1. 引言
长江河口是一个径流和潮汐动力作用为主的大型河口。大通站径流枯季约为10,000~15,000m3/s,洪季可达40,000~50,000 m3/s;口门附近中浚站的平均潮差2.7 m,大潮最大潮差可达5 m。沈焕庭等 [1] 和潘定安等 [2] 对长江河口潮波和潮流的分析,介绍了长江口潮汐的一般特征。谷国传等 [3] 给出了径流对长江口平均海面和潮差的关系。杨正东等 [4] 和刘新成等 [5] 分析了徐六泾以下若干站的年内潮差变化,发现3和9月份的平均潮差比其他月份要大,6和12月份则潮差年内最小。Cai等 [6] 采用解析模型,分析了引起长江河口平均水位沿程变化的动力原因。陈沈良等 [7] 研究发现,长江河口北支受径流影响较小,在喇叭形地形作用出现涌潮,区别于南支及其上游的潮汐特征。这些已有的研究成果,多侧重于某一方面,对径流、潮位、比降、潮流速以及它们之间的相互关系,缺乏整体的分析。
本文通过对大量实测水位、流速资料的分析,研究了长江口地区潮位的变化及其跟径流的对应关系,通过对潮差的研究探寻长江口径、潮流均衡区域的变化范围。通过对比降以及比降周期性变化与径流和潮差的关系的研究,揭示了长江口潮流速周期性变化滞后于比降的自然特性。这些研究成果,对长江口河道治理以及航道整治方案的制定,具有较好的现实意义。
2. 长江口潮位
长江口潮位具有随时间和沿流程变化的特征,其变化主要取决于径流与潮汐动力的相互作用。一般来说,离口门愈近受潮汐的动力作用相对愈强,离口门愈远受径流的影响相对愈显著;洪季径流作用相对强,枯季径流作用相对弱;在不同潮型中,大潮作用强,中潮作用相对较弱,小潮作用更弱 [8] 。因此,潮位与潮差在年际、年内、月内和日内都是一个复杂的变化过程,但又有其内在规律。
2.1. 潮位年际变化
长江口各代表水位站沿程分布见图1,近30年年平均潮位(1985国家高程基准)的变化见图2。由图可知,
Figure 1. Location of tide level stations at the Yangtze Estuary
图1. 长江口各潮位站位置
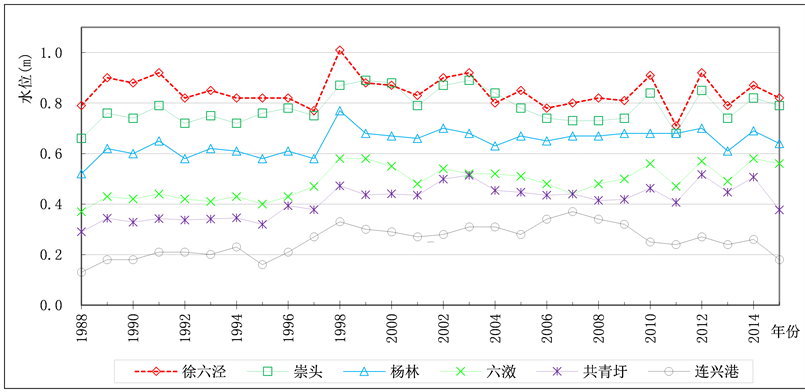
Figure 2. Annual average tidal level change of stations
图2. 各站年平均潮位变化图
徐六泾节点处徐六泾站和南、北支分汊处的崇头站,其年平均潮位在近30年没有趋势性变化。两站年平均潮位年际变化特性基本相似,多年平均值分别为0.85 m和0.78 m;年平均潮位变化幅度分别为0.30 m和0.23 m,年际变化起伏较大。代表南支河段的杨林站、北港下段的六滧站和共青圩站,其年平均潮位年际变化有一个共同的特点,即在1996年或1997年后有明显的抬高,但前、后两个阶段各自变化的幅度较小,也均小于徐六泾站的变化幅度。北支口门的连兴港站比较独特,年平均潮位最低,而且变化幅度最小。
影响各站年平均潮位的因素很多,也很复杂,其中径流应是一个重要的因素。从图2可以看出,上述各站中,徐六泾、崇头、杨林、六滧站的最高年平均潮位发生在大洪水年,即1998年或1999年,其对应的大通站年径流量分别达12,440亿m3和10,370亿m3,是1984年以来的第一、二位;共青圩站最高年平均潮位发生在2002年,对应的年径流量为9,926亿m3,也比较大。可见,径流量大的年份对徐六泾节点段、南北支分汊段、南支河段、北港中下段的年平均潮位具有显著的影响。然而,北支出口连兴港站最高年平均潮位发生在2007年,为0.37m,而相应的年径流量仅为7,685亿m3,比多年平均值8,900亿m3少14%。可见北支口门附近的年平均潮位的变化有其特殊性,径流对潮位的影响与潮汐动力作用相比,处于次要地位。
2.2. 潮位年内变化与径流的对应关系
表1列出了2009年和2010年大通站月平均流量。从小水年2009年来看,南京、镇江、江阴三站最高潮位为8月、7月,与大通站月平均流量大小完全相应,6月和9月也基本对应;以下天生港、营船港、徐六泾、白茆、杨林、石洞口、高桥(二)等七站,最高两潮位为8月、9月和次高潮位为7月、6月也与大通站径流基本对应,但最高两潮位滞后一个月。另一方面,在枯季,2009年白茆站以上各站最低潮位排序是1月、2月、12月、11月,与大通站径流量最小的排序完全一致,而杨林、石洞口、高桥(二)三站仅在11月份有所差异。可以认为,在小水年份,高桥(二)站以上河段的年内最高潮位发生与径流作用关系比较密切。以下横沙、北槽中、牛皮礁、鸡骨礁等站洪季和枯季的潮位与径流的不对应性沿程增强,但径流仍具有一定的影响。对于口门和口外区域,洪季的径流来量在该区域有汇集迭聚,致使汛后潮位抬高的特征。
用同样的分析看丰水年2010年,南京、镇江二站年内各月的潮位均与大通站流量排序相应;江阴、天生港、营船港、徐六泾等4站,最高潮位7月、8月与径流量相应,第三、第四高潮位为9月、6月,与径流排序第三、第四位相错;白茆、杨林、石洞口三站最高潮位为7月与径流相应,第二、第三、第四高潮位为8月、9月、6月,与径流排序相错。以下高桥(二)、横沙、北槽中三站,最高潮位段发生于7月~10月,整体上滞后了一个月,最高潮位则自7月转移至9月。牛皮礁、鸡骨礁与口外绿华等站,最高潮位为10月、9月,第三、第四高潮位为7月、8月,与径流不很对应,但毕竟还有径流的影响,也可看到口门附近和口外区域均有洪季径流来量汇聚迭加对汛后潮位升高的效应。同时,与小水年相比,这种效应的影响似更大更持久。
丰水年和小水年各站年内月平均潮位沿程变化的幅度都趋小,但石洞口站以上丰水年的潮位变化幅度大于小水年,而高桥(二)站以下小水年的潮位变幅大于丰水年。可以认为,石洞口以上受径流作用为主,高桥(二)以下受潮汐动力作用为主,二者之间的区域,径流和潮汐的动力作用相互交错,这大致也是南、北港分流的区域。当然这种判断和划分只是一个方面的参考。
3. 潮差
图3表明年径流量对长江口潮差的影响,可见以徐六泾站为界,以上直至南京站,丰水年2010年(年平均

Table 1. Monthly average flow at Datong station in 2009 and 2010
表1. 2009年和2010年大通站月平均流量(单位:m3/s)
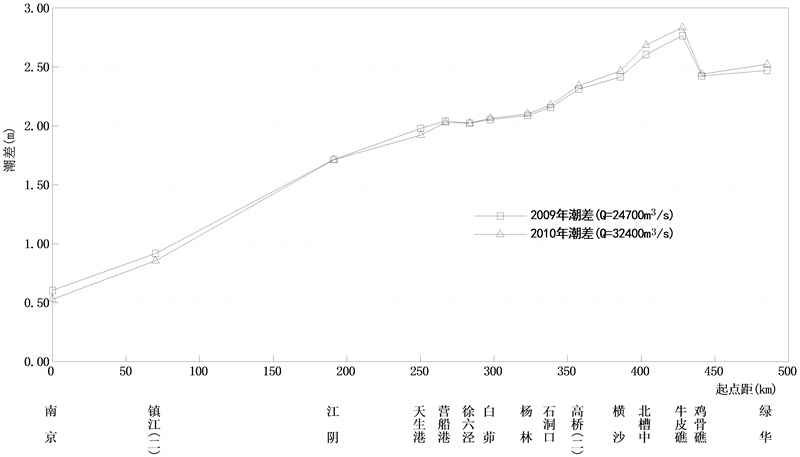
Figure 3. Variation of annual mean tidal range following Nanjing station
图3. 南京站以下各潮位站年平均潮差变化图
流量为32,400 m3/s)的平均潮差小于小水年2009年(年平均流量为24,700 m3/s)的平均潮差;徐六泾站以下直至口门外绿华站,都是丰水年的平均潮差大于小水年的平均潮差,而且距徐六泾站愈远,二者相差愈大。
图4表明在小水年(2009年)内洪季7月份(平均流量为40,000 m3/s)与枯季1月份(平均流量为11,600 m3/s),以及丰水年(2010年)内洪季7月份(平均流量61,400 m3/s)与枯季1月份(平均流量为12,400 m3/s)潮差的比较。可见小水年以白茆站至杨林站为区界,在白茆站以上,洪季的平均潮差小于枯季的平均潮差,杨林站以下至牛皮礁是洪季的平均潮差大于枯季的潮差,而口门处鸡骨礁和口外绿华站,又是枯季大于洪季平均潮差;丰水年以石洞口站至高桥(二)站为区界,其上、下均表现为与小水年潮差变化同样的规律,只是分界由白茆站~杨林站下移至石洞口站~高桥(二)站,这就是丰水年径流作用的结果。
综合图3、图4的共同特点是:① 长江口潮差变化有个分区界限,其上、下段遵循不同的规律;② 这个分区界限随径流的增大而下移;③ 最大潮差发生在进入口门处的牛皮礁站,反映了喇叭型口门潮汐波能传播横向汇聚的结果。
从潮差与潮位的关系(图5,图中数字为月份)可以看出,南京站和江阴站都为潮差随潮位的增大而减小,且涨落水过程基本呈单调升、降的变化特性;其绳套形曲线表明,同潮位下落水过程的潮差大于涨水过程的潮差。徐六泾站月平均潮差随潮位升高而减小的特征在小水年不太明显,在丰水年有一定的趋势,但同潮位下落水期的潮差大于涨水期的潮差,该特征在丰、小水年都十分明显。横沙站在丰水年和小水年总体上有潮差随潮位增高而有所增大之势,虽然这一关系很微弱,但与徐六泾及以上各站潮差随潮位增高而减小在性质上有差别,而且其潮差值较大,表明横沙站不仅潮差明显大于徐六泾站潮差,而且与潮位变化呈正相关趋势。
将横沙站的潮差和潮位与鸡骨礁站对比,鸡骨礁站每月平均潮位均明显小于横沙站,而潮差无论小水年还是丰水年,1~4月鸡骨礁的大于横沙平均潮差,而在5~12月都是横沙大于鸡骨礁的平均潮差。

Figure 4. The tidal range changes of each tidal station in January and July during flood and dry years
图4. 各潮位站小水年与丰水年的1月和7月潮差变化
 (注:图中横沙站的虚框位置与鸡骨礁站实框重叠,为看清楚关系,向左移动了一个框位)
(注:图中横沙站的虚框位置与鸡骨礁站实框重叠,为看清楚关系,向左移动了一个框位)
Figure 5. The relation curve between the monthly average tidal range and monthly average tidal level
图5. 月平均潮差与月平均潮位关系曲线
4. 比降
4.1. 比降年际变化
取长江口南支河段徐六泾站至杨林站和北港上段崇西站至六滧站、北港下段六滧站至共青圩站1984年至2010年平均比降值,分五个时段计算其平均值(见表2),表明徐六泾至杨林间平均比降在年际间有明显减小的趋势,崇西至六滧间和六滧至共青圩间两段比降总体也有减小之势。
分析表明,平均流量较大的丰水年虽然一般也出现较大的平均比降,如徐~杨段1995年、1998年和2010年,六~共段1997年和2010年,但与各时段大通站流量平均值相对照(表1、表3),可以看出径流并无系统增大和减小趋势,说明影响该三段比降年际间减小的主要原因不在于径流,这有待进一步研究。
在上述三段中,徐六泾至杨林间和崇西至六滧间比降的年际变化,每年都是年平均低潮位的比降大于高潮位的比降,而接近口门的北港下段六滧至共青圩间有大多数年份是年平均高潮位的比降大于低潮位比降。
4.2. 比降沿程变化
经分析,取南京、江阴、营船港、白茆、高桥(二)、北槽中、鸡骨礁、绿华等站2010年丰水年和2009年小水年的年平均潮位进行平均比降统计(见表3),可以看出,自径流河段经近河口段至长江口再到口外,其比降沿程变化的规律是逐渐减缓的,而且丰水年的平均比降大于小水年的平均比降。
4.3. 比降年内变化
从表3可以看出,无论丰水年还是小水年,南京以下各段都是洪季(7月)比降显著大于枯季(1月)比降。同

Table 2. Annual change statistics of average slope in the Yangtze Estuary
表2. 长江口平均比降年际变化统计

Table 3. Statistics of segment about slope from Nanjing station to the Yangtze Estuary
表3. 南京站至长江口外逐段比降统计
时,从表4来看,各段在枯季的比降均较小,变化不是很大,而在洪季由于丰、小水年径流相差较大,各段比降相差甚大,可见径流与比降的关系是比较密切的。
为进一步分析比降的年内变化,统计计算了径流段(镇江~江阴)、近河口段(江阴~营船港)、徐六泾节点段(营船港~白茆)、南支至南港(白茆~高桥(二))、南港至北槽段(高桥(二)~北槽中)、北槽口门段(北槽中~鸡骨礁)和北槽口外段(鸡骨礁~绿华)等在小水年和丰水年年内各月的平均比降值(见表4、表5),大通站2009年和2010年的月均流量见表1。由表可见,径流段至南港在丰水年和小水年年内比降随流量的增大而增大,其中径流段(镇江~江阴)变化最显著,且随流量的涨、落呈绳套形,而在近河口段(江阴~营船港)至南港(白茆~高桥(二))这一关系沿程减弱,在接近口门处(北槽中~鸡骨礁)比降与流量关系相关性减弱,当然还是可以看出略有上述比降随流量变化的趋势性和绳套形关系,说明愈接近口门,径流作用愈弱,而潮汐动力作用愈大。在鸡骨礁以外的口外,均呈现负比降,小水年和丰水年负比降值均很小,可见,径流较小的小水年来自口外的逆向平均负比降一般要大于径流较大的丰水年的逆向比降。
4.4. 比降与潮差的宏观关系
应当说,长江河口以及近河口段,其比降和潮差都是径流和潮汐动力相互作用中的两个要素。潮差代表了

Table 4. The monthly average slope of the following Zhenjiang stations during the year of 2009
表4. 镇江以下各站在2009年内月平均比降(10−4)

Table 5. The monthly average slope of the following stations in Zhenjiang during the year of 2010
表5. 镇江以下各站在2010年内月平均比降(×10−4)
水位升降的幅度即潮波的能量,比降则反映了径流和潮汐动力作用的态势,二者对水流的作用反映在涨落潮时对流速过程的影响。潮波上溯潮差沿程减小表明潮波能量的消耗,上、下断面之间潮位的变化决定了比降的大小及其周期性变化,所以比降变化与潮差之间在宏观上存在一定的对应关系。就是说,对于在径流和潮汐相互作用下的水流,潮差的沿程变化体现出一种能量的传递和消耗,它对水流做功体现在涨落潮过程中形成正负比降作用于水流并使流速产生周期性变化,从而在长江口河段驱使水流作往复性流动。
4.5. 潮流比降周期性变化与径流和潮差的关系
长江口随着潮位的涨落,对水流的顶托和消落致使水流的比降产生周期性变化。在涨潮阶段,水位的顶托产生负比降,在负比降的作用下水流产生逆向运动形成负流速,就是说使得原来向下游的径流加上潮汐传播的口门外的潮流一起向上游流动;在落潮阶段由于潮位的消落产生正比降,在正比降的作用下产生的正流速要将一个潮周期的径流量和涨潮期内的涨潮量一起向下游排泄。这种正、负比降和正、负流速是随潮差和径流大小以及平均潮位的高低而变化的。已有成果表明(表6),徐六泾~杨林的比降在丰水年(1998年)洪季(9月)、中水年(2005年)汛前中水期(5月)和小水年(2006年)枯季(1月)分别在大、中、小潮条件下实测潮位的比降统计值,可以看出在长江口节点段至白茆沙汊道段,其周期性变化中的最大正、负比降可以达到相当大的数值,远大于当地当时的平均比降。由于潮汐动力的作用,使得长江口以极小的平均比降汇入口外滨海的水流,变成以较大正、负比降作用下的往复流,特别是涨潮时的负比降更大说明潮汐动力驱使正向流动的巨大径流作逆向流动所提供的巨大能量。可以推测,这种正、负比降的数值在愈近口门处愈大。
5. 潮流速周期性变化滞后于比降的关系
在长江口往复流动中其驱使力直接来自潮位变化形成的比降。当下游水位高于上游水位时产生负比降,在这个负比降的驱动下,水流形成逆向流动的负流速;当下游水位低于上游水位时产生正比降,水流形成正流速。由于径流的存在并有其惯性作用,因而在潮流的周期变化中,流速的变化滞后于比降的变化。图6为2005年1月徐六泾与杨林站在枯季大潮中潮位、比降和流速周期性变化过程。从图中可以看出,在10时许开始涨潮,两站在波谷附近水位相等时比降为0,但在惯性作用下,上、下站流速仍处于减小过程尾端的正向落潮流状态,即仍为正流速;不久,下站(杨林)水位高于上站(徐六泾)水位之差值愈来愈大,形成负比降并愈来愈大(说明:描述正、负比降和流速的增大和减小均指绝对值,下同),下站正流速先降到0并随之形成负流速且愈来愈大,上站正流速随后减为0并随之形成负流速且愈来愈大;当负比降达最大值又变为减小时,两站的负流速一直在增

Table 6. The slope under different hydrologic combination between Xuliujin and Yanglin stations
表6. 徐六泾~杨林在不同水情组合下比降

Figure 6. The hydrographs of tidal level, slope and velocity at Xuliujing and Yanglin stations
图6. 徐六泾站与杨林站潮位、比降和潮流速过程线
大,直到负比降减小过程中某一时刻,下站和上站的负流速达到最大值;然后随负比降继续减小,两站负流速也减小。当负比降减小为0,即两站潮位在波峰附近相等时则开始进入落潮阶段,此时仍由于潮流的惯性作用负流速还在维持并继续减小;随着正比降形成并不断增大,上站、下站负流速先后减小至0并转为正流速;然后随着落潮过程正比降的增大,两站的正流速也增大,至正比降达最大值转为减小时正流速仍在增大,直到正比降减小过程的某一时刻,下站和上站正流速达到最大值;再随着正比降继续减小,两站正流速也减小,直到比降为0而进入第二个涨潮阶段,两站的正流速因径流存在及其惯性作用而仍保持为落潮流较小的正流速。以上就是比降与流速变化周期的全过程。综上所述,流速对于比降的滞后性表现在:涨潮阶段,当比降为0时,上、下站流速仍为正流速,其正流速减小为0的时间滞后于比降为0的时间,其中上站滞后的时间比下站更长;两站负流速达到最大值的时间滞后于负比降为最大的时间,其中也是上站滞后的时间更长。落潮阶段,比降为0时,两站还存在一定的负流速,两站负流速转为0的时间滞后于比降为0的时间,其中上站滞后的时间更长一些;两站正流速达到最大值的时间滞后正比降为最大的时间,其中也是上站更加滞后,而且与涨潮阶段相比,滞后的时间更长。
6. 结论
长江口河段的潮位、比降和潮差有显著的时空变化特征和规律。在南京以下直至长江口门的范围内,年平均潮位向海沿程降低,比降沿程减小,并呈下凹形曲线。年平均潮差表现为从上游向海方向逐渐愈大,在牛皮礁站达到最大,体现了潮汐动力作用沿程不断增强的特性。
长江口潮位、比降和潮差三因素的时空变化及其相关关系受到径流和潮汐动力双重作用的影响。对于口门和口外区域,汛期径流来量的汇集迭聚,以致汛后潮位抬高。从宏观月平均潮位和比降与月平均流量关系曲线来看,愈近下游口门绳套曲线的斜率愈平缓,同流量下汛后落水阶段与汛前涨水阶段相比,潮位和比降相差的幅度愈向下游愈小,而月平均潮差与月平均流量的绳套形曲线的斜率为负向(即该站潮差随流量增大而减小),且愈向下游愈平缓,但同流量下落水阶段与涨水阶段相比,潮差的相差幅度愈向下游愈大。以上特性进一步体现了愈向上游受径流作用相对愈大,而愈近下游口门受潮汐动力作用相对愈强的特性。
长江口由多年平均潮位确定的纵向比降值很小,年内各月无论丰水年或是小水年,由月平均潮位确定的比降值也较小,但由断面间潮位呈周期性变化的瞬时比降值却相当大。这个正、负值均很大且呈周期性变化的比降是形成长江口双向流动力的重要机制,而长江口潮流速周期性变化滞后于比降变化是源自水流惯性的必然。
径流与潮汐相互作用是长江口水流及相应的泥沙运动的动力之源。长江口愈近口门,潮差愈大,潮位顶托和消落愈强,提供潮汐动力的能量愈多,因而产生的瞬时比降愈大,形成的涨、落潮流的流速和潮量也愈大。应该说,潮汐动力和巨大的径流量一样,是长江口河床演变的动力因素,也是一种资源。