1. 引言
近年来我国钢铁工业高速发展,钢铁产量和产能的不断攀升造成了业内的竞争日趋激烈,我国钢铁行业整体上处于微利状态。硅钢作为一种高附加值、高技术含量的品种,我国钢铁企业在其质量控制、品种开发等方面与国外仍存在较大差距 [1] [2] 。目前,国产的硅钢产品仍无法满足市场的需求,需要大量向国外进口。硅钢作为一种特殊的磁性材料,不仅要考虑表面质量和力学性能,更要考虑其磁性能。而钢中非金属夹杂物的存在会显著阻碍磁畴运动,劣化成品带钢的磁性能 [3] [4] [5] [6] 。
非金属夹杂物的数量、尺寸、类型及分布规律直接影响着硅钢的产品质量 [7] 。在开浇、换包等非稳态浇铸时期,卷渣、耐火材料侵蚀以及二次氧化等问题将给铸坯的洁净度带来了严重影响 [8] [9] [10] 。本论文以电工硅钢为对象,通过工业试验和取样分析,研究不同浇铸时期连铸坯洁净度及大颗粒非金属夹杂物的变化规律,研究工作对于电工硅钢的质量改善具有指导意义。
2. 实验
2.1. 实验原料
工业试验在国内某钢厂进行,该企业无取向电工硅钢冶炼工艺路线包括铁水预处理脱硫、180吨复吹转炉冶炼、RH-TB真空精炼以及板坯连铸。本实验所取硅钢试样包括中间包钢液样和连铸坯样。中间包钢液样分别在第1炉开浇时、第1~2炉交接时、第2炉正常浇铸时、最后1炉停浇前在中间包水口上方钢液面以下300~400 mm深度处取得;连铸坯试样分别在第1炉的开浇坯2 m、开浇坯4 m、开浇坯6 m、第1~2炉之间的交接坯、第2炉的中间坯和最后一炉的尾坯中在铸坯宽度1/4处延连铸方向切取长度为150 mm的试样,如图1所示。中间包钢液取样位置与连铸坯取样位置一一对应。
钢样中w(T.[O])和w([N])的分析在氧氮分析仪中进行。大样电解法是针对分析钢中尺寸在50 μm以上的大颗粒非金属夹杂物,其分析过程主要包括电解、淘洗、还原和分离。其分离出来的夹杂物可以按照粒径进行分级,然后结合扫描电镜和能谱分析可以得到铸坯中大颗粒非金属夹杂物的数量、尺寸、成分和形貌。在本试验中,大颗粒非金属夹杂物主要分为< 80 μm、80~140 μm、140~300 μm和>300 μm四个等级。
3. 结果分析与讨论
3.1. 中间包及铸坯中w(T.[O])、w([N])的变化
图2所示为不同浇铸阶段中间包钢液样的w(T.[O])和w([N])的变化。可以看出,头坯对应的中间包钢液中的w(T.[O])和w([N])均明显高于交接坯、正常坯和尾坯对应的中间包钢液,可见在开浇阶段覆盖剂加入之前中间包钢液发生了严重的二次氧化。随着浇铸的进行,开浇阶段中间包钢液的w([N])逐渐减少,说明随着中间包覆盖剂的加入,钢液表面被覆盖剂覆盖,空气被隔绝后中间包内钢液受空气二次氧化的影响逐渐减轻。与w([N])变化规律不同的是,在开浇阶段随着浇铸的进行,中间包钢液的w(T.[O])却不断上升,直到在第1、2炉交接阶段下降到开浇头坯2m处的水平并逐渐稳定,这说明在开浇阶段,钢液注流造成中间包内流场极不稳定,导致发生较为严重的卷渣及耐火材料的侵蚀,造成卷渣和侵蚀对钢液二次氧化的影响从而造成w(T.[O])增加。换包阶段的交接坯和浇铸末期的尾坯对应的中间包钢液

Figure 1. Sampling scheme of the casting slab
图1. 铸坯取样方案

Figure 2. W(T.[O]) and w([N]) of molten steel in the tundish at different casting stages
图2. 不同浇铸阶段中间包钢液样的w(T.[O])和w([N])
w([N])含量基本保持不变,由此可以看出,钢液表面的覆盖剂始终对钢液起着很好的保护作用,有效地隔绝了空气,因此钢液流场的变化并未对空气的二次氧化产生影响。而从w(T.[O])的变化可以看出,换包阶段的交接坯由于钢液液位高度处在一个不受流场影响的位置,所以交接坯的中间包试样并未受到影响,但在浇铸末期的尾坯阶段,w(T.[O])略有升高,这是由于钢液液面下降,使得钢液注流对中间包钢液流场的影响增大,中间包内钢液受卷渣的影响增大。
图3所示为不同浇铸阶段中间包钢液与铸坯中w([N])的对比。可以看出,无论是非稳态的开浇阶段还是稳态的正常浇铸阶段硅钢铸坯中的w([N])均较中间包钢液的w([N])明显增加,这说明由中间包向结晶器中浇铸的过程中水口氩封不严密造成钢液吸气。
图4所示为不同浇铸阶段中间包钢液与铸坯中的w(T.[O])的对比。可以看出,与w([N])的变化趋势不同,无论是非稳态的开浇阶段还是稳态的正常浇铸阶段硅钢铸坯中的w(T.[O])均较中间包钢液的w(T.[O])明显降低,且开浇阶段铸坯的w(T.[O])的变化并未随着中间包相对应位置钢样的w(T.[O])的剧烈波动而波动。可见,在浇铸阶段由于卷渣而带入钢液的大多数夹杂物在钢液浇铸至结晶器凝固之前上浮并被结晶器保护渣吸附去除。虽然水口氩封不严会造成钢液从空气中吸氧,但其对w(T.[O])的影响小于夹杂物上浮去除的影响。
3.2. 大颗粒夹杂物的电解分析
表1是连铸坯头坯和稳态坯中大颗粒夹杂物的大样电解分析结果。从表中数据可以发现,随着浇铸的进行,稳态浇铸阶段铸坯中大颗粒非金属夹杂物的总量较头坯明显下降。
图5所示是硅钢头坯中大颗粒夹杂物的SEM图片,表2中数据为对应的夹杂物成分。通过大样电解分析发现,铸坯中存在不少含K的硅酸盐复合夹杂物,说明浇铸初期结晶器内存在严重的弯月面扰动及过大的表面流速,或钢液的非对称流动,导致保护渣卷入。此外,部分夹杂物钙含量较高,形状接近球形,应为钢包渣或中间包覆盖剂卷入所致。除卷渣所致大颗粒夹杂物外,还分别发现Al2O3夹杂物、SiO2夹杂物以及Al2O3-SiO2系夹杂物,此类夹杂物主要精炼过程中钢液脱氧产生的。

Figure 3. W([N]) of molten steel in tundish and casting slabs at different casting stages
图3. 不同浇铸阶段中间包和铸坯的w([N])
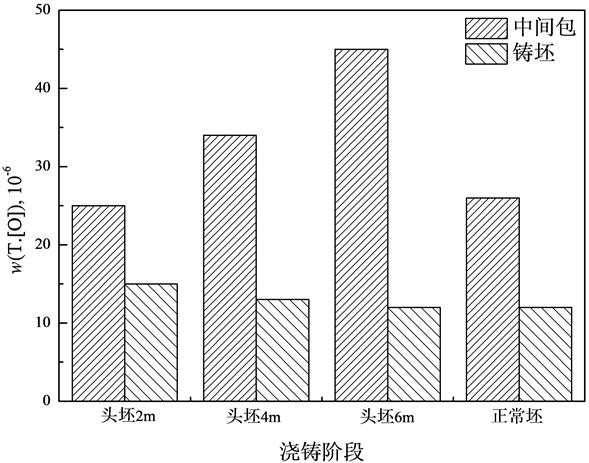
Figure 4. W(T.[O]) of molten steel in tundish and casting slabs at different casting stages
图4. 不同浇铸阶段中间包和铸坯的w([N])
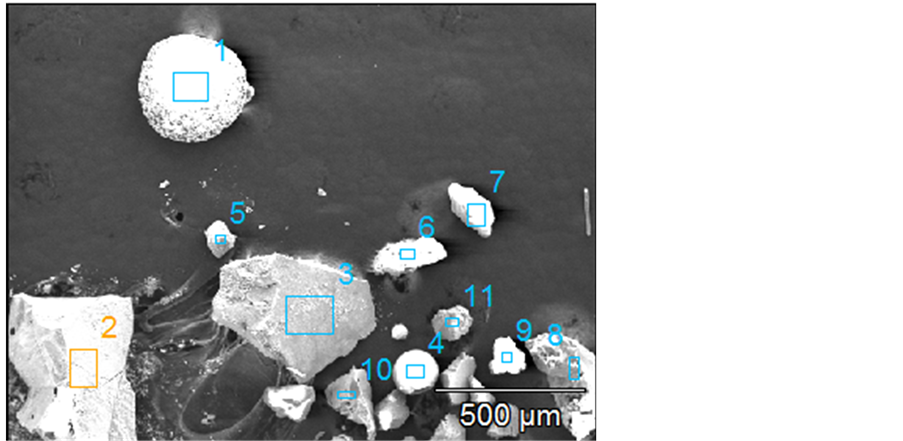
Figure 5. SEM photo of macro non-metallic inclusions in the start-casting slab
图5. 头坯中大颗粒非金属夹杂物扫描电镜图片

Table 1. Statistical results of bulk sample electrolysis of casting slabs at different casting stages
表1. 铸坯大样电解统计结果
图6所示是硅脱氧钢稳态坯中大颗粒夹杂物的SEM图片,表3中数据为对应的夹杂物成分。通过大样电解分析发现,稳态坯中大颗粒非金属夹杂物成分与头坯处有较大不同。首先,未发现能典型代表卷渣的含K的硅酸盐夹杂物,说明开浇到这一阶段时,钢液的卷渣得到了一定的控制。此外,7号点所在夹杂物为Mg含量较高的Ca、Mg复合夹杂物。由于大包和中间包的耐火材料均为镁质,可知随着浇铸过程的进行,耐火材料受钢液的侵蚀而不断进入钢液并残留其中,与其它成分结合,形成了此类夹杂物。2号、5号和8号夹杂物分别为SiO2、硅酸铝和Al2O3,应为钢液成分中的硅、铝受浇铸过程中二次氧化的影响所生成的夹杂物。此外,4号夹杂物为钙铝硅酸盐。从形貌上观察,可以发现该钢样中的大颗粒非金属夹杂物形貌不规则,大小差异大,且有尖锐、长条形夹杂物的存在,对铸坯的力学性能影响很大。
4. 结论
1) 硅钢头坯中w(T.[O])、w([N])明显高于交接坯、正常坯和尾坯,不同浇铸时期硅钢连铸坯中的w([N])均高于中间包钢液中的w([N]),表明中间包–结晶器之间的保护浇铸存在问题,二次氧化严重。

Table 2. EDS analysis of macro inclusions in the start-casting slab (mass, %)
表2. 头坯中大颗粒非金属夹杂物能谱分析(质量分数,%)

Table 3. EDS analysis of macro inclusions in steady-casting slab (mass, %)
表3. 稳态坯中大颗粒非金属夹杂物能谱分析(质量分数,%)

Figure 6. SEM photo of macro non-metallic inclusions in the steady-casting slab
图6. 稳态坯中大颗粒非金属夹杂物扫描电镜图片
2) 连铸坯中的大颗粒夹杂物主要源于渣金混卷和耐火材料的侵蚀,中间包和结晶器内流场的稳定性控制水平有待于提高。
3) 建议严格长水口和浸入式水口氩封操作,最大限度加强密封,并采用中间包塞棒进行开浇挡渣,控制中间包内钢液达到足够的防止卷渣的高度后进行开浇,严格控制中间包下渣。