1. 引言
兴源冲铜矿床地处扬子古板块和华夏古板块结合处钦杭成矿带北侧的宜丰–景德镇板缘深断裂带西段,九岭南缘大型推(滑)覆构造西段[1] -[4]。在九岭南缘已发现20余处铜多金属矿床(点),并有较大范围的Cu、Pb、Zn、Au等多元素综合异常区[3] [5] 。邹建成(2010)报道了矿区具中型以上铜矿资源潜力,李均良等(2012)对兴源冲地区深部找矿潜力进行研究,通过对矿区地、物、化、遥等信息,肯定了矿床具有深部找矿潜力,楼法生等(2012)结合矿区地质特征,探讨了该矿床的成矿地质特征及成因,其后,刘婷等(2013)通过稳定同位素研究成矿物质来源并探讨该矿床成矿机制,但在成矿流体来源方面的研究甚少。因此,本文通过对兴源冲矿床不同矿体矿石中的石英、方解石等脉石矿物进行了系统的流体包裹体测温工作,试图探讨其成矿流体来源。该研究将对进一步认识九岭南缘地区甚至钦杭结合带上同类矿床的找矿勘探有一定的参考价值,并对该地区下一步找矿工作有着重要意义。
2. 矿区地质背景及特征
兴源冲铜矿床所属的黄茅地段地处宜丰–景德镇NEE向深断裂带北侧,九岭南缘大型推(滑)覆构造西段向南弧型大转折与北北东向走滑推覆冲断带复合部位。九岭隆起南缘为多层次大型构造叠置复合成矿地质环境,具有丰富的矿质来源、反复叠加富集的多种热流场和成矿异常复合构造部位,为江西省的重要铜高背景区之一[3] [5] -[9](图1)。
研究区出露地层主要为中元古代蓟县纪宜丰岩组,属一套沉积变质火山岩系,是金、银、铜、铅、锌多金属矿的赋矿层位[3] [10] [11] ;部分地层为晚古生代、中新生代地层。区域总体为一北东东向复合推(滑)覆构造,为本区重要的控矿构造。区内岩浆活动频繁,晋宁早期发生了较大规模“双峰式”火山活动,表现为宜丰岩组中含有变石英角斑岩、变玄武岩、变辉绿岩夹层,其火山岩Sm-Nd等时线年龄值1300 Ma、Rb-Sr等时线年龄值1351 Ma。晋宁晚期大规模中酸性岩浆侵入形成了九岭大型复式黑云花岗闪长岩基。区内燕山期岩浆活动较弱,主要为细粒含斑黑云母二长花岗岩,呈岩株状[6] -[8]。
矿床按地段可分成野猫冲、刘家冲、枫树坳3个矿段。野猫冲矿段是研究区内已知矿化最好、工程控制程度也最高的矿段,段内共发现铜矿体4个[9] 。矿体呈脉状、似层状,多数顺层分布于宜丰岩组岩层
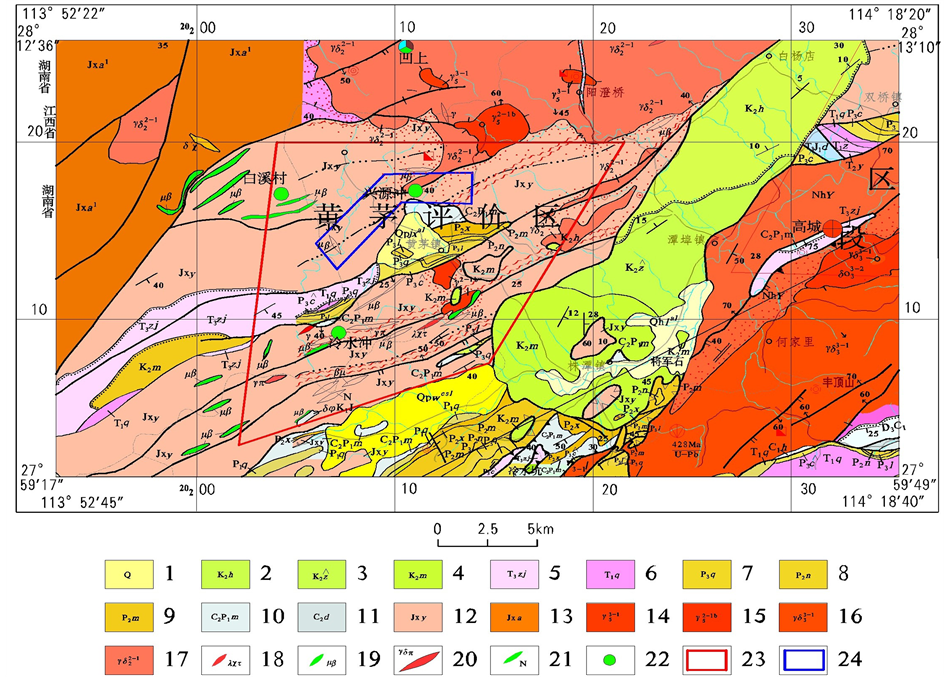
Figure 1. Geological structure of Huangmao area [12]
1、第四系(全新世、更新世);2、河口组;3、周田组;4、茅店组;5、紫家冲组;6、青龙组;7、七宝山组;8、南港组;9、茅口组;10、马平组;11、大埔组;12、宜丰岩组;13、安乐林组;14、细粒白云母二长花岗岩;15、中细粒含斑二云母二长花岗岩;16、中细粒含斑少斑黑云花岗闪长岩;17、花岗闪长岩、英云闪长岩;18、变石英角斑岩;19、变细碧质玄武岩、变辉绿玢岩;20、花岗闪长斑岩、花岗岩脉;21、基性岩;22、铜矿(化)点;23、研究区范围;24、兴源冲矿区范围
图1. 黄茅研究区地质构造略图[12]
中,受北东东向大型推(滑)覆构造带的明显控制[6] -[8]。
3. 流体包裹体研究
流体包裹体测试样品主要采自兴源冲矿床中部的野猫冲矿段不同矿体矿石中的石英、方解石等脉石矿物。通过对薄片及流体包裹体岩相学观察,选择具有代表性的流体包裹体薄片,进行包裹体的均一温度和盐度测定。均一温度的测定是采取气–液两相包裹体的均一法测温(大部分包裹体为气液两相包裹体),盐度则是通过包裹体的冰点测定得出。流体包裹体测温所使用的仪器设备是英国Linkam科仪公司生产的地质冷–热台(仪器型号:THMSG600),显微测温法测定包裹体均一温度和冰点,可测温范围为−196℃~600℃,均一温度重现误差±1℃,冰点温度误差±0.1℃。工作环境为温度低于28℃,湿度小于60%。
实验中对气液两相包裹体先降温,通常在−60~−70℃之间达到过冷却,再进行回温,记录冰块刚好全部融化时的温度,然后再通过加热对均一温度进行测定。实验中升降温速率通常控制在10℃/min左右,当接近冰点时,回温速率控制在0.1℃/min左右,当加热近均一温度时,升温速率降低到1℃/min左右。
3.1. 流体包裹体类型
所测包裹体大多为富液相气–液(LH2O + VH2O)包裹体,气液相比约为5%~25%;大小不等,6~60 μm,一般为6~20 μm;形态各异,有椭圆形、多边形、豆荚状和长条形;包裹体较为集中,但分布规律性不强,偶见条带状分布(图2)。
3.2. 均一温度和盐度
流体包裹体测温结果列于表1,包裹体均一温度在75~440℃之间,变化较大。从均一温度直方图中可以看出包裹体均一温度可以分为两个峰值区间(图3),第一区间主要集中在120~190℃之间,第二区间包裹体均一温度较高,主要集中在210~290℃之间,说明矿床成矿流体应属中低温成矿流体。
兴源冲矿床的流体包裹体盐度近似值是由Bodnar根据Hall提出的H2O-NaCl体系盐度–冰点公式总结出的盐度–冰点关系表得出[13] ,变化范围在1.74 wt%~22.58 wt%之间,平均为12.52 wt%,峰值出现在6.0 wt%~16.0 wt%之间(图4)。
从均一温度与盐度关系图(图5)可以看出温度和盐度主要分布在中低温度和中高盐度区间,且盐度大致随温度的升高而升高。
3.3. 密度
利用NaCl-H2O体系均一温度、盐度、密度关系近似地求得流体的密度[14] 。从均一温度–盐度–密
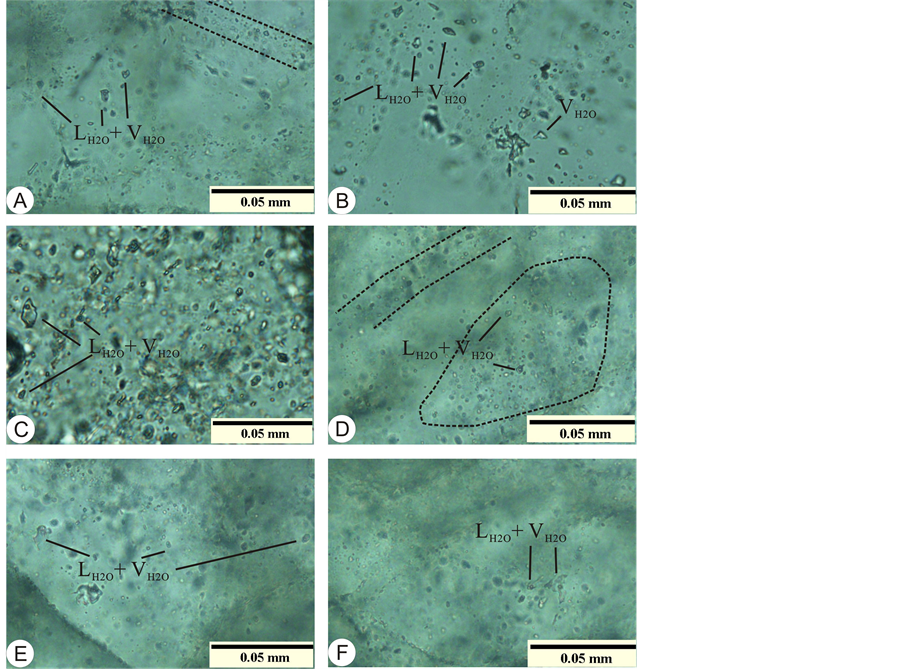
Figure 2. Petrographic characteristics figure of fluid inclusions in quartz grains from Xingyuanchong copper deposit
A、B、C、D、E、F-形态各异的气相分数为5%~25%的富液相气-液(LH2O + VH2O)包裹体,见有不规则状、浑圆状、椭圆状、长条状包裹体,孤立或成群分布;A、C、D-部分包裹体呈带状或成群分布;B-形态各异的液相包裹体。
图2. 兴源冲铜矿床内流体包裹体显微特征图



Table 1. Homogenization temperature, freezing point and salinity of Xingyuanchong copper deposit
表1. 兴源冲铜矿床均一温度、冰点与盐度表
测试单位:东华理工大学省部共建核资源与环境国家重点实验室培育基地[12] 。
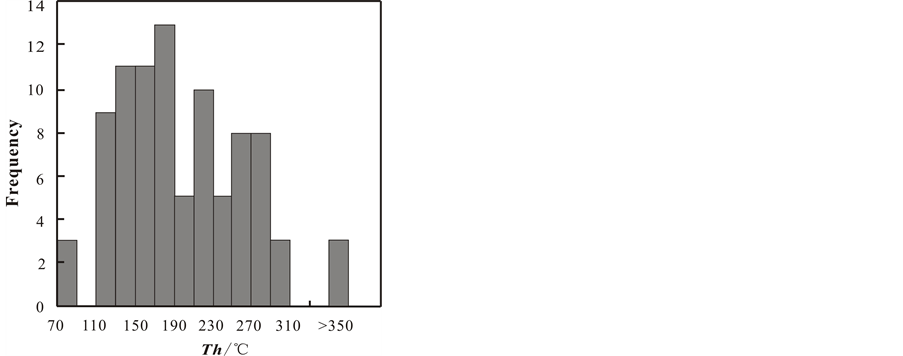
Figure 3. Histogram of homogenization temperatures
图3. 矿区包裹体均一温度直方图
度关系图中可以看出(图6):流体密度较低,变化范围在0.74~1.08 wt%之间,且随着温度的升高而降低。当均一温度在110~190℃之间时,流体密度随着盐度的变化而变化,和温度关系不是很大;而均一温度集中在210~290℃之间时,流体密度比中低温流体要小,但并没有因为温度或盐度的变化而变化,始终保持在0.85~0.95 wt%之间;温度大于320℃的流体密度较小,在0.74~0.75 wt%之间。
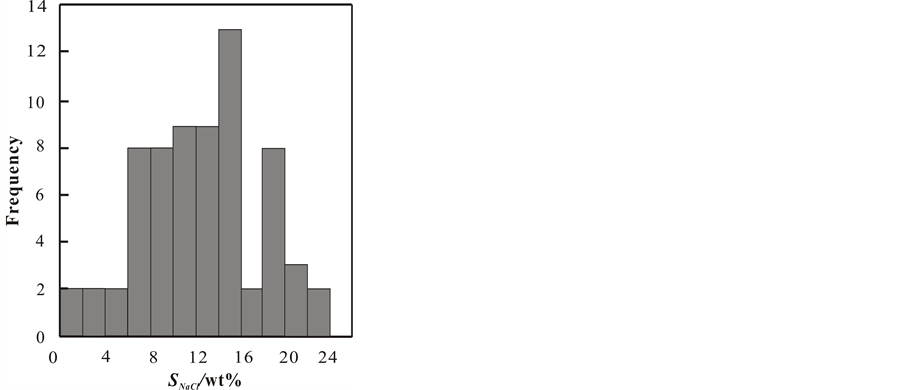
Figure 4. Histogram of salinity
图4. 矿区包裹体盐度直方图
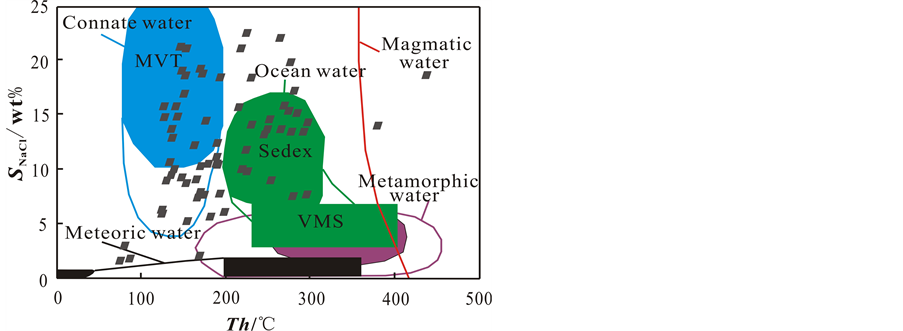
Figure 5. Diagram of homogenization temperature-salinity
图5. 矿区包裹体均一温度–盐度图[15]
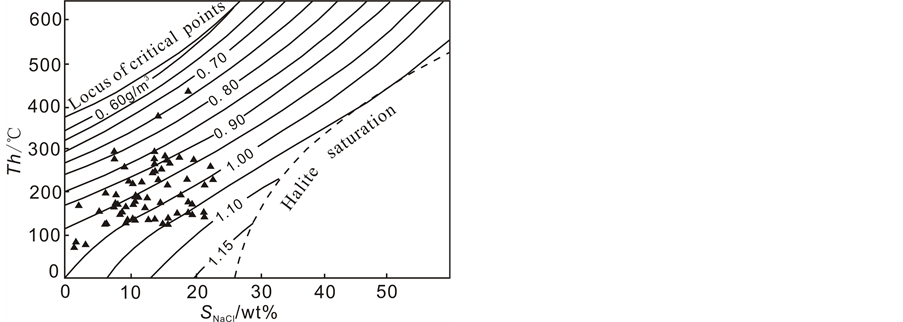
Figure 6. T-W-ρ phase diagram of NaCl-H2O system
图6. 氯化钠–水体系的温度–盐度–密度相图[13] [14]
4. 成矿流体来源探讨
通过包裹体均一温度、盐度、密度及其之间的关系,可以得出兴源冲矿床成矿流体具有多期次活动的特点,受两期成矿流体的控制。根据由热液体系和矿床类型划分出来的典型热液流体类型(图5)可以看出,成矿流体主要落入两个流体体系:低温、中高盐度特征的同生水体系以及中温、中等盐度的海水体系,也有小部分落入高温、中等盐度特征的岩浆热液体系。说明矿区成矿流体可能以海底喷流热液和与成岩作用有关的水为主,也有小部分岩浆热液的混合。这与前人研究兴源冲矿床成矿主要经历了中元古代海底火山沉积和晚元古代晋宁造山期的岩浆热液、动力变质叠加改造两个成矿阶段[6] -[7] [9] 的研究结果不谋而合。
5. 结论
通过对兴源冲矿床石英、方解石中流体包裹体的研究,得出矿区成矿流体具有中低温、中高盐度、低密度的特征,成矿流体系统不断演化,矿床受两期成矿流体控制。结合矿区地质特征,发现兴源冲铜矿床成矿流体主要以海底喷流热液和与成岩作用有关的水为主,也有小部分岩浆热液的混合。