1. 引言
“车祸猛于虎”,当下,汽车正进入千家万户的生活。据统计,我国每年的道路交通伤亡事故高达二十万例,其中恶劣天气——雾天导致的交通事故尤为严重。人们己经越来越认识到交通场景信息采集的重要性,获取实时、全面、准确的道路交通场景信息是预防交通事故的重要前提和基本保障,也是实现城市交通智能化的关键。因此,对雾天驾驶场景及其能见度进行智能识别,是一项必要且急迫的工作,具有很好的现实意义。
传统的雾天及能见度的识别主要依靠物理传感装置(湿度、气压、红外传感器,雷达、激光等),该方法应用较为广泛,但设备的安装和维护成本较高。在图像理解和计算机识别方面,文献 [1] 利用雾的模糊效应,实现雾天的识别,同时结合道路消失点的检测估计能见度。该算法的优点是同时实现了雾天驾驶场景与能见度的识别,但计算量大,易受环境干扰,鲁棒性较差。文献 [2] 提出了利用双目视觉技术结合不同对比度估计能见度的方法,但其不能进行雾天场景的检测。文献 [3] 通过将交通视频的当前背景与晴天背景相减得到差分图像,提取差分图像的纹理特征来识别雾天,实时性较好,但只适用于固定场景下的雾天识别。文献 [4] 利用图像的退化模型获取与天气现象相关的参量,从而达到识别天气的目的。但是在雨或霾的天气条件下,所测得扩散函数的跨度值与晴天和薄雾天气条件下所得的有重叠,会导致天气现象的误判。文献 [5] 通过提取图像功率谱斜率、对比度、噪声和饱和度等特征,构造支持向量机,实现雾天的识别。但其识别率较低,复杂度较高,难以满足实时性的要求。
针对雾天与能见度识别算法存在的算法复杂度高,且难以对两者同时准确识别的问题。本文提出了一种基于单目视觉的雾天识别和能见度估计算法。该算法以柯什米德定律为基础,建立驾驶场景下的摄像机模型。利用Canny算子进行边缘检测,通过限定Hough变换的极角,降低投票空间数据量,降低了车道线检测的计算量和复杂度。自定义的区域增长条件,对道路区域分割的适用性更强,能满足实时性、有效性的要求。利用加权平均的图像亮度拐点估计,进一步保证了拐点估计的准确度。仿真结果表明,算法能实现移动场景下的雾天及能见度识别,精确度、实时性、鲁棒性较好。
2. 驾驶场景模型
在单目摄像机系统,道路被近似假设为平面 [6] ,以估计图像中的像素所对应的实际距离。本文的研究基于车载单目摄像机捕获的视频信息,图1给出了车载单目摄像机在交通场景下的模型。
图1中, 坐标系表示图像中的像素坐标系,其中
坐标系表示图像中的像素坐标系,其中 分别代表像素的行数和列数。
分别代表像素的行数和列数。 为光轴在图像平面上的投影,H为摄像机的相对高度,
为光轴在图像平面上的投影,H为摄像机的相对高度,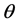 为摄像机光轴于地平线之间的夹角。f表示摄像机的焦距,
为摄像机光轴于地平线之间的夹角。f表示摄像机的焦距, 、
、 为单位像素的水平、垂直尺寸,本文中假设
为单位像素的水平、垂直尺寸,本文中假设 。
。
由于光在大气中传播时会发生衰减,Koschmieder [7] 于1924年提出了一个物体本身光强度与在一定距离处观测到的光强度的关系模型,此模型被广泛应用于计算机视觉领域。其关系如下:
 (1)
(1)
其中为物体本身亮度,为大气亮度,为在距离d处观测到的亮度,表示消光系数。该公式表明在雾天物体的亮度以指数因子递减。将公式(1)左右两边同除以得到下列公式:
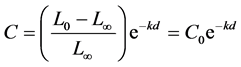 (2)
(2)
其中 表示物体相对于背景的对比度,
表示物体相对于背景的对比度, 表示在距离d处物体的对比度。为了保证物体的可见度,对比度
表示在距离d处物体的对比度。为了保证物体的可见度,对比度 必须大于某一阈值,国际照明委员会将对比度阈值设为0.05。通过求解公式(2)可以推导出能见度距离。
必须大于某一阈值,国际照明委员会将对比度阈值设为0.05。通过求解公式(2)可以推导出能见度距离。
 (3)
(3)
3. 雾天与能见度识别算法
雾天与能见度识别的算法包括基于Canny算子的边缘检测、基于Hough变换的车道线检测、消失点估计、区域增长、拐点估计、雾天和能见度识别等模块,算法流程图如图2所示。
3.1. 边缘检测
常用的边缘检测算子有Sobel、Canny、Prewitt等。本文采用Canny算子,它是于1986年由John F. Canny提出,具有低误码率、高定位精度和抑制虚假边缘等优点 [8] [9] 。原始彩色图像信息量大,处理速度慢,所以首先进行灰度化。对灰度图进行边缘检测,能够提取图像中的灰度级突变、纹理结构变化、色彩变换等信息。

Figure 1. Modeling of the camera in driving scenarios
图1. 交通场景下的摄像机模型
对灰度图进行公式(4)的高斯滤波,去除噪声,得到平滑后的图像 ;
;
 (4)
(4)
然后用一阶偏导的有限差分来计算梯度的幅值和方向。梯度矢量的模和方向分别如式(5) (6)所示, 反映了图像的边缘强度,
反映了图像的边缘强度, 反映了边缘的方向。图像的边缘点则为
反映了边缘的方向。图像的边缘点则为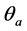 方向上使
方向上使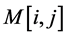 取得局部最大值的点;
取得局部最大值的点;
 (5)
(5)
 (6)
(6)
仅仅得到全局的梯度并不足以确定边缘,因为确定边缘,必须保留梯度最大的点。所以需要进行非极大值抑制。将梯度角离散为圆周的四个扇区之一,以便用3*3的窗口作抑制运算。四个扇区的标号为0到3,对应3*3邻域的四种可能。在每个点上,邻域的中心像素 与沿着梯度线的两个像素相比。如果
与沿着梯度线的两个像素相比。如果 的梯度值不比沿梯度线的两个相邻像素梯度值大,则令
的梯度值不比沿梯度线的两个相邻像素梯度值大,则令 。
。
最后用双阈值算法检测和连接边缘。对非极大值抑制图像作用两个阈值 和
和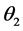 ,其中
,其中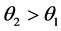 。由于
。由于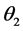 的阈值较高,去除大部分噪音,但同时也损失了有用的边缘信息。而
的阈值较高,去除大部分噪音,但同时也损失了有用的边缘信息。而 的阈值较低,保留了较多的信息。所以结合两个阈值作用的图像,连接边缘。
的阈值较低,保留了较多的信息。所以结合两个阈值作用的图像,连接边缘。
连接边缘的具体步骤如下:对 作用的图像进行扫描,当遇到一个非零灰度的像素
作用的图像进行扫描,当遇到一个非零灰度的像素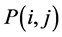 时,跟踪以
时,跟踪以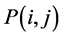 为开始点的轮廓线,直到轮廓线的终点
为开始点的轮廓线,直到轮廓线的终点 。考察
。考察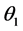 作用的图像中与
作用的图像中与 作用的图像中
作用的图像中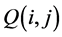 点位置对应的点
点位置对应的点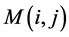 的8邻近区域。如果在
的8邻近区域。如果在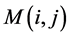 点的8邻近区域中有非零像素
点的8邻近区域中有非零像素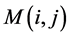 存在,则将其包括到
存在,则将其包括到 作用的图像中,作为
作用的图像中,作为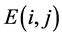 点。从
点。从 开始,重复第一步,直到无法继续为止。当完成对包含
开始,重复第一步,直到无法继续为止。当完成对包含 的轮廓线的连结之后,将这条轮廓线标记为已经访问。回到第一步,寻找下一条轮廓线。重复第一步、第二步、第三步,直到
的轮廓线的连结之后,将这条轮廓线标记为已经访问。回到第一步,寻找下一条轮廓线。重复第一步、第二步、第三步,直到 作用的图像中找不到新轮廓线为止。
作用的图像中找不到新轮廓线为止。
3.2. 车道线与消失点估计
Hough变换是图像处理中从图像中识别几何形状的基本方法之一[10] 。其基本原理在于利用点与线的对偶性,将原始图像空间给定的曲线通过曲线表达形式变为参数空间的一个点。这样就把原始图像中给定曲线的检测问题转化为寻找参数空间的峰值问题。Hough变换的参数方程为:
 (7)
(7)
其中 为图像空间中直线到坐标原点的距离,范围为
为图像空间中直线到坐标原点的距离,范围为 ,
,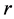 为图像对角线长度;
为图像对角线长度; 为直线与
为直线与 轴之间的夹角,范围为
轴之间的夹角,范围为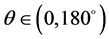 。
。
由于车道线信息主要位于图像的下半部分,而上半部分多为天空、树木、路标等无效信息。所以在进行Hough变换时,只选取部分图像进行处理。不仅减少了信息的处理量,提高运算速度,而且减少了干扰,提高了检测精度。其次,传统离散Hough变换的投票空间为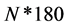 (假设N为图像中的目标点数,
(假设N为图像中的目标点数, 的变化步长为
的变化步长为 ),所以目标点的数量是影响Hough变换计算量的关键因素。为了减少计算量,本文提出了限定
),所以目标点的数量是影响Hough变换计算量的关键因素。为了减少计算量,本文提出了限定 值的思想。根据大量的样本分析和观察,设定
值的思想。根据大量的样本分析和观察,设定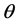 的取值范围为:
的取值范围为: ,
, 的范围为:
的范围为: ,其中
,其中 ,
, 分别为图像的宽度。通过Hough变换后,得到检测的车道线。车道线的交点即消失点。
分别为图像的宽度。通过Hough变换后,得到检测的车道线。车道线的交点即消失点。
3.3. 自定义区域增长
由于图像中的道路部分混杂着雾信息,所以本算法的目的就是通过从下到上一行一行的扫描,寻找连续梯度变化最小的区域。从图像的底部选择灰度等级为该行灰度中间值的点作为区域增长的种子点。从种子点开始,当像素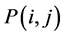 满足下述条件时,才能被加入增长区域
满足下述条件时,才能被加入增长区域 :
:
1) 该像素不属于增长区域:
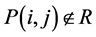 (8)
(8)
2) 该像素不属于边缘点:
 (9)
(9)
3) 该像素与种子点之间满足下述关系:
 (10)
(10)
其中 ,
,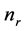 为
为 与
与 之间的线的行数,
之间的线的行数, 为最大垂直梯度。
为最大垂直梯度。
4) 该像素与其下方的像素满足下述关系:
 (11)
(11)
3.4. 加权平均的拐点估计
本文的区域增长算法能较好的分割道路与天空的边界。但是由于道路上可能存在车辆、广告牌、路标等干扰信息,造成灰度变化拐点的不准确。本文提出了取连续三帧图像区域增长极限的纵坐标值,构成一个大的数据集。计算该数据集的加权平均数,以此计算最优的拐点值。
具体方法是,首先去掉数据集中的最大、最小值,然后计算剩余数据的平均值、中值,并将其加入到数据集中。统计数据集中每个数出现的频次,频次与数据总量的比值,作为该数据的权值。最终得到该数据集的加权平均值,作为灰度变化的拐点值。保证实时性的基础上,大大提高了算法的准确度。
3.5. 雾检测与能见度估计
图像灰度变化的拐点代表了雾天驾驶场景下的可视点,而道路的消失点指晴天情况下的可视点。所以当拐点位置低于消失点位置时,可判定为雾天,反之则为晴天。
根据摄像机模型进一步估计可见距离。据图1建立公式:
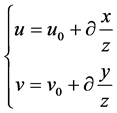 (12)
(12)
由于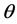 为摄像机光轴于地平线之间的夹角,所以在图像坐标系中,地平线也可以表示为
为摄像机光轴于地平线之间的夹角,所以在图像坐标系中,地平线也可以表示为
 (13)
(13)
结合公式(4)、(5),推导出下式:
 (14)
(14)
根据世界坐标系与图像坐标系的关系,得出下述公式
 (15)
(15)
所以,假设在道路上,距离原点d处有一点M,则其坐标可以表示为: 。将其代入公式(15),得到下式:
。将其代入公式(15),得到下式:
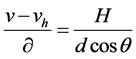 (16)
(16)
最终,得到图像中位于第v行的像素所代表的世界坐标系中的实际距离d,其关系式如下:
 (17)
(17)
其中 代表了图像中的地平线位置,而
代表了图像中的地平线位置,而 。
。
由于 ,将式(17)代入得:
,将式(17)代入得:
 (18)
(18)
对公式(18)中的v求导,得:
 (19)
(19)
再次求导,得
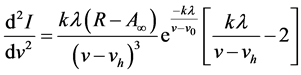 (20)
(20)
令 ,则其有两个解。其中一个解为
,则其有两个解。其中一个解为 ,即消光系数为0,显然无意义。另一个解为:
,即消光系数为0,显然无意义。另一个解为:
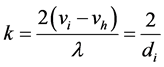 (21)
(21)
所以根据式(3)和式(21),可以得到可见距离的计算公式为:
 (22)
(22)
 为图像中灰度变化的拐点位置,
为图像中灰度变化的拐点位置, 为地平线位置,最终得到可见距离的估计值。
为地平线位置,最终得到可见距离的估计值。
4. 结果分析
图3为多种边缘检测的结果比较,可以看出,Canny算子相比Sobel算子和Prewitt算子,对实际边缘的敏感度较高,且不易带入伪边缘。利用Canny算子的边缘检测要优于Sobel算子和Prewitt算子。图4为车道线检测的仿真结果,结果表明,限定极角和半径的Hough变换,能高效准确的实现车道线和消失点的检测。图5为多种区域分割的结果比较,Otsu阈值分割的准确率不够高,部分天空区域被分割到道路区域。迭代式阈值分割,能有效的分割道路与天空区域,但计算量较大。自定义区域增长的道路分割方法,既能有效的分割天空与道路区域,又能利用车道线的检测结果,压缩区域分割的数据处理量,减少计算量,提高处理速度。且当路面上存在部分遮挡物时,该算法仍能有效地提取道路区域。图6给出了消失点位置与拐点位置。其中,红色线为检测到的车道线及其延长线,交点为道路消失点。黑色线代表地平线,即消失点所在位置。蓝色线为拐点所在位置。
根据柯什米的定律可以计算消光系数,得到可见距离,并将雾天分为低雾、中雾、大雾,如表1所示。表2给出了在不同天气状况下的雾天检测结果统计表(表3为已有文献算法的雾天检测结果)。
仿真结果表明,本文的雾天检测算法对视频样本的正确检测率达到90%以上。通过与文献 [5] 中算法的检测结果的比较,可以看出本文算法检测结果的正确率远远高于文献 [5] 中算法的检测结果。图7给出了本文算法对能见度测量的误差,结果表明,误差距离控制在(−10 m, 10 m)之间。说明了该算法提供了精确的雾及能见度的检测结果(晴、低雾、中雾、高雾)。结果输出时,根据连续三个雾等级信号来判断当前天气状态,提高了系统的精确性。算法运算速度快,满足实时性的要求。摄像机的参数已知时,该算法可以用于不同的安装环境中。
5. 结束语
雾天驾驶场景及其能见度的识别,是预防交通事故的重要前提也是实现智能交通的关键。本文基于计算机单目视觉技术,提出了一种以柯什米德定律为基础的简单高效的移动场景下的雾天及能见度识别算法,并用不同的天气场景数据进行测试,仿真结果表明,算法精确度、实时性、鲁棒性较好,对智能交通具有重要意义。但是本文算法在路面起伏较大的情况下的准确度较差,这是该算法的一个缺点,在后续的研究中将解决此问题。

 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
 (c) (d)
(c) (d)
Figure 3. Comparison of several edge detection operators. (a) Fog; (b) Canny operator; (c) Sobel operator; (d) Prewitt operator
图3. 几种边缘检测算子的比较。(a) 雾天;(b) Canny算子;(c) Sobel算子;(d) Prewitt算子
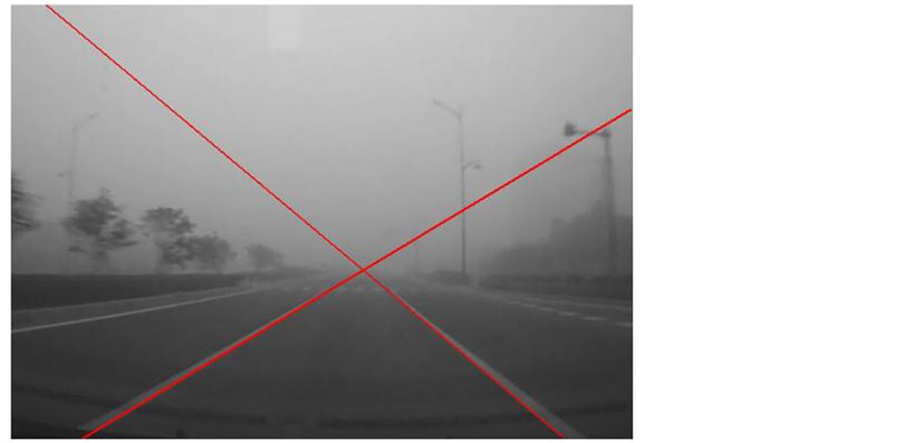

Figure 4. Estimation of the vanishing point
图4. 消失点估计

 (a) (b)
(a) (b) (c)
(c)
Figure 5. Comparison of different region segmentation results. (a) Otsu threshold segmentation; (b) Iterative threshold segmentation; (c) Custom region growing
图5. 多种区域分割结果比较。(a) Otsu阈值分割;(b) 迭代式阈值分割;(c) 自定义区域增长

 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 6. Vanishing point and inflection point estimation in different scenarios
图6. 不同场景下的消失点位置与拐点位置

Figure 7. Error statistics of visibility
图7. 能见度测量误差统计
表1. 雾天分类

Table 2. Fog detection result with the proposed algorithm
表2. 本文算法雾天检测结果

Table 3. Fog detection result in paper [1]
表3. 文献[1] 算法的雾天检测结果
基金项目
上海市自然科学基金(14ZR1442700)。