1. 引言
益生菌能够通过补充肠道正常菌群、纠正菌群失调、分泌抑菌或杀菌物质和增强肠道局部免疫反应等机制,有效地清除病毒和细菌,明显缩短腹泻病程,降低腹泻严重程度,几乎可以应用于所有的腹泻病。一般认为益生菌的作用具有剂量依赖性[1] ,同一制剂不同剂量的效果评价是微生态制剂的研究方向[2] 。枯草杆菌二联活菌颗粒治疗轮状病毒性肠炎早已获临床认可[3] ,但未见不同剂量枯草杆菌二联活菌颗粒治疗轮状病毒性肠炎疗效比较的相关报道。为了探讨枯草杆菌二联活菌颗粒的剂量–效应关系,应用不同剂量枯草杆菌二联活菌颗粒治疗轮状病毒性肠炎进行效果比较观察,现将结果报告如下。
2. 资料和方法
2.1. 一般资料
参照中国腹泻病诊断治疗方案[4] ,选择四川省华蓥市妇幼保健院2011年1月~2012年10月间临床诊断的240例轮状病毒性肠炎患儿,以随机数字表法分成大剂量组和小剂量组。入选病例均具备下列条件:年龄3月~2岁;急性起病,腹泻病程≤3 d;大便次数≥6次/d,色黄,呈稀水样或蛋花样便,无脓血;粪便常规镜检无或仅见少许白细胞(<5个/HP),无红细胞,粪便培养无致病菌生长;粪便轮状病毒抗原检测阳性;患儿父母或监护人签署知情同意书并经院伦理委员会批准。凡具备下列条件之一的均不纳入研究对象:入选前7 d曾服用某种微生态制剂;患有基础病或合并其他疾病,如营养不良、先天性心脏病、消化道畸形、免疫缺陷性疾病、支气管炎、肺炎;严重疾病患儿(包括重度脱水,电解质紊乱及酸中毒患儿);呕吐严重可能影响药物吸收和疗效判定;未坚持服药、中途换药或加药,无法判断疗效或资料不全等影响疗效判断;患儿家属撤回知情同意书者。大剂量组:120例,男59例、女61例,平均年龄(9.63 ± 4.15)个月,平均病程(2.30 ± 0.75)天,日大便(11.05 ± 3.35)次,轻度脱水63例、中度脱水41例;小剂量组:120例,男65例、女55例,平均年龄(9.78 ± 4.18)个月,平均病程(2.31 ± 0.73)天,日大便(11.28 ± 3.41)次,轻度脱水65例、中度脱水38例。两组在性别、年龄、病程、病情方面比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),具有临床可比性。
2.2. 治疗方法
两组均继续饮食,口服或静脉补液,服用消旋卡多曲颗粒(四川百利药业,批号101210,规格10 mg/袋)3~9月龄每次10 mg,10~24月龄每次20 mg,3次/日。小剂量组加服枯草杆菌二联活菌颗粒(北京韩美药品有限公司,批号20101132,规格1 g/支)<1岁,每次0.5 g,1~2岁每次1 g,2次/d;大剂量组加服枯草杆菌二联活菌颗粒(北京韩美药品有限公司,批号20101132,规格1 g/支)<1岁,每次1 g,1~2岁每次2 g,2次/d。疗程3~7d。两组均不用其他药物。
2.3. 观察方法
凡入选病例均详填观察表,记录每日患儿大便次数、性状及伴随症状缓解情况,大便常规检查,观察服药期间有无不良反应。
2.4. 疗效评定
参照中国腹泻病诊断治疗方案[4] ,显效:治疗72小时内粪便性状及次数恢复正常,全身症状消失;有效:治疗72小时时粪便性状及次数明显好转,全身症状明显改善;无效:治疗72小时时粪便性状、次数及全身症状均无好转,甚至恶化。
2.5. 统计学方法
应用SPSS 13.0统计软件,计量资料以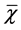 ± s表示,组间计量资料比较采用t检验;计数资料比较采用χ2检验;等级资料比较采用Ridit分析。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
± s表示,组间计量资料比较采用t检验;计数资料比较采用χ2检验;等级资料比较采用Ridit分析。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
3. 结果
3.1. 两组临床疗效比较
治疗3天后,两组临床显效率、总有效率比较差异有统计学意义;两组疗效比较经Ridit分析差异有统计学意义,治疗组优于对照组。见表1。
3.2. 两组治疗前后大便次数比较
两组在治疗前和治疗1 d后便次比较差异无统计学意义,治疗2 d、3 d后两组便次比较差异有统计学意义,治疗组优于对照组。见表2。
3.3. 两组主要症状体征恢复正常时间比较
治疗后两组在大便次数、性状恢复正常时间和腹泻持续时间方面比较差异有统计学意义,治疗组优于对照组。见表3。
3.4. 两组不良反应比较
两组在治疗过程中均未发现不良反应。
4. 讨论
儿童消化系统发育不良,胃酸及消化酶较少,对食物耐受力差;生长发育快,所需营养多,消化道

Table 1. The treatment result comparison of two groups [n(%)]
表1. 两组临床疗效比较[n(%)]

Table 2. Before and after the frequency passed stools of two groups (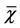 ± s, times/d)
± s, times/d)
表2. 两组治疗前后大便次数比较(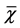 ± s,次/d)
± s,次/d)

Table 3. The main symptoms and signs normal time of two groups (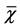 ± s, d)
± s, d)
表3. 两组主要症状体征恢复正常时间比较( ± s, d)
± s, d)
负担重,易致胃肠功能紊乱;肠道中SIgA低,机体抵抗力差;正常肠道菌群欠完善或易失调。上述因素易引起儿童肠道内病毒和细菌感染,导致腹泻的发生[5] 。儿童感染性腹泻是一组广泛存在并严重危害儿童健康的胃肠道传染病,也是当今世界重要的公共卫生问题之一,其发病率仅次于儿童呼吸道感染[6] 。据估计我国5岁以下小儿中约有2.98亿人次患腹泻,发病率为每年0.86~3.9次/人,平均每年2.5次/人[7] 。在中国开展的多项系统监测显示,轮状病毒感染占中国住院腹泻患儿的26%,社区腹泻患儿的10%,是住院腹泻患儿的首要病原[8] 。
迄今轮状病毒性肠炎确切的发病机制仍未被人们完全认识, 普遍认为轮状病毒侵入小肠粘膜绒毛上皮上复制,使细胞发生空泡变性和坏死,其微绒毛肿胀、不规则和变短,受累的肠粘膜上皮细胞脱落,遗留不规则的裸露病变,致使小肠粘膜回吸收水分和电解质能力受损,肠液在肠腔内大量积聚而引起腹泻。同时,发生病变的肠粘膜细胞分泌双糖酶不足,活性降低,使食物中糖类消化不全而积滞在肠腔内,并被细菌分解成小分子的短链有机酸,使肠液的渗透压增高;双糖的分解不全亦造成微绒毛上皮细胞钠转运的功能障碍,两者均造成水和电解质的进一步丧失。更为重要的是轮状病毒性肠炎患儿肠道微生态环境发生紊乱,肠球菌等条件致病菌明显增加[9] 。
目前轮状病毒性肠炎尚无理想治疗药物。口服和静脉应用抗病毒药物较普遍,但抗病毒药物对儿童有很大副作用,且静脉用药不但不方便,还对小儿身体和心理都会产生伤害。轮状病毒型别繁多、交叉保护性差,疫苗的疗效也受到限制[10] 。建议治疗应以调节肠道菌群和对症处理为主,积极推荐早期使用双歧杆菌、乳杆菌、粪链球菌、酪酸梭菌、芽孢杆菌和布拉酵母菌等益生菌药物[2] 。欧州和美国的最新指南和专家共识以及国内的大量报道,均一致推荐益生菌应用于儿童急性轮状病毒水样性腹泻效果最好[11] 。
有效微生态制剂应具备:有活力的细菌、连续每日规律服用、剂量每天30亿~50亿个菌体、抵抗胃酸(大多数被胃酸杀灭)、不被胆盐杀灭(如肠衣)、具备较高的胃肠道内生存能力[6] 。口服益生菌要经受消化道的胃酸、胆汁酸和消化酶的灭活以及消化液和胃肠蠕动的冲刷,目前没有确切的资料证实口服益生菌能有多少活菌被灭活或定植在肠道。因此,要求口服足够剂量的益生菌,如Duggan等提出口服剂量每天>1 × 1010 CFU,加拿大建议剂量每天5 × 109 CFU [12] ,亦有认为益生菌的剂量每48 h >1011CFU可能是最有效的剂量[13] 。国外研制生产的益生菌药物的每个包装中活菌数(108~109 CFU)高于国内药物(>107~108 CFU)的10倍甚至几十倍,国外推荐的使用剂量也明显高于国内[11] 。而1 g枯草杆菌二联活菌颗粒1克含活菌1.5亿个,药品说明书上推荐用法用量:2岁以下儿童,一次1 g,一日1~2次。为此,设计了小剂量组,<1岁,每次0.5 g,1~2岁每次1 g,2次/d;大剂量组<1岁,每次1 g,1~2岁每次2 g,2次/d。
枯草杆菌二联活菌颗粒是目前微生态制剂中活菌数量多、活性高的一种制剂。口服大剂量枯草杆菌二联活菌颗粒,保证了有足够的粪链球菌和枯草杆菌在肠内迅速定植,利于双歧杆菌生长,促进小肠绒毛上皮细胞增加,迁移替代病损的绒毛上皮细胞,减少轮状病毒在肠壁的脱落,促进局部或全身免疫反应,增加轮状病毒特异性抗体。同时枯草杆菌二联活菌颗粒中的锌可通过各种途径维护和修复肠道黏膜,提高肠道上皮细胞刷状缘酶的活性,改善肠道对于水、电解质的吸收[14] 。与小剂量组相比,大剂量组其临床显效率、总有效率更高(P < 0.05),治疗3 d后日均大便次数更少(P < 0.05),腹泻平均持续时间更短(P < 0.05)。在治疗儿童轮状病毒性肠炎中,枯草杆菌二联活菌颗粒剂量与效应呈正相关。
临床观察结果显示,大剂量枯草杆菌二联活菌颗粒治疗儿童轮状病毒性肠炎,能显著提高临床显效率、总有效率,减少大便次数,缩短腹泻持续时间,且无不良反应,安全度高,具有较高的临床应用价值。