1. 引言
在全球及区域气候变暖背景下,长江、黄河、澜沧江三大水系的水资源情势在近几十年来发生变化,长江洪涝、黄河缺水和断流问题频频告急[1] -[3]。这三条水系的源头,即三江源地区,也呈现湖泊萎缩、河流干涸和冰川退缩等趋势,生态环境退化并面临严峻的考验[4] 。相关研究表明,三江源地区气温升高[5] ,三江源地区所处的青藏高原降水和气温在近几十年来也发生变化并存在地区差异性[6] [7] 。
由于三江源地区地理位置、地形条件特殊,实测气象资料少,相关研究主要集中在包括长江源区的长江流域或整个青藏高原地区[8] ,未能充分突出三江源地区的水汽输送变化特征,因此,本文着重以三江源地区为研究区,基于实测气象资料和NCEP/NCAR I再分析资料,研究近几十年来三江源地区不同时间尺度上水汽输送和降水变化特征,为分析该区域的降水变化特征及其与水汽输送变化的可能联系提供参考。
2. 研究数据
本研究采用两部分数据,一部分为实测气象要素数据,包括三江源地区12个地面观测站1971~2010年的逐日降水和气温;另一部分为NCEP/NCAR I再分析资料(下文简称NCEP再分析资料),包括1971~2010年的地面至300 hPa的逐日风场、逐日比湿和逐日温度,格点数据的水平分辨率为2.5˚ × 2.5˚。研究表明NCEP再分析资料在亚洲地区较其他的再分析资料更为合理、可信度更高[9] [10] ,且1970年代前的NCEP再分析资料在青藏高原与实测资料存在较大偏差[11] -[13]。此外,比较2006~2010年三江源地区探空站数据与再分析资料表明,NCEP再分析资料能够比较准确地反映三江源地区大气状况[14] 。
因此,本研究仅选用1971~2010年的NCEP再分析资料分析三江源地区水汽输送变化趋势。三江源地区地面气象观测站和NCEP再分析格点分布见图1,其中NCEP再分析格点只给出三江源区域四个边界上的格点。
3. 研究方法
本研究中,对涵盖三江源地区的NCEP格点计算区域整层纬向水汽输送和经向水汽输送。计算格点整层纬向水汽输送(Qu)和经向水汽输送(Qv)的方法为[15] [16] :
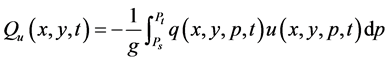 (1)
(1)
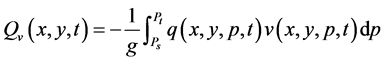 (2)
(2)
其中,Ps为地面气压,单位为hPa;Pt为大气顶部气压,取为300 hPa;q为比湿,单位为g/kg;u为纬向风,单位为m/s;v为经向风,单位为m/s;g为重力加速度m/s2;水汽输送通量单位为g/(s×cm×hPa)。三江源地区地面气压较低,在700 hPa左右,因此当Ps大于700 hPa时,取Ps = 700 hPa;当Ps小于700 hPa时,Ps不变。
对涵盖三江源地区的NCEP格点边界,各边界水汽输送的计算方法为:
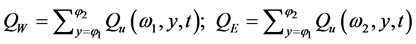 (3)
(3)
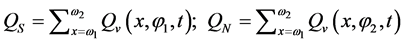 (4)
(4)
四个区域边界的总水汽收支为:
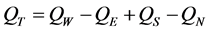 (5)
(5)
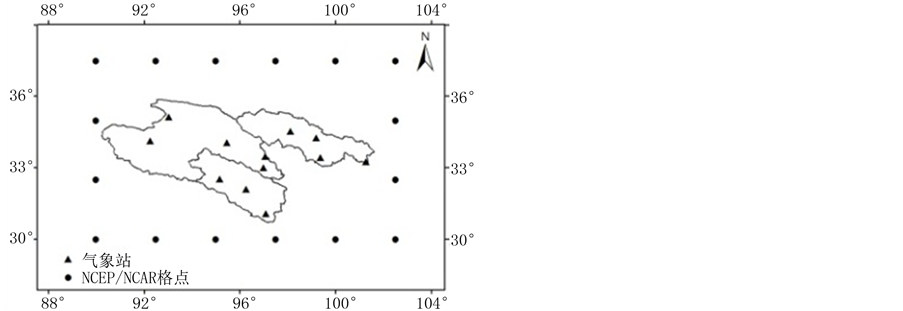
Figure 1. Meteorological stations in the Three Rivers’ Headstream Region and the NCEP Reanalysis grids
图1. 三江源地区气象站和区域边界NCEP再分析格点分布
其中,QW、QE、QS、QN分别为西、东、南、北边界上的水汽输送通量;QT为区域边界的总水汽收支;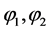 分别为南、北边界对应的纬度,
分别为南、北边界对应的纬度,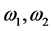 分别为西、东边界对应的经度。以三江源地区南边界与北边界水汽输送之差作为经向水汽输送,西边界与东边界水汽输送之差作为纬向水汽输送,经向与纬向水汽输送之和作为区域边界总水汽收支。
分别为西、东边界对应的经度。以三江源地区南边界与北边界水汽输送之差作为经向水汽输送,西边界与东边界水汽输送之差作为纬向水汽输送,经向与纬向水汽输送之和作为区域边界总水汽收支。
水汽通量的数值和方向只能表示水汽来源,而水汽通量散度能考虑输送来的水汽集中程度及集中区域,因此计算水汽通量散度以分析水汽在某地是汇合或辐散[15] 。水平方向的水汽通量散度A的表达式为:
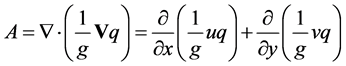 (6)
(6)
其中,A表示水汽通量散度,单位为g/(s×cm2×hPa),其他变量含义与计算水汽通量时相同。若A > 0,则水汽通量辐散,即水汽因输送出去而减少;若A < 0,则水汽通量辐合,即水汽因输送进来而增加。
三江源地区不同时间尺度上的水汽输送变化趋势利用非参数Mann-Kendall方法(以下简称MK方法)[17] 进行分析。MK方法是基于秩的非参数方法,不要求所分析数据服从某一概率分布[18] ,适用于非正态分布的独立性数据序列的变化趋势检验[19] [20] 。
4. 三江源地区水汽输送和降水多年平均特征
4.1. 年平均空间分布
三江源地区全年水汽输送通量的多年平均空间分布见图2,可以看到在东亚季风和印度季风驱动下的西南暖湿气流是三江源地区空中主要水汽来源,其次是来自西边界中东高压中的偏西气流和西风带中的偏北气流,与李生辰等[21] 研究一致。
对三江源地区四个边界而言,1971~2010年,北边界上水汽输送通量为−265.1 g/(s·cm),表明该边界上水汽自北向南输入三江源地区,南边界上水汽输送为1897.2 g/(s·cm),表明该边界上水汽从南向北输入三江源地区,因此经向水汽净收入为正值,即水汽在经向汇入三江源地区;西边界、东边界上水汽输送分别为1008.4 g/(s·cm)、1625.4 g/(s·cm),表明这两个边界上水汽都是自西向东输送,由于西边界上的水汽输送通量小于东边界上的水汽通量,因此纬向水汽净收入为负值,即水汽在纬向输出三江源地区。
由于400 hPa、300 hPa水汽含量和水汽输送通量较小,因此只计算600 hPa和500 hPa的水汽输送通
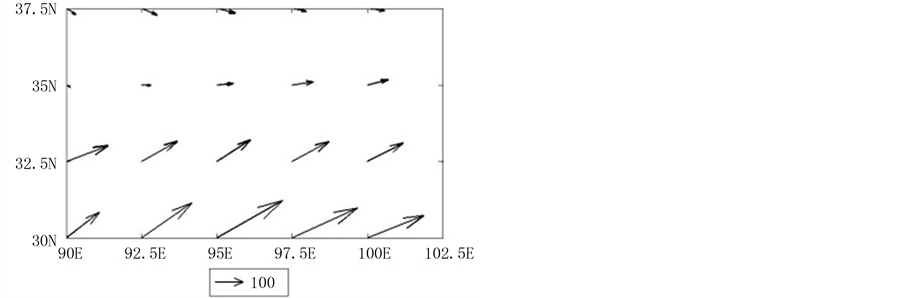
Figure 2. The averaged vertical moisture transport in the Three Rivers’ Headstream Region during 1971-2010
图2. 三江源地区1971~2010年多年平均垂直整层水汽输送(单位:g/(s·cm))
量散度(见图3)。600 hPa水汽输送通量散度在三江源地区为负值,表示水汽辐合,特别是在三江源西南部的长江源头南部和澜沧江源头北部,水汽辐合较大;500 hPa水汽输送通量散度除在长江源头的西南部分为辐合外,在三江源地区其他部分均为正值,即水汽辐散。同时,600 hPa的水汽通量散度值要大于500 hPa,表明自地面向300 hPa,水汽通量散度越来越小,且在500 hPa水汽已为辐散。
三江源地区实测降水多年平均的空间分布与水汽输送及其散度的空间分布具有一定的相关性(见图4),降水较大的地区是水汽输送量值较大且水汽通量散度为辐合的地区,澜沧江源头和黄河流域东部小部分地区年平均降水最大,在长江源头西北部和黄河源区中部年平均降水最小。
4.2. 季节和逐月分布
计算三江源地区区域边界1月至12月总水汽收支在1971~2010年的多年均值表明,三江源地区在1~10月为水汽汇,其中5月至9月水汽输入最多,呈双峰型分布,在11月和12月则为水汽源,即水汽从三江源地区输出(见图5)。有学者利用1948~2007年NCEP再分析资料研究也表明,三江源地区所在的青藏高原在夏半年是一个明显的大气水汽含量高值区,具有显著的“湿池”特征[22] 。三江源地区1月至12月降水则呈单峰型分布,7月降水量在全年最大,说明该地降水不仅与水汽输送条件有关,还与水汽转换效率、温度等因素有关,但总体而言,逐月降水与区域边界总水汽收支的年内分布是比较相似的,夏季各月份所占比重较大,其他月份相对较小。
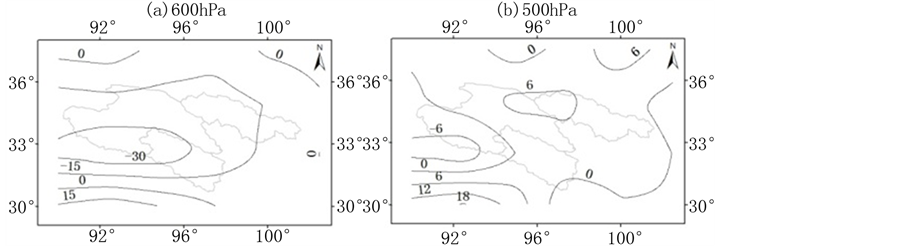
Figure 3. The contours of water vapor flux divergence at 600 hPa and 500 hPa in the Three Rivers’ Headstream Region
图3. 三江源地区600 hPa和500 hPa水汽输送通量散度多年平均等值线图(单位:10−7g/(s·cm2·hPa))
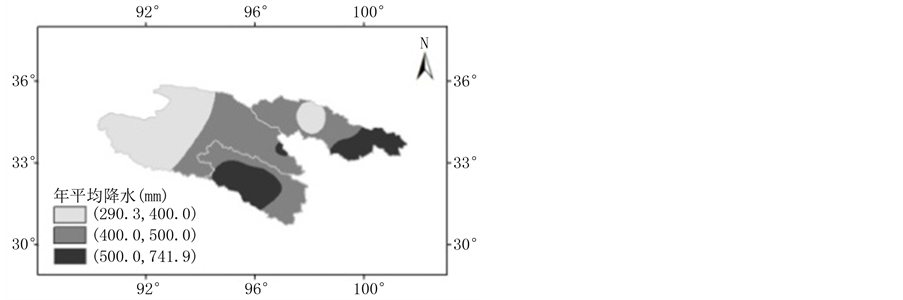
Figure 4. Spatial distribution of precipitation in the Three Rivers’ Headstream Region during 1971-2010
图4. 三江源地区1971~2010年多年平均实测降水空间分布
水汽收支和降水的季节分布进一步表明,三江源地区夏季水汽输送最为活跃,且同期降水量也是年内最大,春季和夏季基本相当,冬季水汽输送和降水都非常少(见图6)。
5. 三江源地区水汽输送和降水时空变化分析
5.1. 年际变化
1971~2010年,三江源地区南边界水汽输送呈显著减少趋势,通过置信度99%检验,一定程度上表明输入三江源地区的西南暖湿气流强度有所减弱,北边界水汽输送则呈明显增加趋势,但北边界水汽输送量值很小,因此经向水汽输送与南边界水汽输送变化趋势一致,呈显著减少,通过置信度99%检验,说明汇入三江源地区的经向水汽减少;西边界水汽输送无明显变化趋势,但东边界水汽输送呈显著减少趋势,通过置信度99%检验,纬向水汽输送因而呈显著增加趋势,即纬向水汽输出的量值在减少(见表1)。
三江源地区区域边界总水汽收支在1971~2010年的变化趋势与经向水汽输送一致,呈显著减少,通过置信度99%检验;降水则呈一定的增加趋势,但未通过显著性检验(见图7),与降水在1956~2004年的变化趋势一致[23] ,即降水变化不明显。
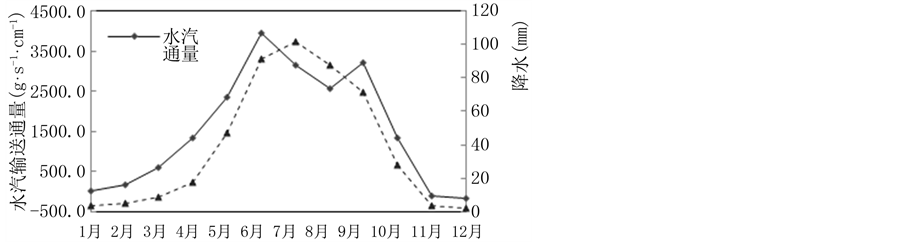
Figure 5. Monthly water vapor budget and monthly precipitation in the Three Rivers’ Headstream Region
图5. 三江源地区年内逐月区域总水汽收支与月平均降水分布
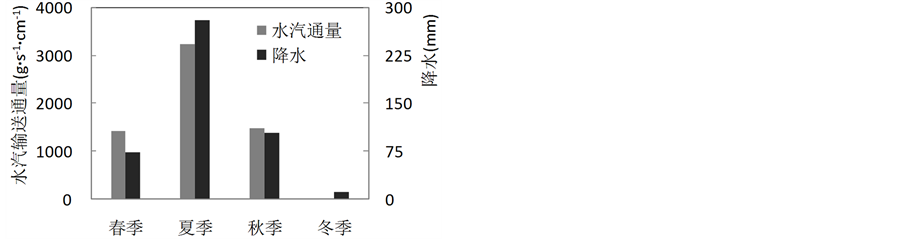
Figure 6. Seasonal water vapor budget and seasonal precipitation in the Three Rivers’ Headstream Region
图6. 三江源地区四个季节区域总水汽收支与降水年内分布

Table 1. MK statistics of water vapor transport and precipitation in the Three Rivers’ Headstream Region during 1971-2010
表1. 1971~2010年三江源地区水汽输送和降水MK统计值
注:*表示通过置信度99%检验。
分析三江源地区水汽输送在1971~2010年的空间变化趋势可知(见图8),三江源地区经向水汽输送的空间变化呈现纬度较高地区减少明显、低纬地区变化不明显的格局,如澜沧江源区、长江源区的南部和黄河源区的南部,经向水汽通量明显减少,但三江源西部和北部地区则无明显变化趋势;纬向水汽输送的空间变化格局为长江源区西部的小部分地区变化趋势不明显,但其他区域都明显减少。综合来看,1971~2010年,三江源地区东南部水汽输送呈显著减少趋势,西北部地区变化趋势不明显。
仍以600 hPa和500 hPa为代表性气压层,分析其水汽输送通量散度在1971~2010年的变化可以发现(见图8),600 hPa和500 hPa水汽通量散度变化趋势不太一致。600 hPa水汽通量散度在三江源地区中部和东南部呈明显增加趋势,三江源地区西北部则变化不明显;500 hPa水汽通量散度除澜沧江源区东南部呈明显增加趋势外,三江源地区大部分地区无明显变化。由上文分析知,600 hPa水汽输送通量散度多年平均在三江源地区为水汽辐合,而1971~2010年该气压层散度呈增加趋势,表明水汽汇聚或辐合程度变
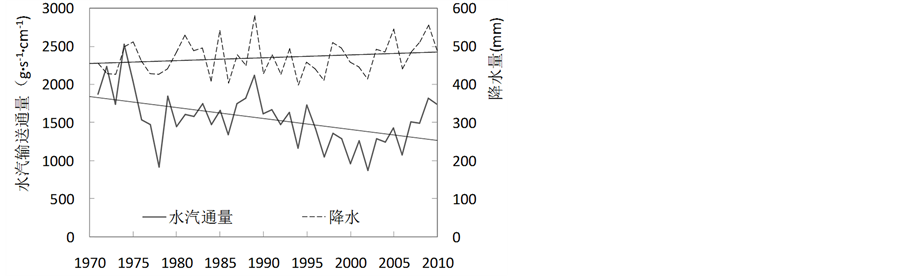
Figure 7. Variations and linear trends of water vapor budget and precipitation in the Three Rivers’ Headstream Region during 1971-2010
图7. 1971~2010年三江源地区总水汽收支与降水变化及线性趋势
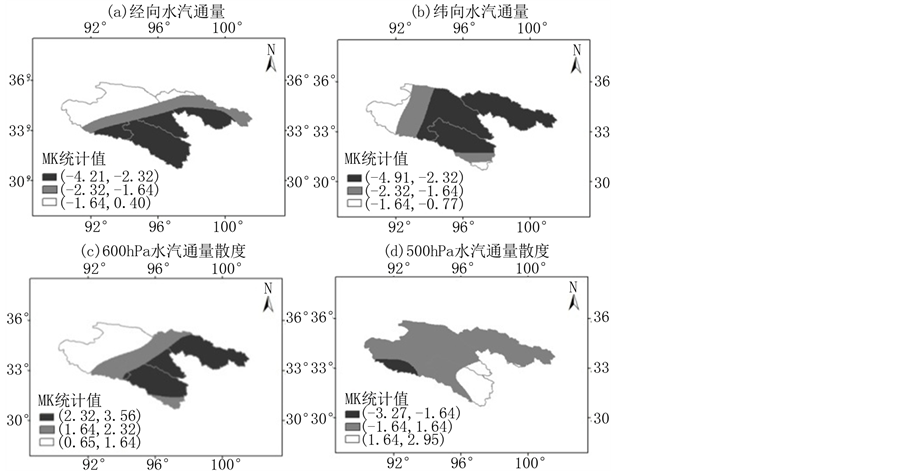
Figure 8. Spatial variations of water vapor budget in the Three Rivers’ Headstream Region during 1971-2010
图8. 1971~2010年三江源地区水汽输送空间变化
小,特别是水汽辐合值较大的长江源头南部和澜沧江源头北部,水汽输送通量散度减小趋势比较明显。这表明,三江源地区近几十年来中低层大气水汽辐合程度有所减少,但高层大气中水汽辐合或辐散变化不大。
对降水而言,与水汽输送明显减少的空间变化格局不同,三江源地区降水在1971~2010年无明显空间变化差异,仅北部很小部分地区呈一定的增加趋势(见图9)。
5.2. 年代际变化
将三江源地区水汽输送与降水在1971~2000年的多年均值作为基准值,分别计算该地区水汽输送和降水的年代际距平变化可以看到(见表2),三江源地区水汽输送在1970s、1980s的变化相对较小,在1990s和2000s的变化幅度则较大,且区域边界总水汽收支在1990s、2000s均减少;降水在四个年代中变化均不大,距平变化率不超过5%。
5.3. 季节变化
1971~2010年,三江源地区纬向水汽通量在四个季节均呈明显增加趋势,通过置信度95%或置信度99%检验;经向水汽通量在四个季节均呈显著减少趋势,通过置信度99%检验;区域边界总水汽收支在春季、夏季和秋季明显减少,冬季变化不大;降水在春季和夏季呈一定的增加趋势,但未通过显著性检验,在秋季和冬季则减少,也未通过显著性检验(见表3)。
5.4. 典型月份变化
由上文可知,三江源地区夏季和秋季(主要是9月份)水汽输送与降水在全年中占很大比重,且区域边
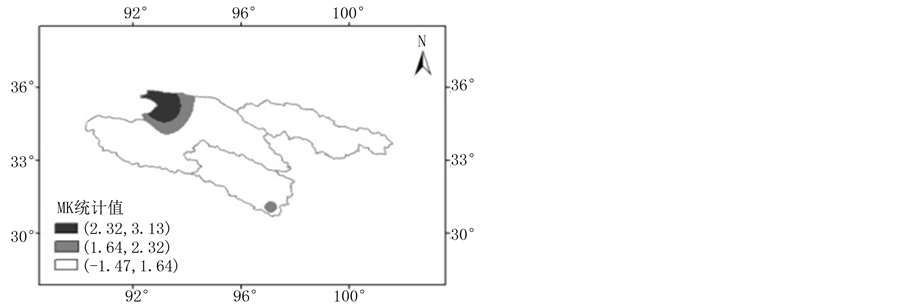
Figure 9. Spatial variations of precipitation in the Three Rivers’ Headstream Region during 1971-2010
图9. 1971~2010年三江源地区实测降水空间变化

Table 2. Decadal anomalies of water vapor transport and precipitation in the Three Rivers’ Headstream Region
表2. 三江源地区水汽输送和降水的年代际距平变化(%)
界总水汽收支在夏季和秋季减少趋势也非常明显,因此着重对夏季的6至8月和秋季的9月四个月份进行分析。结果表明,1971~2010年,三江源地区区域总水汽收支在6月和9月呈显著减少趋势,通过置信度99%检验,在7月和8月无明显变化趋势,未通过显著性检验;降水在6月呈增加趋势,未通过显著性检验,在7月和8月与水汽输送一致,无明显变化趋势,在9月也与水汽输送一致,呈减小趋势,但减少程度比水汽输送小(见表4)。可见,三江源地区水汽输送减少主要发生在夏季6月和秋季9月,且降水在9月份也明显减少,会加剧该地区的秋旱。
5.5. 变化原因分析
1971~2010年,三江源地区的区域总水汽收支呈明显减少趋势,特别是6月和9月减少趋势显著,但降水与水汽输送的变化趋势并不太一致,比如降水在6月呈一定的增加趋势。另外,三江源地区的水汽输送和降水存在空间变化差异,三江源地区特别是东南部年平均水汽输送减少显著,且水汽通量散度在中低层大气中辐合程度降低,但年平均降水在近几十年来并没有明显变化趋势,甚至在局部地区呈一定的增加趋势。
三江源地区降水与水汽输送的变化趋势不太一致,主要是因为降水除了受水汽输送条件影响,还与其他因素如温度、高原地形等诸多因素有关。以温度为例,分析三江源地区地面2 m处气温(基于观测资料)、600 hPa至300 hPa大气温度(基于NCEP再分析格点资料)在1971~2010年的变化趋势可知(见表5),地表至大气中低层的温度升高趋势非常明显,至少通过置信度95%检验。而局地温度升高,水分循环加剧,可能促使局域水汽转换效率增大,从而增加该地区降水。另一方面,三江源地区气温升高,其所在

Table 3. MK statistics of seasonal water vapor transport and seasonal precipitation in the Three Rivers’ Headstream Region during 1971-2010
表3. 1971~2010年三江源地区季节水汽输送和降水的MK统计值
注:*表示通过置信度99%检验。

Table 4. MK statistics of water vapor transport and precipitation from June to September in the Three Rivers’ Headstream Region during 1971-2010
表4. 1971~2010年三江源地区6至9月水汽输送和降水的MK统计值
注:*表示通过置信度99%检验。

Table 5. MK statistics of atmospheric temperature at different layers in the Three Rivers’ Headstream Region during 1971-2010
表5. 1971~2010年三江源地区不同气压层温度的MK统计值
注:*表示通过置信度99%检验。
的青藏高原气温也呈增暖趋势,青藏高原的热力因素改变可能引起亚洲季风区环流变化,从而对高原地区降水产生影响[24] [25] 。
6. 小结
在三江源地区气候发生变化、生态环境退化的背景下,本文利用三江源地区的观测气象资料和NCEP/NCAR I再分析格点资料,对该地区1971~2010年水汽输送及降水的时空特征和变化趋势进行了分析。主要结论包括:
1) 对多年平均尺度而言,三江源地区北边界上水汽自北向南输入,南边界上水汽从南向北输入,水汽在经向汇入三江源地区;西边界、东边界上水汽都是自西向东输送,由于西边界上的水汽输送通量小于东边界上的水汽通量,因此水汽在纬向输出三江源地区。自地面至300 hPa,水汽通量散度越来越小,且在500 hPa水汽已为辐散。三江源地区降水与水汽输送及其散度的空间分布具有一定的相关性,降水较大的地区是水汽输送量值较大且水汽通量散度为辐合的地区,澜沧江源头和黄河流域东部小部分地区年平均降水最大。逐月降水与区域边界总水汽收支的年内分布比较相似,夏季各月份所占比重较大,其他月份相对较小。
2) 从时间变化看,1971~2010年,三江源地区经向水汽输送呈显著减少趋势,主要是由于南边界水汽输入减少;纬向水汽输送呈显著增加趋势,主要是由于东边界水汽输出显著减少。区域边界总水汽收支在1971~2010年的变化趋势与经向水汽输送一致,呈显著减少,通过置信度99%检验;降水在1971~2010年则呈一定的增加趋势,但未通过显著性检验。水汽输送在1990s和2000s的变化幅度较大,且在1990s、2000s均减少;降水的年代际变化不大,距平变化率不超过5%。1971~2010年,三江源地区区域边界总水汽收支在春季、夏季和秋季明显减少,特别是夏季6月和秋季9月显著减少,冬季变化不大;降水在春季和夏季呈一定的增加趋势,未通过显著性检验,在秋季和冬季减少,也未通过显著性检验,但秋季9月降水与水汽输送一致,呈明显减少趋势。
3) 从空间变化看,1971~2010年,三江源地区东南部水汽输送呈显著减少趋势,西北部地区变化趋势不大。同时,三江源地区近几十年来中低层大气水汽辐合程度有所降低,但高层大气水汽辐合或辐散变化不大。与水汽输送明显减少的空间变化不同,三江源地区降水在1971~2010年的空间变化并无明显差异,仅北部很小部分地区呈一定的增加趋势。
三江源地区近几十年来水汽输送显著减少,但实测降水并没有相应减少,甚至局部地区增加。这主要是因为降水不仅受水汽输送条件影响,还与其他因素如温度等有关,需进一步深入研究。
致 谢
本研究所使用的站点资料由中国气象局国家气象信息中心提供。在此诚挚感谢!
基金项目
国家自然科学基金重点项目(51239004);湖北省自然科学基金(2012FFB02206);中央高校基本科研业务费资助HUST (2013TS093,2012QN071)。

NOTES
*作者简介:曾小凡(1980-),女,湖北荆门人,讲师,主要从事水文水资源、气候变化及水文响应研究。