1. 引言
在碳酸盐岩的孔隙演化中,白云石化作用是影响其孔隙发育的重要因素。地质学家在研究白云石化作用时,对白云岩形成机制做了很多探讨和总结,白云岩成因问题一直在沉积学界引起广泛关注,成为延续时间较长的讨论话题。在我国,白云岩从古生代至新生代都有发育,尤其是在西部地区,为白云岩研究提供了良好的地质条件 [1] 。四川盆地东部近年来成为油气勘探重点地区,迄今为止,川东地区碳酸盐岩层位所发育的较好油气储集层大多为颗粒白云岩或生物礁云岩,其中包括白云石化程度较高的上二叠统长兴组白云岩储层。多期次白云石化作用的叠加,对长兴组白云岩储层起到了极其重要的控制作用 [2] 。针对该区白云石化作用多期次性和成因机理的复杂性,结合白云石化多期次的发育情况,研究认为泥–微晶白云岩形成机理与蒸发泵作用有关,即准同生白云石化作用的产物 [3] ,其余各类白云岩,如颗粒白云岩、晶粒白云岩和生物礁白云岩皆为多期次埋藏白云石化作用的产物。以前人研究为基础,笔者拟从地质综合研究角度出发,以岩石学为基础,结合研究区构造和沉积相特征,主要是利用稳定碳、氧同位素等地球化学测试数据,试对研究区各种类型白云岩进行全面的成岩环境分析,增加对川东北长兴组白云岩形成环境的认识,希望能够为盆地白云岩储层预测提供地球化学上的依据。
2. 区域地质背景
四川盆地已经成为我国重要的天然气富集盆地之一,盆地东北部上广泛发育的碳酸盐岩地层具有巨大的勘探潜力。四川盆地经过复杂的构造演化,不同阶段、不同性质的构造叠加,形成了四川盆地东部具有构造叠加性质的川东弧形褶皱带(图1)。中二叠世发生的“峨眉地裂运动”,使川东地区形成了张性断块,其原有的古构造基底格局被彻底改变。随后,中二叠世茅口期和龙潭期之间的东吴运动,使四川盆地整体抬升,在川东北地区形成了一个北东向的古斜坡。构造格局的改变,使西部的峨嵋山和康滇古陆一带为陆源剥蚀区。自龙潭期,沉积古地理格局自西向东依次为海陆交互相、浅海相和深海相。至长兴期,川东地区便以广阔的碳酸盐台地沉积为主,并伴有深海相“台盆”,即“开江–梁平”海槽和“城口–鄂西”海槽 [4] 。研究区即位于开江–梁平海槽东段(图2),在区域构造上,开江–梁平海槽位于川东弧形褶皱带的东北缘,川东弧形褶皱带的空间展布与形成演化对研究区的构造演化具有极其重要影响,进而控制了该区的沉积 [5] 。研究区上二叠统长兴组主要为一套海相碳酸盐岩沉积,其中白云岩构成主要的储集岩类。
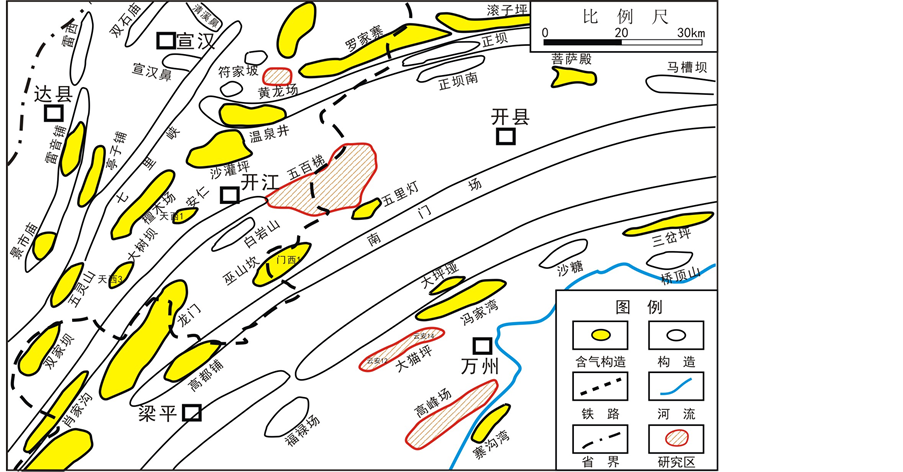
Figure 1. Construction location map of the study area
图1. 研究区构造位置图

Figure 2. Schematic diagram of tectonic-palaeogeographic pattern of Changxing Formation in the eastern section of Kaijiang-Liangping trench
图2. 开江–梁平海槽东段长兴组构造–古地理格局示意图
3. 白云岩岩石学特征
四川盆地东北部上二叠统长兴组白云岩分布较为广泛,岩石类型复杂多样。笔者在研究过程中,将原岩沉积特征和白云岩结构特征以及所具有的特殊构造为主要依据,将研究区长兴组白云岩分为泥–微晶白云岩、粉晶白云岩、细晶白云岩、中-粗晶白云岩和构造碎裂化白云岩等5种类型,各类型白云岩岩石学特征如下。
3.1. 泥–微晶白云岩
泥-微晶白云岩以具有泥-微晶结构为主要特征,晶体形态以他形为主,晶体之间接触紧密呈镶嵌状(图3(a))。常具有泥质条带、鸟眼和石膏假晶等潮汐和暴露成因标志。该类白云岩一般认为与准同生白云石化作用有关,即蒸发条件下的潟湖–潮坪环境中,高Mg/Ca比的卤水交代灰泥形成。
3.2. 粉晶白云岩
该类白云岩的原始沉积构造保存较为完整,有两种主要岩石类型:灰质粉晶颗粒或礁白云岩(图3(b))和粉-细晶颗粒或礁白云岩(图3(c));颗粒组分以生物碎屑为主,前者晶体形态以半自形为主,少数他形,粉晶结构,白云石的晶面较脏,颗粒和礁结构皆保存较为完好;后者在晶体大小和形态上与前者较为一致,颗粒或生物礁结构少量破坏,且几乎不含残余灰质组分。该类白云岩应与生物碎屑或造礁生物被优先白云石化有关。根据其结构特征,表明该类白云岩为埋藏阶段早期白云石化作用的产物。
3.3. 细晶白云岩
该类白云岩晶体大小在0.05~0.25 mm之间,部分为中晶级(0.25~0.5 mm),白云石晶面较脏,晶形较好,且多见雾心亮边结构,白云石化不均匀并伴有强烈的重结晶作用。在该类白云岩的某些岩石类型中,如具不明显残余结构的粉–细晶颗粒白云岩(图3(d))或礁白云岩或部分中–细晶白云岩(图3(e)),礁白云岩中的晶间孔和晶间溶孔十分发育,在较大的溶孔内往往有白云石晶簇分布,除局部充填有少量沥青外,一般不含其他的外来物质,此为深部溶解作用的典型标志,并确定为该类白云岩为埋藏阶段中期白云石化作用形成。
3.4. 中–粗晶白云岩
该类白云岩中晶体大小以中晶级(0.25~0.5 mm)为主,部分为粗晶级(0.5~1.0 mm),晶形较好,部分白云石具有雾心亮边结构(图3(f)、图3(g))。值得注意的是,在粗晶白云石中常见晶体呈马鞍状结构特征。与之相应的是研究区长兴组分布在台内海槽的东段,表明构造活动相伴生的热液流体对长兴组白云岩具有一定影响,该类具马鞍状结构的白云石属于埋藏阶段晚期构造热液活动成因 [6] [7] [8] ,下文会利用地球化学数据进一步分析论证。
3.5. 构造碎裂化白云岩
该类白云岩以发生构造碎裂化作用为特征(图3(h)、图3(i)),伴随有强烈的溶蚀现象,发育呈网状分布的裂缝,导致岩石的原始结构完全消失,溶蚀作用沿裂缝表现较为强烈,孔、洞、缝连通性好并在其内充填有炭质沥青。该类白云岩一般认为是成岩阶段晚期白云岩发生碎裂化作用所导致的。

Figure 3. Photomicrographs for familiar dolostones of in Changxing Formation of study area
图3. 研究区长兴组常见的白云岩类型图谱
4. 碳、氧同位素地球化学特征及成因解释
对研究区上二叠统长兴组多种类型的白云岩样品和灰岩类样品进行了碳、氧同位素分析(表1),并对数据结果进行了统计(表2,图4),分析结果表明:
1) 长兴组白云岩δ
13 C
分布在0‰~4.581‰(PDB),仅一个样品为负值(−0.647‰);δ18O分布在−7.205‰~−2.979‰(PDB)。
2) 与长兴组海相灰岩类δ18O(为−5.019‰)相比,泥–微晶白云岩的δ18O(为−4.405‰)偏大一些,较富集重同位素。根据同位素分馏作用原理,相对较轻的同位素由于蒸发作用散失掉,而使得重同位素水相对富集,这种同位素分馏的动力学原理解释了在蒸发海水环境下形成的泥–微晶白云岩自然要比正常海相灰岩类稳定同位素要偏正一些 [9] 。结合岩石学特征,反映了该类白云岩的形成与超浓缩高Mg/Ca粒间水或蒸发作用有关。但值得注意的是,该类白云岩δ
13 C
平均为1.979‰,δ18O平均为−4.405‰,与理想的准同生白云岩δ
13 C
、δ18O (δ
13C
平均为2‰ PDB,δ18O平均为3.8‰ PDB)相比,该类白云岩δ
13 C
与理想的准同生白云岩δ
13 C
十分符合,同样表明长兴组白云岩碳稳定同位素几乎不受成岩过程改造 [10] ;而δ18O则明显偏负,这并不影响对该类白云岩的成因解释,晚二叠世,研究区较大的一次海退事件,使台地边缘隆起带暴露并遭到强烈剥蚀,同期海水中混入了大量陆源淡水,由此奠定了准同生白云岩的低δ18O,同时反映了该高盐度的白云岩流体来源于上覆下三叠统飞仙关组地层所囚禁准同生海源孔隙水 [11] 。
3) 除准同生白云岩以外,其他各类白云岩的δ18O都较海相灰岩类偏负(表2),具有典型的埋藏特征。这种比同期海水偏负的现象一般认为是“温度效应”以及准同生白云石在埋藏条件下的“转化作用”所致。准同生白云岩中的欠稳定、有序度低的白云石,从地表环境进入埋藏环境时,会经历转化过程,

Table 1. Carbon and oxygen isotopic compositions of carbonate samples in Changxing Formation of the study area
表1. 研究区长兴组碳酸盐岩样品碳、氧同位素组成
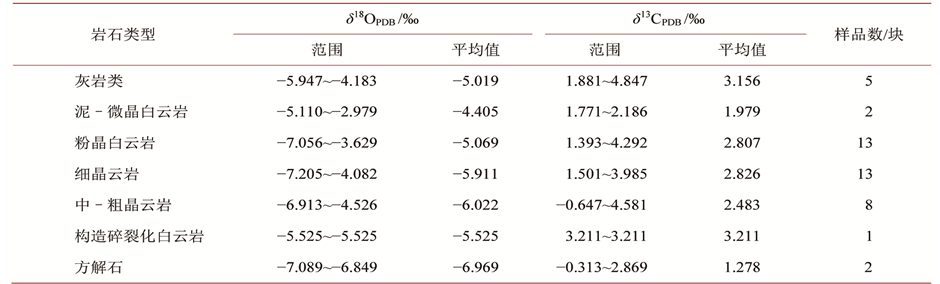
Table 2. The analysis results of carbon and oxygen stable isotope of various types of carbonate rocks in Changxing Formation of the study area
表2. 研究区长兴组各类碳酸盐岩碳、氧稳定同位素分析结果
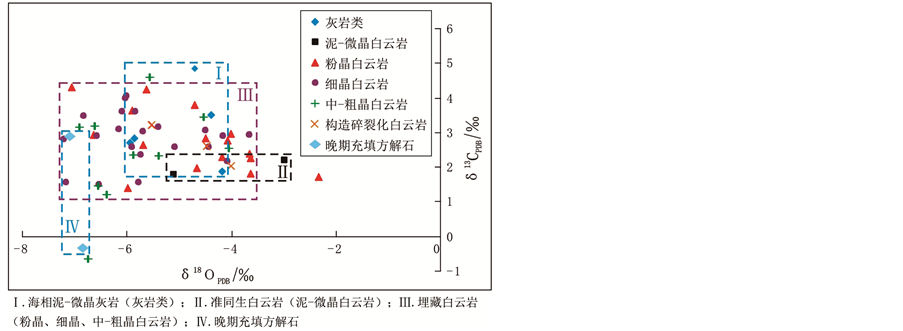
Figure 4. Relationship between δ
13 C
and δ18O of various carbonate rocks and cements
图4. 各类碳酸盐岩和胶结物的δ
13 C
与δ18O关系图
主要表现为重结晶和新生变形,此过程会使得白云石的δ18O在原来基础上向负值偏移,但是这种偏负效应不会“穿越”,即跨过同期海水的δ18O到达埋藏白云石的δ18O [12] ,该类白云岩的δ18O皆比海水的δ18O (−5.019‰)还要偏负,经过分析,可以排除该类白云岩的转化成因。而在埋藏条件下,由于温度升高,相对较轻的同位素氧优先进入到了白云石晶格中,在交代流体中相对富集重氧同位素,因此,埋藏条件下形成的该类白云岩自然具有比同期海水还要偏负的δ18O。
4) 对长兴组各类白云岩的δ18O进行对比分析,并结合岩石学特征,泥–微晶白云岩 → 粉晶白云岩 → 细晶白云岩 → 中–粗晶白云岩的δ18O具有随成岩强度加强而同步负增长的特点,以泥–微晶白云岩(准同生白云岩)负偏值最小,晚期方解石负偏值最大,其他类型白云岩介于两者之间。随着成岩作用的加强,相对重同位素氧吸附于先期交代的白云岩而逐渐消耗,因而表现出随成岩作用加强其δ18O逐渐降低。进一步表明了粉晶白云岩、细晶白云岩、中–粗晶白云岩皆为埋藏条件下交代成因 [13] [14] 。
5) 对全球寒武系至白垩系岩石中鞍状白云石,Allen [15] 曾做过统计,统计结果显示氧同位素变化范围为−18‰~−2.5‰,其中在−12‰~−5‰范围内最为常见,其均一化温度范围大致为80℃~230℃,这些资料表明鞍状白云石具有热液成因 [16] 性质。Allen同时对早期低温白云石δ18O统计显示,其变化范围为−9.0‰~−6.5‰,叠合在高温δ18O区间内。长兴组中–粗晶白云岩δ18O平均值为−6.022‰,结合岩石学特征其常见鞍状白云石晶体,反映了该类白云岩形成于相对高温流体中。而粉晶白云岩和细晶白云岩形成于相对低温流体中。
6) 研究区热液白云岩明显受构造控制,长兴组优质储层围绕广–旺海槽分布,即在拉张性断层控制下,盆地深部热液沿断层向上运移并交代碳酸盐岩岩层,由此形成热液白云岩,该类白云岩可以作为油气的储集相(HTD) [16] 。
5. 结论
1) 根据以上碳、氧稳定同位素分析,结合岩石学特征,表明泥–微晶白云岩为蒸发作用下形成的准同生白云岩,其他各类白云岩为埋藏成因,又δ18O逐渐偏负,成岩作用逐渐加强,粉晶白云岩为低温流体中早成岩阶段的产物,细晶白云岩形成于低温流体条件下中成岩阶段,而中–粗晶白云岩和构造碎裂化白云岩则为晚成岩阶段高温流体交代形成。
2) 结合中–粗晶白云石岩石学特征和碳、氧同位素分析结果,反映了该类白云岩成岩温度较高,在埋藏过程中,随上覆飞仙关组沉积物不断增多,长兴组碳酸盐岩埋深不断增加,温度逐渐升高,并在上覆沉积物压实作用下,热液流体沿断层向上运移从而使白云石化继续进行,有利于形成较好储集层。
3) 不同成岩环境下的白云岩,有各自的岩石学和碳、氧稳定同位素地球化学特征,因而对其岩石学和碳、氧同位素做综合研究,能够更加客观地反映白云岩的成岩环境。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金项目(41402090);2016年大学生创新创业训练计划项目(2016014)。
NOTES
*通信作者。