摘要:
本文通过对山东省沿海地区的地下水资源分布和质量状况的调查,评估省区的地下水资源分布、类型和水质水量以及可开发利用的潜力。调查研究表明:沿海大部分地区地下水主要以基岩裂隙水(浅棕色区域)为主,径流模数小于50,000 m3/km2•年,多年平均地下水天然补给资源量为216.38亿m3,可开采资源量为178.65亿m3。其中,淡水、微咸水天然补给资源量为206.19亿m3。目前,开采现状为123.30亿m3。其中,工业开采27.09亿m3,农业开采77.84 m3,生活用水18.37亿m3。为实现地下水资源的可持续利用,建议采取如下措施:1) 加强地下水开采管理。2) 合理规划,适度开发。3) 采用污水集中收集处理措施和封闭式循环水系统。4) 加强地质普查与水质监测。5) 继续开展井盐水利用与海水入侵关系研究,确保地下水养鱼能迈向可持续发展。
Abstract:
Based on the investigations of distribution and quality of the underground water resources in the coastal of Shandong Province, we assess provincial underground water resources distribution, type and water quality as well as the exploitable potential. The results showed that large part of coastal underground water was in bedrock fissure (light brown). The runoff modulus is less than 50,000 m3/km2/year. Average annual natural recharge of underground water resource is 21.638 billion m3, and the exploitable resources amount is 17.865 billion m3. The natural supply of fresh water, brackish water resource amount is 20.619 billion m3. At present, the extracting amount is 12.33 billion m3. Among them, the industrial exploitation is 2.709 billion m3, agricultural exploitation is 7.784 billion m3 and 1.837 billion m3 of water for daily life. In order to achieve sustainable use of underground water resources, we recommend the following measures: 1) To strengthen underground water management 2) To plan appropriate development of flounder fish culture. 3) To use closed circulating water system and sewage collection and treatment measures. 4) To strengthen geological survey and water quality monitoring. 5) To study on salt water and seawater intrusion, and ensure that fish can move towards sustainable development of groundwater.
1. 前言
1.1. 山东省海洋地理概况
山东省地处暖温带,位于北纬34˚30'~38˚15'、东经114˚50'~122˚50'之间,濒临渤海和黄海。海岸线长达3300多km,占全国的六分之一,毗邻海域面积超过14万km2,与陆地面积相当,日照充足,拥有丰富的海洋生物资源。沿海海岸线曲折漫长,可供增养殖的水域广阔,水质优良,温度适宜,交通便利,自然与社会条件有利于海水增养殖业的发展。
1.2. 山东省海水养殖概况
山东省是海洋渔业经济大省,伴随着国家海洋捕捞“零”增长政策的实施,海水养殖在山东渔业发展中的作用和地位愈发举足轻重。山东的海水增养殖业从二十世纪五十年代开始,经历了海带、对虾、扇贝、鱼类的几大养殖浪潮后,在21世纪,励精图治,向新的目标迈进。
目前的海水增养殖方式主要包括池塘养殖、底播养殖、筏式养殖、网箱养殖和工厂化养殖等多种模式。养殖苗种培育产业逐步壮大,苗种培育技术日臻成熟,渔业资源放流增殖制度逐渐完善,规模逐渐扩大。渔业产量、产值、出口创汇等主要经济指标继续在全国保持领先地位。
2. 调查的目的和方法
2.1. 调查目的
沿海地下水资源的分布和质量状况直接决定鲆鲽类养殖产区的规划、养殖模式以及养殖质量。在国家鲆鲽产业体系项目支撑下,调查小组对山东省养殖主产区地下水资源情况开展调查,旨在摸清省区地下水资源的分布、类型、水量和水质情况及可开发利用潜力,以及当地养殖户对当地地下水资源的开发利用情况,调查结果为集成、优化我国鲆鲽类现有循环水养殖系统,构建全封闭式和半封闭式循环水养殖工厂和技术体系提供基础材料。
2.2. 调查时间、范围
调查小组于2011年5月~11月期间对山东省7个沿海城市青岛、烟台、威海、潍坊、东营、滨州和日照进行了走访调研,往返行程近3000公里(图1)。调查对象包括当地养殖场和海洋与渔业局。
2.3. 调查方法
1) 前期资料收集准备;
2) 走访当地养殖户,现场记录、拍照和摄像,弄清养殖种类、养殖模式、养殖用水情况,该地地下水资源状况及已开发利用情况等;
3) 记录养殖园区坐标范围,绘制养殖园区分布图和地下水资源分布图。
3. 调查结果
3.1. 山东省地下水资源概况
根据山东省地下水资源分布图 [1] [2] [3] (图2),山东省沿海大部分地区主要以基岩裂隙水(浅棕色区域)为主,径流模数小于5万立方米3/千米2·年,东营和滨州沿岸主要为咸水(网格状区域)分布区域,在莱州、龙口、即墨、胶南和日照沿岸有少量松散岩类孔隙水分布,径流模数在5~10万m3/km2·年。山东省地处暖温带,濒临渤海和黄海。海岸线长达3300多km,占全国的六分之一,毗邻海域面积超过14万km2,可供增养殖的水域广阔,有利于海水增养殖业的发展。

Figure 1. The survey road map of coastal groundwater in Shandong province
图1. 山东沿海地下水调查路线图

Figure 2. Distribution of underground water resource in Shandong Province
图2. 山东省地下水资源分布图
3.2. 山东省地下水补给和使用概况
根据国土资源部调查报告表明山东省多年平均地下水天然补给资源量为216.38亿m3,可开采资源量为178.65亿m3 [4] 。其中,淡水、微咸水天然补给资源量为206.19亿m3,可开采资源量为170.45亿m3。目前,开采现状为123.30亿m3。其中,工业开采27.09亿m3,农业开采77.84亿m3,生活用水18.37亿m3。其中,潍坊、烟台、青岛和日照沿海地下水开采量较大 [5] (图3,紫色区域)。
3.3. 山东省鲆鲽类养殖区分布
目前山东省工厂化养殖(大棚养殖)规模已达到499.6万m2,大多数利用地下海水和卤水养殖温、冷水性鱼类,少数利用自然海水养殖,工厂化养殖建设比较密集的区域有潍坊滨海开发区岸段、莱州朱旺至刁龙嘴岸段、蓬莱解宋营岸段、烟台开发区八角至上刘家岸段、荣成寻山岸段、乳山徐家岸段、海阳大闫家岸段、胶南大场岸段及日照涛雒岸段(图4)。主要养殖鲆鲽类的种类为大菱鲆、褐牙鲆、漠斑牙鲆、大西洋牙鲆、半滑舌鳎、条斑星鲽、圆斑星鲽、星突江鲽等、此外,利用地下水养殖的种类还有虾类(凡纳滨对虾、中国明对虾)及刺参、皱纹盘鲍等。
4. 讨论和建议
地下水是可以修补和持续开发利用的资源,为合理进行地下水的可持续开采,实现地下水资源的可持续利用,建议采取如下措施:
1) 加强地下水开采管理。地下水资源需要合理开发利用并有效保护,才能被持续利用。明确管理部门,落实管理措施,对地下水资源统一规划,保护和管理。
2) 合理规划,适度开发。以地下水量来决定养殖面积,按照具体情况,进行点状开发,按条状或带状发展。开发前期做好地下水资源量勘测和水质分析,避免盲目投资。
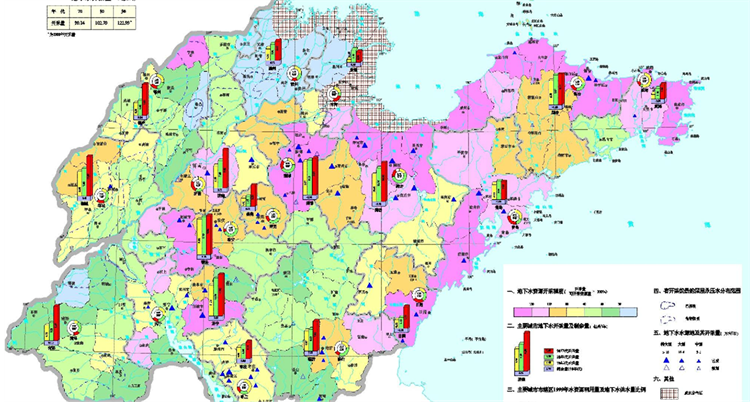
Figure 3. Present situation of exploitation and utilization of underground water resource in Shandong province
图3. 山东省地下水资源开发利用现状图

Figure 4. Coastal intensive factory farming areas in Shandong Province
图4. 山东沿海工厂化养殖集中地区
3) 采用污水集中收集处理措施和封闭式循环水系统,既缓解了经验水的短缺又减轻了无水对海域的污染,封闭式循环水养殖系统可节约60%~70%的地下水。
4) 加强地质普查与水质监测。建立地下水动态监测网,对地下水开采量、地下水水位、水质进行系统监测,为合理开发利用水资源提供科学依据。
5) 继续开展井盐水利用与海水入侵关系研究。采取谨慎严肃的态度,确保地下水养鱼能迈向可持续发展的新阶段。
基金项目
国家鲆鲽类产业技术体系建设项目(CARS-50)。