1. 引言
建筑结构的连续性倒塌(Progressive Collapse)是指结构部分构件或局部发生破坏后其周围构件相继发生破坏甚至导致整个结构完全倒塌的现象[1] 。作为最广为人知的建筑连续性倒塌事件,2001年“9.11”事件中纽约世贸中心两座110层411 m高的钢结构大楼因飞机撞击和随后引发的火灾而倒塌,造成2830人死亡。随着城市化的高度发展,人群密集的高层建筑结构、大跨度建筑结构的连续性倒塌将会带来非常严重的后果,对社会经济、社会秩序乃至人们心理产生巨大的冲击[2] 。因此,对建筑结构进行倒塌分析,采取相应的抗连续性倒塌措施,将逐步成为结构设计的一项重要内容。
目前,结构抗连续性倒塌性能评估中最常用的方法为构件去除法。美国公共事务管理局编制的《联邦政府办公楼以及大型现代建筑连续性倒塌分析和设计指南》(GSA2003)[3] 和美国国防部编制的《建筑抗连续性倒塌设计》(UFC) [4] 均对构件去除法作出了详细的规定。构件去除法要求结构发生局部破坏后,破坏部位周边的构件可以有效地分担并传递破坏部分原来承担的荷载从而保证结构不发生进一步破坏。采用构件去除法对结构进行抗连续性倒塌分析,是根据预设的破坏准则有选择性地假定某个主要承载构件(柱、承重墙)失效,并对剩余结构进行分析,分析结构是否会发生超过规定程度的倒塌。根据分析方法的不同,构件去除法又可以进一步分为静力线性方法、静力非线性方法和动力非线性方法。国内外众多学者使用构件去除法对结构抗连续性倒塌性能进行评估,并得到相应研究成果。Marjanishvili等[5] 结合GSA对构件去除法的相关规定,基于通用结构分析软件SAP2000,分别采用线弹性静力、非线性静力、线弹性动力和非线性动力4种方法对结构抗连续性倒塌性能进行了评估,研究发现GSA中的线性分析方法会低估结构去柱后的响应,而动力非线性分析能得到最精确的计算结果。李玲[6] 使用ANSYS的重启动技术模拟了某钢筋混凝土框架结构在不同去柱工况下的倒塌响应。B. A. Izzuddin等人[7] [8] 提出框架结构倒塌分析的简化评估流程,该流程基于功能平衡的能力方法,通过静力非线性分析方法得到结构的伪静力荷载–位移曲线,最终通过对比伪静力承载能力和真实荷载的大小来判断结构是否具备抗连续性倒塌能力。Kim T等[9] 基于OpenSees平台,使用非线性静力分析法,计算了抗弯钢框架去柱后在竖向推覆荷载(Pushdown)下的响应。从文献[5] 到[9] 可知,构件去除法的分析过程不需考虑造成初始破坏的非常规荷载的具体形式,仅分析结构在主要承载构件失效后的响应特性,因此具有广泛的适用范围。然而,采用静力分析以及线性动力分析时,计算结果与结构实际响应差别较大,并有可能造成不安全的设计[5] ,因此,本文基于构件去除法,采用动力非线性方法对结构的抗连续性倒塌性能进行分析。
2. 分析方法
本文采用动力非线性分析方法,使用显式有限元软件LS-DYNA对某一空间钢框架进行抗连续性倒塌数值模拟。
采用动力非线性分析进行抗连续性倒塌瞬时去柱分析,应分三步实施:(1) 在去柱前,在结构上单调缓慢地施加设计工况荷载,直至结构达到受力平衡状态并维持一段时间,然后停止分析;(2) 按照UFC指南的要求突然去除主要承重构件,更新模型信息;(3) 对去除构件后的模型进行应力初始化,并开始重启动分析,在每个时间步内对所有杆件进行失效判断,最后得到包括节点位移和杆件内力在内的计算结果。
3. 分析对象
依据《钢结构设计规范》(GB50017-2003)[10] 设计了一个4 × 6跨、5层钢框架结构,框架横向及纵向跨度均为6 m,首层层高为5 m,其他层高均为3.6 m。结构所有梁柱均为焊接工字截面,其具体截面尺寸列于表1。钢材弹性模量为2.06 × 105 MPa,密度为7.85 × 103 kg/m3,屈服强度为345 MPa,泊松比为0.3。恒载取10 kN/m2,活载取2 kN/m2。分析时考虑底层角柱失效、底层横向中柱失效及底层纵向中柱失效三种工况,如图1所示。
4. 建模与分析过程
4.1. 材料本构
钢材采用Plastic Kinematic塑性动力模型模拟;该模型通过Cowper-Symonds方程考虑应变率对屈服应力 的影响,即:
的影响,即:
 (1)
(1)
式中,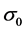 、
、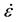 、
、 分别为初始屈服应力、应变率以及有效塑性应变;C、P为Cowper-Symonds应变率
分别为初始屈服应力、应变率以及有效塑性应变;C、P为Cowper-Symonds应变率

Table 1. Section dimensions of beams and columns
表1. 框架结构梁柱截面尺寸
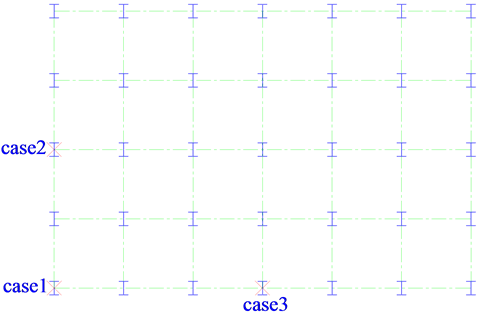
Figure 1. Locations of column removal cases
图1. 去柱工况
参数; 为硬化参数,取0和1分别表示随动强化和各向同性强化,本文取为0;
为硬化参数,取0和1分别表示随动强化和各向同性强化,本文取为0;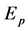 为塑性强化模量:
为塑性强化模量:
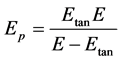 (2)
(2)
式中,E和 分别为弹性模量以及切线模量,本文取
分别为弹性模量以及切线模量,本文取 [11] 。另外,该模型还需要输入失效应变
[11] 。另外,该模型还需要输入失效应变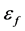 ,当满足
,当满足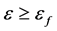 时,单元失效并自动从计算模型中删除,本文
时,单元失效并自动从计算模型中删除,本文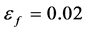 进行分析。
进行分析。
4.2. 单元介绍
结构梁柱均采用BEAM161模拟,选择选用Hughes-Liu算法,其中除底层柱划分成15个单元以外,其他杆件均划分成10个单元。质量单元采用MASS166模拟。为形象地模拟结构连续性倒塌全过程,采用SOLID164单元模拟刚性地面[11] 。所有的接触设置为自动单面接触(ASSC)。
4.3. 模型建立
首先使用ANSYS作为前处理器建立用于LS-DYNA显式动力分析的结构模型,并生成相应K文件。生成的K文件对应的模型如图2所示。
4.4. 分析过程
分析计算分为两步:(1) 0~500 ms计算结构在去柱前的静力平衡阶段,待振动趋于平稳后,在500 ms时刻移除柱子;(2) 500 ms~1000 ms为动力响应阶段,此时需要修正K文件中的几何模型信息,删除应去除的构件所对应的单元,延长计算终止时间,然后使用LS-DYNA solver进行瞬态动力重启动分析,计算结构去柱后的响应。重启动时应使用修正后的K文件,并使用上一步生成的重启动文件进行应力初始化[12] 。
5. 计算结果分析
统计资料显示,首层柱失效更加容易导致整体结构发生连续性倒塌,造成的损失最为惨重,因此本文选择的三个不同去柱工况均发生在首层。去除失效钢柱后,剩余结构中受到影响最大的是失效柱正上方的节点,故选取失效角柱、横向中柱和纵向中柱正上方5695、5653和2890号节点(图3)作为控制点,对比不同去柱工况下结构的响应。
三个不同工况下去柱上方节点位移响应如图4所示。
Figure 2. Finite element model for explicit analysis
图2. 用于显式动力分析的有限元模型
为了阐述结构在去除竖向构件后的抗连续性倒塌以及内力重分布的机制,选取记录CASE1和CASE2中失效柱周边底层柱内轴力和失效柱上端柱轴力(图5~图6)、失效柱周边梁弯矩(图7~图8)和失效柱周边梁上轴力(图9~图10)的内力时程曲线。
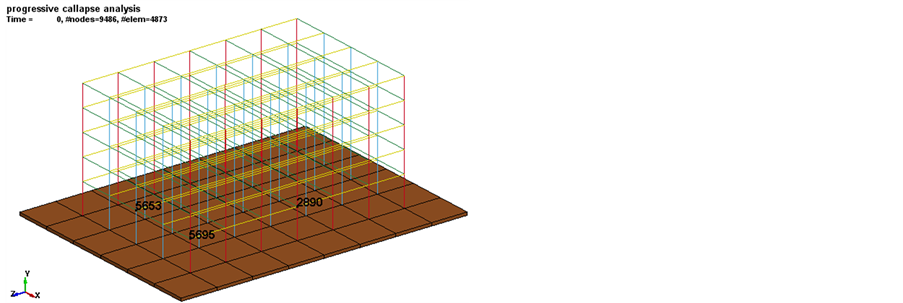
Figure 3. Locations of key nodes
图3. 控制节点位置示意图
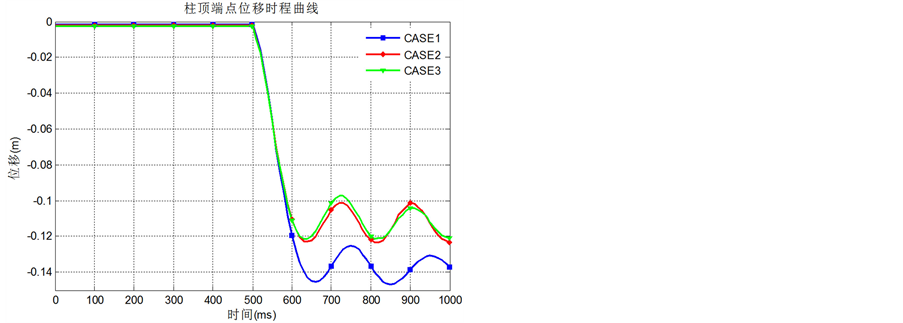
Figure 4. Vertical displacement dynamic response of key nodes for different column removal cases
图4. 不同去柱工况下关键节点竖向位移动力响应
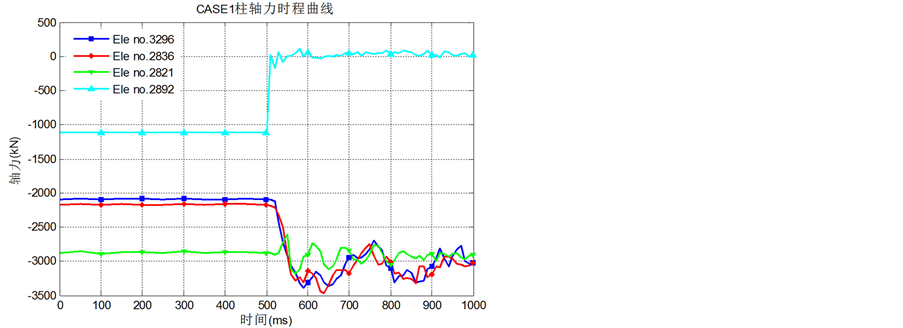
Figure 5. Time curve of axial force for columns near the removal column for CASE1
图5. CASE1失效柱附近柱轴力时程曲线
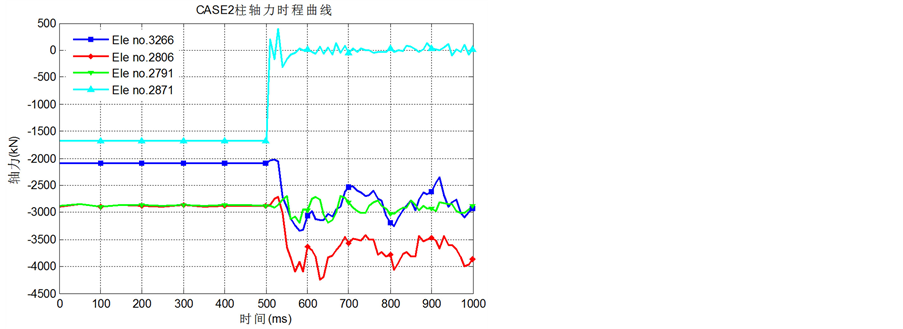
Figure 6. Time curve of axial force for columns near the removal column for CASE2
图6. CASE2失效柱附近柱轴力时程曲线
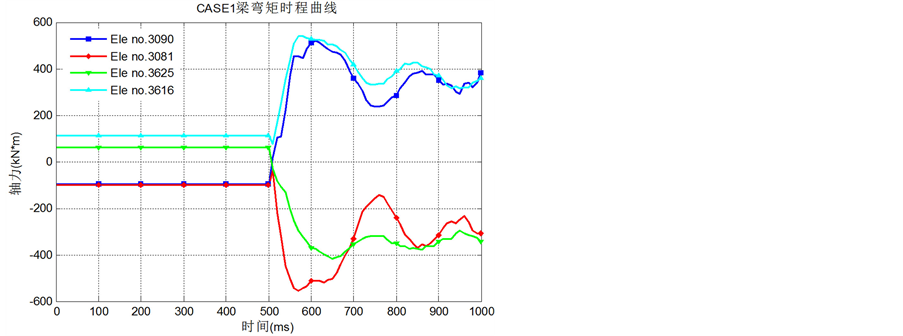
Figure 7. Time curve of moment for beams near the removal column for CASE1
图7. CASE1失效柱周边梁弯矩时程曲线
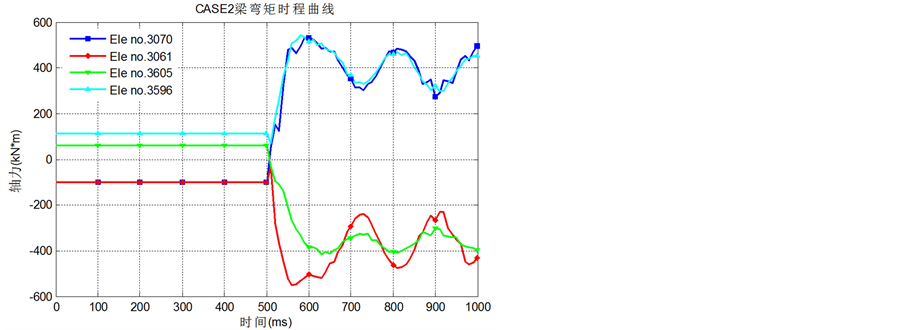
Figure 8. Time curve of moment for beams near the removal column for CASE2
图8. CASE2失效柱周边梁弯矩时程曲线
分析节点位移以及构件时程曲线图可知:
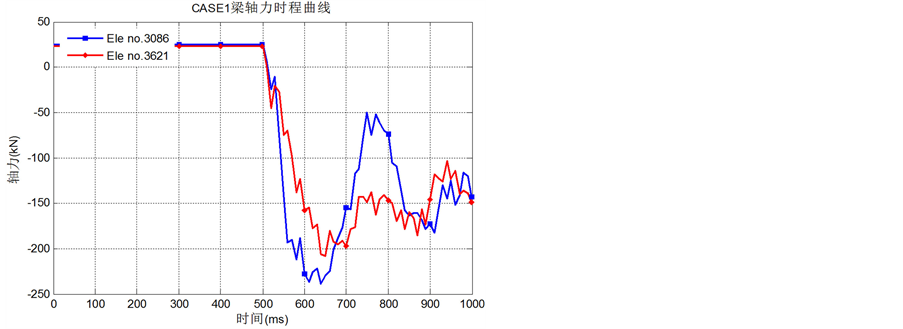
Figure 9. Time curve of axial force for beams near the removal column for CASE1
图9. CASE1失效柱周边梁上轴力时程曲线
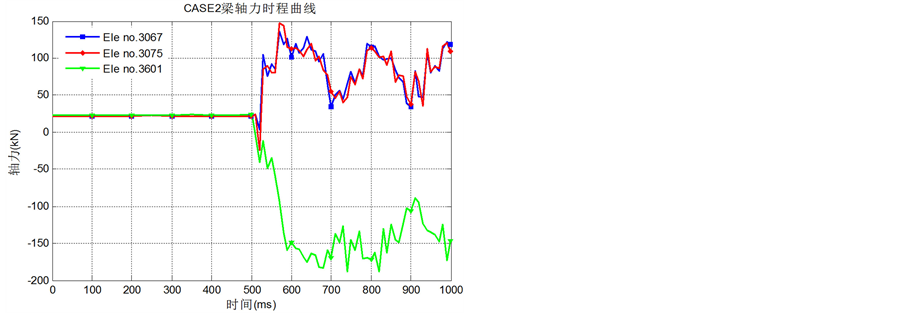
Figure 10. Time curve of axial force for beams near the removal column for CASE2
图10. CASE2失效柱周边梁上轴力时程曲线
(1) 从图4可知,去柱后关键节点位移突然增大,出现明显的振动,且振幅较大,但结构并没有发生倒塌,这证明按照规范设计的钢框架结构在单根竖向构件失效的情况下具有良好的抗连续性倒塌性能;
(2) 从图5、图6可知,失效钢柱所在的横向(B3296和B3266)与纵向(B2836和B2806)跨内柱中轴压力明显增大,失效柱原本承担的竖向荷载被传递给附近底层柱;距离失效柱较远的柱内轴力变化不大(B2821和B2791);同时失效柱上端的柱(B2892和B2871)发生了明显的卸载甚至内力反向,由轴压力变为轴拉力,从而将一部分竖向不平衡荷载传递给上部框架;
(3) 从图4可知,角柱被去除的工况中关键节点的响应最大,横向中柱工况次之,而纵向中柱失效响应最小。可以认为,结构中的角柱是结构倒塌机制中的关键构件。接下来将结合图7~图10的内容阐述角柱和横向中柱失效后剩余结构的内力重分布机制,进而解释形成上述结果的原因。
从图7、图8可知,当钢柱失效时,梁中靠近柱一端的弯矩反向(CASE1中的B3090和B3620;CASE2中的B3081和B3616),而梁远离柱一端的弯矩方向不变数值变大(CASE1中的B3081和B3616;CASE2中的B3061和B3596),这说明角柱或中柱失效,剩余结构都能形成空腹效应,通过弯矩传递进行荷载重分配。图9、图10中的B3086、B3621和B3061的轴力时程图也能说明这一点:这些梁本来在静力荷载作用下受拉,但去除钢柱后变为受压,说明它们与上层构件形成了巨大的无腹杆悬臂空腹桁架,并作为下弦承受压力。
而从图10可知,当横向中柱失效时,失效柱上方两侧横向框架的梁内轴拉力变大,形成明显的悬链线效应,而在角柱失效工况下的梁轴力时程图(图9)中没有观察到类似现象。
因此,当横向中柱失效时,不平衡荷载可通过横向跨度内两端支承的框架的悬链线效应以及与之垂直的悬臂框架的空腹效应重新分配;而角柱失效时,不平衡荷载仅可通过悬臂框架的空腹效应重新分配。因此按规范设计的钢框架在角柱失效时更加容易发生连续性倒塌。
6. 提高结构抗连续性倒塌能力的措施
由上述分析可知,在竖向承重构件失效后,结构主要通过悬链线效应与空腹效应进行荷载重分布,因此,例如节点的转动能力和拉结能力、结构材料的延性、结构整体的冗余度等诸多因素都会对结构的抗连续倒塌能力造成影响。例如,虽然上述分析中的钢框架在单根承重柱失效后,其支承的周边框架梁能够发展悬链线效应和空腹效应,但如果梁柱节点的延性和拉结力不满足要求而在梁构件达到极限承载力前发生破坏,则仍将导致结构抗连续性倒塌能力的丧失。
因此,从结构体系的选择、结构构件的布置到构件、节点设计,结构设计的整个环节都应考虑结构的抗连续倒塌能力。尽量采用冗余度高、鲁棒性好的结构体系,例如梁柱刚接的抗弯框架、剪力墙结构和筒体结构等;创造在构件失效的情况下转变传力路径的条件,例如用双向相交梁替代单向大梁,楼板按双向设计;注重梁柱连接设计,采用能够有效传递剪力弯矩,并具有较大变性能力和拉结强度的节点形式,加强混凝土结构钢筋在支座处的锚固;限制竖向承重构件的轴压比,并对失效后可能引起结构发生倒塌的关键构件进行局部抵抗设计[4] 。
7. 结论
本文利用显式有限元软件LS-DYNA瞬时去柱动力非线性分析,对某一空间钢框架进行抗连续性倒塌数值模拟,阐述了钢框架结构在竖向构件失效后的抗连续性倒塌的荷载重分布机制,并得出以下结论:
(1) 按照规范设计的钢框架结构在单根竖向构件失效的情况下具有良好的抗连续性倒塌性能;
(2) 钢框架在角柱失效时更加容易发生连续性倒塌,角柱应被认为是结构倒塌机制中的关键构件;
(3) 在结构设计的各个阶段均应充分考虑可能影响抗连续性倒塌性能的各种因素,并采用合理的设计方案。