摘要:
根据小反刍兽疫病毒(PPRV) P、N基因保守序列设计了两对引物,分别扩增部分P基因及N基因的全长阅读编码框(ORF),对疑似小反刍兽疫病毒的样品抽取RNA并以其为模板,在RT-PCR的体系中能扩增出预期大小分别为766 bp、1578 bp的目的片段,同时对退火温度,敏感性及特异性等RT-PCR反应条件进行了优化。在最佳反应条件下,该RT-PCR能检出最低850拷贝的PPRV基因组。对N全基因进行RT-PCR扩增并对PCR产物克隆于pMD-19T载体,转化感受态细胞DH5α后,对重组质粒测序,结果表明N基因全长大小与预期完全一致。并且这两个基因与新疆伊犁、北京所发生的小反刍兽疫病毒同源性高达100%,说明该病毒在中国南北方都有存在,其亚型为基因4型。
Abstract:
Two pairs of primers were designed to amplify the partial P gene and full-length N gene based on their own conserved sequences, respectively. RNA of suspected samples with PPRV was extracted and amplified by RT-PCR, from which target fragments of 766 bp and 1578 bp were obtained. Meanwhile, the RT-PCR reaction conditions, including annealing temperature and sensitivity, were optimized and 850 copies of PPRV can be tested under these conditions. PCR product of N gene was cloned into pMD-19T vector and the recombinant plasmid was transformed into DH5α competent cells and sequenced, which showed that N gene was consistent with that expected. Compared with other strains from Yili, Xinjiang province and Beijing, the homologies of N gene was almost 100%, which indicated that PPRV, as lineage 4, was endemic in North and South of China.Two pairs of primers were designed to amplify the partial P gene and full-length N gene based on their own conserved sequences, respectively. RNA of suspected samples with PPRV was extracted and amplified by RT-PCR, from which target fragments of 766 bp and 1578 bp were obtained. Meanwhile, the RT-PCR reaction conditions, including annealing temperature and sensitivity, were optimized and 850 copies of PPRV can be tested under these conditions. PCR product of N gene was cloned into pMD-19T vector and the recombinant plasmid was transformed into DH5α competent cells and sequenced, which showed that N gene was consistent with that expected. Compared with other strains from Yili, Xinjiang province and Beijing, the homologies of N gene were almost 100%, which indicated that PPRV, as lineage 4, was endemic in North and South of China.
1. 引言
小反刍兽疫(peste des petits ruminants, PPR)又别名为小反刍兽伪牛瘟、羊瘟、Kate、胃肠炎–肺炎综合征、传染性脓包状胃炎[1] 。属于副粘病毒科(Paramyxoviridae),麻疹病毒属(Morbolivirus) [2] ,与牛瘟病毒(Rinderpest virus, RPV),犬瘟热病毒(Canine distemper virus, CDV),海豹瘟病毒(Porpoise distemper virus, PDV)同一属[3] 。PPRV是危害山羊及绵羊的高度接触性传染病,以引起口腔溃疡、脓性鼻液及出血性胃肠炎和肺炎为特征的烈性传染病,基于高度接触性传染速度快而被我国农业部列为一类烈性传染病,畜牧生产中一旦发生该疫情必须上报并进行扑杀处理[4] 。该病毒最早于1940年在西非报道,在中东、非洲、阿拉伯半岛及南亚地区都有所波及,至今中国新疆、北京都有所发现。这应引起我国相关地区的高度重视[4] 。
PPRV基因组为单股负链RNA病毒,核苷酸全长大小为15,948 bp [5] ,病毒基因组RNA从3’端至5’端依次排列6个基因片段并编码6种蛋白和2种非结构蛋白,分别是N-P-M-F-H-L,即核蛋白(N)、磷蛋白(P)、基质蛋白(M)、融合蛋白(F)、血凝素(H)、多聚酶蛋白(L)和非结构蛋白C/V [6] 。P基因除了编码P蛋白之外,还编码两种非结构蛋白C和V,P蛋白由509个氨基酸组成,分子量大约为54.9 ku,P蛋白以寡聚体形式参与病毒的复制[7] [8] 。N蛋白为核衣壳蛋白并与RNA紧密结合,对核酸起到保护的作用。M蛋白与病毒的成熟、释放有关;而F、H蛋白与病毒的吸附、侵入有关并决定着病毒的感染性[9] 。
PPRV的诊断方法有很多种,主要有病毒分离鉴定、抗体血清学检测、抗原检测等。自从1995年Forsyth和Barrett根据N基因和F基因设计引物,建立了PPR的RT-PCR检测方法以来,RT-PCR方法在检测PPR得到广泛应用[10] 。本研究通过对P、N基因的保守序列进行分析,分别设计了2对引物,一对通过RT-PCR扩增的方法,用以快速、准确检测小反刍兽疫病毒;一对用于对N全基因全长扩增以及序列比对,分析该毒株与其它毒株的同源性,从而为小反刍兽疫病毒的有效鉴定及输入性疫病的监控奠定良好的基础。
2. 材料与方法
2.1. 材料、试剂
病毒株(CH/GDDG/2014)分离自广东某羊场,克隆载体pMD-19T、DL2000、PrimeScript one step RT-PCR Kit Ver.2均为生物工程(大连)有限公司产品,AxyPrep病毒DNA/RNA提取小量试剂盒,购自康宁生命科学(吴江)生物有限公司,Trizol试剂、胶回收试剂盒及小量柱式质粒提取试剂盒均购自上海华舜公司。氯仿、异丙醇等其他试剂均为国产分析纯试剂。
2.2. 方法
2.2.1. 引物设计
参考GenBank下载的序列,设计下列2对引物,用于扩增P、N基因的扩增,引物由北京睿博有限公司合成,在N上游引物的5’端分别引入SphI,下游引物的5’端引入BamHI酶切位点。
Pf: 5’GGTACCATAGCATCACCGACTC3’
Pr: 5’CCCTTGCTCCTAAGTTTTTTGTAAT3’
Nf: 5’ACATGCATGCATGGCGACTCTCCTTAAAAG3’
Nr: 5’GGGGTACCTTAGCCGAGGAGATCCTTGT3’
预期P、N的扩增产物分别为766 bp、1578 bp。
2.2.2. 病毒RNA的提取
参照AxyPrep病毒DNA/RNA提取小量试剂盒的说明书按步骤对病毒株(CH/GDDG/2014)提取RNA,用DEPC水溶解RNA,于−80℃保存备用。
2.2.3. 目的基因RT-PCR扩增
以提取的RNA为模板进行RT-PCR,分别以Pf、Pr,Nf、Nr为引物,反应体系(25 µL):12.5 µL 2 × 1 step buffer,8.5 µL ddH2O,0.5 µL正向引物,0.5 µL反向引物,2.5 µL模板,0.5 µL Prime Script Enzyme MIX;反应条件:50℃ 30 min,95℃ 5 min,95℃ 30 s,55℃ 30 s,72℃ 50 s,进行35个循环后72℃ 10 min,4℃保存。扩增结束后在1.2%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳,观察结果。
2.2.4. 退火温度优化试验
以上述提取的RNA为模板进行RT-PCR,且设定退火温度分别为53.0℃、54.0℃、55.0℃、55.5℃、56.0℃、56.5℃其他反应条件及体系不变,扩增结束后在1.2%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳,观察结果,来确定最佳的退火温度。
2.2.5. 特异性试验
以广东分离的小反刍兽疫山羊毒株(CH/GDDG/2014),犬瘟热病毒,新城疫病毒,疫苗Nigeria75/1株的RNA为模板及DEPC水为空白对照,并以Pf、Pr为引物进行RT-PCR,扩增结束后在1.2%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳,观察结果。
2.2.6. 敏感性试验
取200 µL提取的RNA,用浓度测定仪测定其初始浓度为108.50 ng/µL,之后对其10倍稀释到10−8 ng/µL并以各自浓度为模板,以Pf、Pr为引物进行RT-PCR,结束后在1.2%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳。
2.2.7. N基因双酶切鉴定
分别以Nf、Nr为引物扩增N全基因,将PCR产物回收后连接到pMD-19T载体,转化到DH5α感受态细胞后,经蓝白斑筛选挑取白斑的单菌落摇菌,抽提质粒并对其进行双酶切鉴定后送测序公司。
2.2.8. N全基因测序结果分析
为了解全球的PPRV毒株的亲缘关系及遗传演化关系,用DNAStar软件比对了本研究分离的PPRV流行毒株(CH/GDDG/2014)和GenBank已发表的国内外代表毒株,选取了包括中国北京分离株(KP260624)、西藏分离株(JF939201)、新疆分离株(KM091959)、埃塞尔比亚分离株(KJ867540)、加纳分离株(KJ466104)、科特迪瓦分离株(EU267273)、肯尼亚分离株(KM463083)、乌干达分离株(KJ867543)、中东分离株(KJ867545)、印度分离株(KJ867542)、塞内加尔分离株(KM212177)、摩洛哥分离株(KC594074)的同源性。用Clustalx 1.8.1和MEGA 6.0软件将选取的各基因型代表参考毒株PPRV1系((EU267273);PPRV2系(KJ466104)、(HQ197753);PPRV3系(KM463083)、(KJ867543)、(KJ867544) 、(KJ867545)、(KM212177);PPRV4系(KP260624)、(KM091959)、(JF939201)及本研究分离的PPRV毒株(CH/GDDG/2014) N基因进行序列比对分析并构建系统进化树。
3. 结果
3.1. RT-PCR检测结果
针对P基因序列的保守区所设计的1对引物,单独对PPRV有正确的扩增,扩增片段大小为766 bp,并且扩增的目的条带没有任何杂带,说明针对小反刍兽疫病毒所设计的引物特异性较好。其扩增结果见图1。
3.2. 退火温度优化试验
以Pf、Pr为引物进行RT-PCR的退火温度的优化,将不同退火温度的PCR产物进行电泳检测,结果表明,在不同的退火温度下均能扩增出目的条带,而在退火温度为55℃的条件下能扩增出明显的条带,因此本实验最佳退火温度为55℃ (见图2)。
3.3. 特异性试验
在以上毒株的RT-PCR扩增并在琼脂糖凝胶电泳中,只有广东分离的小反刍兽疫山羊毒株出现了与预期大小一致的正确条带,而其他的及空白对照都没有条带,结果表明以Pf、Pr为引物的RT-PCR扩增具有明显的特异性(见图3)。
3.4. 敏感性试验
用RT-PCR方法扩增浓度为108 ng/µL的RNA模板以及依次按10倍稀释模板的浓度均出现了明显的目的条带,即可知能检测到的目的基因的最低RNA模板的浓度为1.085 × 10−5 ng/µL (见图4)。
3.5. N基因双酶切鉴定
经过以Nf、Nr为引物扩增N全基因,将回收的PCR产物与pMD-19T载体连接获取的重组质粒分别进行SphI、BamhI双酶切(见图5),说明扩增的DNA片段成功连接到pMD-19T载体上。经引物移步法后,测的N基因的ORF全长序列为1578 bp。
3.6. N全基因核苷酸同源性比对和系统进化树分析
N全基因核苷酸同源性比对结果显示本研究分离的PPRV流行毒株(CH/GDDG/2014)基因组与国内的毒株同源性为90.8%~99.9% (见图6),其中与国内CH/XJYL/2013的同源性高达99.9%;与国外代表毒株基因组的同源性为88.9%~97.7%,其中与Sungri1996MSD分离株(HQ693093)的同源性最高。由此可见我们分离的CH/GDDG/2014毒株的与国内的其他毒株同源性高达99.9%,与其他国家和地区分离株也具有较高的同源性,没有明显的地域性。但总的看来与国内毒株的同源性还是稍高于国外毒株。PPRV目前分为四个系,其中I、II、III型存在于非洲国家,IV系主要来源于亚洲,至今国内还未发现其它3个亚型的PPRV。从系统进化树结果(图7)可以看出,本分离株属于IV系,并且与国内其它地区的毒株处于同一个大分支上,再次说明国内主要流行IV系。

Figure 1. RT-PCR amplifications from samples M. DNA Marker2000; 1. Detection sample; 2. Positive control; 3. Negative control
图1. RT-PCR样品检测图M. DNA标准DL2000;1. 为检测样品;2. 阳性对照;3. 阴性对照

Figure 2. Optimization of annealing temperature of PPRV M. DNA Marker2000; 1 - 6: Annealing temperatures respectively are 53.0˚C, 54.0˚C, 55.0˚C, 55.5˚C, 56.0˚C, 56.5˚C
图2. PPRV的退火温度优化试验结果图M. DNA标准DL2000;1-6:退火温度分别为53.0℃,54.0℃,55.0℃,55.5℃, 56.0℃, 56.5℃

Figure 3. Specificity result of PPRV M. DNA Marker2000; 1. Pest des petits ruminants virus; 2. Canine distemper virus; 3. Newcastle disease virus; 4. Vaccine Nigeria75/1; 5. Positive control; 6. Negative control
图3. PPRV的特异性试验结果图M. DNA标准DL2000;1. 小反刍兽疫病毒;2. 犬瘟热病毒;3. 新城疫病毒;4. 疫苗Nigeria75/1株;5. 阳性对照;6. 阴性对照

Figure 4. Sensitivity results of PPRV M. DNA Marker2000; 1 - 6 sample dilution respectively are: 10−1, 10−2, 10−3, 10−4, 10−5 and 10−6
图4. PPRV的敏感性试验结果图M.DNA标准DL2000;1~6样品稀释度为10−1、10−2、10−3、10−4、10−5、10−6

Figure 5. Dual-Enzyme digestion of N gene M. DNA Marker 5000; 1. dual-Enzyme digestion; 2. recombinant control
图5. N的双酶切鉴定图M. DNA标准DL5000;1. 双酶切;2. 重组质粒对照
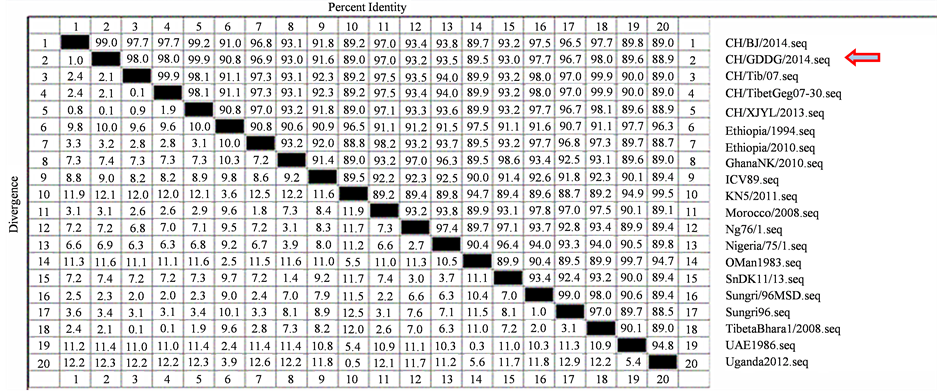
Figure 6. Comparison of nucleotide homology between isolated strains and different subtype reference strains
图6. 分离毒株与各亚型参考毒株核苷酸同源性比较
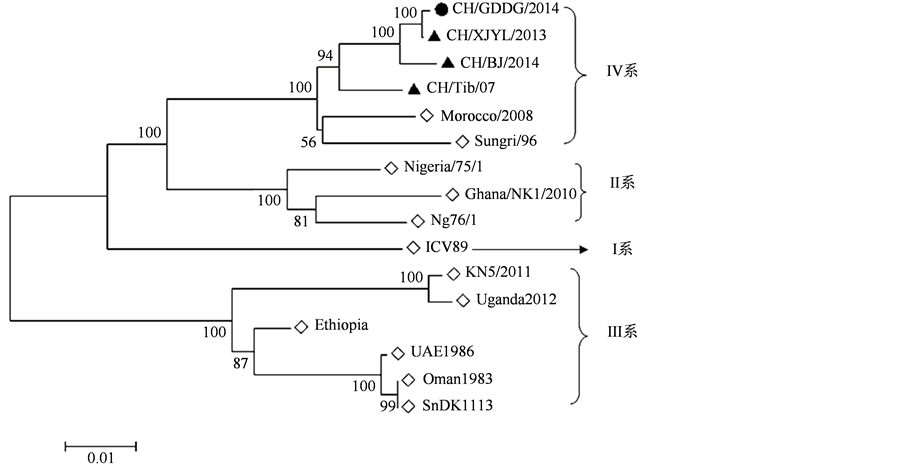
Figure 7. Phylogenetic tree analysis of N gene of isolated strains and reference strains
图7. 分离毒株和参考毒株N基因系统进化树分析
4. 讨论
小反刍兽疫病毒作为我国的一类传染病之一,一年四季均可发生,以春冬季较为流行,其中绵羊最为敏感。该病主要通过呼吸道和消化道感染,其中发病羊群的眼、鼻、口腔分泌物和排泄物携带大量的病毒,可以传染健康的羊群[11] 。同时被污染的饲料、食用的水和食用工具等都是重要的感染方式。该病对我国边境及内陆畜牧业存在着严重的威胁,因为牧群的跨国放牧运输,使得该疫病在防疫工作上存在一定的难度,如在2007年在我国西藏有报道,接着在新疆伊犁也出现流行,2015年又在我国北京也有报道,给养殖业造成巨大的损失。
现阶段的RT-PCR对该病的检测方法很多,检测的基因有N、P、F和M等,为了更准确,快速,灵敏地检测出小反刍兽疫病毒,本研究参照(GB/T 27982-2011)的检测方法,通过扩增部分N基因,获得目的大小351 bp,同时针对P基因设计了一对保守序列建立的RT-PCR方法,经试验表明其灵敏度高,特异性好,为快速准确检测小反刍兽疫病奠定了基础。
小反刍兽疫的结构蛋白中,N蛋白非常保守,并且有很高的免疫原性,可以用来制备诊断抗原,但是N蛋白激活的抗体不能中和病毒[12] 。此外N蛋白在病毒的复制和转录中也起到关键性的作用。本研究对N全基因序列进行分析,并以其他的麻疹病毒属进行核苷酸比对,结果表明本毒株与新疆伊犁,中国北京毒株序列的同源性高达100%。近几年国内小反刍兽疫病在不断地暴发,且流行都为小反刍兽疫病毒基因IV系,目前本病尚无特制治疗方法。发病初期只能使用抗生素类药物控制继发感染[13] 。该病一旦发现,必须进行严密性的封锁,扑杀患畜,彻底消毒。为了更好地对该病进行防范,应加大对该病研究力度,例如对该疫病的流行病学,免疫机制及疫苗等的研究势在必行,为更有效地控制该疫情的发生提供有力的保障[14] 。
基金项目
广东省科技计划项目(No. 2014A070713021;No. 2014B040404061)、广东省农业科学院院长基金项目(No. 201531)。
*通讯作者。