1. 引言
降水作为水循环的主要环节和驱动因素 [1] ,深入了解其结构变化特征有助于分析探讨区域乃至全球水循环的变化规律;为此,国内外学者对区域或全球的降水结构变化特征开展了大量的研究工作。如:Liu等 [2] 通过气候合成模式探讨了自然因素与人类干预对全球降水结构演变的影响;Allan等 [3] 采用卫星观测资料研究发现降水极值变化与气温上升存在着明显的联系;Zolina等 [4] 利用连续湿天历时及强度研究了欧洲降水结构变化特征;宋晓猛等 [5] 采用发生率和贡献率指标分析了北京地区不同降水历时和等级的时空变化特征。
北部湾经济区(图1)地处我国沿海西南端,由广西南宁、北海、钦州、防城港四个地级市所辖行政区域构成,同时纳入近海沿边的玉林、崇左两市统筹规划建设,陆地国土总面积约7.28万km2 [6] 。该区地处华南、西南和东盟经济圈结合部,是我国西部大开发地区唯一的沿海区域,也是我国与东盟国家既有海上通道、又有陆地接壤的区域,区位优势明显,战略地位突出;近十年来,随着中国–东盟自由贸易区建设加快推进,国家高度重视广西沿海地区发展,明确将该区作为西部大开发和面向东盟开放合作的重点区域以及辐射东盟的桥头堡,相关优惠政策也陆续落地 [7] ;最近几年,在复杂的国际形势下,全国经济下行压力持续加大、区域竞争日趋激烈,而该区却保持逆势上扬,经济发展活力十足 [8] 。
我国华南地区(广东、广西、福建、海南)常用“汛期”、“非汛期”反映降水的年内差异 [9] ,汛期(通常指4~9月)降水由于持续时间长,强度大,洪涝、滑坡、泥石流等灾害频发,并造成严重的经济损失和人员伤亡,往往成为研究的热点。本文根据北部湾经济区降水数据统计发现,汛期(4~9月)降水量平均约为1357.88 mm,占全年降水量(约1672.72 mm)的比例为81.18%。因此,研究北部湾经济区汛期降水结构时空演变特征具有重要的理论和现实意义。目前,关于该区降水的研究已做了一些工作,但主要集中于降水量变化趋势及遥联分析 [10] [11] 等方面,对汛期降水结构变化的研究较少。本研究基于北部湾经济区日降水资料,运用降水发生率和贡献率指标,从降水历时方面分析该区汛期降水结构的时空变化特征,对于科学认识区域水量平衡、洪涝灾害时空演变乃至生态安全都具有重要意义,也可为指导区域工农业生产及防灾减灾建设提供科学依据。
2. 数据资料与研究方法
2.1. 数据资料
本文选取北部湾经济区分布较均匀且没有发生位置变更的12测站1961~2011年逐日降水数据资料,数据来源于中国气象局气象信息中心,连续完整,各测站位置如图1所示。
2.2. 研究方法
本文主要从降水历时方面分析北部湾经济区汛期(4~9月)降水结构的时空变化特征。根据气象部门的有关规定 [12] ,日降水量大于等于0.1 mm即为有效降水发生,因此,本文将一次降水过程(日降水量大于等于0.1 mm)从开始至结束的日数定义为降水历时,此段时间内的降水量之和定义为一次降水过程的降水量;对降水历时而言,本文将其分成以下10类,即1 d、2 d、3 d、4 d、5 d、6 d、7 d、8 d、9 d、≥10 d (连续10日以上)。
为了综合评价北部湾经济区汛期各降水历时事件的变化特征,本文借鉴前人的做法,引入了降水发生率和降水贡献率两个指标;降水发生率表示各类降水事件在某种分类情况下发生的次数占总次数的比例,降水贡献率定义为某种分类情况下的降水量占总降水量的比例。对于各类降水事件发生率和贡献率变化趋势的检验,本文采用的是Mann-Kendall (简称M-K)检验法,该检验法最早由Mann [13] 提出,之后经过不断的修改和完善,目前在国内外气象水文学领域已得到广泛应用,也被世界气象组织(WMO)推荐 [14] 。
Figure 1. The sketch map of Beibu Gulf Economic Zone and rainfall stations
图1. 北部湾经济区范围及观测站位置
3. 北部湾经济区汛期各历时降水发生率、贡献率变化特征
3.1. 汛期各历时降水发生率、贡献率区域统计特征分析
图2给出了北部湾经济区汛期不同历时降水事件的发生率及其对总降水量的贡献率。从图中可以看出,各历时降水发生率随降水历时增加大致呈指数形式递减(1 d、2 d、……、9 d、≥10 d历时降水事件发生率分别为32.5%、21.0%、14.8%、10.1%、6.8%、4.4%、2.8%、2.3%、1.2%、4.1%);但各历时降水贡献率变化与发生率变化不一致,而是随着降水历时的增加呈先增加后减小、至≥10d历时又出现显著上升的趋势。在1~9 d历时降水贡献率中,3 d最高(14.0%),其次为4 d (13.8%),再次为2 d (11.8%)、5 d (11.2%);≥10 d历时降水发生率虽然仅为4.1%,但贡献率却高达17.0%。
综合统计分析发现,对于降水发生率而言,以1~4 d历时为主,发生率合计达78.4%;就降水贡献率而言,2~5 d历时达50.8%,其次为≥10 d历时(17.0%);从降水引发洪涝灾害的角度分析,虽然≥10 d历时降水贡献率高达17.0%,但考虑到降水到达地表形成径流泄洪所经历的时间因素,2~4 d历时降水的致灾程度显然超过≥10 d历时降水。
3.2. 汛期各历时降水发生率、贡献率空间差异分析
图3为北部湾经济区12测站汛期各历时降水事件的发生率(a)及其对总降水量的贡献率(b)。从图3(a)可以看出,各站降水发生率都满足随降水历时增加而递减的规律。从区域各站各历时降水发生率大小对比来看,1 d、2 d、≥10 d差别相对较大(图3(a)),即存在着相对明显的区域差异;而3 d~9 d差别较小,各站基本都在平均值上
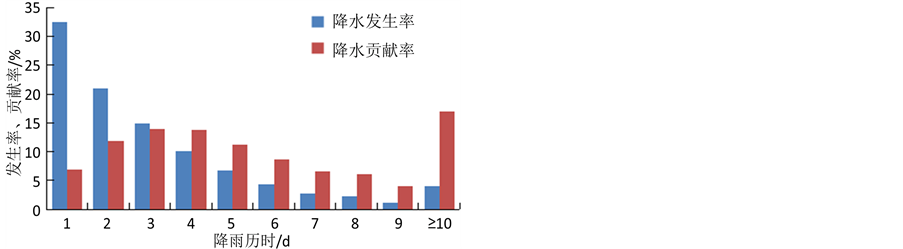
Figure 2. Incidence rate and contribution rate of different precipitation duration in rainy season over Beibu Gulf Economic Zone
图2. 北部湾经济区汛期各历时降水发生率与贡献率
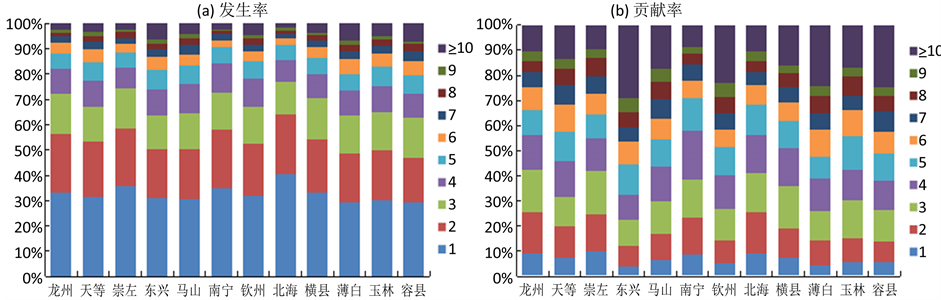
Figure 3. Incidence rate and contribution rate of different precipitation duration at different stations in rainy season over Beibu Gulf Economic Zone
图3. 北部湾经济区汛期各站各历时降水发生率与贡献率
下波动,即空间上没有表现出明显的区域差异;从统计结果来看,12站3 d~9 d历时降水发生率分别在13%~16%、9%~12%、6%~8%、3%~6%、2%~4%、1.5%~3%、1%~2%之间。进一步对比发现,1 d、2 d历时降水发生率空间变化趋势表现基本一致(各观测站具体位置如图1所示,为节省篇幅,这里不再给出空间差异分析图示,下同),均表现为南部的北海和中西部的南宁、崇左、龙州所在区域发生率较高(1 d发生率在34%以上,其中北海高达40.6%;2 d发生率23%~24%之间),马山、东兴及东部的博白、玉林、容县所在区域发生率较低(1 d、2 d发生率分别在29%~30%、18%~20%之间)。≥10 d历时降水发生率空间变化趋势与1 d、2 d相反,东兴站及东部的博白、玉林、容县所在区域发生率较高(5%~7%),北海站和中西部的龙州、崇左、南宁所在区域发生率较低(1.5%~2.5%)。
从图3(b)可以看出,12站各历时降水贡献率基本都满足随着降水历时增加呈先增加后减小、至≥10 d历时又出现显著上升的趋势。相对降水发生率(图3(a))而言,各站各历时降水贡献率大小差别较大。通过各历时降水贡献率大小对比(图3(b))发现,1 d、2 d、≥10 d差别相对较大,而3 d~9 d差别相对较小(贡献率分别在12%~17%、11%~16%、9%~13%、7%~11%、5%~8%、4%~7%、3%~6%之间),这一结果与各历时降水发生率大小对比结果基本一致。进一步分析发现,与1 d、2 d历时降水发生率相似,1 d、2 d历时降水贡献率空间变化趋势表现基本一致,均表现为南部的北海和中西部的龙州、崇左、南宁所在区域贡献率较高(1 d、2 d贡献率分别在9%~10%、15%~17%之间),钦州、东兴及东部的博白、玉林、容县所在区域贡献率较低(1 d、2 d贡献率分别在4%~6%、8%~10%之间)。≥10 d历时降水贡献率空间变化趋势与1 d、2 d贡献率空间变化趋势相反,钦州、东兴站及东部的博白、容县所在区域贡献率较高(23%以上,其中东兴高达29.3%),北海站和中西部的龙州、崇左、南宁所在区域贡献率较低(9%~10%)。
3.3. 汛期各历时降水发生率、贡献率变化趋势分析
图4给出了区域12站汛期各历时降水发生率(a)与贡献率(b)M-K变化趋势检验结果。从图4(a)可以看出,1 d历时有4站呈上升趋势,8站呈下降趋势;2 d、3 d、4 d均表现为上升趋势的站点数明显多于表现为下降趋势的站点数,即分别有8站、10站、8站表现为上升趋势,而表现为下降趋势的站点数分别为4站、2站、4站;对于5 d、6 d、7 d、8 d、9 d、≥10 d而言,均表现为下降趋势的站点数明显偏多,7 d、8 d、9 d甚至出现了所有站点变化趋势完全一致且大部分或全部站点通过了95%水平显著性检验(MK统计量 > 1.96或 < −1.96,下同)的情况。通过对比图4(a)与图4(b)发现,各历时降水发生率、贡献率表现为升降趋势的站点数目对比结果以及
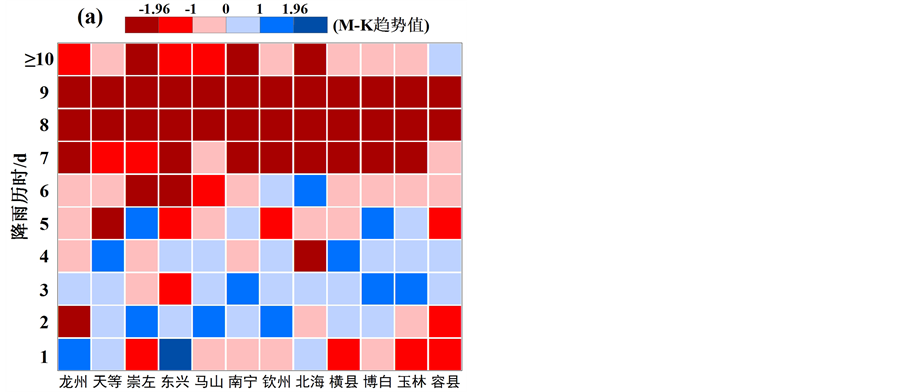
Figure 4. Test results of change trend of incidence rate (a) and contribution rate (b) for different duration in rainy season over Beibu Gulf Economic Zone
图4. 北部湾经济区汛期各站各历时降水发生率(a)与贡献率(b)变化趋势检验结果
通过95%水平显著性检验的情况几乎一致,即二者有着几乎完全一致的区域变化趋势。
综合以上分析可以发现,北部湾经济区汛期各历时降水发生率与贡献率变化趋势表现基本一致,即1 d、≥5 d (即5 d、6 d、7 d、8 d、9 d、≥10 d)历时降水发生率、贡献率主要表现为下降趋势,其中7~9 d下降趋势更加明显,而2~4 d (即2 d、3 d、4 d)历时降水发生率、贡献率主要表现为上升趋势。
4. 结论
1) 北部湾经济区汛期(4~9月)降水量占全年降水量80%以上。汛期各历时降水发生率随降水历时增加大致呈指数形式递减,其中1~4 d发生率合计接近80%;汛期各历时降水贡献率随着降水历时的增加呈先增加后减小、至≥10 d又出现显著上升的趋势;在1~9 d贡献率中,3 d最高,其次为4 d、2 d,三者贡献率合计接近40%,因此,从降水引发洪涝灾害的角度分析,2~4 d历时降水的致灾程度最高。汛期各历时降水发生率与贡献率空间差异表现基本一致,均表现为1~2 d、≥10 d差异较大,3~9 d差异较小;1~2 d、≥10 d空间差异主要表现为南部的北海和中西部的南宁、崇左、龙州所在区域与东部的玉林、博白、容县所在区域反向变化。
2) 汛期各历时降水发生率与贡献率变化趋势表现基本一致,具体表现为1 d、≥5 d主要为下降趋势,其中,≥7~9 d下降趋势更加明显;而2~4 d主要表现为上升趋势,结合前面的结论(即2~4 d历时降水造成洪涝灾害的可能性最大),可以进一步得出,北部湾经济区汛期洪涝灾害很可能将呈上升趋势。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金项目(41361022,41371498,41571091)。