1. 引言
离子交换膜在无电场状态下分离离子的原理是基于Donnan dialysis原理。离子交换膜常用于电渗析除盐,其工作时需在膜两侧外加电压。但根据离子交换膜具有选择透过性以及Donnan dialysis原理,其也可以在无外加电压的状态下分离水中离子。基于Donnan dialysis原理,Fonseca等 [1] 和Velizarov等 [2] 利用离子交换膜分离饮用水中的NO3-并进一步进行生物处理,还对同时去除饮用水中的硝酸盐和高氯酸盐进行了研究 [3] ,并在此基础上扩展到无机带负电荷污染物 [4] - [6] 和金属离子(汞和砷) [7] ,还有研究者 [8] - [10] 基于Donnan dialysis原理对氟的分离去除进行了研究,及将水样中重金属离子分离后进行浓度检测 [11] [12] 。作者选择工业废水中常见的Cu2+、Mn2+、Zn2+为对象,研究了阳离子交换膜对这些离子的去除效果(去除率75%~85%),结果表明重金属水化离子半径和原子序数对分离去除效果有影响 [13] [14] ,并讨论了pH值变化对阳离子交换膜分离去除重金属离子效果的影响 [15] 。以上研究扩展了离子交换膜应用的领域,但关于膜分离过程中离子迁移的速率控制讨论较少。本文将以Donnan dialysis原理和化学势平衡理论为基础详细探讨离子交换膜在无电场状态下分离待处理离子时模型中各区域离子浓度的变化情况以及分离过程机理。
2. 离子迁移的三种状态
根据Donnan dialysis原理和化学势平衡理论,当膜两侧离子的活度比相等时,则离子交换停止。即:
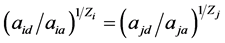
式中, 和
和 分别代表第
分别代表第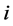 种离子在给体液中和受体液中的活度,
种离子在给体液中和受体液中的活度, 代表
代表 离子所带电荷数,
离子所带电荷数,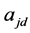 和
和 分别代表第
分别代表第 种离子在给体液中和受体液中的活度,
种离子在给体液中和受体液中的活度, 代表
代表 离子所带电荷数。
离子所带电荷数。
当两者有差值时,会发生离子交换,直到膜两侧离子活度比相等。
浓度与活度有密切关系,为简化考虑,下述讨论中均以物质的浓度代替其活度进行论述。
离子在溶液中迁移是基于化学势平衡,当溶液中存在某种组分化学势不相等时,离子会在化学势差的推动下移动,以使溶液中各处该组分化学势相等 [16] 。
以阳离子交换膜分离二价阳离子为例,二价阳离子用M2+表示,补偿离子为一价阳离子,以K+表示。阴离子均为Cl−。离子交换膜分离过程模拟图如图1所示。

Figure 1. The simulation diagram of ion exchange membrane
图1. 离子交换膜分离过程模拟图
给体池一端连续流入含有待分离的二价阳离子M2+的原水,另一端连续流出。受体池一端连续流入摩尔浓度高于阳离子M2+摩尔浓度的补偿离子K+,另一端连续流出。给体池和受体池均要对溶液进行搅拌,由于搅拌的原因,可以假定主体溶液(给体液和受体液)中离子浓度相同。膜两侧会形成边界层,主体溶液(给体液和受体液)与离子交换膜由于被边界层分隔,所以在Donnan dialysis过程中不起直接作用。
离子交换膜基于Donnan dialysis原理分离离子的过程中的控制步骤,不同研究者有不同的结论,一般认为有2种:一是边界层溶液中的离子迁移过程是控制步骤,二是膜中离子的迁移过程是控制步骤。本文假设存在3种状态分别进行讨论:1) 膜中离子迁移速率是控制步骤,速度较慢,边界层溶液中离子的迁移速率极快,远高于膜中离子迁移速率数量级;2) 膜中离子迁移速率远大于边界层溶液中离子的迁移速率,边界层溶液中离子的迁移速率是控制步骤;3) 膜中离子迁移速率和边界层溶液中离子的迁移速率数量级相近,均为控制步骤。其中,第一种状态和第二种状态是极端状态,以利于理论分析。
此外,还假定二价阳离子M2+和补偿离子一价阳离子K+在边界层溶液中扩散系数相同,以简化分析过程的复杂程度。
各分区浓度的表示方式示例如下:例如, 代表1区(边界层1)溶液中补偿离子K的平均浓度,
代表1区(边界层1)溶液中补偿离子K的平均浓度, 代表3区(给体液3)溶液中待分离阳离子M的平均浓度,
代表3区(给体液3)溶液中待分离阳离子M的平均浓度, 表示边界层1区K浓度的变化量,其他类同。
表示边界层1区K浓度的变化量,其他类同。
三种情况下初始状态均为:


3. 膜中离子迁移速率是控制步骤
从起点开始分析,首先在Donnan dialysis原理作用下,K+从边界层2区中向边界层1区中迁移,同时M2+从边界层1区向边界层2区迁移。根据电中性原理,M2+透过膜的迁移摩尔数量为K+透过膜的迁移摩尔数量的一半。
此时,K1会增加,K2会减少。由于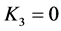 ,
, ,所以在化学势差的推动下,边界层1区中的K+会继续向给体液3区迁移。由于
,所以在化学势差的推动下,边界层1区中的K+会继续向给体液3区迁移。由于 ,所以在化学势差的推动下,受体液4区中的K+会继续向边界层2区迁移。整个过程表现为K+从受体液4区先后通过边界层2区、膜、边界层1区后进入给体液3区。假定边界层溶液中离子的迁移速率极快,所以可以认为存在下列关系式:
,所以在化学势差的推动下,受体液4区中的K+会继续向边界层2区迁移。整个过程表现为K+从受体液4区先后通过边界层2区、膜、边界层1区后进入给体液3区。假定边界层溶液中离子的迁移速率极快,所以可以认为存在下列关系式:

对于M2+,相类似同样有下列关系:

运行一段时间后达到动态平衡(由于给体池和受体池均连续进水,连续出水,膜两侧活度比始终不等,Donnan dialysis过程持续进行,但保持稳定状态,下同),由于边界层溶液中离子的迁移速率极快,远高于膜中离子迁移速率,可以认为边界层中离子浓度与主体溶液中离子浓度差很小,基本相同,此时有下列关系:


此时,边界层不存在离子浓度富集。
但实际条件下,由于离子由边界层进入主体溶液需要浓度差(化学势差)推动,故实际条件下,应有下列关系:


即实际条件下存在边界层浓差极化现象。
4. 边界层溶液中离子的迁移速率是控制步骤
从起点开始分析,首先根据Donnan dialysis原理作用下,K+从边界层2区中向边界层1区中迁移,同时M2+从边界层1区向边界层2区迁移。
此时,K1会增加,K2会减少。由于 ,
, ,所以在化学势差的推动下,边界层1区中的K+会继续向给体液3区迁移。由于
,所以在化学势差的推动下,边界层1区中的K+会继续向给体液3区迁移。由于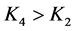 ,所以在化学势差的推动下,受体液4区中的K+会继续向边界层2区迁移。
,所以在化学势差的推动下,受体液4区中的K+会继续向边界层2区迁移。
假定膜中离子迁移速率远大于边界层溶液中离子的迁移速率,则K+从1区向3区的迁移速率会小于K+从边界层2区向边界层1区的迁移速率,那么边界层1区中K+会继续增加,也就是说边界层1区会出现K+的持续富集。
此外,K+从受体液4区向边界层2区迁移的速率也小于K+从边界层2区向边界层1区的迁移速率,所以边界层2区的K+会持续降低。
随着边界层1区会出现K+的持续富集和边界层2区的K+的持续降低,Donnan dialysis的推动力就会持续下降,到达一定程度后,膜中离子迁移速率会与边界层溶液中离子的迁移速率趋同(边界层溶液中离子的迁移速率会比原速度增加),从而最终达到动态平衡。此时,膜中离子迁移速率比初始速率低,等于边界层溶液中离子的迁移速率。
达到动态平衡时存在下列关系式:

按同样的思路分析M2+的迁移,可以得出同样的结论。但达到动态平衡时存在下列关系式(与K各区浓度大小顺序存在差异):

最终达到动态平衡时,膜中离子迁移速率会与边界层溶液中离子的迁移速率相同,两者都是控制步骤。边界层2区M2大于受体液M4,边界层1区K1大于给体液3区K3。
5. 膜中离子迁移速率和边界层溶液中离子的迁移速率均为控制步骤
直接考虑达到动态平衡时的状态,此时有下列关系:
 ,
, ,
,
 ,
,

 ,
, ,
,
 ,
,

浓度大小关系与2中情况(膜中离子迁移速率远大于边界层溶液中离子的迁移速率)达到动态平衡时状态一样。
下面讨论打破膜中离子迁移速率等于边界层溶液中离子的迁移速率这一平衡状态后,是否会再次恢复平衡状态。
假定增加给体池进水M2+的浓度,即增加给体液3区M3。
由于增加了给体液3区M3,因而给体液3区M2+和边界层1区M2+的化学势差增加,给体液3区中M2+会加快向边界层1区迁移,此时其迁移速率会高于膜内离子迁移速率,从而导致边界层1区M1增加。边界层1区M1增加后,根据Donnan dialysis定义式,膜内离子迁移推动力会增加,从而加大膜内离子迁移速率。但由于边界层1区M1增加后,给体液3区和边界层1区M2+的化学势差会随之减少,给体液3区中M2+又会减慢向边界层1区迁移。膜内离子迁移速率增加,同时给体液3区中M2+向边界层1区迁移速率减少,直到两者再次相等,整个系统重新达到平衡。此时平衡速率要高于前次平衡速率。上述分析说明,在不考虑膜内通道容纳能力的情况下,给体池M2+浓度越高,膜内离子迁移速率越高,但这并不说明M2+的去除率会增加(去除率等于平衡时给体液M的浓度除以给体液进水的M2+浓度)。因为作为分母的给体液进水的M2+浓度增加了,去除率反而会降低。实际可以假设:单位膜面积负荷浓度越高,膜内离子迁移速率会越快,但是去除率反而降低。
6. 结论
由于浓度差越大,化学势差就越大,此时边界层溶液中离子的迁移速率越快。同时,浓度差越大,膜内离子迁移的速率也越快。此外,外界温度、压强以及离子本身在溶液中的扩散系数都会对上述两种速率的大小有影响。具体影响关系定量比较复杂,需进一步研究。
本文从理论上分析离子交换膜分离离子时可能存在的3种状态:1) 膜中离子迁移速率是控制步骤,速度较慢,边界层溶液中离子的迁移速率极快,远高于膜中离子迁移速率;2) 膜中离子迁移速率远大于边界层溶液中离子的迁移速率,边界层溶液中离子的迁移速率是控制步骤;3) 膜中离子迁移速率和边界层溶液中离子的迁移速率均为控制步骤,并讨论了各状态下各区域离子浓度的变化规律。
在假定温度、压强等其他影响速率的参数不变的情况下,笔者认为,上述3种状态中,第一种适用于待分离离子及补偿离子高浓度时的情况,第二种适用于浓度极低的情况,第三种适用于中间浓度。因为离子浓度高时,离子迁移数量就相对较多,对于直径不变的膜内部通道而言,会带来拥堵,从而降低膜内离子迁移速率,此时膜内离子迁移速率必然是控制步骤。当离子浓度极低时,不存在这种拥堵现象,同时Donnan dialysis的推动力保持不变,远高于边界层内的离子迁移推动力,则膜内离子迁移速率较快,而边界层内的离子迁移速率相对较慢,是控制步骤。
至于浓度范围与3种状态的定量对应关系,可能与离子种类,所带电荷数以及膜本身性质有关,需进一步研究。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金项目(50778065);湖南省教育厅项目(14C0441);湖南省研究生科研创新项目(CX2015B498)。