1. 引言
随着现代化和城市化的快速发展,越来越多的高层、超高层建筑相继出现,复杂的城市环境出现风能聚集效应,形成局地强风。局地强风影响到了居民们工作、生活的舒适与安全,同时具有一定的风力发电潜能,而我国风力发电场主要设置在偏远人烟稀少的地区,增加了城市供电的成本。城市建筑环境局地强风风能利用为解决风力发电城市化带来的能源的巨大消耗、严重的环境危机、电力紧缺等问题提供了解决思路。近年来,“分布式发电”凭借其投资成本较低、输出功率控制方式灵活、和环境和谐等优点逐渐得到各界重视。城市建筑环境风能利用也为分布式发电提供了新的思路,将小型风力发电机置于城市建筑环境中,变害为利,也能进一步改善风电场远距离输送问题。
建筑环境中风能利用的主要形式是在其中安装风电机组。英国和瑞典从2001年开始研究适应于城区风能发电的平板型及扩散型风能集中器;Metens [1] 较早提出实现城市建筑风能利用必须解决风力强化与集中问题,并运用计算流体方法(CFD)方法分析了不同流线体型建筑的集风特点。国外早前已出现过英国strata大厦、迪拜旋转大楼、巴林世贸中心等一些城市建筑环境风力发电运用的实际案例。国内,已有珠江大厦、青岛“生态大厦”,以及2010年上海世博会出现的“零排放”场馆等实例,但对于在城市建筑环境中风能利用的研究仍处于起步阶段。据估计,到2020年,每年仅靠建筑物环境的风电机组可发1.7~5.0 TW [2] 。因此,城市建筑环境中的风能利用对缓解能源与环境矛盾,推进清洁能源的利用有着重要而深远的意义。
然而以往的研究通常以简易模型代替建筑物,并不能真实反映建筑群内风能的分布情况。本文以华北电力大学主楼建筑群真实模型为例,进行CFD数值模拟,探讨此环境中风能的分布情况,分析风力发电的可行性。尤其针对风能分布密集以及流动复杂区域,设计加密网格划分方案,对建筑环境中风电机组可能的安装位置即夹道、楼顶、拐角等进行了详细分析;最后,为解决城市建筑风能利用的风力强化与集中问题,综合考虑了不同风能利用方式和不同建筑风环境,提出了适应于城市风能利用的风电机组改型的设计要求以改善风力强化与集中问题。
2. 城市建筑环境风能利用
2.1. 城市建筑环境风能特点
城市建筑物聚集,建筑外形各异,布局不同,所处地貌环境差异,增加了风流动时的阻力,降低了城市风速。然而,由于城市的地表面如同地形复杂的山区一般,较为粗糙,同时街道中以及两幢高楼之间,形同山区中的风口具有明显的集风效果,可以在低风速区制造出局地大风来 [3] 。
如图1所示,当风接触高大建筑物时,迎风面高处高能量风遇建筑物阻碍从上而下形成垂直方向的漩涡,形成逆风;背风面楼顶高能量风下降而产生下冲风,气流紊乱,危害很大;楼顶会出现一个较大的风速区,即“楼顶小急流”,环境干扰小,是风能利用最佳位置,根据英国Renewable Devices公司对建筑物附近的风场进行了模拟分析,实验证明受建筑物阻挡后的风速比相同高度其他处风速高20% [4] ;当气流穿过建筑开口部位时,由于迎风面和背风面存在压力差,形成“穿堂风”。如图2所示,来流风受到建筑物的阻挡分离的绕建筑物两侧的自由流区域形成分流风,由于“夹道效应”,可在无风时形成局部大风。
特别需要说明的是,根据风洞实验,位于楼前的涡流区和绕大楼的角流区,风速提高30%左右,若是建筑楼底层设有风道,则风道口附近的风速将提升为平时的2倍左右。此外,下冲风区风能分布不均匀,流线无规则,风向随机变化,常为风害多发区。因此,利用城市建筑环境风能必须首要了解其风力分布特点 [5] 。
2.2. 城市建筑风能利用形式
目前,城市建筑风环境的风能利用主要有以下两种形式:1) 在建筑环境中安装风力发电机组;2) 风能建筑一体化。而供电模式主要有以下几种:1) 独立运行模式,将风力发电机输出的电能经储蓄电池储能,再供用户使用;2) 与其他发电方式互补运行模式,例如风光互补形成风光储一体化发电系统;3) 与电网联合供电模式 [6] 。
3. 风环境数值模拟建模过程
由于城市建筑物均位于大气边界层以内,建筑物附近的空气流动具有紊乱性和随机性,因此本文研究的建筑环境中空气流动属于湍流流动。
为了简化问题,本文对空气流动作如下基本假定:流体是不可压缩的牛顿流体,忽略粘性耗散;流体在固壁上无滑移;流体是各向同性的;流体为稳态情况。
由于城市建筑风环境较复杂,单靠空气动力学在理论上是难以解决的。本文运用软件Gambit进行几何建模和网格划分,再运用FLUENT15.0模拟分析建筑环境中空气流动及流体动力学问题。
3.1. 几何模型建立及网格划分
本文以华北电力大学主楼建筑群为例,进行城市建筑环境风能利用可行性的分析及证明。如图3、图4所示,此建筑群位于北京市昌平区,所处位置较为空旷,西邻京藏高速,北邻平房区。此建筑群所在地盛行西北风,年平均风速为3 m/s [7] 。几何模型根据建筑物真实尺寸建立,建筑物有6个主体部分组成,其楼高36~60 m不等,但明显高于周边建筑物。B栋和C栋、E栋和F栋均靠长廊连接。综合考虑计算精度和计算量,确定如下计算流域:取该建筑群最高60 m为H,建筑物正北面迎风面距入口边界取10 H,正南面背风面距出口边界取20 H,正西面迎风面距入口边界取10 H,正东面背风面距出口边界取10 H,高度取3 H,来流方向设为正西北方向,此时阻塞率为3% [8] 。如图5所示为流域示意图。图6为整体网格截图,采用逐渐增大的网格划分方式,划分了6,451,992个网格。
3.2. 边界条件及计算方法
本文以稳态的雷诺时均Navier-Stokes方程为基础,运用常用且易实现的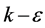 湍流模型进行计算。由于该建筑群盛行西北风,本文将北面和西面均设置为入口,采用速度入口边界条件(velocity-inlet);将南
湍流模型进行计算。由于该建筑群盛行西北风,本文将北面和西面均设置为入口,采用速度入口边界条件(velocity-inlet);将南
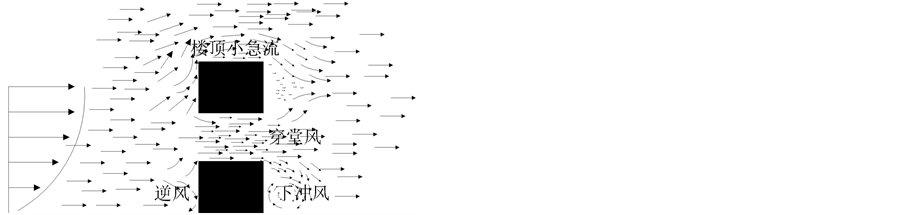
Figure 1. Little jet flow on the roof, through flow inside the building, headwind and undershoot wind
图1. 楼顶风、下冲风、逆风、穿堂风

Figure 2. Strengthened flow between two buildings
图2. 夹道效应
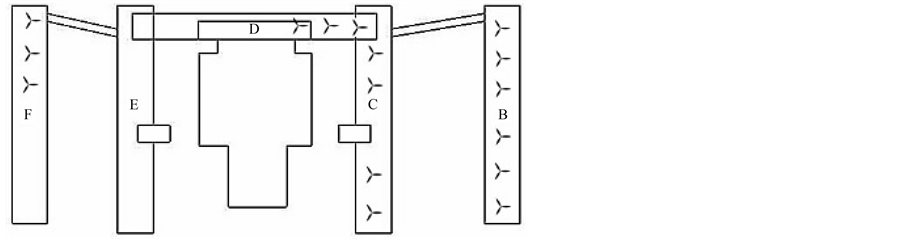
Figure 3. The vertical view of building model
图3. 建筑模型俯视图
面和东面均设置为出口,采用压力出口边界条件(pressure-outlet);将建筑物外表面和地面的壁面条件设置为无滑移。
风吹过地面时,受到地面草、庄稼、森林、房屋建筑等阻碍作用,产生较强的阻力作用而使风风速降低,风速的降低速度也随着离地的高度的增加而降低,与距离地面高度呈幂指数分布规律 [9] ,即为
 (1)
(1)
其中, 为参考高度
为参考高度 处的风速,
处的风速, 为所求高度
为所求高度 处的风速,
处的风速,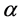 为地表粗糙度指数。表1中列出了一些典型地表的粗糙度长度。
为地表粗糙度指数。表1中列出了一些典型地表的粗糙度长度。
本文取10 m高度为参考高度,此高度年平均风速定为3 m/s,地面粗糙度指数 采用0.33,风向为正西北方向,入口边界采用UDF接口输入。计算精度设置为3D双精度,空气模型设置为不可压缩的常密度空气模型,采用二阶迎风格式对流体进行离散,速度压力耦合定为SIMPLE算法。
采用0.33,风向为正西北方向,入口边界采用UDF接口输入。计算精度设置为3D双精度,空气模型设置为不可压缩的常密度空气模型,采用二阶迎风格式对流体进行离散,速度压力耦合定为SIMPLE算法。
4. 算例分析
运用FLUENT15.0数值模拟分析该建筑群周边风资源分布情况,重点考察4中风电机组可能安装位置处的风速变化情况,根据其风资源特点进行不同小型风电机组的初步选定。

Table 1. Typical longditudinal turbulencelength scales
表1. 典型的地表粗糙度长度
本文共选取三类典型位置,具有代表性的A、B、D、F、G、H六点进行分析。其中:B、D、F三点为楼顶位置;A、G两点为夹道位置,其中A为楼间走廊;H点为拐点位置。
4.1. 楼顶小急流
建筑物楼顶风能聚集明显,是公众认为的风能利用的最佳位置。B、C、D、E、F点均位于楼顶,建筑高度分别是36 m、41 m、60 m、41 m、36 m。考虑到建筑物表面对风速的影响以及风电机组塔架高度,研究位置均取高于楼顶面5 m高度处。
1) B点风场:图7(a)为B栋楼41 m高度处沿建筑长边的风速分布图,可见楼顶风速较同高度风速明显提升,41 m高度处最高速度达到5.5 m/s,越接近背风面风速越低;(b) B栋楼切面图,4.68~6.25 m/s速度层明显下移,产生了明显的集聚效果,为楼顶风能利用提供了可能性。C点风场和B点风场情况类似。
2) D点风场:D点风场为该建筑群最高位置60 m,最高风速达6.3 m/s,图8(a)中可看出建筑物迎风向前端出现高风速区,后端出现低风速区。其原因是迎风方向为建筑物短边,属细长型建筑物,更多流体从侧边流过,导致楼顶后端风速下降 [7] 。
3) F点风场:F楼位于D、E楼之后,且D、E楼均高于F,导致F楼顶沿建筑长边50 m以后区域出现大面积低风速区域。但由图9(a)可知,F楼顶还是出现局部高风速区,风速超过5 m/s,为风能可利用区。
4.2. 夹道
当风流过建筑物时,迎风面会产生较强的高压,而背风面产生强烈的低压,当建筑替有开口或建筑物与建筑物间有夹道时,风从此通道流过就会连接正负压,产生压差,使得风速增加,风能聚集。
1) 1) A点风场:A点为B楼和C楼之间的连体走廊,长56.25 m,宽2.48 m,中空型,长边为迎风面。图10(a)中8~28 m高度为走廊区,风速几乎为零,此建筑结构走廊并没明显的聚风效果,因此本文中不考虑此处安装风电机组。
2) 2) G点风场:G点位于B与C栋楼之间,宽52.9 m,风在通过该夹缝时,受到狭窄通道的挤压,形成强风,即“夹道效应”,可能会出现局地大风,由图11验证了此规律。由于本文采用正西北风向,导致此处出现风速较低区域,后端集风效果更为明显,该区域风向较为稳定,风速较大。
4.3. 拐角
H点风场:H位于B栋楼背风面拐角区,处于下冲风区,背风面楼顶高能量风下降而产生的风。该区由于下冲风与楼梯旁侧的扰流汇合,形成局地大风。该区为风灾害高发区,风速不均匀、流线无规则、风向随机变化。图12为H拐角速度分布。
5. 城市建筑环境下的风能利用设计
5.1. 风力发电可行性分析
风能的利用主要是通过风电机组将风能转化为电能的过程。风能密度是指来流在单位时间内垂直流

 (a) 41 m高度径向风速分布 (b) 速度剖面
(a) 41 m高度径向风速分布 (b) 速度剖面
Figure 7. Wind speed distribution at the roof of building B
图7. B栋楼顶风速分布

 (a) 65 m径向高度风速分布 (b) 速度剖面
(a) 65 m径向高度风速分布 (b) 速度剖面
Figure 8. Wind speed distribution at the roof of building D
图8. D栋楼顶风速分布

 (a) 46 m高度径向风速分布 (b) 速度剖面
(a) 46 m高度径向风速分布 (b) 速度剖面
Figure 9. Wind speed distribution at the roof of building F
图9. F栋楼顶风速分布

 (a) 风速 (b) 速度剖面
(a) 风速 (b) 速度剖面
Figure 10. Wind speed distribution at corridor A
图10. A走廊速度分布图

Figure 11. Wind speed distribution at channel G
图11. G夹道速度分布图
过单位面积的风能,是描述一个地方风能潜力的最方便最有价值的量,单位为W/m2。
 (2)
(2)
由此可知,风能密度跟风速的立方成正比,故风电机组安装时需考虑实际风速以及湍流强度 [10] 。
1) 实际风速是衡量具体位置的风能大小,是最具价值的量,小型风电机组要求风速3 m/s以上,中型风电机组要求4.5 m/s以上;
2) 湍流强度I,衡量风场的湍流程度,对于风电场,湍流强度不宜超过0.25。
由本文模拟结果显示,主要考察位置的风速均超过3 m/s,局部地区更是达到6.25 m/s,为中小型风电机组可利用风速范围内。同时,以B栋楼楼顶湍流强度为例,如图13所示,除背风面下冲风区出现高湍流度外,楼顶区域湍流强度为0.06~0.23范围内,符合湍流强度要求,符合中小型风电机组使用条件。
5.2. 建筑环境下的风电机组选型
常见的用于建筑环境的中小型风电机组有HAWT、VAWT和BAWT三种 [11] ,启动风速为1.5~3 m/s。不同于其他位置的风电机组,建筑环境的特殊性对风电机组的结构安全性、稳定性、舒适度提出了更高要求。
以本建筑群为例,可结合自身建筑特点、风资源分布特点和风电机组的优缺点,选择适宜的风电机组:
1) 楼顶位置B、C、D、F点风场具有较好的风资源,可设置几排风电机组,平面布置图如图3所示。由于该地盛行西北风,该楼为办公区,需要较为安静的环境,且风电机组需建立在建筑体上。因此,重点考察风电机组可能造成的噪声、共振、飞车等问题,需对楼顶进行加固,塔架与建筑一体化,保证风电机组塔架与楼顶平滑、牢固结合,增强稳定性。同时,置于楼顶的风电机组塔架不宜过高,四周需设置安全防护措施,例如在建筑物楼顶四周设置一定的网格结构确保安全;
2) 夹道G点风场风向较为稳定,风速较大。但该区域为人类活动区,是人能触碰到的区域,因此安全性要求极高。传统的小型风电机组用于此环境将严重影响到人们的舒适度及安全,若加网格隔开将影响美观。此处引进浓缩减噪概念对传统水平轴风电机组进行改进,由国内田德教授提出并予以验证 [12] 。在传统的小型水平轴风电机组的风轮处加一轻质导流罩,结构如图14所示。一方面,导流罩将降浓缩风能,降低启动风速,增大年发电量;另一方面自然风流过导流罩后流体均匀化,起到减振降噪的作用;此外,风轮安装在导流罩内将避免水平轴叶片损坏飞落的不安全隐患。安装导流罩后的水平轴风电机组更适合城市建筑环境。
3) H点风场为拐点风场,封面具有风速不均匀、流线无规则、风向随机变化特点,可根据该点实际环境情况,设置一定量的垂直轴风电机组,实现与环境的一体化,同时仍需用网格隔开。
此外,该建筑群为华北电力大学教学楼,若在该区设置风电机组,一方面该校有着新能源电力系统国家重点实验室,拥有强大的技术支撑,同时也为研究人员提供实验测试点;另一方面,将凸显其电力教学背景、电力特色,树立城市新能源利用典范。
6. 结论
本文用CFD对华北电力大学主楼建筑附近的风环境进行数值模拟,对可能安装风电机组的位置进行分析,计算得出主要考察的位置风速均超过3 m/s,局部地区达到6.25 m/s,湍流度在0.06~0.23间,为中小型风电机组可利用风速范围内,证明了其风力发电机组应用的可行性,为城市建筑环境风能分布式发电提供了可能性。同时,综合考虑其安全性、舒适性、经济性,我们提出了在楼顶位置安装风电与建筑
一体化的风电机组;夹道处则引入“浓缩概念”,在传统的水平轴风电机组风轮处安装加轻质导流罩,增强了风力聚集效果;拐点位置可结合环境安装一定量的垂直轴风电机组。
本文仅对建筑环境进行了数值计算和风电机组安装的初步构想,实际工程还需要综合考虑该建筑群实际地面情况对流场的干扰,以及安装风电机组对人们工作、生活的影响。此外,还需结合建筑物动力学进行分析,充分考虑风电机组振动对建筑物的影响。