回归场(填色过90%的显著性检验,(a) 前夏,(b) 前秋,(c) 同期冬季,(d) 后春)

Figure 8. The Arctic sea-ice concentration (shadings; above the 90% confidence levels) anomalies regressed by inter-decadal component of the EMT frequency in the north China (upper) and the south China(lower) ((a),(e) the preceding summer, (b), (f) the preceding autumn, (c),(g) the simultaneous winter, and (d),(h) the following spring)
图8. 年代际变化尺度上冬季北方区域和南方区域极端低温频数对北极海冰的回归场(填色过90%的显著性检验,(a)~(b) 分别为北方区域的前夏、前秋、同期冬季和后期春季,(e)~(h)同(a)~(b),但为南方区域)
常,冬季北方区域极端低温事件偏多促使后春波弗特海和巴芬海海冰异常融化。与南方区域极端低温频数变化相联系的海冰异常与北方区域的明显不同,分析图(图8(B)-(g))可以发现,冬季南方区域极端低温频数距平与巴伦支海北部、喀拉海、拉普捷夫海、东西伯利亚海和楚科奇海海冰异常呈显著负相关关系,与格陵兰海和白令海海冰异常正相关。前夏和前秋东西伯利亚海海冰异常融化和格陵兰海海冰异常偏多的信号就存在(图8(B)-(e),图8(B)-(f)),对应冬季南方区域极端低温频数偏多,南方区域极端低温频数偏多又会导致后春格陵兰海和白令海海冰异常增加(图8(B)-(h))。
5.3. 年际变化分量
在年际变化尺度上,冬季北方区域的极端低温频数变化与楚科奇海和新瓦尔巴群岛以北海区海冰异常有负相关关关系,与其他海区海冰异常没有显著相关(图9(A)-(c)),前期秋季新地岛以北和北地群岛东北(80~85˚N, 100˚E~170˚W)海区海冰异常也与冬季北方区域极端低温频数距平呈显著负相关(图9(A)~(b))。冬季南方区域的极端低温频数变化主要受太平洋扇区海冰异常的影响,存在显著负相关关系(图9(B)~(g)),前秋格陵兰-巴伦支海海冰则与冬季南方地区极端低温频数距平呈显著正相关(图9(B)-(f))。另外,在年际变化尺度上,南、北方地区极端低温频数的变化对春季北极海冰均无显著影响(图9(A)-(d),图9(B)-(h))。
6. 结论
本文利用1961~2010年站点资料和再分析资料,分南、北方区域分析中国冬季各尺度下极端低温事件与海温和海冰的关系。研究发现:
1) 中国南、北方区域极端低温频数长期变化趋势与全球变暖有关,特别是印度洋和北大西洋海区海温的增暖。前夏、前秋北极各边缘海海冰异常增多(减少)使得冬季中国南、北方地区极端低温事件偏多(偏少),极端低温事件偏多(偏少)又反过来促进格陵兰海–巴伦支海、白令海和鄂霍次克海海冰生成(融化)和太平洋扇区其他边缘海海冰异常融化(生成)。
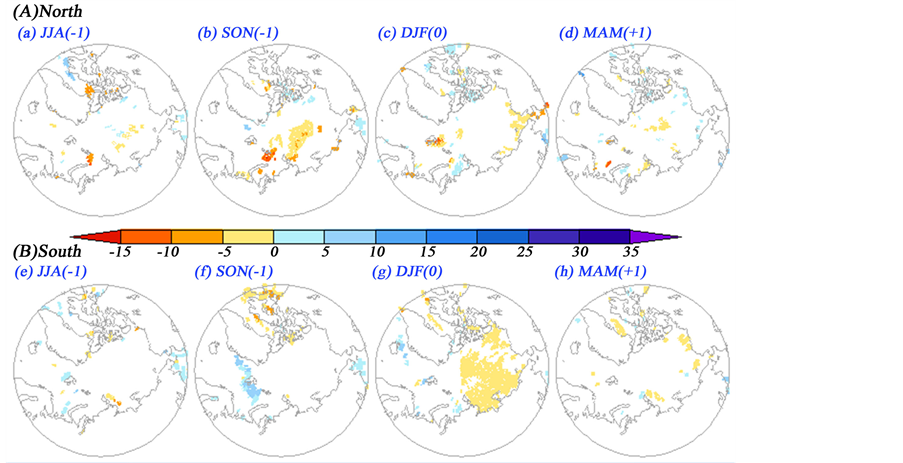
Figure 9. As Figures 5-7, but for inter-annual component of the EMT frequency
图9. 年际变化尺度上冬季北方区域和南方区域极端低温频数对北极海冰的回归场(填色过90%的显著性检验,(a)~(b) 分别为北方区域的前夏、前秋、同期冬季和后期春季,(e)~(h)同(a)~(b),但为南方区域)
2) 年代际变化尺度上,冬季北太平洋海温北负南正的信号使得阿留申低压偏北偏弱,格陵兰海–巴伦支海海温负异常和格陵兰–巴伦支海海冰正异常激发EU型大气遥相关正位相,使得中国北方区域极端低温事件偏多。南方区域极端低温频数偏多与PDO冷位相的海温异常分布影响,还与格陵兰海和白令海海冰异常正相关,与其他边缘海海冰异常呈显著负相关关系。
3) 年际变化尺度上,北方区域极端低温频数偏多时,冬季北太平洋中部与北美西岸海域出现西负东正的海温异常分布,北美东岸海温负异常,与楚科奇海和新瓦尔巴群岛以北海区海冰异常负相关。前期阿拉斯加湾和白令海海温异常偏冷,对应着冬季南方区域极端低温事件偏多;与冬季太平洋扇区海冰异常存在显著负相关关系。此外,南、北方地区极端低温频数的变化对春季北极海冰均无显著影响。