1. 引言
金属–有机骨架(MOF)是最近几年来逐步发展起来的一种新型功能性孔道材料,这种材料具有多种强大的功能,在存储、吸附、分离、催化领域及药物选择性分离和缓释等领域具有重要的生产意义和应用前景 [1] [2] [3] [4] 。在合成MOF孔道材料的过程中我们采用了刚性的羧酸配体,例如间苯二甲酸、间苯吡啶二酸、5-羟基间苯二甲酸等线性的桥联配体。一般情况下,由羧酸配体构筑可以支撑出稳定的框架,从而得到稳定多孔的MOF [5] [6] [7] 。
我们利用了含羧基的刚性桥联配体5-硝基间苯二甲酸。5-硝基间苯二甲酸中的5位上的取代硝基对间位上的两个所羧基具有活化作用。有关5-硝基间苯二甲酸的研究比较少,但其可以和多种金属离子形成配位化合物,在这些配合物中,配体展示了多种多样的配位模式,构筑了不同的配位聚合物 [8] [9] [10] [11] 。
Cu是一种重要的金属元素,属过渡金属,在空气中具有较强的抗腐蚀能力。在实际的化工生产过程中有广泛的应用:氯化亚铜不仅在无机化工中有重要作用,在有机合成工业中可做催化剂。是人体必需元素。由于铜是第四周期第一副族元素,价电子结构为3d104s1,具有空的电子轨道,能够接受配体的孤对电子,形成配合物。
本论文采用刚性配体5-硝基间苯二甲酸和铜反应,结合溶剂热反应,合成了一个新的稳定的超分子MOF孔道材料。
2. 5-硝基间苯二甲酸铜配合物(化合物1)的合成过程
2.1. 试剂与仪器
合成配合物实验所需试剂与仪器如表1。
2.2. 化合物1的合成
使用电子天平称取Cu(NO3)2∙6H2O 0.0048 g (0.02 mmol)和5-硝基间苯二甲酸0.0042 g (0.02 mmol)于20 mL反应釜中并加入1 mL DMF使其溶解并混合均匀,利用乙酸和三乙胺调制pH = 4,加入缓冲溶液后将反应釜搅拌10分钟后置于烘箱中,设定温度为140˚C,加热晶化3天,最终得到蓝色块状晶体。经清洗3次后过滤收集。产率约为0.2% (按Cu(NO3)2·6H2O计算)。
表1. 试剂与仪器
3. 5-硝基间苯二甲酸铜配合物的表征
3.1. 晶体学数据的测定
化合物1的晶体X-射线衍射数据是在SMART APEX II CCD单晶衍射仪上收集,石墨单色器,Mo-Kα射线,测试温度22.85˚C。晶体结构用最小二乘法F2精修改,用SHELXTL程序以直接法解析 [12] 。化合物中碳原子被理论加氢,并对所有非氢原子进行了各项异性的修正。对于化合物1,孔道内有溶剂配位,高度无序,见图1,化合物1的晶体学数据见表2,化合物1的键长键角数据见表3。
3.2. 化合物1的晶体结构
单晶X-射线研究表明该化合物是一个通过rod-like堆积作用形成的具有相当稳定性的二维层结构。表2中列出了与相关化合物一致的选择性键长/键角。在该化合物的基本建筑单元中如图1,包含三个Cu,三个5-硝基间苯二甲酸配体。Cu1与Cu2和Cu3中心的构型相同为标准的四方锥构型。每一个Cu中心与四个5-硝基间苯二甲酸上羧基氧原子,一个配位DMF上的氧原子配位从而完成五配体四方锥的配位模式。每个羧基以双齿桥联配位的模式连接两个Cu。
从空间堆积方式来看,如图2,每个Cu中心通过桥联羧基和桥联水分子连接相邻的Cu中心,形成了双核Cu簇。每个Cu簇连接四个5-硝基间苯二甲酸。每个5-硝基间苯二甲酸连接两个双核Cu簇,由于5-硝基间苯二甲酸配位模式类似间苯二甲酸,起到连接框架的作用,从而整个化合物为二维层结构。框架沿c轴方向含有菱形孔道。以孔道内相对的最近两个原子计,孔道直径为12.7 Å。孔道内填充了高度无序的水和DMF分子。 有趣的是两个Cu离子通过四个羧基配体联结成浆轮形。每个浆轮可以看成次级结构单元,每个浆轮状次级结构单元通过配体苯环进一步连接形成二维层状结构,非常有趣的形成不同结构孔道,未配位硝基指向六边形孔道内部。对于三个Cu离子和三个5-硝基间苯二甲酸分子间形成的配合物应该高度对称,但形成本文中的堆积方式并不常见,有可能与加入DMF,利用乙酸和三乙胺调制pH = 4有关。
尽管框架的孔道是由双核Cu簇棒状堆积形成的,框架十分稳定。从结构上看,每个单配合物单分子之间是交错结构,彼此间挤在一起,向任何方向均难以移动,所以框架稳定。其框架的稳定性也被红外

Table 2. Crystal data and structure refinement for compound 1
表2. 化合物1的晶体学数据表
aR1 = Σ||Fo|-|Fc||/Σ|Fo|; bwR2 = Σ[w(Fo2-Fc2)2]/Σ[w(Fo2)2]1/2.
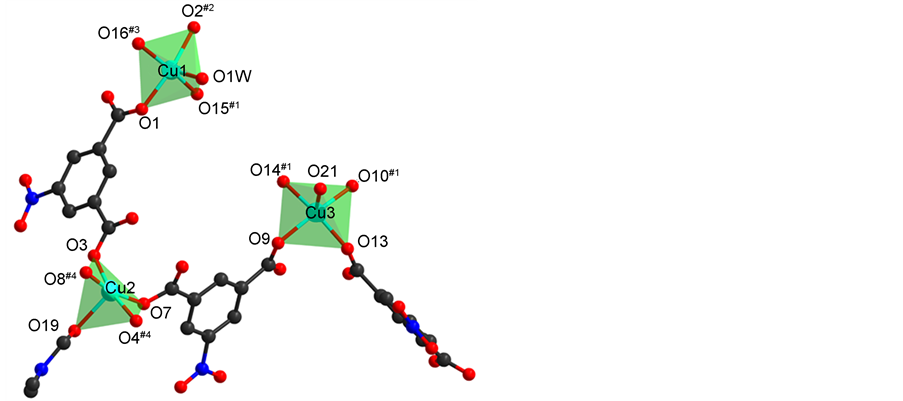
Figure 1. The coordination environment of the Cu (II) ion in compound 1
图1. 化合物1中Cu(II)离子的配位环境图

Table 3. Selected bond lengths (Å) and angles (˚) for compound 1
表3. 选择性键长 [Å] 和键角 [o]
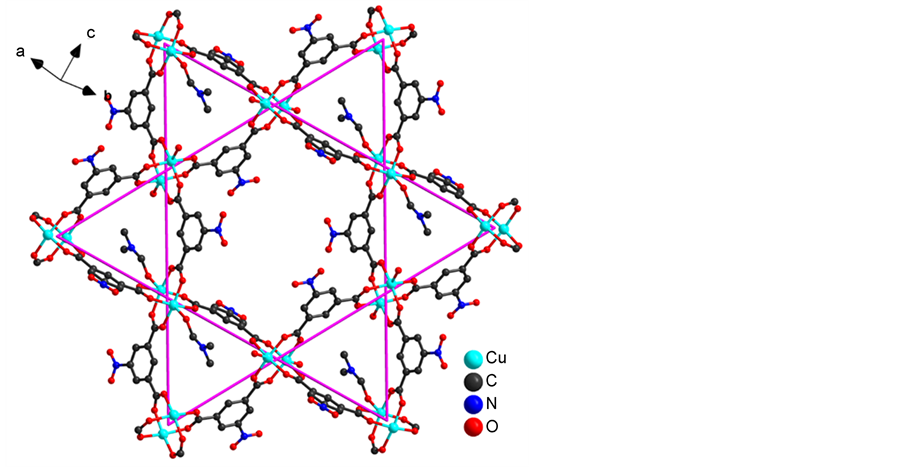
Figure 2. View of 2D layer structure of compound 1
图 2. 化合物1的二维层状结构
所证明。这种用双核Cu簇棒状堆积形成的稳定孔道是不多见的。
邻近的二维层之间又通过分子间氢键作用和芳环之间的π电子相互作用进一步扩展称为三维超分子结构(图3)。由于晶格水分子上的氢原子未能加上,所以具体的氢键相互作用未被讨论。芳环之间的π-π相互作用主要为螯合配体5-硝基间苯二甲酸分子之间较强的错位π-π堆积作用。
采用标准PLATON程序对该化合物进行了分析。结果表明溶剂可填充的有效体积为5520 Å3,化合物单胞体积V = 2149.1(16) Å3,有效孔积率为25.7%。尽管具有较小的孔积率,考虑到该化合物含有稳定的超分子纳米孔道,该化合物仍不失是一个好的有特点的孔道材料。
3.3. 红外分析
合成的该配合物中配体5-硝基间苯二甲酸在1725~1750 cm−1处的羧基的特征吸收峰,由图4此可以得出该配合物中羧基参与了配位,形成稳定框架。在1565~1543 cm−1处应归结为配体5-硝基间苯二甲酸中硝基的特征峰,配体在1400~1500 cm−1的吸收峰属于五硝基间苯二甲酸中苯环的特征峰。

Figure 3. View of the 3D structure for compound 1.
图3. 化合物1的三维结构
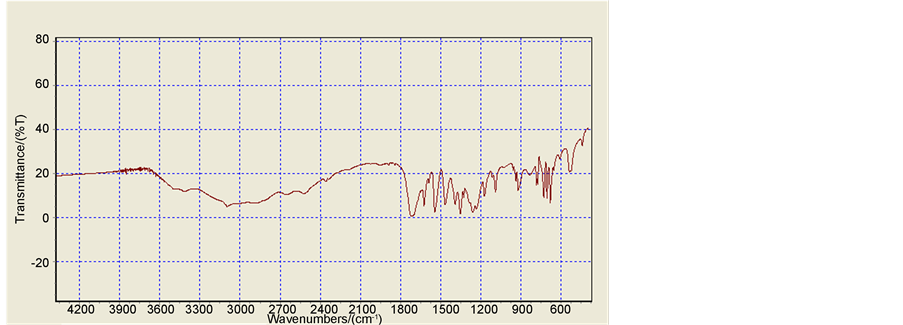
Figure 4. IR spectrum obtained from compound 1
图4. 化合物1的红外光谱图
4. 论文小结
本论文利用刚性桥连的羧酸配体,5-硝基间苯二甲酸作为中性桥连含氮配体,与过渡金属Cu反应,合成一个新的MOF孔道材料。结构分析表明该配合物属三斜晶系,空间群均P-1,a = 11.674(5) Å, b = 11.752(5) Å, c = 17.213(7) Å, α = 102.093(5)˚, β = 102.282(5)˚, γ = 104.251(5) (10)˚, V = 2149.1(16) Å3。我们对化合物进行了结构表征和初步的红外性质测定,得到了一些初步的结论。单晶分析表明框架具有稳定性,有可能会成为一个良好的稳定MOF。我们以后会进行荧光和热重性质的研究。
致谢
本论文得到2014年省教育厅“十二五”规划项目2014第396号《基于改性氨基酸的手性MBioF孔材料的合成及其对天然产物的手性分离》项目和大学生创新创业训练项目编号为201610202002《具有药物分离作用MOF膜的制备与应用开发》等项目的资助。
NOTES
*通讯作者。