大气中CH4、CO2、N2O是最重要的温室气体,对温室效应的贡献率近80% [1] ,由此引发的一系列生态环境问题,受到人们的广泛关注。为了改善现状,人们积极采取各项节能减排措施。同时从农田生态系统出发,农田土壤和作物排放的气体主要成分为CH4、CO2、N2O,对生态环境影响较大,因此许多学者在此领域也进行了多方面的研究 [2] [3] 。很多地区通过静态箱法进行过土壤和矮秆作物的温室气体的收集测定与研究,它是研究农业源温室气体的重要方法之一,不论是在水田、旱地还是草地,甚至是森林中,都得到广泛应用 [4] 。近年来,采用的静态箱种类繁多,在对土壤和作物温室气体排放的研究中发挥重要的作用。2013年,来自中国农业科学院的李迎春等人描述了一种用于收集麦田温室气体的便携式装置,该装置包括环形底座与静态箱,所述环形底座与静态箱配合,环形底座的顶部上设有水封凹槽,静态箱的下部为开口,静态箱的顶部设有第一开孔与第二开孔,第一开孔中设有高弹性硅橡胶塞 [5] 。此外中国农业科学院万运帆等人公开了一种可上下自动开闭温室气体取样箱,用于农林业环保温室气体自动取样监测,能提高大气温室气体测量的自动化程度,减少与自然条件下环境的差异性 [6] 。
目前,大部分温室气体收集装置仅仅适用于单作模式下的大豆、水稻等矮杆作物 [7] 。由于玉米高度过高,设计难度系数相对增大,所以基本上没有针对像玉米这种大型高秆作物或间套作模式下设计过静态箱装置的记录 [8] 。在科学研究中,结果的获取在很大程度上依赖于研究方法和工具。针对此现状,本文介绍了一种适用于间套作模式下温室气体收集装置的结构和使用方法,该装置可根据共生作物调节容量和分层收集,以及不同时期的高度调节取气口的位置,适用于后期有效地测定作物排放的温室气体CH4、CO2、N2O含量,并通过不同大豆套种方式来验证该装置对温室气体的收集效果,为完善该装置提供技术参数。
1. 温室气体收集装置设计
1.1. 基本原理
在作物的间作或套作模式下,首先将底座下侧开口插入土壤中并向下插入一定的深度以固定于土壤中。然后根据作物高度,将加长版集气箱或加长版取气箱连接在底座上侧,在作物的生长过程中,可根据作物的高度变化增减集气箱数量,调节取气高度。在取气前,用橡胶夹子关闭用于保证气压平衡的接口,打开设置于取气箱壁的风扇,保证箱内气体混合均匀。取气时,打开用于保证气压平衡的接口,拉动注射器,即可实现气体的收集。在此静态箱组合安装完成后,大体呈“L”型,加长箱层内设有百叶隔板,百叶隔板处于闭合状态时,可单独收集一种作物排出的温室气体,百叶隔板处于连通状态时,可收集套作状态下的温室气体。
1.2. 温室气体收集装置结构设计
本装置根据套作共生气箱层,其中加长高矮作物呈“L”形结构。该装置包括风扇、取气箱层、集气箱层、百叶隔板、三通阀、橡胶套等。本装置的各个组件连接紧密,每个箱层之间设置有榫卯结构,通过凹槽与凸起对应连接,组装和拆卸均方便快捷。此外,该装置包括不锈钢框架、不锈钢框架上的透明PC塑料板和用于密封PC塑料板与不锈钢框架的连接处的橡胶件,以保证箱体每个边部的密封性和箱体的强度。
底层是锯齿状底座,四角设计为三角形,尺寸为200 × 50 × 30 cm (长 × 宽 × 高,下文提到的尺寸均以此为标准),利用三角形的稳定性,便于插入土壤中。
中层为加长版集气、取气箱层,其中集气箱层为没有底盖和顶盖的长方体,尺寸为200 × 50 × 50 cm,取气箱层,为无底和有四分之三顶盖的长方体箱层,大小与第二层箱层一致。在两个箱层的左侧四分之一处设置百页隔板,其由扇叶和包裹扇叶边缘的橡胶套组成,可通过外置转轴控制隔板的开合状态,闭合状态下可使底座和集气、取气箱层紧密相接。取气箱层右侧壁设有三通阀取气装置,右上壁有使气体流动均匀的风扇。
上层为普通集气箱层和取气箱层,集气箱层包括三个无顶盖及底盖的正方体,尺寸为50 × 50 × 50 cm,可根据植株的生长来依次安装。取气箱层尺寸为50 × 50 × 50 cm,箱体右壁同样设有三通阀和风扇,顶盖独立于箱体,可以随植株高度和任意集气箱体配合,以保证取气时高度适宜和箱体气密性,具体如图1所示。
1.3. 装置优点
静态箱能够通过箱层组合设置,并通过百叶隔板地开合控制,可以实现套作系统中作物的单独取气和同步取气。同时静态箱的高度控制较为方便,便于运输与存放,能够根据作物的实时高度调节取气高度,田间原位观测性较好,制作简单,能够满足同一时期的高矮不同的共生作物的取气需求。其中,PC塑料板是一种综合性能优良的非晶型热塑性树脂,具有优异的延伸性、电绝缘性、尺寸稳定性及耐化学
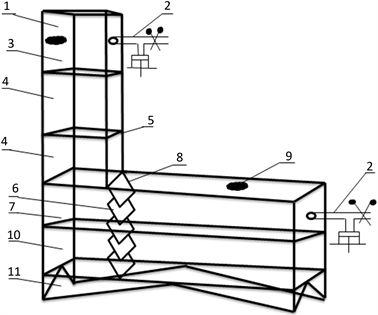 1-PC塑料板;2-三通阀;3-普通取气箱层;4-普通集气箱层;5-榫卯结构;6-百叶隔板;7-加长取气箱层;8-橡胶套;9-风扇;10-加长集气箱层;11-底座
1-PC塑料板;2-三通阀;3-普通取气箱层;4-普通集气箱层;5-榫卯结构;6-百叶隔板;7-加长取气箱层;8-橡胶套;9-风扇;10-加长集气箱层;11-底座
Figure 1. The overall structure
图1. 整体结构
腐蚀性、耐热性和耐寒性,还具有自熄、阻燃、无毒等优点,价格相对低廉。相对比于玻璃材料,PC材料透光性较好且重量较轻,对实验产生的影响较小。三通阀的运用,包括连通管,注射器和夹子,减少取气箱体孔的设置,有利于提高箱体的密封性。
2. 试验效果验证
2.1. 试验地基本情况
试验地点位于四川省现代粮食产业(仁寿)示范基地(104˚11'E, 30˚02'N),地形以丘陵和山地为主,气候为亚热带季风湿润气候,年均气温17.4℃,年均降雨1009.4 mm,年均日照1196.6小时,无霜期312天。供试玉米品种为“登海605”,大豆品种为“南豆25”。
2.2. 试验设计
本试验一共有三个处理方式,分别是玉米–大豆套作(IMS),大豆单作(SS),休闲(CK)。每个处理3个重复,共计9块试验小区。套作与单作处理连续种3带,带长6 m、带宽2 m,小区面积36 m2。大豆单作(SS)采用宽窄行种植,大豆宽行60 cm,窄行40 cm,大豆穴距17 cm,穴留1株;玉米–大豆套作采用宽窄行种植,宽行160 cm,窄行40 cm。套作下玉米、大豆穴距17 cm,玉米穴留1株,大豆穴留2株。大豆单作穴距17 cm,穴留1株;玉米密度5.85万株/hm2;大豆密度均为11.7万株/hm−2。玉米、大豆单作与套作的种植密度相同。各作物保证在单、套作方式下,单位土地面积的种植密度和施肥水平一致 [9] 。玉米、大豆施氮总量(玉米、大豆施氮比例为3:1) 240 kg∙hm−2,根据当地玉米与大豆的总施N量确定,单、套作玉米及单作大豆的磷钾肥随底肥施用,玉米施用量为105 kg P2O5∙hm−2、112.5 kg K2O∙hm−2,大豆施用量为63 kg P2O5∙hm−2、52.5 kg K2O∙hm−2。玉米氮肥分两次施用,即玉米底肥和大喇叭口期追肥,大豆氮肥一次性施用。大豆单作(SS)按传统株间穴施方式施肥。玉米–大豆套作(IMS)体系按玉米、大豆一体化施肥方式,玉米底肥统一按72 N/kg∙hm−2实施,底肥采用株间穴施;玉米大喇叭口期追肥则与大豆磷钾肥混合一起同时施用,在玉米、大豆之间,距玉米25 cm处开沟施肥 [10] [11] 。如图2所示。

Figure 2. Maize-soybean relay strip intercropping and soybean monoculture
图2. 玉米/大豆套作模式、大豆单作模式
2.3. 气体取样方法
该试验分别于大豆的V3、V5、R3、R4期,即7月18日、8月12日、9月22日、10月27日。将温室气体收集装置设于每个试验小区,进行大豆间作、单作两种状态的气体取样。取样时间在上午9:00~11:00之间,选定作物测量位点,将底座固定于土壤中,根据玉米、大豆生长高度,在底座上方由下至上设置加长版集气和取气箱层,普通集气和取气箱层,并盖好顶盖。取气前,使加长版箱层中的百叶隔板处于闭合状态,用橡胶夹子关闭用于保证气压平衡的三通阀,静置30 min后,打开大豆集气箱内的风扇,转动5 min,使箱内气体混合均匀。然后,用带有三通阀的针筒取气,再注入全塑开关阀铝箔复合膜采气袋中,每个静态箱采样4次,分别于闭箱后0、10、20、30 min时采集,试验过程中同时记录箱内温度。接下来使百叶隔板处于连通状态,进行重复操作,完成大豆气体取样。最后,将注射器放入做好标记的密封袋里,将集气袋带回实验室进行分析。
2.4. 气体测定
CO2、N2O、CH4气体浓度采用GC2010-PLUS型气相色谱仪测定。测定CH4和CO2的检测器为FID,检测度300℃,柱温60℃,载气为99.99%的高纯氮气,流速30 ml/min;测定N2O的检测器为ECD,检测温度300℃,柱温60℃,载气为99.99%高纯氩/甲烷气(95%氩气 + 5%甲烷),流速40 ml/min。用医用输液器抽取50 ml气样,手动不分流进样,总进样时间7 min。
2.5. 气体计算方法
在单位时间和单位面积内,被测气体各组分的排放速率利用下式可求得 [12] [13] [14] :
式中,
F为气体排放速率(通量);
M为目标气体的摩尔质量;
P0为理想气体标准状态下的空气压力带(1013.25 hpa);
T0为理想气体标准状态下的气温(273.15 K);
V0为气体在标准状态下的摩尔体积,即22.41
;
H为采样箱内气室高度;
P和T分别为采样时箱内的实际气压和气温;
为箱内目标气体浓度随时间变化的回归曲线斜率。
得出各组分排放通量如表1。
2.6. 数据分析
利用excel和spss数据处理软件对数据进行统计分析。
2.7. 结果与分析
2.7.1. N2O排放通量
由表1和图3可得,大豆在SS、IMS、CK处理下的N2O平均排放通量分别为2.42 ± 2.23 mg/(m2∙h)、1.97 ± 1.82 mg/(m2∙h)、1.21 ± 0.95 mg/(m2∙h)。方差分析表明,SS、IMS、CK处理下的N2O平均排放通量之间存在显著差异(P < 0.05)。
2.7.2. CO2通排放通量
由表1和图4可知,各处理下的CO2排放通量变化趋势基本相同,均呈现先上升后下降趋势。SS处理下的平均排放量为13,263.93 mg/(m2∙h),IMS处理下的平均排放通量为10,085.67 mg/(m2∙h),CK处理下的平均排放通量为1852.90 mg/(m2∙h)。
2.7.3. CH4排放通量
表1和图5列出了各处理下,各个生长时期的CH4通量测定结果,可以看出,CH4排放通量基本为负值,土壤成为CH4吸收汇。SS、IMS、CK处理下的CH4平均排放通量为−0.17mg/(m2∙h)、−5.75mg/(m2∙h)、−4.34 mg/(m2∙h)。
3. 讨论
本实验利用针对套作系统温室气体收集静态箱,该装置在被使用的过程中,根据了共生作物高度,调节箱体容量和取气口位置,从而详尽测定了不同种植模式下和时期下,大豆土壤排放的主要温室气体组成成分,包括CO2、N2O、CH4。其中N2O排放较高,此阶段作物生理活性较强,固氮作用旺盛 [15] ,气温高和施肥水平 [16] [17] ,可能是排放高的主要原因。这与已有文献对大豆农田生态系统N2O排放研

Table 1. GHG emissions in different treatments
表1. 不同处理温室气体排放量
究情况相一致 [18] [19] 。CO2排放量表现为套作比单作模式少,SS处理下的平均排放量为13,263.93 mg/(m2∙h),IMS处理下的平均排放通量为10,085.67 mg/(m2∙h),说明玉豆套作在一定程度上可以减少温室气体排放,此结论在其他研究中也有所体现 [16] 。CH4排放量表现为大豆的三种种植模式处理中土壤基本为CH4的汇 [2] 。这与黄坚雄 [16] 等人在对玉米/大豆间作农田温室气体排放相关研究结果相吻合。
但是,将试验数据结果与王重阳 [20] 等人对下辽河平原大豆田CO2和N2O排放通量研究相对比发现,该试验测得大豆休闲模式下CO2的平均通量为1852.90 mg/(m2∙h),远远高于下辽河平原偏东的CO2排放通量108.7 mg/(m2∙h) [20] ,可能是由于CO2的释放具有很大的时空变异性 [21] ,相比于下辽河平原,成都平原气候明显温和,气温偏高,使得土壤微生物活性增加,通过有氧呼吸释放更多的CO2 [22] 。由于本装置在试验中密闭时间较长,导致氧气减少,N2O又被重新还原成氮气。在大豆套作模式下,大豆完熟期,土壤成为CH4的吸收汇 [23] ,SS、IMS处理下的CH4平均排放通量为−0.17 mg/(m2∙h)、−5.75 mg/(m2∙h),排放通量明显低于单作处理下的排放通量。
通过与传统容气体收集装置对比和本试验数据分析,本文设计的套作系统温室气体收集装置能有效测定作物排放的温室气体含量的要求。可加层箱体和百叶隔板设置,有利于容纳套作模式下的不同高度作物,同时收集两种作物的气体,为研究两种套作植物的相互影响提供便利。大量研究表明套作可以明显提高光能利用率和土地利用率,对于提高单产、较少虫害、草害都有明显优势 [24] 。大豆会通过其根系分泌物及其分泌脱落物以及对细小根系的矿化分解有效改变土壤养分供给状况,调节两种作物的养分吸收和根系微生物的呼吸情况 [25] ,进而影响温室气体的排放。
4. 结论
静态箱是学者们进行土壤和作物温室气体的收集测定与研究的重要工具 [26] [27] ,本文所描述的装置弥补了传统装置笨重,容量小等缺陷 [28] ,改进为一套有效、便捷可调、适应作物高度的,能够实现套作模式下的农田作物温室气体收集的装置。在对该装置进行效果验证中,通过对每种模式的重复试验,以及与以往的实验结果对比,具有相对一致性,说明本装置有效且具有广阔的推广应用前景,能为高校、科研机构、从事于农田生态系统研究的学者提供有效帮助。在使用的过程中须注意:在安置底座时,要插入一定深度,以免在箱体加层的过程中会有箱体倾斜或倒塌的现象;在取样时,要将作物完全容入箱体内,箱层之间要紧密贴合,三通阀合理开合;在进行单作模式下取气时,要保证紧闭百叶隔板。在气样的保存过程中,注意保持气样不被空气污染,降低对实验的影响。
基金项目
国家重点研发计项(2016YFD0300202);国家自然科学基金项目(31671625,31271669)。