1. 引言
粘土矿物是由细分散的含水层状硅酸盐和含水非晶质硅酸盐矿物组成的,它是地层中含量最丰富的矿物,碎屑岩中常见的粘土矿物有高岭石、绿泥石、伊利石和混层粘土[1] 。粘土矿物具有分布广泛、晶体结构独特、形成机制复杂等特性,这些特性决定了它在油气开发过程中的重要意义 [2] 。20世纪60年代我国就有学者开始对粘土矿物进行研究,但当时粘土矿物的分析方法还是以热分析和透射电子显微镜分析为主,直到1975年X射线衍射分析仪的引入,碎屑岩中粘土矿物的研究才得到进一步的发展。随后Needham利用X射线衍射对粘土矿物的结构进行了研究,研究发现自生粘土矿物在砂岩孔隙中的孔隙度、渗透率基本上按分散质点式—薄膜式—搭桥式的顺序依次降低 [3] 。徐同台等人在前人的基础之上对粘土矿物进一步深入研究,于2003年出版了《中国含油气盆地粘土矿物》这是我国当前最具代表的粘土矿物研究著作之一 [4] 。随后粘土矿物的研究进入一波热潮,黄思静等通过研究发现碎屑岩中绿泥石包膜大大降低了压实作用对储层孔隙的破坏,并使原生孔隙与次生溶孔都得到了较好保存,同时他运用热力学、动力学方法对储层砂岩中粘土矿物进行模拟研究,使粘土矿物研究从定性分析向定量分析发展 [5] 。李明瑞利用粘土矿物X-射线衍射、砂岩薄片等方法对粘土矿物进行了研究,得出了粘土矿物分布的主要控制因素 [6] 。从前人的研究发现很少有学者对碎屑岩中粘土矿物的形成机理和蚀变规律进行探讨。粘土矿物作为砂岩重要的胶结物和填隙物同时是页岩的主要组分,其形成机理和蚀变规律直接影响和控制着碎屑岩的粒间孔隙,因此探讨碎屑岩中粘土矿物的形成机理及蚀变规律对碎屑岩中油气的勘探、开发具有指导性意义。本文在前人研究的基础上,系统总结了碎屑岩中不同类型粘土矿物的形成机理和蚀变规律,并分析了粘土矿物蚀变对储层孔隙的影响。
2. 研究方法
本文利用X衍射、扫描电镜、铸体薄片等方法,对济阳坳陷始新统孔店组68个碎屑岩样品进行了研究,其中,68件样品做了普通薄片分析,分析测试在复杂油气田勘探开发重庆市重点实验室进行;34件样品做了X射线衍射分析,分析测试在胜利油田地质院测试中心进行;23个样品做了扫描电镜实验,分析测试在复杂油气田勘探开发重庆市重点实验室进行。X射线衍射分析的基本原理是:利用X射线衍射图谱进行粘上矿物的定量分析,根据布拉格定律:d = nλ/2sinθ (d为晶面间距;n为正整数;λ为入射X射线的波长;θ为产生衍射峰值时X射线的入射角)衍射的峰值计算出晶面间距,判断出粘土矿物的类型,推断出样品中各种粘土矿物的百分含量。
3. 粘土矿物的类型及特征
3.1. 粘土矿物的类型
通过济阳坳陷始新统孔店组4口具有典型代表的井进行观察后得出该地区黏土矿物的类型及各自相对含量如图1所示,粘土矿物主要为伊利石、高岭石、绿泥石和伊/蒙混层等。其中,HK1井含的粘土矿物主要为绿泥石占46%,其次是伊利石占29%,其它粘土矿物含量较低;W46井则主要含伊利石占68%,伊蒙混层占23%,其余粘土矿物的含量不足10%;WX131井和W100井粘土矿物的含量与前面两口井差异较大,它们所含的粘土矿物主要为伊/蒙混层,分别占73%和64%。HK1井与W46井具有一定的水平距离,对比这两口井粘土矿物的种类和含量可知,不同地区粘土矿物的含量具有差异;对比HK1井与W46井,两口井的深度相差不远,可认为在是一个时期沉积形成的,结果显示不同地区同一时期,形成的粘土矿物可能不同。由此得出不同地区粘土矿物的类型、含量、分布等存在着一定的差异,同一地区也可能有差别 [7] 。这现象的出现可能与当时的沉积环境、粘土矿物的形成机理和蚀变有关。
3.2. 粘土矿物的镜下特征
通过对济阳坳陷始新统孔店组粘土矿物的电镜观察表明(如图2),伊利石在扫描电镜下其微观结构如图2中(a)、(b)所示,单体形态呈丝带状、条片状和羽毛状,集合体形态呈蜂窝状、丝缕状和丝带状;蒙脱石是常见的2:1型层状结构硅酸盐,具有膨胀吸水的特性。在扫描电镜下的微观结构如图2中(c)所示,可见不规则细粒状、鳞片状、绒状颗粒,结晶度差,轮廓不清楚 [8] ;高岭石是碎屑岩中常见的一种粘土矿物。其微观结构如图2中(d)所示。在扫描电镜下其单晶体呈自形或半自形假六方板状,而集合体则表现为平直堆叠或波状堆叠的书页状、蠕虫状、手风琴状、及扇状等 [9] ;绿泥石是2:1:1型的由镁、铁、银按不同比例组成的含水层状硅酸盐矿物,其微观机构如图2中(e)所示,在扫描电镜下呈叶片状、细鳞
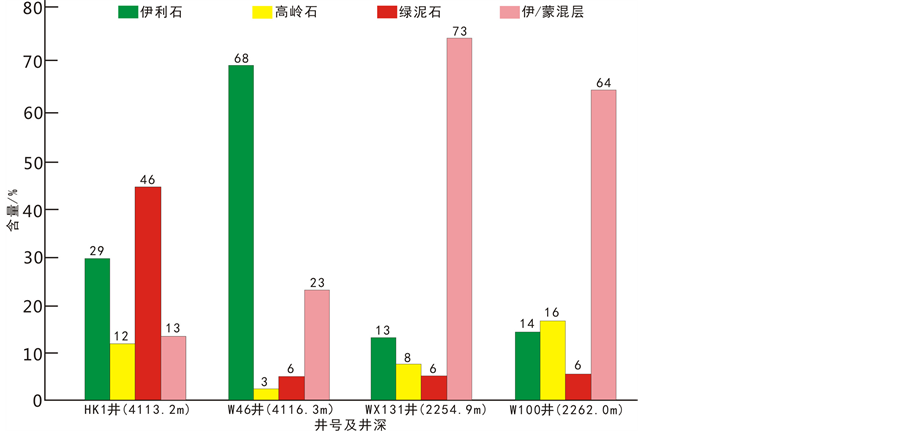
Figure 1. The eocene Kongdian formation of clay minerals in Jiyang depression histogram average relative content
图1. 济阳坳陷始新统孔店组粘土矿物平均相对含量柱状图
 (a)、(b) 粉砂岩中粒间充填的伊利石,Wang46-8,2952.29 m;Wang46-15,2997.88 m;(c) 含砾砂岩,孔隙中分布的蒙脱石,Wang46-27,3786.79 m;(d) 泥质粉砂岩中粒间充填的高岭石,Wang46-35,3791.35 m;(e) 粉砂岩中粒间充填的绿泥石,Wang46-21,3391.90 m;(f) 泥质粉砂岩孔隙中分布的伊/蒙混层,Wang46-31,3788.25 m
(a)、(b) 粉砂岩中粒间充填的伊利石,Wang46-8,2952.29 m;Wang46-15,2997.88 m;(c) 含砾砂岩,孔隙中分布的蒙脱石,Wang46-27,3786.79 m;(d) 泥质粉砂岩中粒间充填的高岭石,Wang46-35,3791.35 m;(e) 粉砂岩中粒间充填的绿泥石,Wang46-21,3391.90 m;(f) 泥质粉砂岩孔隙中分布的伊/蒙混层,Wang46-31,3788.25 m
Figure 2. Scanning electron microscopic characteristics of the clay minerals of the new system in Jiyang depression
图2. 济阳坳陷始新统孔店组粘土矿物的扫描电镜特征
片状、玫瑰花状,叶片状;伊蒙混层如图2中(f)所示,在扫描电镜下其单体既具有伊利石的丝带状、条片状和羽毛状,又具有蒙脱石的不规则细粒状、鳞片状、绒状,其集合体形态呈蜂窝状、丝缕状和丝带状。
3.3. 粘土矿物在水介质中的分布特征
粘土矿物形成时受水体pH值的影响,可形成晶体结构、形态及类型各异的粘土矿物,不同的粘土矿物能在一定程度上反映形成时的水介质条件及环境。通过对济阳坳陷始新统孔店组粘土矿物的研究发现:在此K+/H+比率低的弱酸性(pH = 5~6)氧化环境中SiO2和Al2O3胶体中和生成高岭石 [10] ;而在较大贫K+且富Na+和Ca2+的弱碱性(pH = 7~8.5)环境中则有利于蒙脱石的形成和保存;伊利石在K+/H+比率高的碱性(pH = 8)环境中容易形成,绿泥石则形成于温度相对较高富含Mg2+的较强碱性(pH = 9~10)的环境 [11] 。
4. 粘土矿物的形成机理及影响因素
一般地,碎屑岩中的粘土矿物按形成机理如图3所示,可分为陆源碎屑粘土矿物和成岩过程中新形成的自生粘土矿物2大类 [12] 。沉积成岩过程中形成的粘土矿物进一步细分为原生(自生)和次生(蚀变)粘土矿物2种,前者是沉积期及成岩早期所形成的粘土矿物,而后者则是成岩晚期及以后在次生作用下形成的新粘土矿物。
根据图3可知同一种粘土矿物可由不同的形成机理形成,形成之后又可蚀变,所以粘土矿物的形成机理相当复杂,下面以济阳坳陷始新统孔店组为例,着重探究粘土矿物的两种主要的形成机制,即成岩过程粘土矿物的形成机理和陆源碎屑粘土矿物的形成机理,成岩过程粘土矿物的形成机理又可进一步分为自生粘土矿物的形成机理和由其它硅酸盐矿物蚀变而形成的粘土矿物。
4.1. 陆源碎屑粘土矿物的形成机理
陆源碎屑粘土矿物是地表岩石在风化、剥蚀作用下形成陆源碎屑物质,在一定条件下,经过地表水的搬运作用发生机械分异而沉积形成的。这种沉积主要发生在滨浅湖、半深湖、深湖与半深湖的过度相里。一般该过程形成的陆源碎屑粘土矿物,充填在碎屑岩的颗粒之间形成杂基。通过对济阳坳陷始新统孔店组陆源碎屑粘土矿物研究发现,该地区陆源碎屑粘土矿物的形成机理遵循的一般规律是:蒙脱石→伊利石、高岭石→伊利石,其产状主要有6种:1) 千枚岩屑、泥质岩屑、板岩屑中的粘土;2) 砂岩屑内的粘土、粉砂质泥岩纹层、泥砾 和泥质团块;3) 与粉砂同时沉积的粘土;4) 生物搅动引入的粘土;5) 泥岩中的大部分粘土。济阳坳陷始新统孔店组陆源碎屑粘土矿物的形成机理如图4所示,(a)为陆源碎屑粘土矿的湖泊相沉积,在大气淡水的淋滤作用下母岩遭受风化剥蚀,形成陆源碎屑物质,陆源碎屑物质在地表水的搬运过程中发生机械分异作用和化学分异作用;粉砂颗粒在清水中的沉降速度为1.5 × 10−2 mm/s 至6 × 10−2 mm/s;粘土颗粒在清水中的沉降速度为9.375 × 10−4 mm/s至1.5 × 10−2 mm/s,当流水的流速小于沉降速度的12倍时,此时流水的动力不足以克服悬浮碎屑物质的重力,碎屑物质发生沉积。如图4中(b)所示,P = 1.5 × 10−2 mm/s,当流动强度小于等于P时,粘土矿物开始沉积 [9] 。图4中的(c)为当流动强度急剧减小到1.5 × 10−2 mm/s或更小时,形成的分选较差,砾、砂、粉砂和粘土的混合沉积物。(d)则是与模型c对应的济阳坳陷始新统孔店组的浊流沉积;作浊流沉积主要发生于大陆边缘地区,当发生地震、滑坡、暴风浪时,粘土矿物随富含悬浮固体颗粒的高密度水流,在重力驱动下顺坡向下流动发生浊流沉积形成分选较差的碎屑物质与粘土矿物同时沉积的混合沉积物,该过程是将陆源物质由浅海输送到深海的重要机制。

Figure 3. Model of the formation mechanism of clay minerals (Walker, 1975)
图3. 粘土矿物的形成机理模式图(据沃克,1975)

Figure 4. Genetic pattern of clay minerals in the lake of Jiyang depression
图4. 济阳坳陷孔店组湖泊环境下粘土矿物成因模式图
4.2. 自生粘土矿物的形成机理
自生粘土矿物指的是由孔隙溶液直接沉淀出的,或硅酸盐经过溶解之后再沉淀形成,以及其它硅酸盐矿物蚀变形成的矿物。
4.2.1. 自生高岭石的形成机理
济阳坳陷始新统孔店组的自生高岭石比较发育,结合扫描电镜和X射线衍射分析结果,发现济阳坳陷始新统孔店组自生高岭石由长石、铝硅酸盐等矿物,在弱酸性环境中,通过大气淡水的淋滤作用,脱去碱性离子富集硅铝晶化而形成 [13] ,如图5所示,长石、云母以及其它硅酸盐矿物溶解形成 [14] [15] 高岭石其反应式如:式(1)、(2)、(3)、(4):
 (1)
(1)
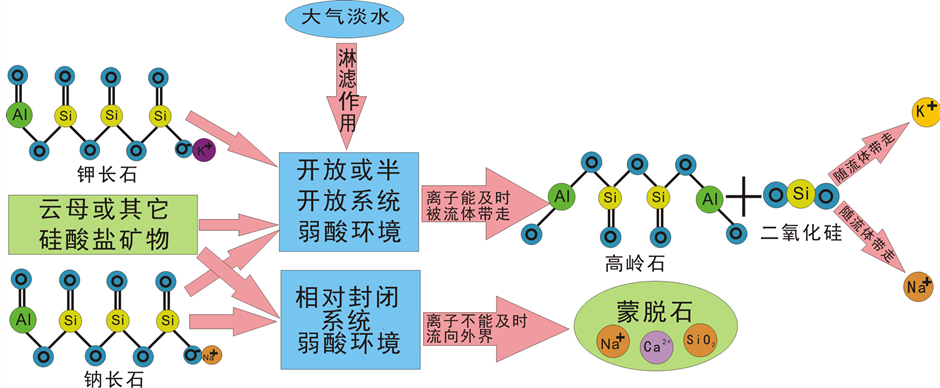
Figure 5. Authigenic kaolinite in Kongdian formation of Jiyang depression pattern formation mechanism
图5. 济阳坳陷孔店组自生高岭石的形成机理模式图
 (2)
(2)
 (3)
(3)
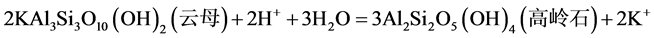 (4)
(4)
由上面4个化学反应式以及图5可以得出,长石或云母形成高岭,要求源源不断的大气淡水参与为反应提供一个弱酸性条件[16] 。同时要求反应所产生的K+、Na+、Ca2+能被及时带出,也就是说高岭石的形成过程是在一个开放或半开放性成岩体系中完成的 [8] 。所以受大气的控制,高岭石常常形成于近地表环境中。如果当时的成岩体系封闭,则会造成SiO2和Ca2+、Na+等离子的浓度过高,使高岭石被蒙脱石所替代。
4.2.2. 自生蒙脱石的形成机理
蒙脱石是常见的2:1型层状结构硅酸盐,在电镜下其单晶体呈自形或半自形假六方板状,集合体为平直堆叠或波状堆叠的书页状、蠕虫状、手风琴状、及扇状等 [9] ,常以孔隙充填的形式存在于粒间。济阳坳陷始新统孔店组的自生蒙脱石也表现出相同特征。蒙脱石晶粒间结构比较疏松,在流体冲刷作用下容易随流体移动,从而堵塞、分割粒间的孔隙和喉道等特性,因而备受人们的关注。碎屑岩中的蒙脱石常形成于温带半湿润区,它的形成需要在碱性介质(pH = 7~8.5)条件下完成,并且与水解强度有关,只要有充足的水分长石和硅酸盐矿物就可以蚀变形成蒙脱石。
如图6所示,钠长石和钙长石在碱性环境中容易形成蒙脱石,因为钠长石和钙长石在碱性环境中溶解形成Ca2+、Na+参与反应,而钾长石溶解产生的K+将阻碍蒙脱石的形成。
4.2.3. 自生伊利石的形成机理
伊利石因其自身的特殊的性质,它对储层孔隙的影响比其他粘土矿物更大。主要表现为,伊利石在开发注水阶段容易会发生断裂,断裂的伊利石常常堆积在吼道处,从而减低储层的渗透率。因此近年来,伊利石形成机理的研究 [12] [14] ,越来越受到人们的重视。自生伊利石的形成机理与相对封闭条件下长石溶解有关,刘昊年、黄思静等对川西坳陷上三叠统须家河组砂岩中粘土矿物的研究也证明了这一点 [17] 。通过对济阳坳陷始新统孔店组的研究发现,该储层中伊利石的形成机理主要有两种。一种是在相对封闭

Figure 6. The formation mechanism model of Montmorillonite
图6. 蒙脱石的形成机理模式图
系统中,钾长石溶解提供K+或原孔隙流体中就富含K+时,长石与机酸反应形成伊利石,同时伴随着自生石英的形成。其反应式为:

从上式可知随着埋藏深度的增加,温度、压力也随之升高,相对封闭系统中的钾长石不断溶解,储层中伊利石的含量也不断增加。另一种形成机理,则是在富K+相对开放系统中,通过蒙脱石的蚀变而形成,该反应要求反应过程中的地温在70℃~100℃之间。
4.2.4. 自生绿泥石的形成机理
绿泥石是一种富铁、镁的层状硅酸盐矿物,是砂岩储层中的重要组分,并且绿泥石的存在,对储层原生孔隙具有保护作用。因此,有关绿泥石的形成机理一直是国内外研究的热点。绿泥石一般形成于富铁、镁较强碱性(PH = 9~10)的半封闭系统 [11] 。绿泥石可由钾长石、黑云母等矿物,在富Fe2+、Mg2+的碱性环境中形成 [18] ,除此之外也可由高岭石蚀变而形成,济阳坳陷始新统孔店组自生绿泥石的形成化学反应式如下:
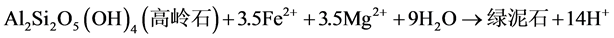
从上式可知,系统中的这些铁、镁物质在成岩早期水解,为绿泥石的形成提供了一个半封闭的碱性还原环境,绿泥石的形成可以分为两个阶段:首先是颗粒表面的粘土矿物在富铁、镁的环境中转化形成颗粒包膜,然后由孔隙水中沉淀出来的绿泥石将其包裹起来,并且从颗粒边缘向孔隙中心逐步形成,绿泥石的自形程度较好,具有明显的世代性。
5. 粘土矿物的蚀变规律
粘土矿物的蚀变与古地温、成岩流体中的酸碱度有着直接的关系。随埋藏温度的升高,镁铝蛇纹石蚀变形成绿泥石,说明古地温对粘土矿物的蚀变起着控制作用 [19] 。孙庆峰、陈发虎等通过研究发现成岩流体中的酸碱对粘土矿物的蚀变也有影响 [10] 。下面以济阳坳陷始新统孔店组为例,就古地温、成岩流体中的酸碱,这两个影响粘土矿物蚀变的主要因素进行探究,从而得出粘土矿物的蚀变规律。
5.1. 古地温与粘土矿物蚀变
温度是控制粘土矿物蚀变的一个主要因素,随埋藏深度的增加和温度的不断升高,在开放系统中当温度在70℃~100℃时蒙脱石和高岭石发生蚀变形成伊利石,只要温度在该范围内,该反应就会地层中不断的发生 [8] ,图7为蒙脱石蚀变形成伊利石和高岭石蚀变形成伊利石的模式图,其反应如式(1)和式(2):
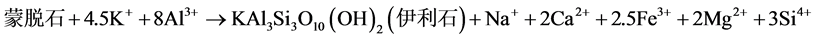 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
当温度高于130℃时,伊利石生长所需的K+主要有钠长石溶解来提供,从而高岭石在钾离子参与下发生蚀变形成伊利石和石英,其反应如式(3):
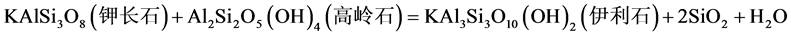 (3)
(3)
由图7可知,高岭石的蚀变成伊利石所需的K+几乎全部来自钾长石的溶解,因此在该封闭系统中的高岭石和钾长石不能共存 [20] 。本文利用X射线衍射法对济阳坳陷始新统孔店组高岭石与钾长石进行了研究,发现高岭石蚀变形成伊利石,其矿物组合可根据高岭石和钾长石相对含量的关系分为3种。1) 高岭石含量大于钾长石含量,此时钾长石全部溶解,高岭石部分发生蚀变,地层中高岭石与伊利石共存;2) 高岭石含量等于钾长石含量,此时钾长石全部溶解,高岭石全部蚀变,地层中只保存着伊利石;3) 高岭石含量小于钾长石含量,钾长石只溶解一部分,高岭石全部蚀变形成伊利石,地层中保存的是伊利石和钾长石。蒙脱石→伊利石/蒙脱石混层→伊利石,这一蚀变过程的蚀变温度约为:70℃~140℃ [21] 。张哲、陈小明等对山东济阳坳陷,古地温与伊利石/蒙脱石混层中各自含量做了研究,结果表明粘土矿物的蚀变与古地温有关,当温度100℃~140℃左右时,伊利石/蒙脱石混层发生蚀变形成伊利石 [22] 。由图7可看出,在储层中随着深度的增加地温不断升高,先发生蚀变的粘土矿物是蒙脱石,蒙脱石蚀变形成伊/蒙混层矿物,随着温度进一步的升高,伊/蒙混层矿物开始蚀变最终形成伊利石。说明了粘土矿物的蚀变与古地温有着直接的联系。
5.2. 成岩流体性质对粘土矿物蚀变的影响
成岩流体中的盐度和酸碱度在粘土矿物的蚀变过程中发挥了重要的作用。通过对济阳坳陷始新统孔店组粘土矿物薄片观察,发现粘土矿物分布、蚀变受成岩流体中的盐度和酸碱度的影响。不同的流体条件控制着不同粘土矿物的蚀变,成岩流体的酸碱度和盐度对粘土矿物蚀变的关系如图8所示。下面对济阳坳陷始新统孔店组成岩流体中影响粘土矿物蚀变的这两主要因素进行探讨。储层中粘土矿物的蚀变不仅受地温的影响,也受蚀变时成岩流体中酸碱度的影响,不同的粘土矿物的蚀变能在一定程度上反映蚀变时成岩流体的酸碱度。蒙脱石可在富钾的碱性流体条件下发生蚀变形成伊利石 [12] 。在济阳坳陷始新统孔店组发现了,在富钾的碱性流体条件下蒙脱石蚀变成伊利石,其过程为:流体中的Al3+、K+与蒙脱石中的Fe2+、Mg2+发生置换并脱水其化学反应式如(1)式:
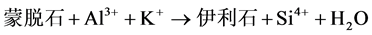 (1)
(1)
由反应式可知蒙脱石要蚀变形成伊利石除了成岩流体质条件为碱性外,还要求系统中含有充足的K+,当该反应在封闭系统中发生时,K+可由系统中钾长石溶解提供,若该封闭系统储层孔隙中缺K+和钾长石贫泛,则该反应不会发生。发生蚀变时如果水介质中富含的是Fe3+、Mg2+而不是Al3+、K+,则蒙脱石可蚀变形成绿泥石。济阳坳陷始新统孔店组成岩流体中富含Al3+、K+而贫Fe3+、Mg2+离子,所以在该储层中伊利石和绿泥石比较发育,而蒙脱石很不发育。
由此可知成岩流体条件中,对粘土矿物蚀变影响较大的因素除了酸碱度外还有盐度。王少依等对中国18个陆相含油气盆地粘土矿物分布特征与成岩流体条件的关系进行研究后发现,在富镁的储层中大量存在绿泥石;而富钾的储层中大量存伊利石 [23] ,这一特点与济阳坳陷始新统孔店组中绿泥石和伊利石的分布特征相符。这样的现象也说明了,成岩流体中盐度变化会引起粘土矿物的蚀变。在碱性系统中当储
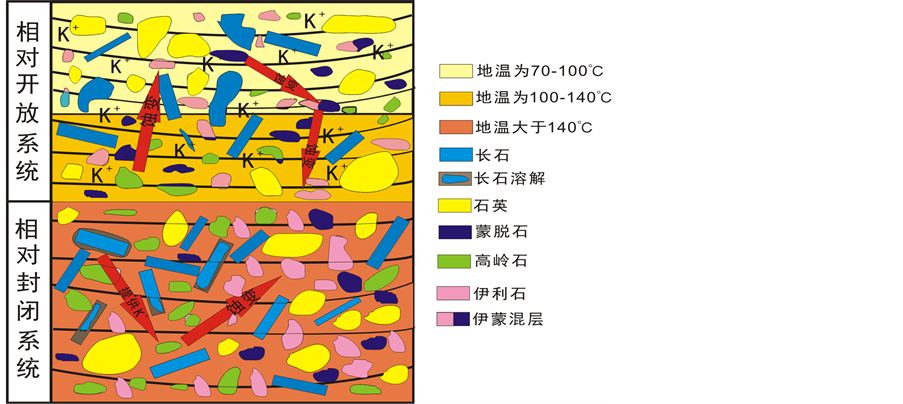
Figure 7. The relationship between temperature and the clay mineral alteration
图7. 地温与粘土矿物蚀变的关系
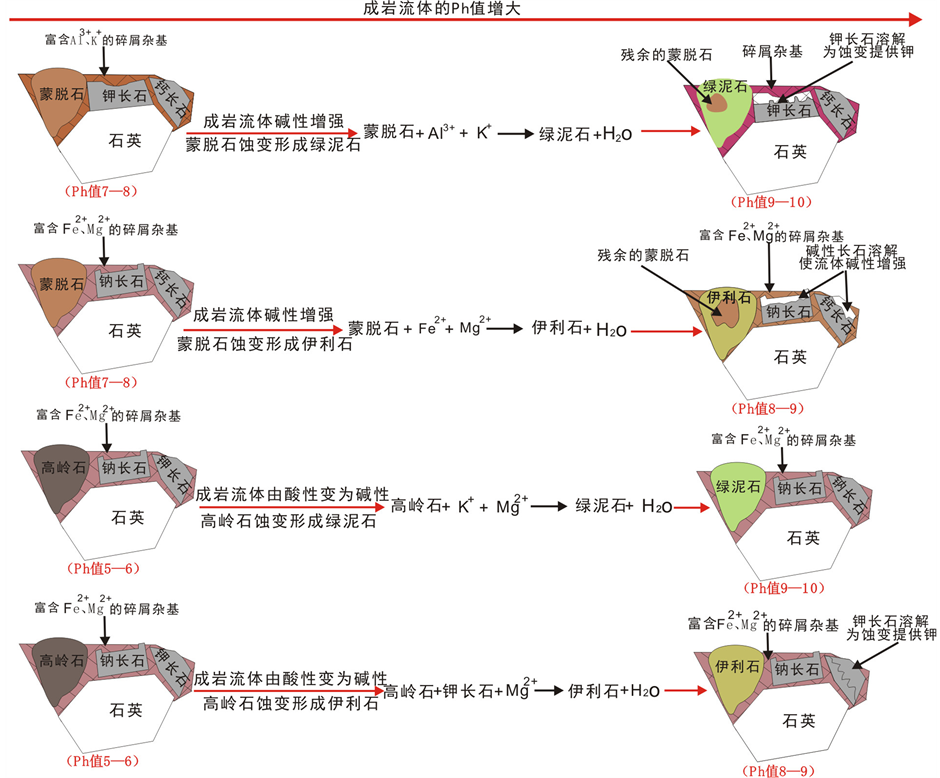
Figure 8. The influence of fluid properties on the clay mineral alteration in the Jiyang depression
图8. 济阳坳陷孔店组成岩流体性质对粘土矿物蚀变的影响
层里含大量的Al3+、K+时,蒙脱石很容易发生蚀变形成伊利石。这现象说明了成岩流体中的盐度会影响粘土矿物的蚀变,同一种粘土矿物发生蚀变,若参与的盐不同则形成的粘土矿物也会不同。如图8所示,在较强碱性水介质条件下,当温度较高时绿泥石可由高岭石蚀变形成 [11] [12] ,其反应式如(2)式:
 (2)
(2)
该反应的发生需要在富含Mg2+的较强碱性(pH = 9~10)的成岩流体条件下完成。在K+/H+比率低的弱酸(pH = 5~6)氧化性水介质条件下,高岭石可有其它硅酸盐粘土矿物蚀变而成。
综上所述,当储层中成岩流体条件的酸碱度由酸性变为碱性过程中,高岭石可能发生蚀变形成绿泥石;当成岩流体条件的碱性逐渐变强时,伊利石和绿泥石可能由蒙脱石蚀变形成;当成岩流体条件由碱性变为酸性过程,高岭石可由其它粘土矿物蚀变形成。蒙脱石在富含Fe2+、Mg2+蚀变形成绿泥石,而在富含Al3+、K+的成岩流体条件下容易蚀变形成伊利石。说明了成岩流体性质会影响粘土矿物的蚀变。
6. 粘土矿物的油气地质意义
6.1. 自生粘土矿物对储层的影响
粘土矿物的存在对储层有重要的油气地质意义。济阳坳陷始新统孔店组中的自生伊利石是在相对高温的深埋藏封闭条件下,由钾长石溶解或高岭石的伊利石化所形成,高岭石蚀变成伊利石需要消耗钾离子,这两个过程都促进了钾长石的溶解,钾长石的溶解对储层次生孔隙的形成具有显著的积极作用 [24] 。成岩阶段在有机酸的参与下,钾长石大规模的溶蚀,这是济阳坳陷始新统孔店组次生孔隙形成的主要因素 [25] 。由此可知,自生伊利石的形成,对储层次生孔隙的形成与保护有着积极的作用。
本文通过对济阳坳陷始新统孔店组绿泥石的扫描电镜观察得出,含有绿泥石的储层中,砂岩颗粒接触强度很低,没有石英的次生加大,孔隙度较高;若储层中缺乏绿泥石时,则砂岩颗粒表现出具有很高的接触强度、较强的石英次生加大和极低的孔隙度,说明了绿泥石的存在大大的降低了压实作用对岩石颗粒间孔隙的破坏作用 [26] 。
6.2. 粘土矿物的蚀变对储层孔隙的影响
本文利用扫描电镜分析,对济阳坳陷始新统孔店组粘土矿物进行研究,发现粘土矿物的蚀变可能引起粘土矿物的种类、成分和产状中的一种或多种发生变化,从而影响储层的发育。图9为济阳坳陷始新统孔店组粘土矿物的扫描电镜图,蒙脱石在富钾的碱性开放系统中,可发生蚀变形成伊利石,其反应式可表示如下:
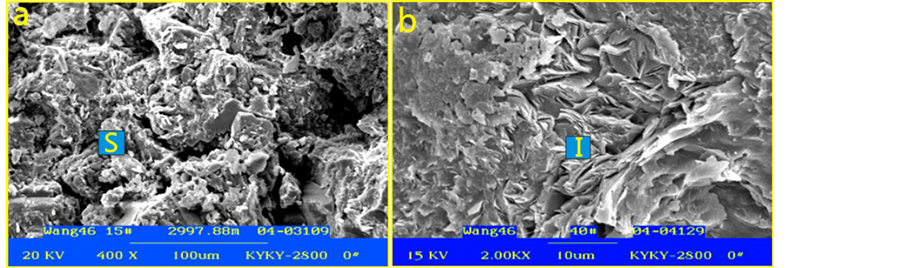 (a) 粉砂岩中粒间充填的蒙脱石,Wang46-15,2997.88 m;(b) 粉砂岩孔隙被伊利石分割,Wang46-40,2864.37 m
(a) 粉砂岩中粒间充填的蒙脱石,Wang46-15,2997.88 m;(b) 粉砂岩孔隙被伊利石分割,Wang46-40,2864.37 m
Figure 9. Effect of montmorillonite on the porosity of the reservoir in Jiyang depression
图9. 济阳坳陷孔店组蒙脱石蚀变成伊利石对储层孔隙的影响
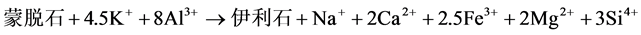
如图9(a)所示,蒙脱石是一种常见的层状结构粘土矿物,其颗粒呈不规则细粒状、鳞片状,粒度较小,结晶较差;而伊利石则以纤维状、卷片状存在于储层中,当储层中的蒙脱石大量蚀变为伊利石时,因伊利石常以网状搭桥式分布于储层中,会把大量的孔隙和喉道切割成微细的束缚孔隙,从而使孔隙和喉道减小,降低储层的渗透率,如图9(b)所示。
除此之外还发现,济阳坳陷始新统孔店组中的高岭石在储层中常以孔隙充填的形式存在于粒间孔隙,晶粒间结构比较松,在流体冲刷作用下容易随流体移动,从而堵塞、分割粒间的孔隙和喉道;而绿泥石则以孔隙衬垫包于颗粒表面,使储层中的原生孔隙得以较好的保存。当储层中的高岭石蚀变形成绿泥石时,储层的孔隙度和渗透率会因高岭石的粒间充填转变为绿泥石的孔隙衬垫而增大。
7. 结论
1) 济阳坳陷始新统孔店组的粘土矿物比较发育,主要以伊利石、高岭石、绿泥石和伊/蒙混层为主;在扫描电镜下其各自的特征分别是:伊利石呈蜂窝状、丝缕状和丝带状,高岭石呈书页状、蠕虫状,绿泥石呈叶片状、细鳞片状,而伊/蒙混层则呈不规则细粒状、鳞片状;伊利石一般分布于K+/H+比率较高的碱性环境,高岭石在K+/H+比率低的弱酸性至中性环境中较稳定,绿泥石分布于富Mg2+的强碱性环境,伊/蒙混层分布于贫K+的弱碱性环境。
2) 济阳坳陷始新统孔店组粘土矿物的形成机理大致可分为两种:一种是母岩在大气淡水的淋滤作用下,发生分化、剥蚀形成陆源碎屑物,再经地表水搬运,当水流强度小于1.5 × 10−2 mm/s时,陆源碎屑物中的粘土开始发生沉积形成陆源碎屑粘土矿物;另一种是,地层中的长石、云母以及其它硅酸盐矿物,在一定的成岩条件下发生溶蚀,与成岩流体中的离子发生一系列反应,再次沉淀形成自生粘土矿物。
3) 影响粘土矿物蚀变的因素有很多,主要因素有三种,分别是成岩流体的酸碱度、盐度和古地温;粘土矿物的蚀变具有一定的规律:当成岩流体由弱酸性变为碱性时,高岭石会蚀变形成绿泥石;当成岩流体碱性逐渐变强时,蒙脱石会蚀变形成伊利石和绿泥石;当地温为70℃~140℃时,蒙脱石和高岭石会蚀变形成伊利石;当地温升高到100℃~140℃时,伊/蒙混层会蚀变成伊利石;当成岩流体中富含Fe2+、Mg2+等离子,蒙脱石就会蚀变形成绿泥石,如果成岩流体中缺乏Fe2+、Mg2+等离子而富含Al3+、K+离子,蒙脱石则会蚀变形成伊利石。
4) 通过对济阳坳陷始新统孔店组粘土矿物的研究发现,不同粘土矿物对储层有着不同的油气地质意:高岭石的形成和蚀变都会促进储层中钾长石的溶解,钾长石溶解又是储层次生孔隙形成的主要原因之一;储层中绿泥石的存在会大大的降低压实作用对岩石颗粒间孔隙的破坏;储层中伊利石的存在会使孔隙和喉道减小,降低储层的渗透率,因为伊利石常以网状搭桥式分布于储层中,会把大量的孔隙和喉道切割成微细的束缚孔隙。
基金项目
本文为国家自然科学基金项目(41202043);中国石油科技创新基金项目(2014D-5006-0108);重庆科技学院大学生科技创新项目(2015024);国土资源部页岩气资源勘查重点实验室开放基金(BSYS2014-01)资助成果。
*通讯作者。