1. 引言
伴随着全球气候的增暖变化和人类对水资源的非理性开发利用,我国干旱呈现出受旱范围扩大、发生频率增加、灾害损失加重的发展趋势[1] -[3] 。干旱是某时段由于蒸发量和降水量的收支不平衡,水分支出大于水分收入而造成的水分短缺现象[4] 。在气象指数中,相对湿润度指数(M)是表征某时段降水量与蒸散发量之间平衡的指标之一,能够综合反映降水量和蒸发量不平衡收支关系的干旱指数,针对区域干旱的研究应从干旱形成的物理机制出发,避免了仅以降水减少或温度上升的单因素不足以较好反映环境变化下的区域干旱化特征的问题[5] 。连续无雨日数是指连续无有效降雨的天数,能够具体反映年内例次干旱的起始时间、结束时间、持续时间及干旱频次,干旱频次可重点描述在不同的年代里某个季节发生季节性干旱的频繁程度。
潮白河流域是我国“三北”防护林工程、太行山绿化工程、京津风沙源治理工程等重点防护林体系建设区及密云水库上游国家级水土保持重点治理区,流域内土地覆盖类型以林地、草地、耕地为主[6] 。20世纪80年代以来潮白河上游的年径流量呈现明显的减少趋势,到20世纪90年代的流域径流量平均值仅为60年代的75.18%[7] ,年降水和潜在蒸散发量没有显著变化,气温则呈显著上升[6] ,但降水频率(日均降水场次)呈下降趋势,降水强度场均降水量呈增加趋势,这将导致极端降水事件如暴雨、干旱发生的概率增大[8] 。植被活动的年际变化主要由气候波动引起,水资源的不均衡使得潮白河流域内植被的生长,甚至威胁京津地区的用水安全。本文根据地理位置和水文特征,将潮白河流域划分为潮河区、白河区和下游区三个二级区,基于潮白河流域1980~2012年丰宁、张家口、塘沽3个气象站点的连续观测资料,从年和季两种时间尺度分析潮白河流域气候因子及干旱指数的时空变化特征,旨在揭示研究区内干旱的时空演变规律,为区域林草植被经营管理、农作物耕作等提供参考。
2. 数据与方法
2.1. 研究区概况
潮白河流域位于华北平原北部,东经115˚25'~117˚45',北纬39˚9'~41˚39'。是海河流域北系四大河流之一,发源于燕山北部山区,流经河北、北京、天津三个省市(如图1)。地处山地与平原的过渡地区,流域内地势西北、东北高,东南低。全流域面积1.9万多平方公里,其中山区占87%。上游分潮河、白河两大支流,潮、白两河在密云水库汇合之后,形成下游的潮白河[9] 。据此,本文将潮白河流域划分为潮河区、白河区和下游区三个二级区。
潮白河流域属于中纬度大陆性季风气候,冬季干寒,春秋季多风。多年平均气温9.8℃,年均降雨量约553 mm,降水年际变化大、年内降水分配不均,多集中在汛期(6~9月),约占总降水量的85%,导致其年内径流丰、枯悬殊,春、冬旱频发。
2.2. 数据
气象资料来自中国气象科学数据共享服务网中的中国气候地面资料日值数据集,包括研究区内丰宁、张家口、塘沽三个气象观测站1980~2012年的观测数据,如逐日气温、降水、日照时数、相对湿度、风速、气压、风向等。
2.3. 研究方法
2.3.1. 相对湿润度指数
流域年度干旱等级的确定采用国家标准《气象干旱等级GB/T20481-2006》中的相对湿润度指数法[10] ,相对湿润度指数(M)是表征某时段降水量与蒸散发量之间平衡的指标之一。该等级标准可反映作物生长季节的水分平衡特征,适用于季节旬以上尺度的干旱监测和评估,表1为相对湿润度气象干旱等级划分标准。M指数的计算公式为:
 (1)
(1)
式中:P为某时段的降水量,单位为毫米(mm);PE为某时段的可能蒸散发量,单位为毫米(mm),采用FAO Penman-Monteith方法计算[11] 。P-M公式如下:
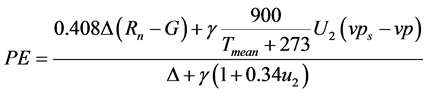 (2)
(2)
式中: 为冠层表面净辐射,MJ/(m2·d);G为土壤热通量密度,MJ/(m2·d);
为冠层表面净辐射,MJ/(m2·d);G为土壤热通量密度,MJ/(m2·d);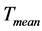 为2 m高处日平均气温,℃;
为2 m高处日平均气温,℃; 为2 m高处风速,m/s;
为2 m高处风速,m/s;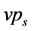 为饱和水汽压,kPa;
为饱和水汽压,kPa; 为实际水汽压,kPa;
为实际水汽压,kPa; 为水汽压曲线斜率,kPa/℃;
为水汽压曲线斜率,kPa/℃; 为干湿球常数,kPa/℃。
为干湿球常数,kPa/℃。
2.3.2. 连续无雨日数
选取连续无雨日数作为划分季节性干旱等级的指标,将干旱按季节分为春旱、夏旱、秋旱、冬旱四

Figure 1. The location of Chaobai river basin
图1. 潮白河流域地理位置

Table 1. Drought classification standard of the relative moisture index
表1. 相对湿润度气象干旱等级划分标准
种类型,并将每种类型的干旱划分为四个等级,等级划分标准见表2 [10] 。
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 气候因子年际变化趋势
利用流域内气象站点的日温度、降水和其他气象要素资料,根据P-M公式计算可能蒸散发量PE,分析各二级区的温度、降水量和蒸散发量的年际变化趋势,见图2。潮河区多年平均温度为7.1℃,白河区9.2℃,下游区13.1℃。各二级区年际温度变化较为平稳,但总体呈现一定的变暖趋势。多年平均降水量下游区 > 潮河区 > 白河区,其中潮河区降水量有减少趋势,白河区和下游区呈现一定的增加趋势,且年际波动较大,尤其是下游区年际降水量差异较大。蒸散发量受温度影响较大,各区多年平均蒸散发量与温度大小顺序相同,即下游区 > 白河区 > 潮河区。潮河区蒸散发量呈上升趋势,白河区和下游区呈现降低趋势,下游区年际波动变化相对于其他区域明显较大。
3.2. 年度干旱的时空演变
3.2.1. 各二级区年度干旱等级判定
年度干旱指标采用相对湿润度指数(M),基于潮白河流域各二级区内气象站点的1980~2012年2 m高处的温度、相对湿度;10 m高处的风速;日照时数等资料,通过FAO Penman-Monteith法求取逐日逐日

Table 2. Drought classification standard of consecutive days without rain
表2. 连续无雨日数气象干旱等级划分标准


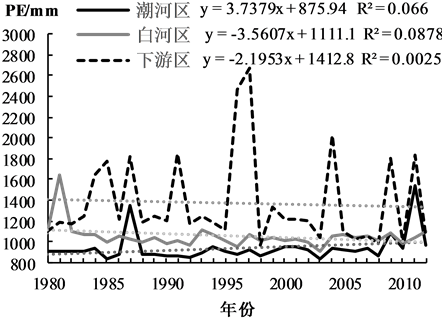
Figure 2. The interannual variation trend of temperature, precipitation and PE in Chaobai river basin
图2. 潮白河流域温度、降水和蒸散发量年际变化趋势
可能蒸散发量,统计全流域逐月、逐年的蒸发量,结合流域降水量计算流域内各站点的M指数(公式(1))。根据相对湿润度气象干旱等级划分标准(表1)逐年判定干旱等级,统计流域内各二级区不同干旱等级的发生频次(图3)。
结果表明:33年中潮河区3年为无旱年,26年为轻旱年,1984年、2009年和2011年为中旱年;白河区19年为轻旱年,14年为中旱年,且连续性均在5年以下;下游区1980~1988年持续轻旱年,之后干旱情况年际波动较大(7个无旱年,8个轻旱年,7个中旱年,2个重旱年)。
3.2.2. 年度M指数时空变化趋势
1980~2012年潮河区M指数线性拟合斜率为−0.002,白河区斜率为0.002,下游区斜率为0.003,但相关性并不显著。本文通过分析年度M指数和距平M指数发现,潮河区M指数有两个变化阶段(图4(a)):1980~1998年M指数呈明显上升趋势到1998年达最大值,之后逐渐降低,P值均小于0.005;白河区和

Figure 3. The drought grade statistical figure of Chaobai river basion from 1980 to 2012
图3. 1980~2012年潮白河流域干旱等级统计图
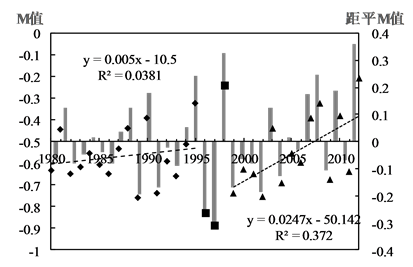

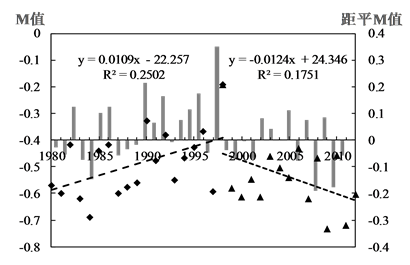
Figure 4. Temporal evolution of relative moisture index and their anomalies in Chaobai river basin from 1980 to 2012
图4. 1980~2012年相对湿润度指数(M)变化趋势及其距平变化
下游区的根据波动规律具体可分为三个周期(图4(b),图4(c)):1980~1995年上升期、1995~1998年动荡期和1998~2012年重新上升期,两个上升期P值均小于0.001。
3.3. 季节性干旱的时空演变
3.3.1. 季节性气候时空变化趋势
根据公式(1)计算各二级区每年的季度M指数,发现各区多年季度M均值表现为冬季 < 春季 < 秋季 < 夏季。其中,夏季M指数各区差异较大,白河区明显较低;其他季节较为接近。整体来看,春、夏、秋三个季节潮河区各季度M均值最大,白河区最小,冬季相反。
从年际变化趋势来看(表3),潮河区和白河区夏季M值有下降趋势,但不显著,表明两区域内夏季旱情有一定程度的加重趋势;其他各季节M值均有不同程度的上升趋势,尤其是秋季上升斜率较大,且相关性显著。表明在潮白河流域,秋季降水量相对于蒸散发量的亏损量呈明显变小趋势。
3.3.2. 季节性干旱发生频次时空特征
M指数可以对一个时间段内的降水与蒸散情况进行归一化定量评价,但是不能充分反映季节内的干旱发生次数。本研究在M指数基础上,选择连续无雨日数干旱等级划分标准法,统计潮白河流域各的季

Table 3. The change trend of season M values in Chaobai river basin from 1980 to 2012
表3. 1980~2012年潮白河流域季节M指数变化趋势
备注:**表示通过0.01的显著性检验(双侧检验),*表示通过0.05的显著性检验(双侧检验)。
节性干旱发生频次。由图5可以看出,1980~2012年间,潮河区共发生季节性干旱105次,白河区95次,下游区103次。潮白河流域以春旱和冬旱为主,其中,春小旱发生频次最高,其次为冬小旱、春中旱和冬中旱。由于潮白河流域降水主要集中于夏季和秋季,因此夏旱和秋旱较少发生,且无大旱或特大旱。
统计不同干旱等级年份各季节性干旱发生频率(图6),结果表明:在无旱年,春旱和冬旱占92%,夏旱占8%,以小旱和中旱为主;在轻旱年,春旱和冬旱占89%,秋旱和夏旱共占11%,大旱和特大旱比例上升;在中旱年,秋旱和夏旱比例上升至22%;重旱年中共发生小旱7次,且均匀分布于四季,冬中旱和夏中旱各1次,特大旱在夏季发生1次。总体而言,随着年度干旱等级升高,秋旱和夏旱、大旱和特大旱发生频率也随之增大。秋旱和夏旱均为小旱或者中旱,主要在中旱年和重旱年发生,表明秋季和夏季的气候变化将对年度干旱水平影响较大。
4. 讨论
本研究通过分析气象站的观测数据发现潮白河流域有变暖趋势。气候变暖会对陆地生态系统的植被及土壤产生深远的影响,不仅能够提前平原地区植物的开花期和结果期,也能改变高山地区植物的营养生长[1] 。潮河区土地覆盖类型以林地为主,林地以落叶阔叶林和温带针叶林为主,白河区以草地为主,下游区以耕地为主[6] 。植被活动的年际变化主要由气候波动引起,并且由于植被生物特性存在差异,导致植被对气候和干旱的响应机制也有所差异。
经研究发现潮河区春旱和冬旱多发,而在春季萌芽前,为落叶树种的树体需水时期,如冬春干旱常将延迟萌芽,将影响树木生长季的发育。白河区土地覆盖类型以草地为主,草地植被的生长受降水、温度影响较大,这与草地植被的本身根系特征及生长周期等生长特性有关[12] ,冬季降水量(降雪)的增加有助于减少冬季的土壤风蚀以及保持土壤的温度和春季土壤的湿度,有助于草本植物和新的苗芽、灌木丛等度过整个冬天。下游区土地覆盖类型主要为耕地,以小麦、玉米等轮作作物为主,该区域大旱和特大旱发生频次较少,适合农作物耕作,但年际降水量和蒸散发量波动较大,人工灌溉工作应根据气候变化给予调节。


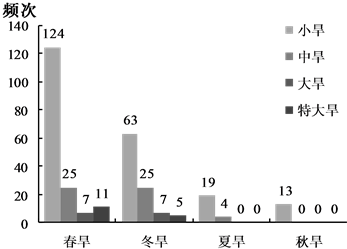

Figure 5. Seasonal drought frequencies of Chaobai river basin from 1980 to 2012
图5. 1980~2012年潮白河流域季节性干旱发生频次空间特征
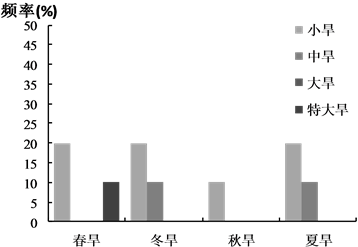


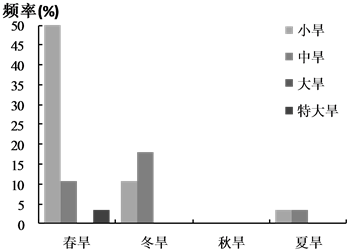
Figure 6. Seasonal drought frequencies of Chaobai river basin from 1980 to 2012
图6. 1980~2012年潮白河流域不同干旱等级年份季节性干旱发生频次
5. 结论
本文基于1980~2012年气象站的连续观测资料,分析潮白河流域气候因子的变化趋势,并选取相对湿润度指数(M)和连续无雨日天数两种干旱指数,分别从干旱强度和干旱频次两个角度对研究区年度干旱和季节干旱进行评价。
潮白河流域从上世纪80年代以来整体有变暖趋势,而降水量、蒸发量和干旱特征各二级区内表现各异。其中,潮河区以轻旱年为主,但降水量呈逐年减少趋势,蒸散发量呈上升趋势,干旱有加重趋势,尤其是1998年以后干旱加重趋势明显;白河区为轻旱年或中旱年,下游区干旱情况年际变化较大,两区域降水量逐年增加,蒸散发量减少,干旱呈现一定的好转趋势。
从季节干旱变化趋势来看,潮河区和白河区夏季干旱有加重趋势,其他各季干旱情况均有所好转,尤其是秋季M值上升斜率较大,且相关性显著。季节性干旱中春旱频次最高,其次为冬旱。随着年度干旱等级升高春旱和冬旱发生频率增加,小旱和中旱发生频率减少,大旱和特大旱发生频率随之升高。秋旱和夏旱发生较少,均为小旱或者中旱,且集中于中旱年和重旱年,表明秋季和夏季的气候变化将对年度干旱等级影响较大。
项目基金
国家973课题(2012CB955403)。