1. 引言
高浓度氯离子废水来源主要有冶金、制革(鞣革)、化学制药、造纸、电厂脱硫废水等行业所排放的工业废水以及人类生活所产生的生活污水,其中工业排放是最主要来源,氯离子是氯最为稳定的形态,微生物不能利用Cl−,并且废水中氯离子含量会抑制微生物的生长,阻碍生物法处理废水效率。目前废水中氯离子的去除方法主要有离子交换 [1] 与化学吸附法 [2] 、沉淀法 [3] 、膜处理法 [4] 、蒸发法、电吸附法 [5] ,冷冻法 [6] [7] 微电解法 [8] 等,但这些方法都存在缺点,其中离子交换与化学吸附法,吸收率低,树脂交换膜容易达到饱和,需要再生 [9] ;沉淀法所使用的沉淀剂成本昂贵 [10] ;分离拦截法如果氯离子浓度过高会超过膜分离技术的界限并且造成大量有机物对膜产生污染 [11] ,同时费用过高;蒸馏法能耗高,且容易结垢,只适用于小量废水;电渗析法及电吸附法对进水水质要求高,处理成本较高 [12] 。
本论文设想通过电化学方法,利用氯碱工业催化脱氯原理 [13] [14] [15] 及本课题组专利“ZL 2012 1 0398371.0” [16] “一种活性炭篮作阳极电化学降解有机废水的方法及装置”的一种篮式阳极装置的方法相结合。阳极为塑料或难溶金属(如钛篮)制作的网状篮或框,里面填充有颗粒状的由本研究制备的Ru-Ti-AC多孔催化材料。这样,整个电化学过程中,阳极的作用有两个:1) 不断地通过阳极正电荷的电场力的吸附作用和Ru-Ti-AC催化材料大的比表面积的吸附性能把废水中的氯离子浓缩到本方法所述的篮式阳极上,2) 把浓缩过来的氯离子,又通过Ru-Ti-AC催化材料的催化作用在大大降低氯离子过电位的作用下,由阳极电流氧化成氯气源源不断地分离出去 [17] ,本文首先用溶胶凝胶法制备了Ru-Ti-AC催化材料,然后使用Ru-Ti-Ac催化材料的电极在不同的入水PH,反应时间,电流密度等因素条件下探讨对废水中氯离子的去除效率,通过间断性实验和连续性实验分析各个部分氯的含量,确定氯离子的去除途径和去除机理,同时通过工业化实验验证了该种电极催化方式对实际高氯脱硫废水的氯离子处理效果。
2. 材料和方法
2.1. 钌钛活性炭复合电极的制备方法
(1) 将活性炭用5%硝酸水溶液泡12~36 h,过滤后将滤饼用去离子水洗涤至检测到洗涤液的pH值为7,然后将滤饼在100℃的干燥箱内烘干,获得预处理后的活性炭,备用;
(2) 将(1)所述预处理后的活性炭与氯化钌溶液,钛酸丁酯、柠檬酸混合,搅拌均匀后制得混合反应液,然后向所述混合反应液中逐滴滴加碱性水溶液,调节反应液的pH值为6.5~8.5,再在70℃~90℃水浴条件下反应1 h,反应结束后生成粘稠状浆液;其中Ru与Ti质量分数占所制备Ru-Ti活性炭总质量20%,Ru与Ti摩尔比为1:2。
(3) 将(2)所述制得的粘稠状浆液在100℃~120℃恒温油浴中蒸干,将蒸干后得到的固体置于120℃~150℃干燥箱中烘干,制得含金属钌钛氧化物(或氢氧化物)的活性炭固体;
(4) 向(3)所述得到的活性炭固体中加入P2O5粉末,混合均匀后置于马弗炉中在300℃~700℃条件下焙烧3~7 h,冷却后,得到所述的Ru-Ti-AC催化材料。
2.2. 实验装置
参照专利“ZL 2012 1 0398371.0一种活性炭篮作阳极电化学降解有机废水的方法及装置”,设计一电化学处理装置,见图1,一种篮式阳极,阳极为塑料或难溶金属(如钛篮)制作的网状篮或框,里面填充有大颗粒状的活性炭与催化剂 [18] ,填充方法为活性炭与催化剂颗粒互混,阴极为惰性电极纯活性炭,电源为恒流电源,容器上部装有圆锥形上盖通过导管连接到装有5% NaOH溶液的容器,收集电解过程产生气体。
2.3. 试验用水
实验用水分为两个部分,第1部分为模拟高盐度废水,由NaCl配置的氯离子浓度为12,000 mg/L,第2部分为实际的高浓度氯离子脱硫废水,废水pH为8.26,Cl−浓度为11,787.13 mg/L。
2.4.1. 氯离子去除单因素实验
配置12,000 mg/L固定浓度的氯离子模拟废水,分别改变模拟废水PH,电解时间,电流强度等实验条件,通过单因素实验判断去除氯离子的最佳反应条件。
2.4.2. 氯离子去除机理研究实验
为研究该方法去除氯离子机理,配置氯离子浓度为12,000 mg/L的模拟废水,在上述最佳反应条件下进行多次重复实验,分别收集反应结束时反应装置中气体、剩余水和生成的絮状物,用以分析氯离子去除途经。将收集的气体,用5%的NaOH溶液吸收,絮状物用马弗炉烧至灰分,剩余的水,通过国标法硝酸银滴定测量其中氯离子含量,并对使用前后的Ru-Ti-AC催化电极进行SEM和EDX测试观察其变化 [19] 。
2.4.3. 实际高含量氯离子废水(电厂脱硫废水)氯离子处理效果试验
在以上单因素实验室试验所得最佳反应条件下,实际测试该方法对电厂脱硫废水)氯离子的处理效果,

Figure 1. Schematic diagram of experimental set-up
图1. 实验装置图
计算氯离子去除率。
2.5. 分析与测试方法
2.5.1. 水质检测
水质、pH、Cl-的检测采用国家标准方法。
2.5.2. 催化阳极性能表征
Ru-Ti-AC催化材料的表征,将水处理前后的催化剂和未经处理的三种活性炭小颗粒进行SEM电镜扫描和EDX测试(JSM6510LV)来表征其表面结构和物质组分构成。
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 氯离子去除效率
对于电化学反应通常情况下是在中性条件下进行 [20] ,一般条件PH值在6和7之间,呈弱酸性。氯离子发生氧化反应的最佳PH值的范围为6~7,这时氯离子不受溶液中其他离子的在点解过程中氧化还原的影响,即产生阴阳极发生反应的优先级竞争。当溶液ph远小于7时,溶液中H+向阴极移动减少了阴极材料与溶液的接触;或者当溶液偏碱性时,溶液中OH−向阳离子移动,在阳极发生氧化反应生成氧气,这与氯离子移向阳极发生氧化反应相竞争,减少了氯气的生成。通过以上条件可以分析出,溶液为中性时对氯离子的降解拥有最佳的促进作用。
确定入水PH为7,Cl−浓度12,000 mg/L,电流密度400 mA,分别改变电解时间进行实验,如图2所示,Cl−去除率随电解时间增大而增大,60 min时达到80%左右,60 min后Cl−去除率增加放缓,因此实验采用停留时间60 min。
确定电解时间为60 min,入水Cl−浓度为12,000 mg/L,电流密度400 mA,改变进水PH研究PH对Cl−去除率的影响,结果如图3所示,PH为7时去除率最高。
确定入水PH为7,Cl−浓度12,000 mg/L,电解时间为60 min,改变电流密度以研究电流密度对Cl−去除率的影响。图4所示结果,在以上反应条件下,电流密度在400 mA时,Cl−去除率即可达到最高,电流密度小于400 mA时,Cl−去除率下降,电流密度高于400 mA时,Cl−去除率无明显增长。
3.2. 复合电极的组分以及表面结构
将负载钌钛催化剂前后的活性炭电极,分别制样,用测定EDX和SEM以研究组分和表面结构。图5、图6分别为EDX和电镜扫描图片。根据图5中特征峰显示,Ru与Ti以氧化物形式负载于活性碳上,且比例与制备配比相同为1:2。图7中的A、B为负载催化剂前的电极表面特征,可以看出,经活化处理的活性炭电极为多孔状,这能提高微电解过程中电子转移效率,增加反应电子的对数,因此有较强的吸附Cl−和降解的能力 [20] [21] 。图7中C、D为负载催化剂后电极表面特征,可以看出Ru-Ti催化剂均匀负载在活性炭表面,且表面存在粗糙龟裂和大量空腔,拥有更大比表面积,在吸附Cl−的同时高效氧化Cl−。
3.3. 钌钛活性炭复合电极催化机理研究
为更好地研究Cl−去除的机理,配制Cl−浓度为12,000 mg/L的NaCl溶液,通过静态实验,在最佳反应条件下进行多次重复实验,分别分析出水、絮凝沉淀、收集的气体中氯的含量,用来确定Cl−的去除途径。由图7可以直观地看出,Cl−的整体去除率大约80%左右,其中大部分以气态形式逸出,小部分的Cl−被复合电极吸附,更小部分通过絮凝去除。
气体主要成分为Cl2,由此可见去除氯离子途径主要是将氯离子氧化为氯气释放,催化机理如下 [15] :
(1) 通过阳极直接对电极上吸附的氯离子催化作用:
阳极反应:
(氧化反应)
(2) 上述吸附氯离子的反应是由在电解过程中阳极电极表面产生的一系列中间反应达成,用xPS分析处理过高盐度废水后的RuO2和RuO2-TiO2表面发现RuO3缺位结构并发现表面有两种类型的氯,一种为Cl−离子,一种为Cl·原子,反应如下:
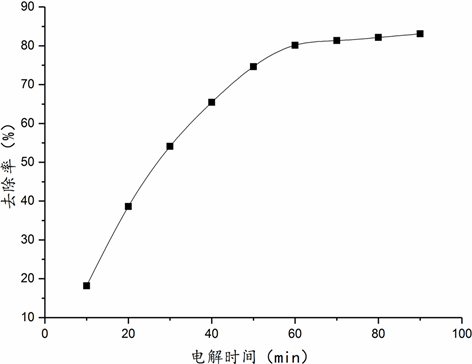
Figure 2. Effect of Electrolytic time on Cl− removal rate
图2. 电解时间对Cl−去除率的影响
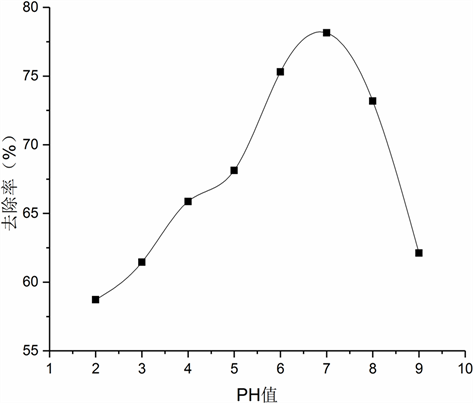
Figure 3. Effect of PH on Cl− removal rate
图3. PH值对Cl−去除率的影响
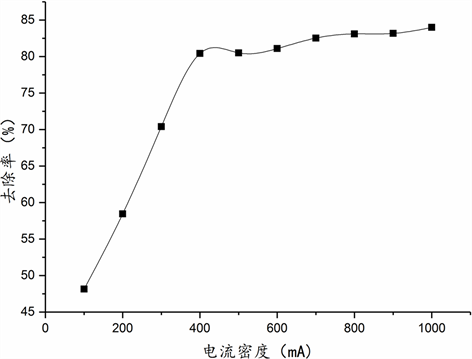
Figure 4. Effect of electric current density on Cl− removal rate
图4. 电流密度对Cl−去除率的影响

Figure 5. Effect of electric current density on Cl− removal rate
图5. 电流密度对Cl−去除率的影响
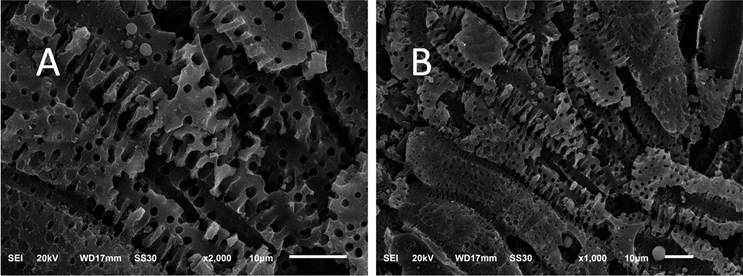

Figure 6. SEM photograph of activated carbon and activated carbon with supported Ru and Ti
图6. 负载Ru-Ti催化剂前后活性炭的扫描电镜图片

Figure 7. Cl− content percentage in various components
图7. Cl−在各个组分中的平均分布
或
随后按
3.4. 去除率最高的条件下电极材料的耐久性
通过重复性实验,配置Cl−浓度为12,000 mg/L的实验用水20份,PH为7,电解时间为60 min的条件下重复性实验20次,EDX测试如图8,负载催化剂的阳极成分含量未发生较大变化,反应结果如图9所示,可以看出该Cl−去除率稳定在70%以上,耐久性高。
3.5. 脱硫废水中氯离子的处理
根据以上实验,可以看出该催化电极对氯离子的去除有较好效果,现利用该方法对实际高氯脱硫废水进行处理,采用单因素实验确定的最优反应条件,即pH为7,电解时间为60 min,电流密度大小为

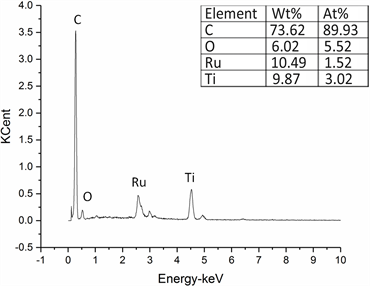
Figure 8. EDS result of activated carbon
图8. 重复试验后负载催化剂电极的能谱测试结果

Figure 9. Cl− removal rate correspond to each experiment
图9. 试验次数对应的Cl−去除率
400 mA,对出水水质的分析结果见图10,反应时间60 min时,Cl−去除率为75%。
4. 结论
(1) 本研究中钌钛复合活性碳电极材料(Ru-Ti-AC)对废水中的Cl−有较好去除效果,去除途径有电解生成Cl2,絮凝吸附和电吸附等,但主要途径为电解生成Cl2。
(2) 通过Ru-Ti氧化物催化剂的催化作用,大大降低氯离子的氧化过电位,SEM电镜扫描显示复合电极表面存在许多微孔,拥有大的比表面积,在吸附氯离子的同时高效氧化废水中的Cl−,EDX结果显示,电极相中含有NaCl,电极对NaCl有较强的吸附能力。

Figure 10. Cl− removal rate reality FGD wastewater
图10. 实际脱硫废水的Cl−去除效率
(3) 此种钌钛活性炭复合电极材料(Ru-Ti-AC)对实际高盐废水也有较好的处理效果,高盐脱硫废水在最佳条件下Cl−去除率能达到75%以上。
(4) 针对高氯废水的处理,此种工艺流程简洁,处理时间短,是生物处理前预处理较理想的处理方法。