1. 引言
21世纪以来,我国湖泊的富营养化和重金属、有机污染形势日趋严峻,水质的恶化加剧了水资源短缺,严重威胁了饮用水安全以及生态环境健康。湖泊水环境污染已成为制约国民经济发展的重要瓶颈,引起了国家和各级政府的高度关注,急需加强湖泊污染治理、管控等方面的综合研究 [1] 。了解湖泊现代过程不仅有助于掌握实时湖泊生态系统的基本特征,而且为进一步探究与理解湖泊演变规律及其记录的气候环境变化重建提供现实证据,有助于深入理解过去气候环境变化记录的意义,并有可能提供新的研究路径 [2] - [9] 。同时,也为湖泊污染控制和富营养化治理提供科学决策依据。
同时,湖泊也是良好的环境变化记录器,因此一直是人们关注的重点并进行了多方面的研究,Richard Bindler [10] 在对瑞士湖水沉积物分析的基础上,指出过量硫引起了流域土壤中快速的阳离子交换,改变了湖水中的铁–磷循环,使湖泊碱化。朱育新等 [11] 以阳宗海为例,研究表明生物贫化和耐酸物种的扩张使湖泊沉积物重现酸沉降。Benison等 [12] 对酸性湖泊的古环境记录进行了研究,结果表明地球的理化和生物进化规律可以在太阳系其它星球探索中提供参考。杨艺萍 [13] 把腾冲青海湖晚冰期以来的沉积记录及古植被与古气候演划分为四个阶段,认为太阳辐射量变化是响应该区域环境和气候变化的主要驱动因素。张虎才、史正涛等 [14] [15] [16] 对云南主要湖泊进行了大范围的考察和钻孔岩芯提取。党心悦等 [17] 对中国酸碱度不同湖泊四醚脂类分布影响因素及对湖泊古环境重建进行研究,结果表明:湖水含氧量能够影响湖泊古菌群落结构,从而影响古菌iGDGTs的分布。
根据湖水pH值,湖泊可分为碱性、中性和酸性三大类。地表绝大多数湖泊由于阳离子的积累和生物作用,湖水pH值大于6.5,属中性或碱性湖泊。由于自然酸性湖泊和湖泊酸化在本质上同为高浓度H+对湖泊系统长期的理化和生物作用的结果,故两者常表现出相似的环境特点和演化趋势,因此人们越来越重视自然酸性湖泊的理论研究,力图为大气污染诱发的湖沼酸化提供自然模板。
对湖水温度的季节性变化的研究表明,它是影响生物群落结构及生态系统生产力的主要因素之一 [18] [19] [20] [21] ,但在酸性湖泊中的理化指标特征及季节性变化的监测及其参数相关性、对沉积过程、生物过程和水化学过程的影响等诸方面研究不多。从这方面讲,对酸性湖泊水体季节性理化指标特征研究,对于深入理解不同指标的环境指示意义和探讨酸性湖泊生态系统的变化尤为重要。
云贵高原处于南亚与东亚季风交汇地带,气候受南亚和东亚季风和西风带与高原垂直气候的影响。这里湖泊众多,分布面积广,对区域环境变化敏感,在重建各种尺度气候和环境演化序列上,具有其它自然载体所无可比拟和替代的特性,是揭示湖区古气候和环境演变的良好指示器 [14] 。
腾冲盆地位于我国西南边陲横断山脉南端云滇西高原,全年多西南风,属受印度洋暖流所影响的中亚热带季风型气候 [22] 。腾冲青海是我国到目前为止被发现的唯一的自然酸性湖泊 [18] 。本文以腾冲青海2015年和2016年六次湖泊调查取样和分析结果为依据,对季节性变化特征等进行分析探讨,为我国酸性湖泊的研究提供有益补充,并为酸性湖泊水质参数及季节变化的规律提供对比依据。
2. 材料与方法
2.1. 研究区概况
青海,又名澄镜池,因“四周花木环绕,水清荣澄洁”,故名(王苏民等,1998)。该湖位于腾冲县大苴乡双海村(25˚08'06''~25˚07'44'N,98˚34'11''~98˚34'26''E),属于大盈江流域(图1)。当湖面高程为1885 m时,面积仅有0.21 km2,湖水容积5.4 × 105 m3,最大水深为5.9 m,流域面积1.5 km2。青海为一火山口湖类型,是一个典型的高山湖泊,水质呈微酸性,是全球为数不多的酸性水湖之一 [19] [20] [21] 。湖水主要的补给来自流域径流和地下水,但由于流域面积很小,故湖泊水位较稳定,湖泊自然状态下无湖水出流,当雨季降水高度集中时,湖水从湖泊东北部哑口溢出,从大苴乡附近汇入到大盈江–瑞丽江–伊洛瓦底江,最终在缅甸仰光附近地区注入印度洋安达曼海。另因湖底常年有地下水补给,故不论天气旱雨,湖泊水位基本保持稳定(据腾冲县水利志)。1958年以后,在湖东北部修建水闸人为干预湖水出口并抽水灌溉,使得湖泊水位与水量发生非气候性变化。
湖区在大地构造上位于欧亚板块和印度板块的镶接部位,受两大板块的强烈碰撞挤压,区内地震活动频繁,地热资源丰富。据1951~1980年气象数据(中国气象局气候资料室提供的月平均降水资料和月平均地面气温资料),研究区多年平均气温14.7℃,极端最高气温30.5℃,极端最低气温−4.2℃;多年平均降水1425 mm,其中5~10月雨季的降水量占全年总雨量的84.3%,年平均潜蒸发量约1575 mm,属亚热带高原湿润季风气候 [22] 。
2.2. 数据采集
于2015年11月~2016年10月在腾冲青海了六次进行调查工作,分别在深水湖面北部、中部、南部共采集18个采样点数据(图1)。运用YSI6600V2多参数水质监测仪(预先校准),在采样现场以0.5~1.0 m深度间隔,垂直向下测定水样的温度(Temp)、pH、叶绿素a (Chl-a)、溶解氧(DO)、浊度(NTU)。本研究采用GPS卫星导航仪对监测点进行定位,便于数据对比分析。
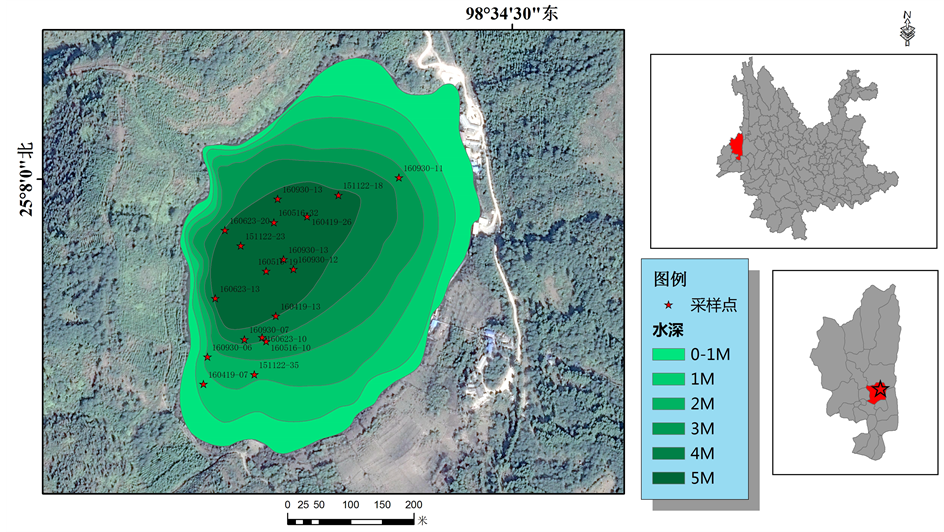
Figure 1. Sampling point location and water depth of Qinghai Lake in Tengchong
图1. 腾冲青海湖地理位置及样点、水深图
3. 结果分析与讨论
3.1. 腾冲青海湖水基本理化性质
分层湖泊(水库)水体水温分布及温跃层的形成和消失对湖库水化学参数具有重要影响。对于表征湖水的基本参数来讲,叶绿素a浓度是浮游植物现存量的重要指标,其浓度的高低能够反映水体的营养状况;溶解氧则是湖泊初级生产力及水动力条件的综合反映,藻类光合作用消耗水中的CO2,使pH值升高,溶解氧升高;水体pH值的高低和溶解氧浓度的大小,反映水体中藻类的生长及水环境变化的情况。因此,对深水湖泊的研究,有必要明确温度分层的形成和发展过程,确定温度分层发生和消失后湖泊水体pH值,叶绿素a浓度、溶解氧等水化学参数的变化,这对深水湖库富营养化预防及水质保护具有现实意义 [23] 。
3.2. 水体中pH值垂直分布特征
pH值是水体酸碱度的指标,大部分湖泊中其值变化于6~9之间,天然酸性湖泊pH为一般5~6。水体中H+浓度影响到包括CO2在内的一些营养物质,改变水体pH值会影响磷、氨、铁及微量元素的赋存形式和沉积过程 [24] 。
在一般湖泊中,表层水体由于浮游植物和水气间的CO2平衡作用,消耗大量CO2,使得pH值较高,水体呈弱酸性至碱性,而深层水体中透光性逐渐降低致使光合作用减弱,藻类的大量死亡使CO2积累,并且有机质分解产生酸,使得pH值急剧减小。
青海火山口湖监测数据显示,水体pH值变化明显(图2),2015年11月的pH值在5.3~5.7之间,三个监测点之间变化比较一致。2016年4月数据显示湖水pH值呈现表层高,中层、底层递减的规律,且出现北部较高,南部较低的态势。5月为总体pH值较低月份,其北部测到最低为4.7,在中部最低仅
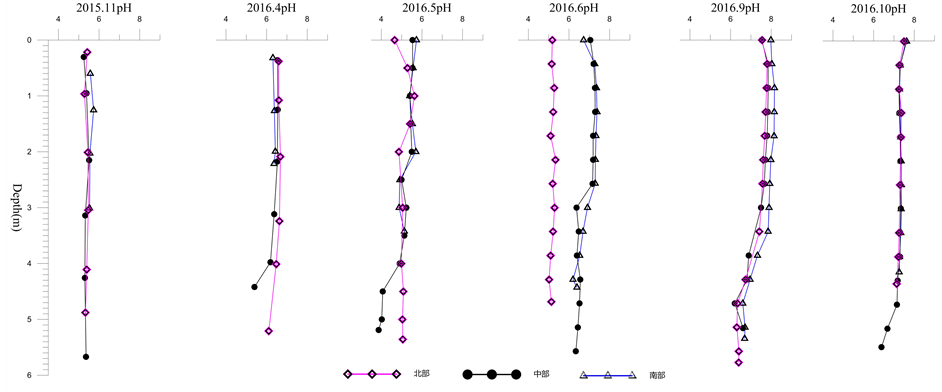
Figure 2. Vertical profile of pH in the Qinghai Lake
图2. 青海pH值垂直剖面变化
为3.9,是直到目前监测到的最低值,相关成因有待持续监测及水质其它参数的测定分析结果。6月23日北部20号采样点(25˚07'57.4''N, 98˚34'15.3''E)获得数据均低于中部南部,分析附近可能有酸性水流涌出。2016年9月和10月的监测数据显示,pH值表层呈现弱碱性,且随着时间的变化,弱碱性趋势向中下层蔓延,10月份4~5 m处pH值呈现中性到弱酸性变化趋势。与2015年11月对比,发现pH值年际变化较大,这可能与湖底酸性物质涌出量减少有关。
本文为进一步关注、监测和分析青海水体不同深度水年际变化的规律,在现有数据的基础上,采用2015年11月和2016年6月、10月的监测数据进行了空间插值分析,拟合出监测时间的0~1 m、1~2 m至2~3 m三个深度的等深面pH值变化趋势图(如图3所示),随着深度的加深,湖面面积逐渐减小,具体可参见图1。从pH值变化趋势上看,纵向左侧三幅图为2015年11月旱季情况,湖泊西北部和东南部较小区域pH值浓度较高,可能存在酸性水体涌出,但整体来看,湖泊的pH值较6月份来说,变化范围较小,变化不明显,即整个湖泊呈现弱酸性,pH值变化范围在5~6之间。从中间纵向三幅图看,分别表示2016年6月23日三个深度的pH值变化趋势,从全湖看,监测时间内湖泊pH值明显分为南北两个区域,北部的pH值明显偏低,呈现酸性,而南部的值基本呈现弱酸性和中性,从右侧纵向三幅图看,分别表示2016年10月26日三个深度的pH值变化趋势,全湖呈现弱碱性。从监测数据看,全年呈现复杂的pH值变化,以待今后持续监测找出规律。因为插值过程中使用的是IDW (Inverse Distance Weighted)反距离权重插值法。此处做一个干湿两季的对比(如图3所示),定性分析湖泊的pH值情况,为今后的研究打下基础,为进一步分析湖泊水质特征的季节性变化,甚至更大尺度的变化规律的研究提供线索。
3.3. 水温季节性变化特征
腾冲青海北、中、南不同部位水温垂直剖面显示(图4),4月~6月间出现水体热力分层逐渐加强的现象,随着气温的升高,上层水体快速增温并逐渐与下层水体因深度加深、增温慢形成对比,时至六月出现明显的温跃层(thermocline)。
从时间上看,11月为本文所讨论六个监测月份中温度最低的,其中南部浅水区域的温度较低,变化在14.6℃~14.94℃之间,相差不大,表现为上下层水体温度比较一致。北部和中部区域表层水温较高,达到16.04℃,但2 m以下的下层水体温度低于15℃。尽管如此,上、下层水体总体温度差不足1℃。4~6月随着太阳辐射增强及气温上升,表层水温快速增加,与深层水温温差增大,水体出现分层现象。随着
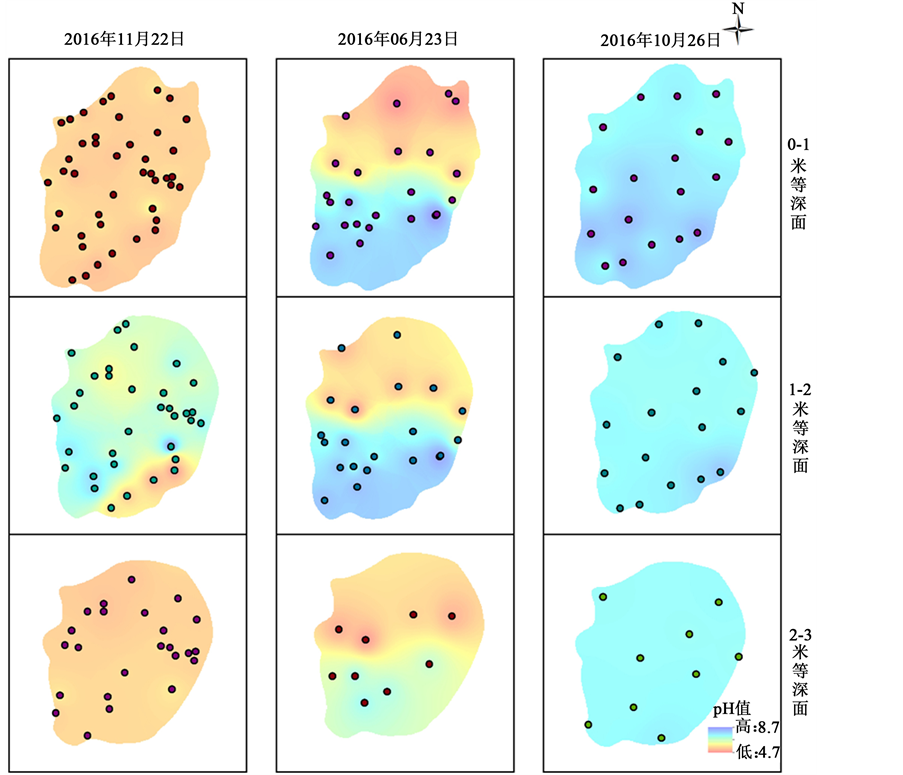
Figure 3. The change trend of pH value in wet and dry season in Tengchong Qinghai Lake
图3. 干湿季腾冲青海等深面pH值变化趋势图
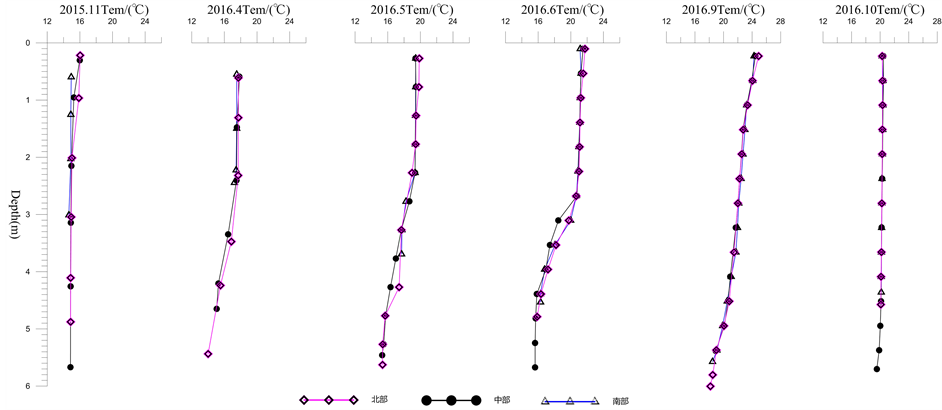
Figure 4. Vertical profile of water temperature in Qinghai Lake
图4. 青海水温垂直剖面变化
热量持续向下传输,最大温差减小,温跃层下降,温度分层逐渐明显。具体分析,4月份的表层水体温度在17.51℃~17.84℃,较11月份上升1.5℃~3℃左右,水深1~2 m内基本保持这一温度,2 m以下随着深度的增加,水温降低,北部点2~5 m从17.7℃降低到14.01℃,温度与深度程负相关关系。5月份的表层水温为19.42℃~19.86℃,与上年11月份相比,表层水体升温2℃左右,且1~2 m深度基本保持19℃以上温度。2~4 m水体温度与深度程负相关关系,水温从19.35℃下降到15.69℃,但4 m以下水体水温保持稳定。如果定义水温梯度超过0.2℃/m的水层为温跃层 [25] [26] ,那么4月份北部水体2~4 m水温梯度达到1.65℃/m,监测点出现温跃层,水体出现分层。6月份表层水温继续升高,监测点表层达到21.14~21.73℃,且0~2.5 m水温均保持在21℃附近,2.5~4.5 m中部监测点水温从20.91℃下降到16.94℃,水温梯度达到1.98℃/m,监测点温跃层较前一月位置有所下降,并且更加明显,水体分层现象明显,到9~10月份,中下层水温持续下降,这是由于上层低温渗透导致,到冬季水体分层现象消失。
3.4. 水体中叶绿素a垂直分布特征
叶绿素a是表征浮游植物现存量的重要指标,也是湖泊水质的重要指标 [27] ,叶绿素a浓度的高低变化可以反映水体的营养状况。
青海水体叶绿素a浓度表现出明显的季节性特征(图5)。11月至次年6月随着水温上升、藻类生长,叶绿素a浓度增加,四次监测结果表明1~3 m水深为样点的峰值区间。从时间上看,11月水温低,外界营养盐输入少,叶绿素a浓度低,4~6月,随着水温升高和雨季到来,流域物质输入量增加,叶绿素a浓度逐渐增加。水体叶绿素a浓度与藻类的分布密切相关,表层水体受营养盐限制及光照影响,叶绿素a浓度较低;中、上层(1~3 m)由于水温高、光照充足、营养盐的补充,藻类大量繁殖使叶绿素a大量积累;深层(3 m以下)受光线、营养盐限制,叶绿素a浓度保持在很低水平。所以,叶绿素a浓度整体表现为表层低、中上层高、深层低的特征。在不同监测断面,叶绿素a浓度垂直剖面变化趋势相似,当浓度区间和数值随着温度增高而增大,季节性变化更加明显。从空间分布来看,虽然2016年6月中部监测点4 m深度数据最大值为37.7 ug/L,较之5月中部、南部2.5 m深度最大值21 ug/L,24.9 ug/L叶绿素a浓度更高,但整体来看,4月水深1~3 m处叶绿素a浓度较高,代表了藻类大量快速繁殖的时期和过程,依据现有资料说明腾冲青海酸性湖泊藻类生长的爆发时期为温度升高、雨季开始的初期,9月,叶绿素含量呈现从上中层到下层逐渐增加的趋势,这与水体中的植物和浮游生物的生命过程(如死亡等)有关,10月份叶绿素在水体中各层均减少。这对于认识湖泊藻类生长、繁殖、死亡过程,进而研究控制藻类爆发具有重要的价值和意义。
3.5. 水体中溶解氧垂直分布特征
溶解氧是指溶解在水中的分解态氧,它是维持水体生态环境动态平衡的重要因子和水生生物生存的必要条件,同时还参与部分物质转化 [28] 。有关研究表明,DO在淡水中的溶解度主要取决于水温,在气压一定时,水温越低,溶解氧浓度越高。溶解氧也具有强烈的日变化和季节变化特征。较清洁的湖泊溶解氧一般在7.5 mg/L以上,当水体中溶解氧低于5 mg/L时,湖泊中各种浮游生物则无法生存 [29] 。温跃层的存在阻止上层水体溶解氧向下层扩散 [30] ,使上、下层水体形成明显的溶解氧梯度 [31] 。
为了消除日变化因素,六次测量均是在上午进行。腾冲青海的溶解氧11月至次年10月期间六次监测结果也呈现出一定的梯度效应(图6)。在深度方向上,上层(1~2 m)水体的气体交换和藻类光合作用为上层水体提供溶解氧,而中层(2~3 m)水体由于水生生物呼吸和有机物的降解,消耗水体中的溶解氧,水体热分层阻碍了上、下层水体的进一步交换,使深层(3 m以下)水体溶解氧无法得到有效补偿,导致深层水体处于缺氧状态,易引起底泥营养盐的释放。同时,春季水体的对流和混合,导致底泥营养盐向上层
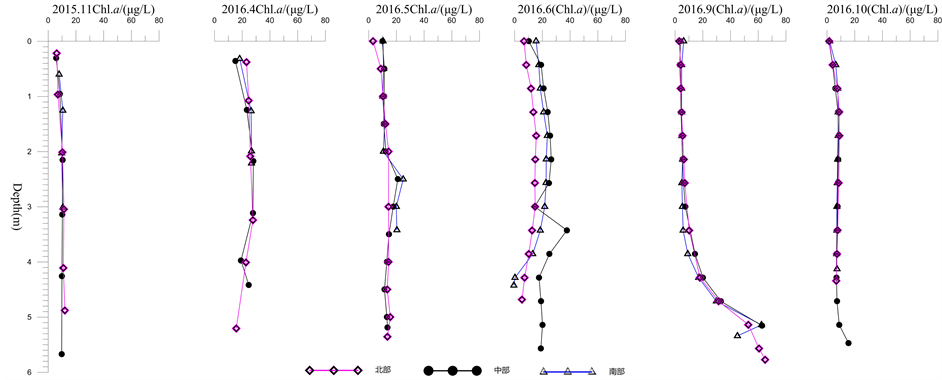
Figure 5. Vertical profile of chlorophyll-a concentration in Lake Qinghai
图5. 青海叶绿素a浓度垂直剖面变化
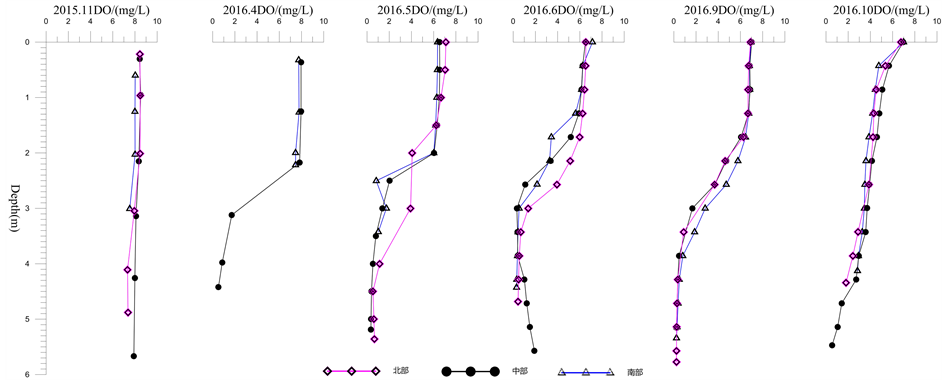
Figure 6. Vertical profile of DO in Qinghai Lake
图6. 青海溶解氧垂直剖面变化
扩散,对水体水质产生不利影响。水平向看,溶解氧梯度效应随着季节的变化逐渐明显,与其他碱性湖泊先增后减不同,呈现上层丰富(11月北部测定为8.44 mg/L),中层强烈变化逐渐减少(5月南部2~2.5 mDO从6.01下降到0.83 mg/L),深层稀少(6月南部5.5 m处为0.31 mg/L)的明显特点。从9~10月份的数据显示,梯度效应逐渐减弱,全湖垂直方向上溶解氧含量逐渐趋同,湖水逐步回归混合状态。
3.6. 水体浊度垂直分布特征
青海水体浊度的季节差异较大(图7),从测量结果来看,11月浊度最低在1.8~2.7之间波动,但4~6月的浊度及其波动均远高于11月。从幅度上看,4月份的值在7.9~11.4之间,5月份为5~10.2,6月为2.7~9.2。从统计均值看,11月浊度均值为2.27,其中北、中、南区分别为2.35、2.23、2.24;4月浊度均值为9.49,其中北、中、南区分别为8.55、9.95、10.2;5月浊度均值为8.69,其中北、中、南区分别为8.23、8.58、9.43;6月浊度均值为7.42,其中北、中、南区分别为8.05、7.0、7.25。这可能与采集时间前是否有强烈的对流现象或降雨相关,也可能是湖泊处于混合过程中,通过9月和10月的监测数据分析,
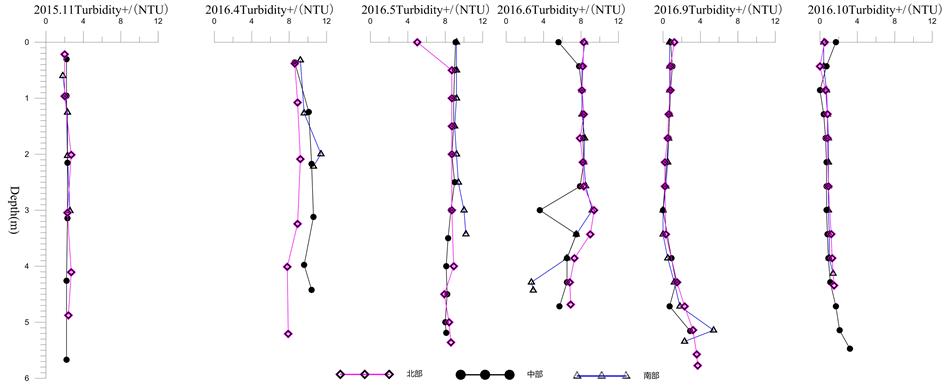
Figure 7. Vertical profile of Turbidity in Qinghai Lake
图7. 青海浊度垂直剖面变化
认为进入秋冬季以后,湖水的浊度明显降低,9月份下层水体浊度较10月份偏高,这与叶绿素a和溶解氧在这一垂直层上的数据吻合,说明9月湖中深层湖水中有生物、化学作用进行,到10月11月趋于稳定。
4. 讨论与结论
湖泊水温与气温一样具有明显的季节变化,相应地,湖泊水体热力分层现象也呈现不同的季节格局 [24] 。湖泊学研究最有效的分析方法之一就是对湖泊理化、生物的长期数据进行分析,采用短期数据往往会导致错误的结论 [32] 。本文利用代表雨季结束后的11月和次年雨季开始的4~6月水质监测信息,对湖泊水质的特征和变化过程进行了讨论。随着监测时间的延续和数据的积累,必将对青海水质在年际尺度上的变化给出更明确的解释,进一步分析高原酸性湖泊湖水的分层与混合动力机制,与其它高山深水湖泊比较,其生态环境、物理、化学反应机制的异同,从而为湖泊学的研究提供现实参考和理论依据。
湖泊调查是湖泊学研究的基本工作,基于对半年多的监测数据对青海这样一个典型而唯一的酸性湖泊进行了首次理化参数分析,得出如下几点认识:
腾冲青海酸性湖泊水体pH值季节变化明显,水体与多数湖泊不同大多数月份呈现酸性。其中5月为总体pH值较低月份,在湖北部表层测到4.7的低值,中部底层测到3.9的最低值,而9~10月监测结果显示弱碱性,其变化比较复杂,相关成因有待持续监测和水质分析。我们认为,首先应当搞清楚的问题是,湖水这种强酸性变化是因为湖底强酸性水体的输入还是CO2、SO2或其它气体释放与水体反应形成H2CO3、H2SO4或其它酸类?其变化有什么规律?如果是气体释放是否与构造运动或深层岩浆活动有关等等。同时,腾冲青海监测期出明显水体热力分层现象,表现出上层和下层水体温度随深度加深缓慢下降,中层温度随深度加深急剧下降的特点。青海水体叶绿素a浓度表现出明显的季节性特征,其浓度整体表现为表层和深层低、中上层高的特征。从空间分布来看,一些极值点具有一定的关联。青海的溶解氧呈现出梯度效应,再次证明了温度梯度的客观性。垂直方向上,上层溶解氧富集,而中层减少,深层处于缺氧状态。水平向看,溶解氧梯度效应随着季节的变化逐渐明显,与其他碱性湖泊先增后减不同,呈现上层丰富,中层强烈变化,深层稀少的明显特点。
青海水体浊度的季节差异较大,变化复杂,可能与实地测量前水体具有强烈的对流现象或降雨相关,今后有待长期观察和监测分析,以长期数据为支持找出酸性湖泊水质变化的特征和内在机制。
基金项目
云南省领军人才计划(No.2015HA024)和云南省高端人才引进项目(2010CI111)资助。
NOTES
*通讯作者。