1. 引言
桉树具有适应性广、抗性强、种植容易、用途广、速生高产等特点,是三大速生树种之一。目前广西是我国桉树种植推广最快的省区之一。桉树的大面积种植,必然对肥料产生很大的需求量,尽管当前对桉树的养分需求和施肥规律已经有了比较全面地研究,但对于桉树体内贮藏氮素的研究很少。探究桉树氮素贮藏的的季节性规律,有利于提高氮素利用率,指导合理施肥。陈慧洁等 [1] 对桉树叶片蛋白质的提取方法、溶解方法、溶解条件和上样量进行了优化。马松亚等 [2] 以尾叶桉广林4号无性系为试验材料,对蛋白质样品获取、双向电泳等方法进行了优化。目前在桉树的种苗培育、养分需求和施肥规律 [3] 等方面已经做了大量研究工作,并对桉树中蛋白质的提取和测定有了一定的研究,但这一部分的研究主要局限在生长季节中的某一特定短暂时期内,对不同季节的可溶性蛋白质及相关酶的动态变化规律很少涉及,所以这方面的内容具有很高的研究价值。测定不同季节桉树叶中的可溶性蛋白质含量及谷氨酰胺合成酶、谷氨酸合成酶等与氮素代谢密切相关的酶活性,从中找出可溶性蛋白及两种酶的动态变化规律,为提高桉树林对氮素的利用率,指导合理施肥及提高产量提供理论依据。
2. 材料和方法
2.1. 材料
实验所用的材料选自于玉林师范学院东校区校内的广林九号桉。广林9号桉为尾巨桉(E. urophylla × E. grandis)无性系,是在对尾叶桉(E. urophylla)和巨桉(E. grandis)优良个体选择的基础上,通过人工控制授粉获得的杂交种,具有生长迅速、适应性强、遗传性状稳定、出材率高等特点,已成为主要栽培品种。每月下旬采集一年生的桉树叶1次,样品采回后立即整理挂上标签后,分开封袋,并及时放进超低温冰箱保存待用于各项指标的测定分析。
2.2. 方法
2.2.1. 可溶性蛋白质含量的测定
采用考马斯亮蓝法 [4] 。称取0.5 g桉树叶片,加入5 ml 0.06 mol/L Tris-HCI缓冲液(pH 7.8),冰浴研磨充分后,把匀浆倒入离心管,在15,000 r/min,4℃下离心40分钟后,去除沉淀,上清液则为蛋白质提取液。用考马斯亮蓝染色法测定上清液中蛋白质含量。取提取液1 ml,加5 ml考马斯亮蓝G-250试剂,放置2 min后,测定595 nm下光密度值。
2.2.2. 谷氨酰胺合成酶活性的测定
参考金正勋的测定方法 [5] ,略有改动;取新鲜桉树叶片1 g剪碎后置于预冻的研钵中,加预冷的0.05 mol/L Tris-HCl (pH 8.0)提取缓冲液10 mL,冰浴研磨。12,000 r/min离心10 min,上清液为粗酶提取液;取0.8 mL粗酶液加入酶反应液1.1 mL (对照管是先加1.8 ml反应终止液,再加酶提取液),在40℃下反应30 min后,测试管加入反应终止液1.8 mL,放置10 min后,测定540 nm下的OD值。计算酶的活性.每个样品做3个重复,后取平均值。
2.2.3. 谷氨酸合成酶活性的测定
参考熊丹的测定方法 [6] ,略有改动;取新鲜桉树叶片1 g剪碎后置于预冻的研钵中,加预冷的0.05 mol/L Tris-HC1缓冲液(pH 7.6) 4 mL,冰浴研磨,12,000 r/min离心10 min,上清液为粗酶提取液;反应混合液包括0.5 ml 0.02 mol/L的α-酮戊二酸,0.4 ml 0.02 mol/L的L-谷氨酰胺,0.1 ml 0.01 mol/L的氯化钾,0.2 ml 0.003 mol/ L NADH (烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸)和0.3 ml酶液,反应混合液总体积为3 mL,不足部分可用0.025 mol/L的Tris-HC1缓冲液(pH 7.6)补充;酶反应启动后,置于紫外可见分光光度计中,在340 nm波长下每20秒测定1个OD值,连续测定11次,取OD值稳定减少的一段来衡量酶活性。
2.3. 数据分析工具
实验数据均采用Excel和SAS for Windows统计分析软件处理,用Duncan氏法进行差异显著性检验。
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 不同季节桉树叶可溶性蛋白质含量的比较分析
由图1可看出,桉树叶中的可溶性蛋白质含量在2月份较高,从2月到3月期间可溶性蛋白质含量缓慢升高,并于3月末达到最高值。3月~4月可溶性蛋白质含量快速降低。4月~7月,叶片中可溶性蛋白质含量显著升高。7月到10月可溶性蛋白质含量缓慢降低。10月~11月呈显著的下降趋势,从66.094 µg/ml降低到14.799 µg/ml,在11月底降到最低水平。此后10月~12月桉叶片中可溶性蛋白质快速增多。
对不同季节可溶性蛋白质含量变化进行方差分析及多重比较,结果表明,在不同季节桉树叶可溶性蛋白质含量的差异达到极显著水平(F = 1379.65, P < 0.0001)。除了在4月和12月及7月和10月,桉树叶片中可溶性蛋白质含量差异不显著外,其余可溶性蛋白质含量均达到显著差异水平。在桉树生长的2月~3月、4月~7月、11月~12月期间,桉树叶中可溶性蛋白质含量显著增加,3月的可溶性蛋白质含量极显著高于4月~12月。在3月~4月、10月~11月期间,可溶性蛋白质含量显著降低,其中11月含量极显著低于2月~4月、10月、12月。7月~10月的可溶性蛋白质含量变化不显著。
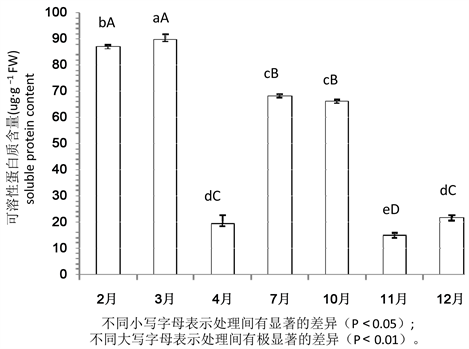
Figure 1. Changes of soluble protein content in leaves of Eucalyptus in different seasons
图1. 不同季节桉树叶可溶性蛋白质含量的变化
3.2. 不同季节桉树叶谷氨酰胺合成酶活性的比较分析
由图2表明,桉树叶中谷氨酰胺合成酶活性在不同时期发生较明显的波动。2月~3月,谷氨酰胺合成酶活性保持相对稳定水平。3月~4月,谷氨酰胺合成酶活性快速降低。4月~7月,叶片谷氨酰胺合成酶活性显著升高,在7月末达到最高值。7月~10月,酶活力大幅度降低。10月~12月,谷氨酰胺合成酶活性以先快后慢的速度上升。
对不同季节桉树叶片中谷氨酰胺合成酶活性的变化进行方差分析及多重比较,结果表明,在不同季节中桉叶谷氨酰胺合成酶活性的差异达到极显著水平(F = 32.41, P < 0.0001)。除在7月和12月及2月、3月和11月,桉树叶片中GS活性差异不显著外,其余GS活性均达到显著差异水平。在桉树生长的4月~7月、10月~12月期间,桉树叶中GS活性显著增加,7月的GS活性极显著高于2月~4月、10月。在3月~4月、7月~10月期间,桉叶中GS活性显著降低,其中10月GS活性极显著低于2月~7月、11月~12月。2月~3月的GS活性变化不显著。
3.3. 不同季节桉树叶谷氨酸合成酶活性的比较分析
由图3可看出桉树叶中谷氨酸合成酶活性在不同季节发生较明显的波动,在春季和秋季各有一个高峰。2月~3月,桉树叶中谷氨酸合成酶活性缓慢下降。3月~4月,谷氨酸合成酶活性显著上升。4月~7月,叶中谷氨酸合成酶活性快速减弱。7月~10月,酶活性保持相对稳定,呈现缓慢降低趋势,至10月底降到最低水平。10月~11月,酶活性大幅度上升,在11月达到最高值5.773 mg∙min。11月~12月,谷氨酸合成酶活性快速降低。
4. 结论与讨论
4.1. 可溶性蛋白含量
可溶性蛋白质是植物体内氮素存在的主要形式,可溶性蛋白质含量的多少与气象因子及植物体的生理代谢和衰老密切相关 [7] ,王改萍等 [8] 研究表明银杏叶中可溶性蛋白质含量的变化与树木营养生长的变化规律相一致,银杏叶片中可溶性蛋白质的含量在生长旺季较高,在秋季末降至最低,说明叶片脱落时

Figure 2. Changes of glutamine synthetase activity of Eucalyptus in different seasons
图2. 不同季节桉树叶谷氨酰胺合成酶活性的变化

Figure 3. Changes of glutamate synthetase activity of Eucalyptus in different seasons
图3. 不同季节桉树叶谷氨酸合成酶活性的变化
养分发生转移。郭红彦 [9] 经研究也指出随着新叶的展开,树体的光合能力增强,营养物质开始积累,可溶性蛋白质含量开始上升。本试验结果与以上结论基本一致。本实验结果表明桉树叶片中可溶性蛋白质含量表现为明显的季节变化规律。2月采摘的桉树叶中可溶性蛋白质含量已呈较高数值,系冬季所积累;从2月到3月期间可溶性蛋白质含量缓慢升高,分析3月份的气象可知,3月气温升高且降雨量增大,桉树的生理活动能力比较强,可溶性蛋白质含量稍有上升。4月降水变少,气温缓慢升高,蒸发量大大超过降水量,相对湿度较低,桉树生长相对迟缓,但此时有较多叶片长出,新叶在生长前期因为叶片小,组织未完全成熟,叶片中叶绿体较少,所以不完全具备光作用能力,叶片中可溶性蛋白质含量比较低。5月的降雨量开始增多并明显超过蒸发量,湿度也较大,各种环境条件基本满足,林木生长加快,桉树叶处于展叶期,随着叶片的不断生长,其光合作用能力不断增强,代谢旺盛,光合产物积累增多,主要表现为桉树叶中可溶性蛋白质含量不断增加,直至7月含量达到最高值。7月到10月期间持续高温,各种环境条件优越,桉树的生理活动能力较强,林木处于速生期,此时桉叶成熟,代谢减缓、变弱,可溶性蛋白质含量保持相对平衡,以满足自身生长的需要。10月~11月,可溶性蛋白质含量急剧降低,可溶性蛋白质减少的原因可能有两种:一是11月气温降低,降水少,蒸发量大大超过降水量,叶片代谢能力减弱,可溶性蛋白质生成量少,不能满足自身生长需求;二是桉树老叶脱落现象较其他月份多,叶内氮化物转移和再分配到生活力较高的部位。从11月到12月期间气温降低,但降雨量增多,桉树生长缓慢,可溶性蛋白质含量快速上升。本实验研究发现,桉树叶中可溶性蛋白质含量在春季初达到最大值,随着较多桉叶生长成熟,可溶性蛋白质含量由少增多,直至秋季叶片中含氮物质发生转移和再分配,可溶性蛋白质含量急剧减少,在冬季期间贮藏氮素增加。
4.2. 谷氨酰胺合成酶
谷氨酰胺合成酶是植物体中氮代谢过程的关键酶,外界的硝态氮进入植物体内必须首先同化成氨,然后经过GS-GOGAT循环等一系列反应,形成氨基酸和酰胺,最终才能参与蛋白质、核酸、叶绿素和含氮次生代谢物的生物合成,以满足植物体生长代谢需要 [10] 。高等植物的种子、叶、根、根瘤和果实等器官中分布着多种GS的同工酶。在植物叶片中存在2种GS同工酶:一种定位于细胞质部分,称为胞液(胞质)型GS-GS1;另一种定位于叶绿体部分,称为叶绿体型GS-GS2 [11] 。在高等植物中GS1的功能是:参与在种子萌发时贮藏氮源的转运,在叶片衰老时氮源的转移再利用。GS2的功能是:参与光呼吸氨、还原氨(初级氮)、循环氨的再同化 [12] 。测定桉树叶中谷氨酰胺合成酶活性的变化,有利于了解氮素代谢在不同季节的反应强弱。徐志文 [10] 研究发现水稻中谷氨酰胺合成酶的活性随着生育期的变化而变化,其中酶活性在分蘖期最强,随着生育期向后发展,谷氨酰胺合成酶活性逐渐降低,成熟期最弱。Machdao等 [13] 研究也发现GS活性与子粒产量之间呈显著正相关,与氮素代谢相关。本实验结果与以上研究结论有部分相似,即都认为GS活性与植物的生理代谢强弱相关。本实验结果可看出桉树叶片中谷氨酰胺合成酶活性表现为明显的季节性变化规律,这与桉树的生理代谢密切相关。2月~3月所采摘的桉叶外形较成熟,谷氨酰胺合成酶活性先升后降,随着叶片的生长,代谢能力减弱,GS活性逐渐减弱。3月~4月桉树长出较多叶片,此时叶片较嫩,叶片中叶绿体较少,不完全具备光作用能力,GS活力还很低,随着叶片的不断生长,其光合作用能力不断增强,GS活性快速增强,在7月下旬达到叶片生长阶段的最高值。4月~10月,桉树处于速生期,随着大部分桉树叶的发育成熟,GS活性逐渐降低,在10月达到最低水平。这与徐志文 [10] 的研究结果相一致,即:谷氨酰胺合成酶活性在成熟期最弱。进入11月后气温降低,降水少,叶片代谢能力减弱,含氮物质从叶片中转移和再分配到生活力较高的部位,GS参与氮源的转移和再利用,故其活性急剧增强。12月气温降低,降雨量增多,桉树生长缓慢,为抵御寒冷,叶内含氮物质仍然进行转移和再分配,故GS活性增强。
4.3. 谷氨酸合成酶
植物叶片通过GS/GOGAT途径进行氨的同化,在这个途径中GOGAT和GS起到协同作用 [14] 。植物叶片中的GOGAT主要存在于质体中。GOGAT可分为3类,其中Fd-GOGAT占总谷氨酸合成酶活性的96%,Fd-GOGAT在叶绿体基质中主要负责同化光呼吸及氨的同化,而在叶片韧皮组织中分布较多的则是NADH-GOGAT,NADH-GOGAT主要参与氮化合物的转移运输 [15] 。梁成刚等 [16] 研究表明,水稻籽粒中谷氨酸合成酶活性的提高可以促进稻米中氨基酸与蛋白质的合成。熊丹 [6] 认为叶片中GOGAT活性的提高利于氮素的转运和再利用,即与籽粒中GLU的积累有一定联系。测定桉树叶中谷氨酸合成酶活性的变化,有利于了解氮素代谢在不同季节的反应强弱。本实验结果可看出桉树叶片中谷氨酸合成酶活性的变化趋势与GS活性的变化趋势相似,但变化幅度相对要小些,这与植物体的氮素代谢密切相关。在2月到3月期间所采摘的桉树叶外形较成熟,谷氨酸合成酶活性在叶片成熟期最弱,因此2月到3月期间谷氨酸合成酶活性较低,随着叶片的成熟度加深,代谢减缓、变弱,故GOGAT活性逐渐减弱。3月~4月,桉树开始长出较多叶片,此时叶片较嫩,叶片中叶绿体较少,不完全具备光作用能力,部分营养物质可从其他部位转移到桉叶中,GOGAT参与氮化物的转移运输,故GOGAT活力快速上升,在4月下旬达到叶片生长阶段的最高值。4月~10月,桉树处于速生期,随着桉叶的生长成熟,GOGAT活性缓慢降低。进入11月后气温降低,降水少,叶片代谢能力减弱,氮化物从叶片转移和再分配到生活力较高的部位,GOGAT参与贮藏氮素的转移再利用,故其活性急剧上升,在11月末达到最高值。12月气温降低,叶内氮化物的转移减少,光呼吸及氨的同化降低, GOGAT活性呈快速降低趋势。
基金项目
广西自然科学基金资助项目(2014GXNSFAA118083);广西区级大学生创新创业训练计划项目(201510606070)。