1. 推理心理学与条件句的研究
推理心理学(Psychology of reasoning)是关于人们如何推理的研究,从广义的角度来看,它包括人们如何作判断与决策。从这个意义上看,它属于问题解决的心理学的一个分支。在本文中,我们对推理心理学取狭义的理解:它是关于人们如何作演绎与归纳推理的研究。必须注意的是,在目前的文献里,论及推理心理学通常是形式逻辑(Forma logic或Symbolic logic)为主导(Rips, 1994),即演绎的研究。最近,研究者们开始把Bayes推理模式应用于条件句的研究(Oaksford & Chater, 2008),取得了引人瞩目的成果。而这是推理心理学的归纳方面。本文的重点是呈现这些成果。
推理心理学的研究需要一个关于推理的逻辑理论作为实验的参考,因为只有这样,实验结果与理论要求之间的偏差才可以得到理解。所以推理心理学的研究包含规范和描述(Normal and descriptive)的两个方面。必须指出的是,把推理心理学分为规范的方面和描述的方面,一开始并不是十分明显的。规范的方面是指人们推理应该遵守形式逻辑规则,如果人们在实际推理过程中没有遵守形式逻辑规则,那么心理学家应该寻找犯逻辑错误的认知原因。描述的方面是指形式逻辑规则不是评价人们实际推理表现的准则,人们实际推理无对错之分,心理学家应该做的是寻找背后的心理机制以及寻找别的不同于形式逻辑规则的推理规则。从Wason的纸牌选择任务实验开始,中间经过Johnson-Larid,Evans(2005)和Chater(2001)等人的工作,推理心理学界开始反思形式逻辑规律是否是人们在推理过程中应该遵守的规范,因而有了推理心理学中的规范与描述方法之争。如果形式逻辑规则不符合实验结果,那么,什么样的规则才是符合实验的?我们认为规范的部分不应是形式逻辑的规律,而是基于贝叶斯规则上的因果推理模式。人们在日常推理实际中是使用归纳推理而不是演绎推理。
条件句推理的研究一直是推理心理学的中心课题,是其重点和难点(Evans & Over, 2004),难点是在形式逻辑方面。在很多推理心理学文献中,由于对条件句的理解是混淆的(演绎与归纳难以分辨清楚),这导致这些文献里发现所谓的许多有趣而特殊的推理现象。从今天的概率观点来看,这些推理现象都可以从贝叶斯统计的框架内得到较好的解释。本文在回顾推理心理学是怎样转向贝叶斯规则的概率模型时,重点关注形成概率模型时的几个源头:用Ramsey测试来理解条件句推理机制;用逻辑程序来解释条件句推理的非单调特性;用贝叶斯规则条件句推理的信息加工机制。所以其他方面的文献由于主题的原因较少提及。
从形式逻辑的规则看,条件句的推理规则如下:
1) 如果天下雨,那么地是湿的

对应的逻辑形式是
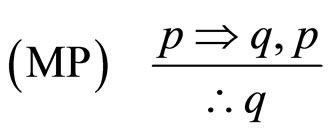
2) 如果天下雨,那么天是湿的

对应的形式是:
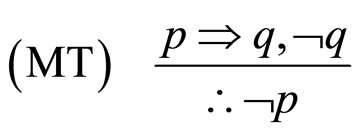
式中,pÞq表示条件句推理如果p,那么q;Øp和Øq分别表示对p,q的否定。无效的推理形式是:
3) 如果天下雨,那么地是湿的

对应的逻辑形式是
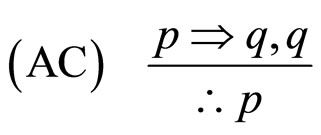
4) 如果天下雨,那么地是湿的

对应的形式是:
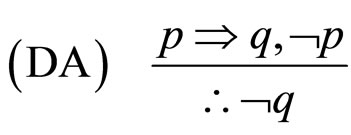
MP是指演绎推理的分离规则,MT是后件否定,AC是前件肯定,DA前件否定。
图1表明这四种类型的条件句推理形式与实际推理过程之间既有重合的一面又有不同的一面(Marcus & Rips, 1979)。
值得注意的是,有效的推理形式MT并没有象MP那样普遍。为什么人们在实际推理过程中常常违反这种有效的逻辑规律?Wason选择实验亦表明MT遭到几乎一半比例的被试的违反(Wason, 1969)。这方面的研究表明人们推理的确有一种规律(心智逻辑)在起作用。

Source: Marcus and Rips, 1979
Figure 1. The comparison between the four forms of conditional reasoning
图1. 四种类型的条件句推理形式选择比较
Johnson-Larid对推理心理学中的条件句推理提出了如下问题(Byrne and Johnson-Larid, 2009):
1) 为什么有些条件句推理特别难?而当且仅当(if and only if)的推理很容易?
2) 条件句究竟是什么?
3) 在什么条件下条件句为真?
4) 为什么反事实条件句特别?
5) 一个条件句的否定是什么?
6) 什么是一个条件句的概率?
这些问题既涉及形式逻辑,又涉及实际的人类推理过程,涉及逻辑,哲学,心理学、社会学和人工智能等领域。
2. 有关条件句推理的假设和争论
心智逻辑(Mental Logic)假定人类心灵包含接近于逻辑演算的形式规则集合,人们在作推理时把这些规则与任务所提供的句子结构形式相匹配(Braine & O’Brien, 1998)。前面提到的条件句推理四种基本逻辑形式(其中只有MP、MT是有效的逻辑形式)反映了人类推理时所经历的四种推理的部分策略,推理过程就是寻求证明的过程。推理的错误(规范的角度)来自于表达错误,无效的规则等。心智规则理论最大的问题在于:它难以解释为什么人类推理使用MP和假想推理(Suppositive reasoning),在论证上有逻辑循环之嫌。
心智模型理论(Mental model theory)由JohnsonLarid等人发展起来的关于人类推理(尤其是演绎推理)的心理过程理论,对心智模型理论的表述,JohnsonLarid的提法有一些差异,早期他认为心智模型是建立在对推理(Argument)的知觉和形象理解上,后来他认为心智模型是对推理相关的可能性的抽象表达,当然它涵盖知觉、形象,这一点在关于空间推理和时间、事件的推理上尤其突出,此时空间表达与时间次序在完成此类推理任务时十分关键(Johnson-Larid, 2001)。在对Wason选择任务实验的结果解释上,心智模型理论认为涉及否定的推理容易出错,因为它必须处理更多的心智模型,需要更多的信息加工,而人们往往在推理过程中本着经济的本能,从而忽视某些心智模型。这可以解释选择否定形式的MT的比例是如此之低。
另一个理论是逻辑程序理论,它是由计算机科学家Bob. Kowalski首创(Kowalski, 2008),之前由K. Stenning和M. van Lambalgen作了一些铺垫(Stenning & Van Lambalgen, 2008)。这个铺垫的要点是,if…then条件句其实其含义是含糊的(ambiguity),if是个多义引导词。这个理论的重要推论是,关于条件句推理的四种模式都是合理的,它们的合理性全都在逆推逻辑程序(Abductive Logic Programming, ALP)的框架下得到合理解释:
首先,if…then应理解为三种不同的产生式规则(productive rules):
反应式规则:A(刺激)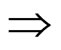 B(反应)
B(反应)
逻辑规则:A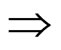 B(MP)
B(MP)
操作语义:A(条件)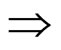 B(行动)
B(行动)
推理过程是一个目标搜寻的过程,它由前向推理链(Forward chaining)和子目标生成过程(用Prolog语言表示)
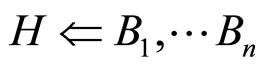
H, B1, B2, …, Bn称为Horn子句,对应于通常的命题。
其次,否定“非”被解释为动作或先决条件不满足,即Negation as failure(NAF),其解释如下:非P P的定义(Horn子句形式推出非P)或就现有的信息推不出P,前者表示当动作条件不满足时,是不会执行动作P的,后者是一个基于不完全信息下的推理(有时称为非单调推理(Nonmontonic reasoning))。
P的定义(Horn子句形式推出非P)或就现有的信息推不出P,前者表示当动作条件不满足时,是不会执行动作P的,后者是一个基于不完全信息下的推理(有时称为非单调推理(Nonmontonic reasoning))。
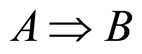
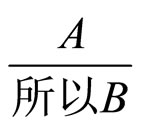
这个模式解释为如果产生规则的条件是A,如果满足,则执行相应的动作B(用反应式规则解读,亦是同样的结果),这就解释了MP规则有几乎100%的接受率,更重要的是,在ALP下,
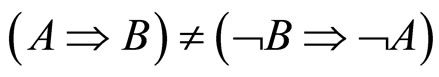
ALP理论的最大功劳是合理地解释了为什么选MT的人的比例为什么少,而且更重要的是它的发现: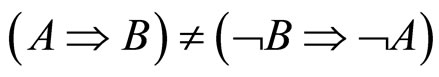 。而这与Mental rule理论和Mental model理论的共同假设和基础相矛盾,而反事实条件句就是这样的特征!这也是为什么把反事实条件句称为各种理论和模型的试金石。下面我们来讨论基于Bayes规则的模型。
。而这与Mental rule理论和Mental model理论的共同假设和基础相矛盾,而反事实条件句就是这样的特征!这也是为什么把反事实条件句称为各种理论和模型的试金石。下面我们来讨论基于Bayes规则的模型。
3. 为什么是Bayes模型?
Bayes模型为什么是条件句推理的较为合适的模型?最主要的理由是它给出了不同的条件句推理现象的统一而简明的定量解释,使推理心理学的研究向模型和理论的完善前进了不少。Bayes模型是建立在Bayes规则概率模型,它使用信息增值的期望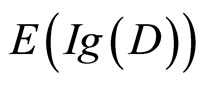 来表达人们在作假设选择时偏爱能带来最大不确定性的信息或证据的心理特征(Wason纸牌选择任务可以看做人们在作假设选择的过程),它是对人类推理能力的理解作理性分析的组成部分(Anderson, 1991)。接下来是关于Bayes模型的主要内容。
来表达人们在作假设选择时偏爱能带来最大不确定性的信息或证据的心理特征(Wason纸牌选择任务可以看做人们在作假设选择的过程),它是对人类推理能力的理解作理性分析的组成部分(Anderson, 1991)。接下来是关于Bayes模型的主要内容。
Bayes规则是:用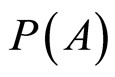 ,
, ,
,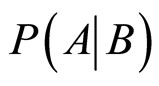 分别表示随机事件A,B,
分别表示随机事件A,B,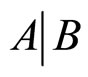 (条件事件)的概率,如果
(条件事件)的概率,如果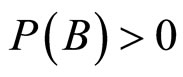 ,则Bayes规则是
,则Bayes规则是
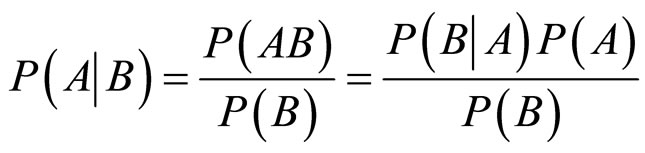
对于选择实验任务(Oaksford & Chater, 1994)运用概率方法(基于Bayes法则)来计算所谓的每一个选择的信息增值(Information gain),而且假定信息增值与此选择实际的排序结果(基于被试选择的频数)一致.其解释过程如下:首先按照信息熵的定义,n个互相对立排斥的假设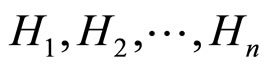 的信息熵I是
的信息熵I是
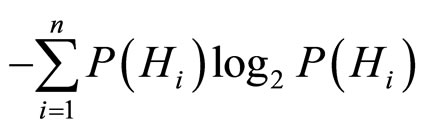
在接受证据D之后,信息熵ID变成
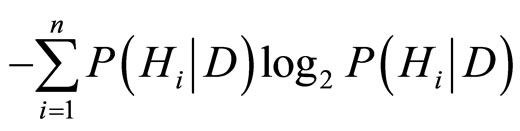
而 的计算是由Bayes定理给出:
的计算是由Bayes定理给出:
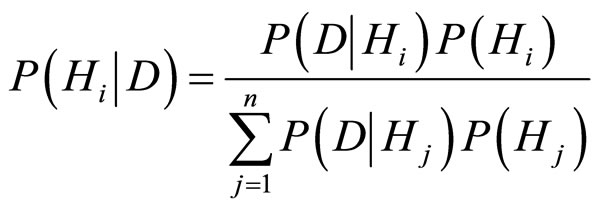
其次信息增值定义为

对信息增值的期望(对所有的证据求期望值)是
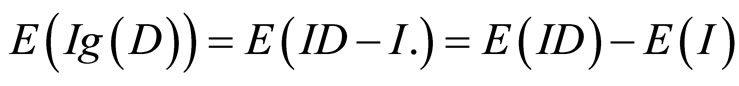
而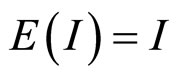 ,且
,且 为
为
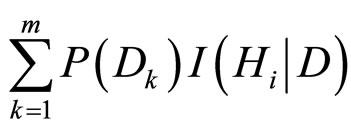
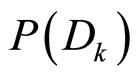 由全概率公式给出:
由全概率公式给出:
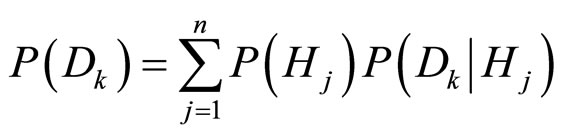
对于下面的关于纸牌选择任务的实验材料,我们理论上可以分别算出关于P,NotP,q,Notq的期望信息增值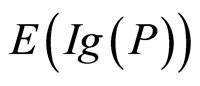 ,
,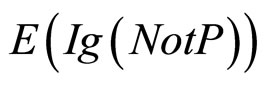 ,
,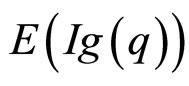 ,
,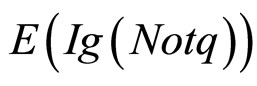 (假设
(假设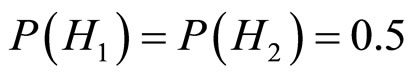 ,
,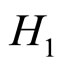 表示条件句的前件和后件有很高的逻辑关联,
表示条件句的前件和后件有很高的逻辑关联,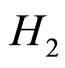 表示条件句的前件和后件是高度独立的,即我们可以合理地假设在翻牌之前,被试对于
表示条件句的前件和后件是高度独立的,即我们可以合理地假设在翻牌之前,被试对于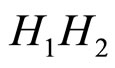 这两个竞争假设没有特殊的偏好;以及数据最优选择(Optimal data selection):人们通常在面临两个及两个以上的竞争假设时,特别偏好选择那些能带来最大惊奇的证据来评价这些假设,所谓的惊奇,是指新证据所包含的新信息能否证假设的程度,它可以用本节引进的信息增值的期望值来刻画)。但在许多研究中,信息增值的期望
这两个竞争假设没有特殊的偏好;以及数据最优选择(Optimal data selection):人们通常在面临两个及两个以上的竞争假设时,特别偏好选择那些能带来最大惊奇的证据来评价这些假设,所谓的惊奇,是指新证据所包含的新信息能否证假设的程度,它可以用本节引进的信息增值的期望值来刻画)。但在许多研究中,信息增值的期望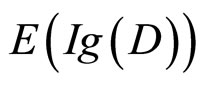 多通过经验可以修正为
多通过经验可以修正为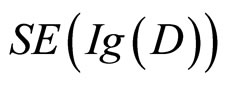 (Scaled expected information gain),它的计算需要一些参数,即
(Scaled expected information gain),它的计算需要一些参数,即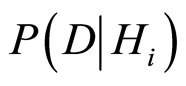 ,
, 的值,其他的参数可以通过Bayes定理和全概率公式来计算出。
的值,其他的参数可以通过Bayes定理和全概率公式来计算出。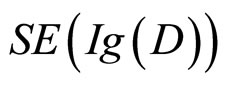 的大小反映出被试对选择后果的惊奇程度,
的大小反映出被试对选择后果的惊奇程度,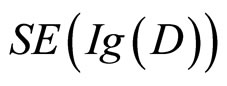 越大,说明被试越想作出有利于证据D的选择,反映在纸牌选择任务中的表现就是:四个选择中那个
越大,说明被试越想作出有利于证据D的选择,反映在纸牌选择任务中的表现就是:四个选择中那个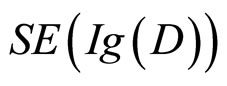 最大,这个最大的选择被被试选择的机会最大,因而在这一组被试中选中的次数也最大,其余的选择以此类推。所以,
最大,这个最大的选择被被试选择的机会最大,因而在这一组被试中选中的次数也最大,其余的选择以此类推。所以,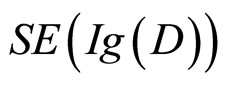 的大小次序应与每个选择的频数的大小次序是一致的。下面的例子来源于Oaksford. M, Chater. N(1996)。它的条件句规则是:如果房间里有水壶落地(P),那么就会传来撞击声(q)。选择任务是下面那些牌要翻以有必要检验条件句规则的真假:
的大小次序应与每个选择的频数的大小次序是一致的。下面的例子来源于Oaksford. M, Chater. N(1996)。它的条件句规则是:如果房间里有水壶落地(P),那么就会传来撞击声(q)。选择任务是下面那些牌要翻以有必要检验条件句规则的真假:
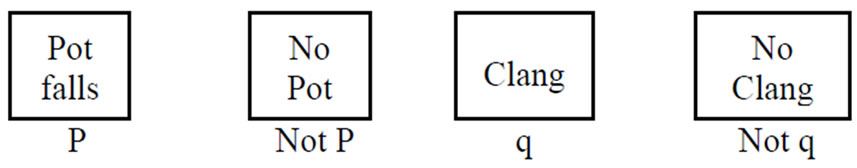
应用Bayes模型的数据最优选择分析程序,理论上有
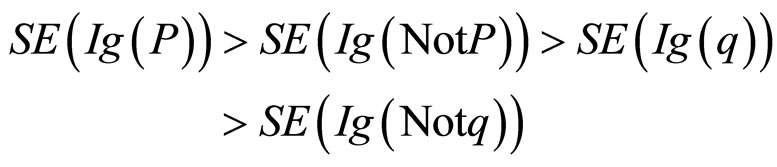
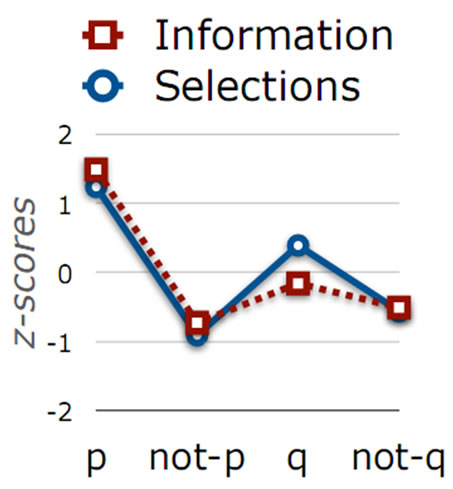
这个实验结果显示与理论分析一致(Z-分数),见图2(图例Information是指应用Bayes模型的数据最优选择分析程序的理论值,图例Selection是该实验的结果)。
这个模型的另一个要点是Ramsey测试(Ramsey test),它把条件句AÞB理解为假定A为真,在这样的情景下,B是否会发生以及发生的可能性有多大。用条件概率P(A|B)来描述这样的推理过程。4个条件句的逻辑形式的条件概率分别如下:
若 P(A) = a,P(B) = b,P(非B|A) = e,则
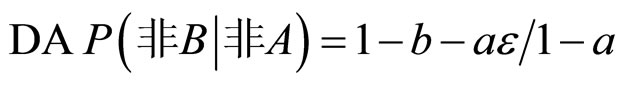


这个模型与其他模型在这个实验结果的比较见图3。
图3的实验有A,B,C和D四个结果。A是Mental Rule模型与实验结果的比较,B是Mental Rule模型补充当且仅当(if and only if)的推理后与实验结果的比较,C是未修正的概率模型与实验结果的比较,D则
Source: Oaksford & Chater, 1994
Figure 2. The fitting of optimal data selection (information selection) model for the experimental results
图2. 最优数据模型(基于信息的选择)对实验结果的拟合
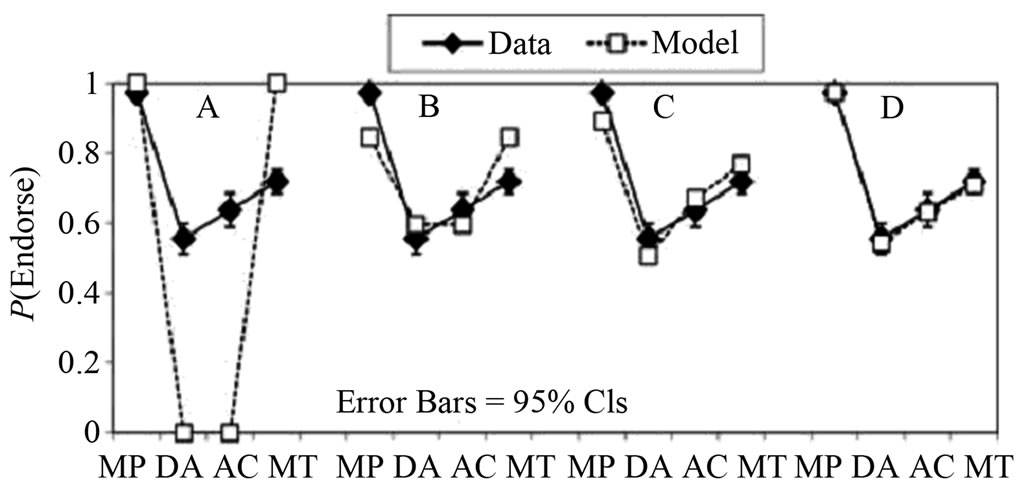
Source: Schroyens and Schaeken, 2003
Figure 3. The comprison between the mental rule model and the probabilistic model (A, B are the mental rule models; C, D are the probabilistic model based on the Bayes rule)
图3. Mental rule模型和概率模型与实验结果的比较(A,B是mental rule模型及其修正与实验结果的比较;C,D是概率模型及其修正与实验结果的比较)
是修正的概率模型与实验结果的比较,结果在误差范围内符合得相当好(Schroyens & Schaeken, 2003)。
Bayes模型的数据最优选择分析程序是一个通用的解释模式,应用它可以解释范围广泛的选择任务实验结果,例如,条件句前件和后件是归纳相关的,涉及双向条件的,涉及否定形式的,涉及内容和主题效应的,基于社会规范的推理等(Oaksford & Chater, 1994)。到目前为止,Bayes模型是推理心理学里解释力最强的又有较为合理的理论基础的假设。从理论的简洁和解释力来比较,基于Bayes规则的概率模型是最优的。
4. 反事实条件句为什么是特殊的?
反事实条件句是这样的条件句:它的前件是假想的,在现实中是假的。但是,反事实条件句是在表达人们对假想的命题的信念,因此是有意义的条件句。对于反事实条件句的真假判断标准,通常是相似世界语义学,即如果在与现实世界相似的假想世界中前件为真,那么在这些假想世界中后件为真,就说该反事实条件句为真。很明显这个判断标准是不同于以逻辑规则为基础的其它类型的一般条件句,所以Mental rule和Mental model两个模型无法解释反事实条件句的意义。如果用Bayes模型来解释反事实条件句,就会遇到一个原则上的限制:反事实条件句的前件的概率为0,所以此时是不能应用Bayes规则。
也许有希望的模型是认为推理者是用Ramsey测试来进行推理,但是,Ramsey测试有一些问题,例如,在解释干预型反事实条件句时,现有的用于Ramsey测试的语义模型有内在的困难。从目前的研究来看,这方面的探讨有待深入。另一个建议是应用Bayes因果推理网(Pearl, 2001)或图模型(Graph model),因果推理网来实际上是探索反事实条件句的所隐藏的因果关系,对因果推理网的说明超出了本文的范围,也许它比基于Bayes法则的概率模型更好地解释反事实条件句推理的实验结果。但这需要更多的研究。
Anderson, J. (1991). Is human cognition adaptive? Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 14, 471-484.
Braine, M. D. S., & O’Brien, M. D. S. B. D. P. (1998). Mental logic. London: Routledge.
Byrne, R. M., & Johnson-Larid, P. N. (2009). “If” and the problems of conditional reasoning. Trends in Cognitive Science, 13, 282-287.
Evans, J. S., et al. (2005). Suppostion, extensionality and conditionals: A critique of Johnson-larid and Byrne (2002). Psychological Review, 112, 1040-1052.
Kowalski, R., & Sadri, F. (2009). Integrating logic programming and production systems in abductive logic programming agents. In: A Polleres, & T. Swift, (Eds)., Web reasoning and rule system. Springer, 5837.
Marcus, S. L., & Rips, L. J. (1979). Conditional reasoning. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 1, 199-223.
Oaksford, M., & Chater, N. (1994). A rational analysis of the selection task as optimal data selection. Psychological Review, 101, 608-631.
Oaksford, M., & Chater, N. (1996). Rational explanation of the selection task. Psychological Review, 103, 381-391.
Pearl, J. (2003). Causality: Models, reasoning and inference. Cambridge: Cambridge University.
Schroyens, W., & Schaeken, W. (2003). A critique of Oaksford, Chater and Larkin’s (2000) conditional probability model of conditional reasoning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory and Cognition, 29, 140-149.
Stenning, K., & Van Lambalgen, M. (2008). Human reasoning and cognitive science. London: MIT press.