1. 引言
随着工农业迅速发展,人口不断增加,不合理开发利用以及污染地下水的现象日益严重,使地下水受到不同程度的破坏,引起地下水位不断下降、水量减少、水质恶化等一系列问题 [1] [2] 。地下水一旦受到破坏,其治理和恢复的难度和代价都是十分巨大的,甚至在一定时期内完全恢复是不可能的 [3] [4] 。特别是在干旱半干旱地区,水资源的污染加剧了水资源的紧缺状况,供需矛盾更加尖锐 [5] [6] 。因此,合理开发和保护地下水资源就显得十分重要。地下水脆弱性研究是合理开发与保护地下水资源的基础性研究工作。通过地下水脆弱性研究,区别不同地区地下水的脆弱程度,评价地下水潜在的易污染性,圈定脆弱的地下水范围,从而可以警示人们在开采利用地下资源的同时,采取有效的防治保护措施。
目前,国内所进行的地下水脆弱性研究多是关于湿润或半湿润地区的,且主要从地下水水质的角度出发,采用迭置指数法、过程数学模拟法、统计方法和模糊数学方法等研究地下水潜在的易污染性 [7] [8] 。由于内陆干旱区的地下水的形成条件和结构功能完全不同于湿润地区,因此,抛开地下水系统所处的环境孤立地去研究地下水的易污性是不合理、不全面的。基于此,本文以西北内陆河典型流域石羊河流域为例,通过对地下水系统脆弱性的内涵、地下水系统脆弱性表现特征进行分析,揭示内陆干旱区的地下水脆弱性机理,从而为干旱区地下水资源保护提供理论指导意义。
2. 石羊河流域地下水系统的特征及其脆弱性内涵
石羊河流域为我国西北地区典型的内陆河流域,该区自然条件极为恶劣,降水量小而蒸发量大,除此之外,该区特殊的水循环系统也是造成该区地下水脆弱性的一个重要因素。内陆河独特的水循环系统造就了其独特的生态系统,但与此同时,生态系统又影响着与其紧密联系的水循环系统,两者互相依存、互相作用和互相发展。近几十年来,人类在进行大规模水资源开发利用活动的同时,也极为显著地改变了地下水的循环条件和路径,而这相应地会引起生态系统的改变。有序合理的水资源开发利用活动会对生态环境产生正面的效应,而无序盲目的水资源开发利用会对生态环境造成负面影响;反过来讲。健康良性的生态环境会涵养和保护水资源,而恶劣的生态环境会加快地下水资源枯竭的进程。因此,研究石羊河流域地下水系统的脆弱性机理,不仅要分析自然因素和人为因素对地下水系统的影响,还要考虑与地下水系统息息相关的生态系统的影响,不能把地下水系统的脆弱性归结于某一个方面。石羊河流域地下水系统作为一个开放性的自然人工复合系统,地下水作为核心与人类活动、生态环境、地表水发生紧密联系,而人类活动、地表水和生态环境之间又相互联系,进而影响到地下水系统。各因素间相互作用,且紧密联系是石羊河流域地下水系统的典型特征。
在地下水脆弱性的定义方面,广为人们所接受的是美国国家科学委员会所提出的将其分为固有脆弱性和特殊脆弱性两类;基于此,本文将石羊河流域的地下水脆弱性也分为固有脆弱性和特殊脆弱性。由石羊河流域地下水系统本身的条件所导致的地下水系统的脆弱性称之为固有脆弱性,由人类活动、生态环境等外部因素所导致的地下水系统的脆弱性称之为特殊脆弱性。地下水系统与各因素相互联系,地下水的脆弱性是各因素相互作用的结果,即地下水的脆弱性是其固有脆弱性和特殊脆弱性的综合表现。因此,绝对的划分地下水系统的固有脆弱性和特殊脆弱性也是不科学的。本文将从自然因素、人为因素和生态环境因素三个方面分析石羊河流域地下水系统的脆弱性机理。
3. 地下水系统脆弱性影响因素
3.1. 自然因素
采用甘肃省水利厅石羊河流域管理局的气温、蒸发、降水和实际监测的径流量等基础数据,用以分析各自然因素的变化情况及其对地下水系统脆弱性的影响。
3.1.1. 气温变化
石羊河流域因地处我国西北内陆干旱地区,降水量小,蒸发量大是其主要特征。近50年来,在降水量和蒸发量基本保持不变的情况下,流域内温度不断升高,出山径流量不断减小,使得原本就恶劣的自然条件愈加恶劣,从而对水资源系统和生态环境都产生了明显的影响。
分别选取民勤、武威和古浪三个代表站1959年~2000年的年平均气温进行分析,分析结果可如表1所示。从表中可以看出,民勤、武威和古浪的气温变化呈特显著或显著的上升趋势。
3.1.2. 蒸发量变化
石羊河流域各代表站蒸发量变化示意图如图1所示。从图1可以看出,在20世纪60~80年代,各站蒸发量均有小幅度地减少,古浪站和肃南站的减小幅度相对其它各站较大,分别为11%和5%;自80年代以后,各站蒸发量有高有低,没有呈现出一致规律。其中,张掖和武威代表站多年来的平均蒸发量分别为2036.2 mm和1964.4 mm。如此高的蒸发量使得极其有限的降水还未来得及转化为地表径流或者入渗补给地下水便转化为无效蒸发,这对地下水的补给无疑是雪上加霜。
农作物需水量与种植区的气候类型关系十分密切,在从干旱和半干旱地区向湿润和半湿润地区的过渡中,需水量呈现出减少的趋势,即,干旱地区的作物需水量大而湿润地区的作物蓄水量小 [9] 。流域所辖张掖、古浪均为农业县,极低的降水量不能满足作物需求,加之近几十年来,农业灌溉面积不断增大,因此,在节水灌溉技术不能普及的情况下,开采地下水以满足农业需求便成了唯一的解决方法。
3.1.3. 降水量变化
降水量变化石羊河流域各代表站多年平均降水量变化可如图2所示。图2表明,除1950~1960年间,各站降水量变化较大之外,自1960年后,多年降水量基本持平。其中,古浪、民勤和武威代表站多年来的平均降水

Table 1. The change of the temperature of Minqin, Wuwei and Gulang from 1959 to 2001
表1. 民勤、武威、古浪1959~2001年气温变化分析表
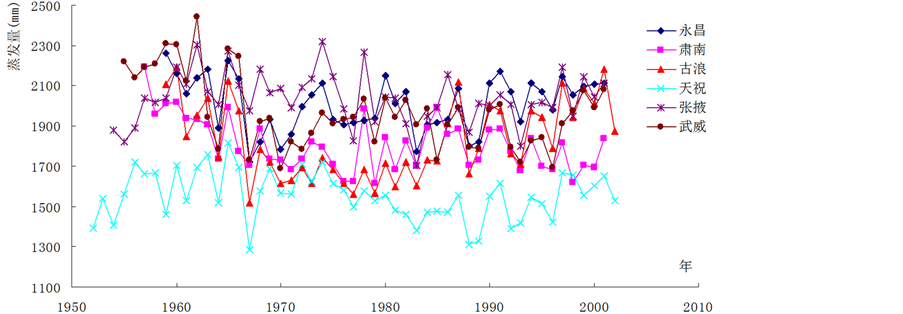
Figure 1. The evaporation of the typical stations of Shiyang River Basin
图1. 石羊河流域各代表站蒸发量变化示意图

Figure 2. The variation figure of the precipitation-time of the typical stations of Shiyang River Basin
图2. 石羊河流域各代表站降水量变化示意图
量分别为357.3 mm、111.6 mm和162.7 mm。极低的降水量使得降水对地下水的补给非常小(石羊河流域地下水的补给仅有0%~15%来自于降水凝结水等天然补给)。极少的降水量使得当地植物及农作物无法靠其生存,加之地表径流越来越少,因此,大规模地开发利用地下水在所难免,并通过改变流域的下垫面条件,改变了降水对地下水的入渗补给路径,从而也使得降水对地下水的入渗补给不断减少。
3.1.4. 径流量变化
取出山口处的黄羊河水库、杂木寺、南营、四沟嘴、古浪、沙沟寺、插剑门、大靖峡水库以及红崖山水库共九个水文站1961~2000年的径流资料进行Kendall秩次相关法分析,选取95%的置信度时,显著水平为0.05 m的临界检验值为1.96。
从表2可以看出,但就整个序列长度而言,流域的径流量呈现出不同程度的减少。除西大河与大靖河外其余六河径流量减少程度均很显著,其中又以红崖山水库为最,其Kendall标准化变量值达−8.408。影响干旱内陆河流域出山径流的气候因子主要为降水、气温和蒸发量。概括地说,降水多,蒸发少,则径流多,反之则少。根据流域的气温、降水量和蒸发量的分析可知,近40年来流域气温呈增高趋势,蒸发量高而降水量小,因此减少了出山口的径流量。红崖山水库入库径流量的减少,一方面是自然因素的影响,另一方面是由于上游水利工程大规模的兴建,使得上游拦水能力增加。
径流量减少的直接后果是当地表径流不足以满足人类对水资源的巨大需求时,大规模地开发利用地下水便在所难免。以民勤县为例,红崖山水库入库径流量的减少使得人们大量开发利用地下水,2000年地下水位年下降幅度达0.6 m,并引发了一系列生态环境问题,从而在量上降低了地下水作为一种储量资源的功能,并降低了地下水系统的生态环境的维持支撑功能。
3.1.5. 流域特殊的水文地质构造
流域特殊的水文地质构造使得地表水与地下水在各带相互重复转化,形成了独具特色的河流¾含水层系统。在此系统内,无论是天然条件下,还是人为因素干扰,河水、地下水的水盐动态均衡状况均会产生强烈的相互影响;无论是引用河水还是开采地下水,整个流域及河系的区域水文效应势必被影响,从而引起大范围内地下水径流补给和排泄条件的改变 [10] 。因此,在这种水文地质条件下,径流减少和近几十年来人类对地表水和地下水大规模的开发利用对流域内水文循环系统的影响就更加显著。人类对水资源的不合理开发利用使得这种水文循环呈现一种恶性循环,并在地下水的形成、补给和排泄方面直接对地下水系统的脆弱性形成了一种负影响,使其功能衰减。
综上所述,不管是流域恶劣的气候条件还是特殊的水文地质构造均加剧了地下水的固有脆弱性和特殊脆弱性。恶劣的气候条件及其变化使得石羊河流域出山径流减少,极低的降水量和极高的蒸发量使得作物需水量增大和地表水对地下水的入渗减少。而地表水对地下水极低的补给直接从量上导致了地下水作为一种储量资源功能的衰减。径流的减少和作物需水量的增大使得当地表水不能满足人类对水资源的需求时,人们通过开发利用

Table 2. The analysis of of the runoff volume according to Kendall rank correlation
表2. 径流量Kendall秩次相关法分析表
地下水来满足生产需求,当开发演变为无序开发时,便会导致地下水系统功能的衰减。因此,恶劣的气候条件在地下水入渗方面直接地影响着地下水的固有脆弱性,并通过对径流、农业的影响,进而促使人类对地下水的开发利用来间接地影响地下水的特殊脆弱性。
3.2. 人为因素
资源和环境是人类生存和发展的必备条件。一方面,人类通过对资源的开发获得物质和能量,并改善其赖以生存的生态环境;另一方面,资源和环境的质量、数量极其分布特征又制约了人类的生存和发展;两者在长期的历史进程中彼此共生、相互联系,并始终处于一种动态的平衡中。作为处于这种关系主导地位的人类活动,如若能与资源和环境的可承载能力协调,则地下水系统与其周围的环境处于良性演替,否则,地下水系统将会逆向演替,并导致地下水系统脆弱性的加剧。
3.2.1. 土地资源的不合理开发利用
由于干旱区地表水资源贫乏,作为干旱区最重要的水源和最佳供水选择的地下水资源往往成为维持干旱区生命绿洲的首要因素,而地下水资源对沙漠荒漠地区的社会经济发展尤为重要。对于整个世界而言,地下水资源在解决干旱区缺水问题中所起的作用是不可替代的,因此,合理开发利用和管理地下水资源的重要保证和必要前提是对地下水资源进行科学论证和有效管理,其中,如何正确评估人类活动的影响便成为制定区域地下水利用规划的关键所在。以往对干旱区地下水系统影响的人为因素分析,主要强调地下水开发利用的强度及其合理性,忽略了土地利用变化的影响。研究表明流域土地利用与下垫面覆被变化对地下水系统的影响是巨大的。石羊河流域15年来的土地利用与下垫面覆被变化是十分强烈的,主要表现为灌溉耕地增加、人工绿洲扩张、天然草地减少和原有河道的废弃,天然绿洲逐渐被人工绿洲速代替,这种变化势将驱动整个水资源的时空分布特征发生根本变化,并对地下水资源系统的补给、径流和排泄产生较大影响 [11] 。
近几十年来,在流域盆地冲洪积扇的中下部以及沿两岸的河谷地带,耕地面积进一步增大,呈现出向老绿洲外围延伸的状态。原有分布在山前洪积扇上游的河道以及冲洪积扇下游的河道,则演变为裸岩土地或者耕地。以此为特征的土地利用变化,尤其是灌溉绿洲的发展和空间变化,主要是通过土地利用面积的变化影响对地下水的入渗补给,在驱动地表水系统的循环和空间分布发生改变的同时,影响了地下水系统。
其中潜水蒸发是土地利用对地下水排水系统影响最直接的表现。由于潜水蒸发主要发生在水位埋深较小的地带,而原有覆盖度较低的草地以及半固定和固定沙丘的减少,使得潜水蒸散发变得强烈。
除此之外,土地利用方式的变化也可直接导致水资源利用方式和强度的改变,如灌溉面积不合理的增长,主要靠过度抽取地下水来灌溉,从而导致地下水位下降,形成降落漏斗,同时加速地下水与地表水体之间的水量交换。水利工程建设通过直接破坏流域的连续性,缩短了流域水循环的路径,并孤立了生态系统,紊乱了生态格局,而生态系统中的植被可在多个层面上对蒸发、降水、入渗和径流产生影响,从而在一定程度上影响水资源的重新分配。除此之外,随着流域社会经济的发展和人口的增加,城镇工业废水和生活污水排放量未经处理直接或间接排入河道,从而造成地表水质的污染。在地表水与地下水的水量交换中,被污染的地表水因此进入到地下水系统。
但是,在人类对资源进行开发利用的过程中,不合理利用的现象总是存在,而脆弱的生态环境便是土地过度垦殖的典型负面效应。
综上所述,人类对土地资源的不合理开发利用通过影响地下水的补给水量和水质,导致地下水系统循环发生改变、地下水质量恶化,并通过生态环境影响加剧了地下水系统的脆弱性。
3.2.2. 水资源的不合理开发利用
1) 地表水与地下水转化条件的变化
对于石羊河流域来讲,其独特的水循环系统主要是指地下水与地表水之间频繁的转化关系。这种频繁的转化,一方面为绿洲农业的可持续发展提供了宝贵的水资源,但是,另一方面,这种频繁的转化加剧了人类活动对地下水系统的干扰,减少了地下水的入渗补给,增加了地下水系统的脆弱性。
“灌溉农业,绿洲经济”是干旱区内陆流域经济发展和生态环境的重要特征。为发展绿洲农业,人们在加强水资源开发利用的同时,也加强了对地下水循环条件的干预,从而加剧了外部环境对地下水系统的影响 [5] [12] 。山区水库的修建、天然河道渠网化,不仅改变了出山径流的时程分配,也使河道渗漏补给量减少;绿洲农业发展使作物生产力提高,既增加了非回归性耗水量,也使地表水转化为地下水的数量减少;中游盆地地下水补给量的减少和开采量的增加,进一步减少了冲洪积扇前缘地带泉水溢出量,进而使平原区水库的径流量减少。这些人为因素改变了自然条件下的两水转化关系,打破了自然界的水盐均衡。这种改变,在使人工绿洲不断扩大的同时,也由于水资源的不合理开发利用造就了土壤次生盐渍化及流域下游的荒漠化和沙漠化。
2) 地表水和地下水补给量减少,地下水开采量过大
流域水土资源开发利用活动的加强,使大量的山水被引入更多的灌区,使原有的地表水于出山口处的下渗转化带遭到严重破坏,地表水来不及在出山口处下渗,就被引入各河流出山口水库或中游灌区,加上各灌区的高标准渠系衬砌,阻碍了地表水地下水转化,非回归性用水逐年增加,地下水补给量逐渐减少,平原区50年代地下水年补给量为15.87亿m3,90年代则已经下降了近50%,降至7.25亿m3。地下水资源量的减少导致中游泉水溢出带的泉水溢出量减少,部分泉水甚至枯竭,使原有的井泉灌区逐渐演变为纯井灌区,为保证灌区的灌溉水量,大量开发已经失去补给来源的地下水。下游民勤盆地缺乏上游地表水水源,广大的灌溉面积所需水源越来越依赖于地下水的超采,其水位已经下降到威胁民勤人民生存的程度。
综上所述,地下水严重的补排失衡使得地下水系统输出要素中的地下水位急剧下降,泉流量大幅度削减。前已述及,地下水位的大幅度下降降低了地下水的资源储量功能和生态环境的支撑功能,从而加剧了地下水的脆弱性。
3) 地下水污染及盐化
石羊河流域各支流出山口以上,人类活动相对较弱,地表水体尚未受到污染,水质较好。自各支流出山口至武威市以北的白疙瘩,污染逐渐加重,武威市工业废水及生活污水的大量排放,严重污染了地表水体,并进而通过入渗对地下水造成污染。除此之外,随着农业面积的增大,有机肥料的大范围使用使得地下水体中的硝酸盐含量也迅速增大。随着地下水的污染和大量开采,下游民勤盆地的地下水矿化度增长速度剧烈,约为0.1 g/L,水质不断恶化。根据中国科学研究院兰州地质研究所气体地球化学国家重点实验室史基安等人 [13] 的研究表明,石羊河流域武威盆地北和民勤盆地南、北等不同地区地下水位下降幅度与矿化度变化存在明显的正相关关系,矿化度变化量随着地下水下降幅度的增大而增大。
除此之外,流域内从上游到下游,土壤盐渍化程度不断加重。除了强烈的蒸发作用使盐分在地表累积,从而形成盐渍化土地外,流域内反复开采日益盐化的地下水进行灌溉,再加上部分土地弃耕后,强烈的蒸发作用使盐分沿毛细管上升于地表,导致土壤地表积盐,进而形成次生盐渍化。根据甘肃省治沙研究所监测资料,1998~2003年的五年期间内,民勤绿洲盐渍化程度由中轻度向重度发展,土地盐渍化程度在加剧。
综上,人类活动主要通过不合理的土地开发利用以及对地下水资源的过度开发造成了地下水水质恶化,水量锐减,地下水位大幅度下降等,并进而导致了一系列的生态环境问题,使得地下水储存、传输、调蓄地下水量的功能和生态环境支撑功能衰退,加剧了地下水系统的特殊脆弱性。
3.3. 生态环境因素影响
对于干旱区内陆河流域而言,其生态环境抗干扰能力极小,生态系统具有明显的脆弱性。一般而言,干旱区主要有三种生态系统,即荒漠生态系统、人工绿洲生态系统和天然绿洲生态系统。三者互相依存,构成了干旱区内陆河流域独特的生态系统,其主要特点表现为系统内部自然要素数量少,植被稀少,种属联系性差,种群结构简单,且荒漠生态系统占据主导地位,自然恢复能力极低,且具有很强的不可逆性。天然绿洲生态系统对地下水的依赖性很强,地下水资源的量、质、时空分布以及地下水的开发利用方式和强度都强烈地影响着整个绿洲生态系统中生物种群的数量、分布面积及演化方向。生态系统内部各要素都通过水环境、植被环境和土壤环境的变化对地下水系统产生作用 [14] 。比如绿洲生态系统植被的衰败造成了沙丘活化、土地沙化,从而降低了地下水系统的生态环境支撑功能;地下水的污染和盐化进一步降低了地下水资源作为一种储量资源的可利用价值,使地下水系统的功能衰减。
4. 结论
作为干旱内陆河流域,石羊河流域地下水系统是一个开放性的自然¾人工复合系统,地下水作为核心与人类活动、生态环境、地表水发生紧密联系,而人类活动、地表水和生态环境之间又相互联系,进而影响到地下水系统。由此出发,从气温、蒸发量、降水量、径流量、水文地质构造等自然因素方面、土地资源及水资源的不合理开发利用等方人为因素方面以及生态环境因素三个层面揭示了地下水系统脆弱性机理。综上所述,石羊河流域地下水系统的脆弱性是自然因素、人为因素和生态环境因素共同作用的结果。其中,在人类活动影响下,地下水和生态环境互为因果的恶性循环关系在使生态环境恶化的同时,也在水质和水量方面加剧了地下水系统功能的衰退。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金项目(41401038)。