1. 引言
这篇文章里所有的图都是有限的,简单的,无向的。在 [1] 中可以找到没有被定义的术语和符号。图
,
是G的顶点的个数,
是G的边的个数,v的邻集NG(v)是G中所有与v相邻的顶点的集合。因为G是简单图,所以有
。
假设V'是V(G)的一个非空子集。图G的导出子图
定义为
并且
当且仅当
。两个图
,
的并,记为
,点集是
,边集是
。如果它们不交,即
,它们的并记为G + H。
图G的线图L(G)的点集是E(G),其两个顶点相邻当且仅当它们在G中相邻。图G的全图G+++,它的点集是
,任意两点相邻当且仅当它们在G中或者是相邻的,或者是关联的。吴和孟 [2] 推广了全图的概念,并且引入了一些新的变换图。我们也采用了Gxyz这个符号,
,这个符号是在 [2] 中被引入的。
如果一个图可以在平面中画出来使得他们的边不交,只有在端点处相交,我们就说这个图在平面上是可嵌入的,或者是可平面的。图G的剖分是在G的边上插入一系列的点之后得到的。Behzad [3] 刻画了图G的变换图G+++是可平面的。刘 [4] 给出了图G的变换图G−−−是可平面的充要条件。吴等 [5] 证明了图G的变换图G−++可平面的充要条件是G点数至多为4。读者可参考 [6] - [13] 了解更多的关于图Gxyz的结论。按习惯,n个顶点的完全图,圈,路分别记为Kn,Cn,Pn。两部分中的顶点数分别为m,n的完全二部图记为Km,n。
文章的第二部分我们使用了著名的Kuratowski [1] 定理。
定理1.1:一个图是可平面的当且仅当它不包含K5或者K3,3的剖分。
推论1.2:每个可平面简单图都有一个顶点的度数至多为5。
下面是这篇文章的主要结论。
定理1.3:对于一个边数为m的图G,G+−−是可平面的当且仅当m ≤ 2或者G与下面的某个图同构:C3,C3 + K1,P4,P4 + K1,P3 + K2,P3 + K2 + K1,K1,3,K1,3 +K1,3K2,3K2 + K1,3K2 + 2K1,C4,C4 + K1,2P3。
证明:由引理2.1~2.5的结论可以立即得到。
2. 证明
下面的结论容易证明,但很有用。
引理2.1:如果H是G的子图,那么H+−−是G+−−的子图。
由引理2.1,如果H+−−是非可平面的,
,k是一个整数,并且k ≥ 1,那么G+−−是非可平面的。我们很容易检测到对于边数m ≤ 2的图,G+−−是非可平面的。接下来我们考虑边数为3的图,在图1中我们精确地给出了所有边数为3的并且没有孤立点的5个图。
引理2.2:对于一个边数为3的图G,G+−−是可平面的当且仅当
.
证明:充分性:正如图2中所示:
G+−−:3K2 + 2K1,P3 + K2 + K1,K1,3 + K1,C3 + K1,P4 + K1的变换图G+−−是可平面的。根据引理2.1,C3,P4,P3 + K2,K1,3,3K2,3K2 + K1的变换图G+−−也是可平面的。
必要性:对于每一个图
,其变换图
是非可平面的,因为它们都包含K3,3的剖分,如图3所示。

Figure 1. All graphs of size 3 without isolated vertices
图1. 所有边数为3的没有孤立点的图
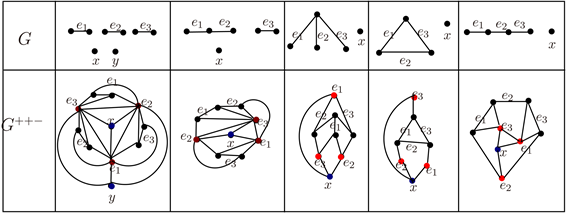
Figure 2. Transformation graph G+−− of 3K2 + 2K1, P3 + K2 + K1, K1,3 + K1, C3 + K1, P4 + K1
图2. 3K2 + 2K1,P3 + K2 + K1,K1,3 + K1,C3 + K1,P4 + K1的变换图G+−−

Figure 3. Transformation graph G+−− of P3 + K2 + 2K1, K1,3 + 2K1, C3 + 2K1, P4 + 2K1
图3. P3 + K2 + 2K1,K1,3 + 2K1,C3 + 2K1,P4 + 2K1的变换图G+−−

Figure 4. All graphs of size 4 without isolated vertices
图4. 所有边数为4的没有孤立点的图

Figure 5. Transformation graph of some graphs of size 4
图5. 一些边数为4的变换图

Figure 6. Transformation graph of some graphs of size 4
图6. 一些边数为4的变换图
现在我们来考虑边数为4的图,我们精确地给出了11种边数为4的没有孤立点的图,如图4所示。
引理2.3:对于一个边数为4的图G,G+−−是可平面的当且仅当
。
证明:充分性:在图6和图7中我们给出了
,
平面嵌入,因此
,
是可平面的,由引理2.1,
也是可平面的。
必要性:设G是一个边数为4的图,那么G可以由图4增加一些孤立点得到,由图4~图7和引理2.1,如果
,G+−−是非可平面的。
现在我们来考虑边数为5的图。我们精确地给出了边数为5的没有孤立点的图,如图8所示。
引理2.4:对于边数为5的图G,其变换图G+−−是非可平面的。
证明:因为图G是一个边数为5的图(如图8所示),G包含一个边数为4的子图H,不同构于
。由引理2.3,H+−−是非平面图。又由引理2.1知,H+−−是G+−−的子图。所以,G+−−也是非平面的。
引理2.5:如果图G的边数m ≥ 6,那么G+−−是非可平面的。

Figure 7. Transformation graph of some graphs of size 4
图7. 一些边数为4的变换图

Figure 8. All graphs of size 5 without isolated vertices
图8. 所有边数为5的没有孤立点的图
证明:显然,G包含一个边数为5的子图H,由引理2.1得到H+−−是G+−−的子图。更进一步,由引理2.4得到G+−−是非可平面的。
参考文献
[1] 1Bondy, J.A. and Murty, U.S.R. (1976) Graph Theory with Applications. Macmillan, London. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-349-03521-2
[2] Wu, B. and Meng, J. (2001) Basic Properties of Total Transformation Graphs. Journal of Mathematical Study, 34, 109-116.
[3] Behzad, M. (1967) A Criterion for the Planarity of the Total Graph of a Graph. Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 63, 679-681. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0305004100041657
[4] Liu, X. (2006) On the Planarity of G−−−. Journal of Xinjiang University (Science & Engineering), 23, 159-161.
[5] Wu, B., Zhang, L. and Zhang, Z. (2005) The Trnasformation Graph Gxyz When x, y, z Î {+, −}. Discrete Mathematics, 296, 263-270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.disc.2005.04.002
[6] Chen, J., Huang, L. and Zhou, J. (2012) Super Connectivity and Super Edge-Connectivity of Transformation Graphs G+−+. Ars Combinatoria, 105, 103-115.
[7] Deng, A. and Kelmans, A. (2017) Laplacian Spectra of Digraph Transformations. Linear and Multilinear Algebra, 65, 699-730. https://doi.org/10.1080/03081087.2016.1202183
[8] Deng, A., Feng, M. and Kelmans, A. (2016) Adjacency Polynomials of Digraph Transformations. Discrete Applied Mathematics, 206, 15-38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dam.2016.01.032
[9] Deng, A., Kelmans, A. and Meng, J. (2013) Laplacian Spectra of Regular Graph Transformations. Discrete Applied Mathematics, 161, 118-133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dam.2012.08.020
[10] Li, J. and Liu, J. (2014) Some Basic Properties of a Class of Total Transformation Digraphs. Ars Combinatoria, 116, 205-211.
[11] Xu, L. and Wu, B. (2008) Transformation Graph G−+−. Discrete Mathematics, 308, 5144-5148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.disc.2007.09.040
[12] Yi, L. and Wu, B. (2009) The Transformation Graph G++−. Australasian Journal of Combinatorics, 44, 37-42.
[13] Zhen, L. and Wu, B. (2013) Hamiltonicity of Transformation Graph G+−−. Ars Combinatoria, 108, 117-127.