1. 引言
钙华是富含钙质的地下泉水接近或出露于地表时形成的碳酸盐沉积物,是地球碳循环中的重要组成部分。根据钙华沉积过程的主导因素,钙华成因分为非生物控制因素(物理、化学)和生物控制因素(细菌、藻类、植物体) [1] [2] 。根据沉积环境分为热泉型和冷泉型钙华。以美国黄石公园为代表的热泉型钙华沉积,水温高,水体呈酸性,含硫量高,水体分布的微生物多数为耐热、嗜硫类或嗜盐类微生物 [3] [4] 。以黄龙为代表的地面岩溶冷泉型钙华沉积,水温常年处于低温,碳酸盐含量较高,水体中N、C元素含量丰富,水体呈弱酸性或中性,适宜普通微生物生长 [5] [6] 。热泉体系因其地球化学环境与地球早期或太阳系其它星球非常相似,研究微生物对热泉型钙华沉积过程的影响及作用机理,对于生命起源及进化研究可提供重要线索,因而受到了国内外学术界的极大关注 [3] [7] [8] 。相对而言,关于微生物对冷泉型钙华沉积的影响及作用机理的研究相对较少。已有的大量研究表明微生物群落会影响钙华沉积,但未明确微生物在钙华沉积过程中的参与程度及作用机理 [9] - [11] 。
近年对四川黄龙沟地表水体的研究发现,现代黄龙钙华共生有大量硅藻、蓝藻等优势藻类种属和多类细菌种属 [12] [13] (图1)。对微生物是否参与钙华沉积及其在沉积中的作用得到了国内外学者极大关注。本文从历史钙华剖面的矿物特征出发,寻找历史生物因素参与黄龙钙华沉积作用的证据,为明确黄龙钙华的形成机理和历史演化过程提供科学证据,完善古、现代相结合的钙华沉积研究体系。

Figure 1. The ESEM images of modern travertine; (A) Low magnification microscopic image; (B) High magnification microscopic image
图1. 现代钙华ESEM图;(A) 低倍图;(B) 高倍图
2. 黄龙钙华概况及研究方法
2.1. 黄龙钙华分布概况
四川黄龙风景区位于四川省阿坝藏族羌族自治州松潘县境内,岷山主峰雪宝顶的东北侧,地理坐标为东经103˚50',北纬32˚45',海拔3100~3600 m,总面积达1340 km2。黄龙风景区气候属于高原温带季风气候,年均降水量759 mm,年均气温1.1℃,常年水体平均温度5℃。研究区核心部分黄龙沟钙华形成年代为80 ka前后的新世中晚期,宽110~250 m,厚9~20 m,全长3.6 km [5] [6] 。
2.2. 样品采集
黄龙历史钙华沉积剖面样品采集于距黄龙沟风景区20 km的张家沟石板棚,选择完整钙华纵剖面,至沟谷而上,间隔50 cm采集钙华样品(图2)。选取代表性样品,按照年代由远及近标记为P1-P7。
2.3. 矿物学特征分析
将历史钙华剖面的代表性钙华样品,制成薄片,在偏光显微镜(BX51, Olympus)下观察钙华的偏光特征。钙华剖面样品经玛瑙研钵磨细过200目筛后,做进一步矿物学特征表征。
微区形貌观察使用电子扫描电镜(SEM, S440, Leica)。钙华物相表征使用X射线衍射分析(XRD, X’Pert Pro, Panalytical)。测试条件为:铜靶,单色化波长CuKa,λ = 1.5418 Å,管电压40 kv,电流20 mA,2ϴ扫描范围20˚~90˚。物相分析软件为仪器自带的X’PertHighScore Plus,并利用Rietveld方法对物相进行结构精修 [14] 。钙华粉末样化学成分定性分析使用飞行时间二次离子质谱仪(TOF-SIMS V,ION-TOF GmbH),定量研究使用X射线荧光(XRF, Axios, Panalytical)。ATR-FTIR测试在红外吸收光谱仪(Nicolet-5700,美国尼高力仪器公司)的ATR附件上进行摄谱。
3. 结果与讨论
钙华剖面采集点的钙华沉积厚度约11米,剖面钙华生长层明显,呈明暗交替的互层分布,年层呈典型的韵律结构(图2)。通常暗色层呈浅黄色,泥质含量较多,较薄,一般仅数毫米厚。纯净的白色质层较厚,颜色较浅,较厚,在数毫米到十几毫米不等。
在偏光显微镜下,白色质形态不规则,矿物颗粒较大,粒度分布不均匀,主要成分可能是较为纯净
的结晶CaCO3 (图3A,图3C)。浅黄色质部分,矿物颗粒粒度小,且粒度分布较为均匀(图3B,图3D)。浅黄色质沙化严重,可能含有来源于地表水带来的泥质等成分。
电子显微镜下观察发现,钙华剖面的钙华可见典型的立方体方解石晶粒结构,但被侵蚀严重,形成沟槽和孔洞等侵蚀结构(图4)。钙华沉积剖面样品电子显微镜下,未见显著微生物化石。可能是因为沉积
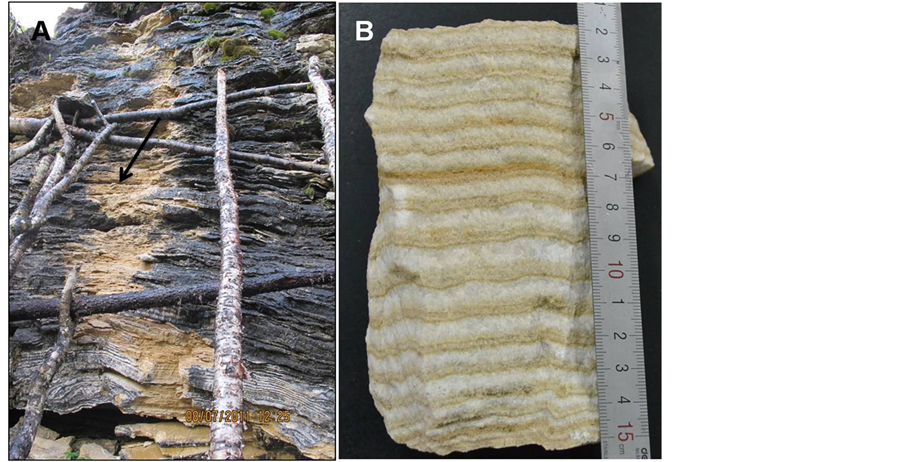

Figure 2. The collected travertine deposition profile at Huanglong Sichuan; (A) Low magnification image; (B) Typical collected sample image
图2. 黄龙钙华采集剖面;(A) 远视图;(B) 采集的典型钙华照片
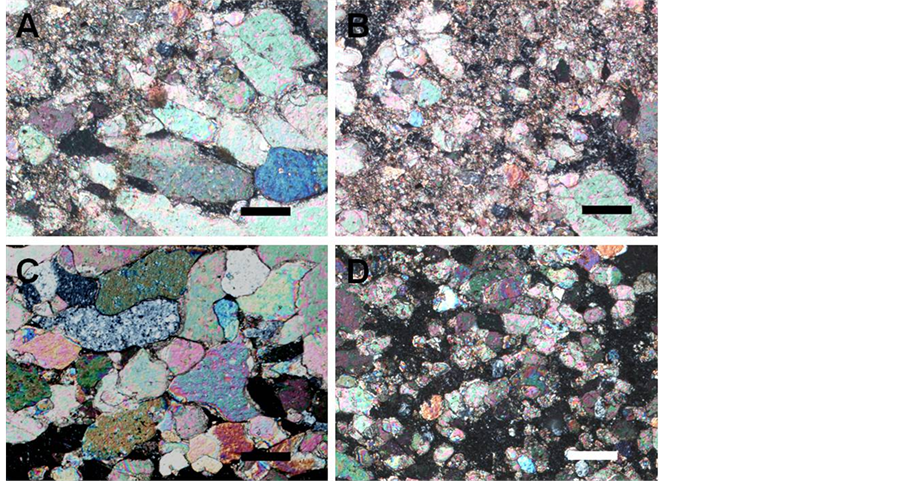
Figure 3. The characteristics of typical optical thins of travertine deposition profile at Huanglong, Sichuan under polarizing microscope; (A) (C) White travertine prosodic structure; (B), (D)Yellow travertine prosodic structure. Scale bars: 100 μm
图3. 偏光镜下黄龙钙华剖面的典型薄片特征;(A) (C)钙华韵律结构白色质部分;(B) (D)钙华韵律结构浅黄色质部分。标尺:100 μm

Figure 4. SEM images of microscopic morphological characteristics of Huanglong travertine profile
图4. 黄龙钙华剖面的SEM显微形态特征
的钙华样品中的微生物没有现代钙华沉积样品中的活跃,镜下难以检出。但也有很大可能是微生物经过数十Ka年代的作用已经分解,进而在镜下进行种属的标识。
钙华样品的XRD矿物物相表征结果表明,现代和历史沉积的钙华均为三方晶系方解石结构单一物相,衍射峰与PDF卡片(01-086-2334)方解石结构高度吻合,未见其他物相存在。经进一步的结构精修的晶体学解析发现,历史沉积的钙华方解石晶胞特征与生物成因方解石结果相似,均存在晶胞C轴拉伸,晶胞体积较无机控制机制形成的方解石大(表1) [15] 。值得关注的是热泉型钙华的方解石,沿晶胞C轴方向,存在压缩,表现为001方向的晶面间距缩小,晶胞体积收缩 [10] 。
典型的钙华TOF-SIMS质谱分析显示,钙华样品除含Ca,Mg,Si,Na,K,Al等常规元素外,还含有较多的有机大分子(表2)。值得注意的是,钙华中硫的存在形式为有机的C8H7SO3。黄龙钙华沉积环境属于低温冷泉型,钙华样含有的有机硫可能主要来源于微生物有机体,水体中的无机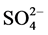 未显著参与钙华沉积。微生物参与热泉型生物成因钙华沉积,是通过泉水中大量硫滋生的硫化细菌参与钙华的沉积过程,含硫生物分子插入方解石晶层,引起C晶轴扭曲 [10] 。黄龙风景区低温环境、水体成分等因素决定了与热泉型水体中微生物种类的不同,因而可能存在的生物参与机制,也有可能不一致。TOF-SIMS未检出铁、锰等可能存在颜色的元素,进一步印证了对于黄龙,偏黄的原因,有可能是来源于微生物产生的论点。
未显著参与钙华沉积。微生物参与热泉型生物成因钙华沉积,是通过泉水中大量硫滋生的硫化细菌参与钙华的沉积过程,含硫生物分子插入方解石晶层,引起C晶轴扭曲 [10] 。黄龙风景区低温环境、水体成分等因素决定了与热泉型水体中微生物种类的不同,因而可能存在的生物参与机制,也有可能不一致。TOF-SIMS未检出铁、锰等可能存在颜色的元素,进一步印证了对于黄龙,偏黄的原因,有可能是来源于微生物产生的论点。
X射线荧光定量分析(XRF)表明,黄龙钙华的主要成分为CaCO3,历史沉积钙华CaO含量达到97.5% (表3)。

Table 1. The results of XRD quantitative structure refinement of Huanglong travertine profile from different depths; PDF-STD represents standard spectra of calcite (01-086-2334) in PDF database
表1. 黄龙钙华剖面不同深度钙华的XRD定量结构精修;PDF-STD为PDF数据库方解石标准谱图(01-086-2334)

Table 2. TOF-SIMS analysis of Huanglong travertine profile
表2. 黄龙钙华剖面的TOF-SIMS分析

Table 3. The quantitative components analysis of Huanglong travertine profile by XRF. *Carobon contents were tested by Vario EL CUBE
表3. 黄龙钙华剖面的成分XRF定量分析。*碳元素含量由Vario EL CUBE元素分析仪测得
综合热分析(DSC-TG)测试结果(表4)显示,钙华碳酸钙成分热分解温度在760℃左右,较无机成因方解石热分解温度低。在200℃~500℃温度区间,历史沉积钙华1.2%左右的失重。热分解完成后,钙华有43%左右的失重,经计算碳酸盐含量在97.8%~99.4%。热分析样品在测试之前经105℃过夜热处理,因而可排除样品表层吸附水的影响。200℃以下,钙华样品可能含有的吸附水、层间水和结构水等各种形态的水均会热挥发,可见200℃~500℃温度区间的失重不是来源于钙华样品中的水,可能来源于钙华样的有机成分,最大可能来源于微生物的热解。钙华中的碳酸钙热解温度较无机成因的方解石型碳酸钙热解温

Table 4. The DSC thermal characteristics of Huanglong travertine profile
表4. 黄龙钙华剖面的DSC热特征
度低,较合理的解释是,在500℃以下,存在方解石晶格中的生物分子的有机碳热解完成,使得方解石晶格遭到破坏,进而降低了碳酸钙的热解温度。综合热分析结果从另一面证实了,微生物参与黄龙钙华的沉积,并且控制钙华沉积过程。
4. 结论
本文对地质历史钙华沉积剖面和现代钙华的显微结构、物相和化学成分等的研究,确定了黄龙钙华的矿物特征和指示意义。研究表明黄龙钙华物相为三方晶系方解石单一物相,与无机成因方解石晶胞相比,存在明显的C晶轴拉升和晶胞体积扩大。黄龙钙华表面侵蚀形成沟槽和孔洞等结构表明,微生物可能参与了钙华的沉积过程,其特征符合生物分子控制方解石形成机制。值得注意的是,微生物虽然对黄龙钙华沉积具有显著影响作用,但钙华沉积控制因素非微生物单一因素,钙离子、温度、CO2分压以及地表水季节性变化等环境因素对钙华沉积可能也会产生重要的影响作用。本文研究表明,传统矿物学特征与生物分子标记物等前沿手段相结合才能有利于对于黄龙钙华历史演化过程的研究,以及为微生物是否参与沉积作用提供科学证据。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金项目(41572035)。