1. 引言
作为地表与大气界面的关键参量,地表温度是全球与区域气候变化的指示因子。大范围地表温度的获取是地气间能量交换、陆地生态系统监测等研究的关键环节。自上世纪八十年代以来,如何利用星载遥感获取高精度的地表温度数据一直是定量遥感研究领域的热点问题。针对卫星热红外遥感数据反演地表温度的单窗算法/单通道算法、分裂窗算法及地表温度/发射率分离算法等相继建立 [1] 。目前,基于卫星热红外遥感数据反演地表温度的理论与方法已趋于成熟,并已有相关的业务化产品。如美国宇航局发布的MODIS地表温度产品,其精度已达到1.0 K以内,有力地促进了陆面过程研究,并已在全球与区域气候变化研究中发挥了举足轻重的作用。
在热红外谱区,大气中水汽对地表长波辐射具有强烈的吸收作用,严重限制了全天候条件下地表温度的反演。相对于热红外遥感而言,被动微波受天气因素影响较小,这使得被动微波遥感在反演地表温度方面具有更广泛的应用范围和更大的应用潜力。近年来,学术界围绕利用星载被动微波遥感数据反演地表温度这一科学问题开展了深入的研究,并建立了一系列模型与算法。自1978年起,在轨运行的被动微波传感器就有SMMR、SSM/I、TRMM TMI、AMSR、AMSR-E等,这使构建较长时间序列的地表温度数据集成为可能。被动微波遥感提供的地表温度时间序列数据集。同时,AMSR2、FY-3微波成像仪陆续升空,为被动微波遥感提供了丰富的数据源。可以预见,基于被动微波遥感反演地表温度,具有广阔的应用前景。
与热红外遥感相类似,基于被动微波遥感反演地表温度也存在病态反演的问题。同时,作为反演地表温度的关键参数,微波发射率主要由介电常数决定,受多种因素复杂影响。目前实用的微波发射率计算模型还很少。最近几年来,学术界提出协同热红外与被动微波遥感开展地表温度反演研究,并取得了一定的成果。然而,由于被动微波遥感尤其是低频通道所获信息往往具有一定的深度,是一定连续体的有效温度(或称为“等效温度”),而热红外遥感仅能获取地物皮肤表面温度,二者在本质上具有一定联系但存在显著的差异。将热红外遥感获得的肤面温度简化处理为被动微波遥感的有效温度,在裸土和稀疏植被区域可能存在较大误差。在另一方面,被动微波遥感影像空间分辨率很低,仅适用于大陆与全球尺度研究,无法满足干旱监测、生态系统建模、气候变化分析等区域尺度上的实际需求。
本文回顾了近年来关于热红外与被动微波遥感协同反演地表温度的相关研究报道,指出了尚待深入研究的问题。
2. 热红外与被动微波遥感协同反演地表温度的原理
对于被动微波遥感而言,描述地表-大气-传感器过程的辐射传输方程与热红外谱区的辐射传输方程是非常相似的。对于低频通道(频率v < 117 GHz),描述温度与辐亮度的Planck方程可根据Rayleigh-Jeans近似:
 (1)
(1)
因此,可将辐射传输方程中的辐亮度均由式(1)替换,得到由温度表示的被动微波通道的辐射传输方程 [2] :
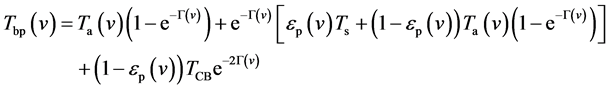 (2)
(2)
式中,p表示极化类型,如水平极化和垂直极化;Tbp为被动微波传感器观测所得的亮温;Ta为大气有效温度;Г(v)为光学厚度, 为大气透过率,
为大气透过率, 为大气发射率;TCB为宇宙背景辐射亮温。
为大气发射率;TCB为宇宙背景辐射亮温。
研究表明,TCB在2.75 K左右,加之地表反射、大气透过率对其的衰减作用,故宇宙背景辐射对被动微波传感器观测信息的贡献可以忽略 [2] 。此时,被动微波通道的辐射传输方程可表示为:
 (3)
(3)
地表温度的解析式为:
 (4)
(4)
式(3)、(4)表明,从被动微波遥感数据反演地表温度与热红外遥感类似,也是一个病态反演问题。反演地表温度,前提在于确定大气透过率、大气有效温度(与大气上行辐射、下行辐射紧密联系)和地表发射率。对于低频通道如AMSR-E的6.9 GHz、10.7 GHz,大气的影响基本可以忽略,故式(4)可简化为式(5)。随频率增加,大气影响增强,地表温度的反演中需考虑大气影响。
 (5)
(5)
对被动微波遥感而言,主要的大气影响来源于大气成分(主要是氧气和大气水汽)、云与雨区中的水滴。一方面,在晴朗的天气条件下,频率低于15 GHz的通道所受的大气影响很小,频率低于10 GHz的通道所受的大气影响可忽略。另一方面,云与雨区中的水滴对被动微波遥感的影响则较大。
3. 热红外与被动微波遥感协同反演地表温度的研究进展
被动微波遥感不受云雾等天气因素的影响,是地表温度遥感反演的重要数据源。总体而言,基于被动微波遥感反演地表温度的算法,可分为经验算法、半经验算法和物理算法 [3] 。
经验算法将被动微波遥感相关通道的亮温、亮温组合及衍生参数与地表温度“真值”、“相对真值”或“替代真值”进行回归,得到地表温度反演的经验方程。如McFarland et al. (1990)针对SSM/I数据,通过亮温剔除了水体、积雪和降水等像元,对各通道的亮温与近地面气温进行了回归,面向农用地、干燥土壤和湿润土壤构建了地表温度反演的经验方程:
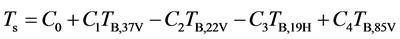 (6)
(6)
式中,Ci ( )为拟合系数;TB,37V、TB,22V、TB,19V和TB,85V分别为37 GHz、22 GHz、19 GHz和85 GHz垂直极化通道的亮温。分析结果表明,SSM/I的37 GHz垂直通道是反演地表温度的主要通道,37 GHz垂直极化与19 GHz水平极化通道的亮温差可修正地表水体的影响;22 GHz垂直极化和37 GHz垂直极化通道的亮温差可修正大气水汽的影响,85 GHz垂直极化的亮温则主要用于修正大气的影响 [4] 。
)为拟合系数;TB,37V、TB,22V、TB,19V和TB,85V分别为37 GHz、22 GHz、19 GHz和85 GHz垂直极化通道的亮温。分析结果表明,SSM/I的37 GHz垂直通道是反演地表温度的主要通道,37 GHz垂直极化与19 GHz水平极化通道的亮温差可修正地表水体的影响;22 GHz垂直极化和37 GHz垂直极化通道的亮温差可修正大气水汽的影响,85 GHz垂直极化的亮温则主要用于修正大气的影响 [4] 。
李万彪等在分析SSM/I各通道对地表水体、大气水汽、大气云雨粒子等因素订正的基础上,建立了中国东部地区地表温度的经验算法:
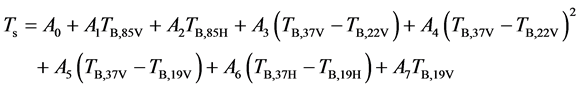 (7)
(7)
式中, 为系数,通过近地表气温与各通道亮温拟合得到 [5] 。
为系数,通过近地表气温与各通道亮温拟合得到 [5] 。
此外,Owe & Van De Griend (2001)研究发现,SSM/I 37 GHz垂直极化通道亮温能够较好地预测地表温度,并利用实测气温与热红外遥感反演的地表温度建立回归方程,借此估算地面站点对应的长时间序列地表温度;将该长时间序列的地表温度与37 GHz的垂直极化通道亮温建立回归关系。研究结果表明,因白天土壤温度梯度较夜间大,对白天与夜间分别建立回归方程能获得更好的精度 [6] 。毛克彪等选择青藏高原为研究区,以MODIS地表温度作为“真值”,建立了一个针对AMSR-E反演地表温度的物理统计算法,并认为89 GHz垂直极化通道作为主要的反演通道精度最高 [7] 。Holmes et al.针对全球的分析结果则表明37 GHz垂直极化通道是反演地表温度的最佳通道,该通道辐射能量来源深度较浅,其对土壤特征的敏感性较低,同时具有较高的大气透过率。Holmes et al.进而建立了适用于全球地表温度反演的经验算法:
 (8)
(8)
式(8)的适用范围为TB,37V > 259.8 K,即该算法适用于非结冰和无积雪覆盖的地表。分析表明,该方法对于全球70%的植被覆盖地区反演误差在1 K以内,但对于裸地、稀疏植被覆盖区域及灌丛地,该算法无法获得准确的反演结果。总体而言,对于林地反演误差在2.5 K以内,对于低植被覆盖地区反演误差在3.5 K以内 [8] 。进一步的,Holmes et al. (2013)构建了一个框架,利用五种被动微波传感器反演的地表温度,提高数值预报模型地表温度的预报精度 [9] 。
利用37 GHz垂直极化通道亮温反演地表温度的思想在局地尺度也得到应用。Salama et al. (2012)选用青藏高原那曲站实测的0.2 cm土壤温度与SSM/I的37 GHz垂直极化通道的亮温进行了回归分析,发现二者呈显著的线性关系:
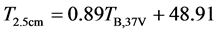 (9)
(9)
式中,T2.5cm为2.5 cm处的土壤温度。Salama et al.的反演结果采用了MODIS的地表温度产品、全球陆面数据同化系统GLDAS和气象站点观测的气温数据进行了验证,取得了较好的效果 [10] 。
Parinussa et al.基于澳大利亚NAFE’06实验数据分析了37 GHz通道反演获得的地表温度与实测地表温度、1 cm土壤温度和MODIS肤面温度的关系,发现被动微波遥感地表温度与红外遥感地表温度具有较好的相似性,呈线性关系,但前者的动态范围相对较小,可能是由于穿透深度的影响 [11] 。
半经验算法围绕被动微波遥感辐射传输方程,从物理机制出发,以理论数据为基础反演得到地表温度,具有经验模型简单易行的优点,兼具一定的物理意义。如Njoku通过给定不同参数值(大气中总水汽含量、地表温度、土壤湿度、植被含水量)的组合,使用微波辐射传输模型进行正向模拟,生成模拟数据集。基于该模拟数据集,构建了地表温度反演的统计方法 [12] :
 (10)
(10)
基于已经的全球SSM/I发射率数据(利用ISCCP数据集,热红外提供的地表温度和NCEP大气廓线模拟得到大气参数计算得到),Fily et al.发现高纬度地区无积雪与冰覆盖地表在SSM/I的19 GHz和37 GHz的垂直极化和水平极化发射率均存在显著的线性关系,如对于45N-70N、60W-170W的区域有:
 (11)
(11)
 (12)
(12)
式中,ε19V、ε19H、ε37V和ε37H分别为相应通道对应的地表发射率。
式(11)、(12)有助于减少多个通道联立方程中的未知数个数。结合经验确定的大气透过率、大气上行有效温度和下行有效温度,Fily et al.实现了地表温度的反演。然而,该算法的最主要缺陷在于,地表温度的反演结果对式(18)、(19)的误差非常敏感 [13] 。Royer & Poirier针对SMMR和SSM/I的37GHz垂直极化和水平极化通道,通过建立这两个通道地表发射率的经验关系(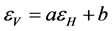 ),并假定大气透过率、大气上行辐射亮温、下行辐射亮温为常数,求解了地表温度,并用于北美地表温度时空分析 [14] 。
),并假定大气透过率、大气上行辐射亮温、下行辐射亮温为常数,求解了地表温度,并用于北美地表温度时空分析 [14] 。
Gao et al.以亚马逊森林为对象,针对AMSR-E数据提出了一个极化比方法。其中,极化比定义为:
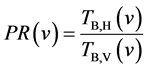 (13)
(13)
Gao et al.通过模型模拟发现,对于AMSR-E的6.9 GHz、10.7 GHz和18.7 GHz通道,极化比与水平极化通道的发射率存在良好的相关关系,这为确定水平极化通道的发射率提供了可能。研究结果表明,对于植被覆盖地区,18 GHz水平极化通道的地表发射率可通过该通道的极化比的二次方程精确计算;对于非植被覆盖地区,则可通过6.9 GHz和18 GHz的极化比共同确定。基于该确定的18 GHz水平极化通道的地表发射率,在忽略大气影响的前提下,可直接计算18GHz水平极化通道对应的地表温度 [15] 。
此外,还有部分研究引入被动微波亮温的衍生参数,用于构建地表温度反演算法。这些衍生参数主要用于描述地表特征(如土壤湿度、植被覆盖状况等)。如Zhao et al.在青藏高原土壤湿度反演中,将微波极化差值指数(MPDI)引入地表温度反演中,认为MPDI可降低土壤湿度和植被变化对地表温度反演的影响,利用4 cm深度处的土壤温度为真值,将其与AMSR-E的10.7 GHz、19 GHz、37 GHz垂直极化通道亮温和MPDI进行了回归,建立了地表温度反演的经验方程 [16] 。
相对于经验算法与半经验算法,物理算法具有明确的物理意义,基于被动微波遥感的辐射传输模型,尝试从地表发射率入手求解地表温度。如Basist et al.通过分析SSM/I不同通道发射率之间的关系,在忽略大气影响的前提下建立了地表温度计算方法。在该算法中,由于垂直极化通道发射率的变化较小,故选取垂直极化通道进行地表温度反演。当地表为干燥状态时,假定其地表发射率为ε0(模拟结果表明,地表水体覆盖比例为0时,发射率不随频率变化)。由于湿度导致的发射率变化可表示为:
 (14)
(14)
由于湿度导致的发射率变化可表示为相邻通道发射率差值的加权和:
 (15)
(15)
根据上面三个方程,可求解地表温度:
 (16)
(16)
式中,v1、v2与v3分别为19 GHz、37 GHz和85 GHz垂直极化;ε0确定为0.95;系数β0、β1根据全球的SSM/I观测数据模拟得到 [17] 。
此外,Jones et al.引入Fily et al.构建的垂直极化与水平极化通道发射率之间的线性关系,推导出垂直极化通道亮温、水平极化通道亮温和地表温度之间的线性方程,针对低频通道,忽略大气影响和植被散射作用,在对辐射传输方程进行简化的基础上引入了上述线性方程,构建了地表温度的迭代反演方法 [18] 。
总体上,目前利用被动微波遥感反演地表温度仍主要以经验模型和半经验模型为主。由于被动微波发射率确定极为复杂,物理模型的使用并不广泛。热红外遥感在辅助被动微波遥感反演地表温度时,常将前者反演的地表温度作为后者对应的地表温度“真值”,为算法训练和验证服务。
4. 热红外与被动微波遥感的协同机制
如全文所述,热红外遥感与被动微波遥感的主要用途之一,即实现地表温度等参数的反演。二者具有不同的优势,使得协同反演成为可能。面向地表温度及相应参数反演这一目标,协同机制的研究,重点在于面向地表温度及相应参数反演中,如何解决二者的差异并实现优势互补。然而,虽然国内外学术界在面向特定目标中已有较多的研究涉及到热红外遥感与被动微波遥感的综合使用,关于热红外与被动微波遥感的协同机制的专门研究还很少。
热红外遥感在使用中的主要局限性在于受到天气因素的重要影响,但其空间分辨率相对较高,且其反演获得的地表温度在地表辐射与能量平衡建模、气候变化等领域的应用已较为成熟。被动微波遥感的主要优势在于受天气因素的影响较小,而其主要劣势在于空间分辨率极低。此外,由于被动微波遥感传感器在不同频率、不同极化通道观测获得的能量来源于一定深度,而这种深度往往具有很大的不确定性,这使得被动微波遥感反演获得的地表温度的物理意义是模糊不清的,甚至获得的温度是否为真正意义上的“地表温度”尚存在较大疑问。进一步的,这种物理意义模糊不清的“地表温度”尚无法像热红外遥感提供的“地表温度”与实际应用有效衔接。
协同反演的宗旨是实现个体协同的成效大于个体各自成效之和。因此,若暂不考虑二者反演的地表温度物理意义上的差异,二者的协同即是一个“取长补短”的过程。就热红外与被动微波遥感受天气影响的差异而言,被动微波遥感反演所得的地表温度,是热红外遥感地表温度的重要补充。目前,被动微波遥感反演地表温度的理论与方法还不成熟,而热红外遥感反演理论与方法较为成熟,故在二者的协同反演中,被动微波遥感是主体,热红外遥感是客体,客体为主体服务。
4.1. 协同机制1:空间尺度匹配
由于地表在热红外通道的辐射能量较在被动微波通道大,故热红外遥感影像的空间分辨率一般高于被动微波遥感影像。此外,具有热红外通道的星载光学遥感传感器往往同时具有反射通道,反射通道遥感影像的空间分辨率可能高于热红外通道。如AVHRR影像的反射通道、热红外通道星下点空间分辨率均为1.1 km。MODIS影像反射通道星下点空间分辨率为250 m、500 m,热红外通道则为1 km。SMMR的6.6 GHz、10.7 GHz、18.0 GHz、21.0 GHz和37.0 GHz通道的空间分辨率分别为150 km、90 km、55 km、45 km和25 km。SSM/I的19 GHz、22 GHz、37 GHz和85.5 GHz通道的空间分辨率分别为50 km、50 km、30 km和15 km。AMSR-E的6.9 GHz、10.7 GHz、18.7 GHz、23.8 GHz、37 GHz和89 GHz通道的空间分辨率分别为50 km、50 km、25 km、25 km、15 km和5 km。
热红外遥感与被动微波遥感像元空间分辨率存在的较大差异,使得二者在协同反演中,至少存在以下方面的困难:
1) 在对同一区域成像后,当利用热红外遥感为被动微波遥感服务时,对地形平坦、均一像元,可通过平均聚合的方法获得到被动微波遥感像元尺度的热红外观测信息;然而,对于异质性地表,这种简单的平均聚合可能存在较大的不确定性,这涉及到热红外遥感的空间上采样问题。
对于平坦区域的地表温度空间上采样,常通过下式进行:
 (17)
(17)
式中,Ts为低空间分辨率像元的表面温度;fi为低空间分辨率像元内部第i个高空间分辨率像元的比例;Ti为第i个高空间分辨率像元的表面温度;n为高空间分辨率像元数目。
式(17)实际上是在对地表温度数据空间上采样采用平均的重采样方法求得。实际上,在上采样过程中,需采用能量加权平均的方法:
 (18)
(18)
式中,εi为第i个高空间分辨率像元的宽波段发射率;ε为低空间分辨率像元的宽波段发射率。
对于起伏地形,Liu et al. (2006)提出了空间上采样方法:
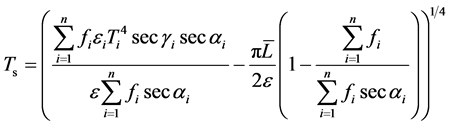 (19)
(19)
式中,γ为传感器观测路径与地表法线的夹角;α为地表坡度; 为地表周围地物的平均辐亮度。式(19)考虑了地形与邻边效应对地表温度空间上采样的影响,有助于解决复杂地表热红外遥感地表温度与被动微波遥感数据的空间尺度匹配问题 [19] 。
为地表周围地物的平均辐亮度。式(19)考虑了地形与邻边效应对地表温度空间上采样的影响,有助于解决复杂地表热红外遥感地表温度与被动微波遥感数据的空间尺度匹配问题 [19] 。
2) 在上采样过程中,由于地物-热红外遥感传感器和地物-被动微波遥感传感器观测几何条件可能存在差异,并由此产生的热辐射方向性特征,给热红外遥感与被动微波遥感的协同带来困难。
4.2. 协同机制2:有效温度与肤面温度转换
热红外遥感获得的地面辐射信息一般来源于地表面以下数个微米深度处,故学术界将据其反演得到的地表温度又称为肤面温度(skin temperature)。微波对于土壤具有一定的穿透性,故被动微波遥感获得的地面辐射信息,除来源于其肤面辐射外,还包含有其下一定深度,随着距离地表的深度增加,各层辐射信息对最终观测结果的贡献越小。
对于被动微波遥感,有三种重要的“深度”,即热采样深度(Thermal sampling depth, TSD)、皮肤深度(Skin depth, SD)和穿透深度(Penetration depth, PD)。其中,为被动微波遥感传感器提供绝大部分可观测的微波辐射信息的深度,被定义为热采样深度;电磁波幅度衰减到1/e的深度被定义为皮肤深度;电磁波强度或能量衰减到1/e的深度被定义为穿透深度。热采样深度主要受到表面介电常数和近地表介电常数梯度的影响,一般为波长的数十倍。
因此,热红外遥感与被动微波遥感协同中,涉及到前者观测的“肤面温度”与后者获取的“有效温度”的转换。对于裸土而言,土壤的热传导方程将有助于实现这种转换:
在地面精细实验观测的基础上,研究肤面温度与被动微波遥感获取的有效温度的关系。如对于裸露地表,某深度的土壤温度可表示为:
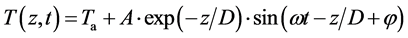 (20)
(20)
式中,z为深度;t为时刻;Ta为某深度的温度常数;A为温度变化幅度;D为衰减深度。利用式(20)构建土壤肤面温度与被动微波遥感获取的有效温度的转换是可行的,但必须充分结合热红外与被动微波遥感多次观测、地面实验获得的先验知识等。对于稀疏植被地表,在式(20)中需加上植被修正项 [20] 。
实际上,对于面向被动微波遥感地表温度反演的经验算法或半经验算法,当使用热红外遥感提供的肤面温度或模式模拟的0 cm表面温度作为地表温度的“真值”时,训练所得的算法系数中,已在一定程度上蕴含了土壤有效温度至肤面温度的转换方法。对于涉及到不同频率通道的半经验算法和物理算法,尤其是低频通道,这种转换对于最终计算结果非常重要。如目前大多数计算被动微波地表发射率的方法中,直接使用热红外遥感反演的肤面温度作为被动微波低频通道的地表温度,将对发射率计算结果产生较大误差。在使用不同通道时,若不考虑各通道有效温度之间的转换,对于最终反演的地表温度将产生的不确定性。另一方面,目前热红外遥感反演的肤面温度在实际应用中较为广泛。因此,如何利用被动微波遥感获取的遥感信息提取肤面温度,将是未来一个重要的发展方向。
4.3. 协同机制3:空间分辨率提升
目前被动微波遥感的空间分辨率极低,仅能满足大陆或全球尺度的相关应用,距离区域尺度的应用需求尚存在较大差距,这涉及到被动微波遥感空间分辨率提升的问题。
被动微波地表温度空间分辨率提升,依赖于低空间分辨率的被动微波遥感地表温度和较高空间分辨率的辅助参数。其中辅助参数除热红外遥感观测信息外,还可有其他光学传感器提供的观测信息及衍生参数、地理信息数据等。根据尺度推演原理,在低空间分辨率尺度上建立的映射关系,可以推演至较高空间分辨率;同时,尺度推演会导致一定的误差。参考热红外遥感地表温度空间分辨率提升模型的相关理论,在空间分辨率提升中,被动微波遥感地表温度与其他信息的协同可表示为:
 (21)
(21)
式中,TsPW为被动微波遥感地表温度;函数g表示地表参数与被动微波遥感地表温度的映射机制;ρi为地表参数,可能包含热红外遥感地表温度TsTIR、植被指数VI、植被覆盖度fv、发射率ε等。
获得函数g的显式或隐式表达后,空间分辨率提升后的被动微波遥感地表温度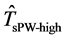 表示为:
表示为:
 (22)
(22)
式中, 为提升后空间分辨率尺度的地表参数集合;
为提升后空间分辨率尺度的地表参数集合; 为原始空间分辨率尺度上式(22)的预报误差。
为原始空间分辨率尺度上式(22)的预报误差。
目前,针对被动微波土壤水分空间分辨率提升已有部分研究报道,针对被动微波遥感地表温度的相关研究还非常少。与热红外遥感类似的,被动微波遥感地表温度空间分辨率提升面临着最优地表参数(集合)、回归窗口等确定的困难。同时,由于被动微波辐射可能来源于一定深度(与地表覆盖类型、土壤湿度等密切相关),其地表温度空间分辨率提升对于最优地表参数(集合)等存在特殊要求。
5. 总结与展望
被动微波遥感反演的地表温度,是热红外遥感地表温度的重要补充。然而,前者的相关研究尚不成熟,关于被动微波与热红外遥感协同反演地表温度的机制尚不明晰,相关理论与方法距离实际应用仍有较大差距。在综合分析前人成果的基础上,作者认为应该着重以下方面的研究:
1) 在机理上,掌握热红外获取的肤面温度与被动微波获取的有效温度的内在联系与转换机理。
2) 在机制上,解决被动微波遥感与热红外遥感在协同中存在的空间尺度差异观测条件差异。
3) 在方法上,改进与发展被动微波遥感地表温度反演方法,并构建其空间分辨率提升模型,提高被动微波遥感地表温度的空间分辨率,满足区域尺度实际应用需求。
基金项目
中国气象局成都高原气象研究所高原气象开放实验室基金(LPM2014012)。
NOTES
*通讯作者。