1. 引言
电磁轨道发射装置从理论提出到现在已经经过近百年的研究,世界上一些国家投入了大量的人员和资金,建立了许多电磁发射研究实验室[1] 。现在这些研究团队中美国的研究处于国际领先状态。特别是在电磁发射系统的发射器身管研究方面取得了重大突破。
电磁轨道发射研究目前都处在实验室研究状态,主要研究发射装置的受力、摩擦、烧蚀、速度等问题。由于早期是对发射机理的研究,所以能量比较小,电枢质量比较轻,对试验装置的要求也比较低。电磁发射机理研究就是研究电磁发射的极限速度能达到多少。理论上讲只要有足够的能量,电磁轨道发射装置的身管足够长,电枢就可以一直加速,速度达到无穷大[2] 。但实际应用中受到诸多因素的影响,首先身管的设计要满足高速发射的使用要求,其次电枢质量以及口径的大小都直接影响着电枢发射速度。
在身管的研究过程当中,对身管自身的重量和所受电磁扩张力提出了严格的要求。故在身管的设计过程中就要对身管的受力情况进行仿真计算。电磁轨道发射装置的身管不同于常规发射装置的身管,完全靠电磁力推动弹丸加速运动。电磁发射装置身管的设计不仅要考虑身管的受力还要考虑轨道与壳体的绝缘,因此对身管设计带来了一定的难度。
2. 身管材料特性
电磁轨道发射装置的身管所使用的材料不同于常规发射装置的材料。通常情况下,电磁轨道发射装置身管由以下几种材料组成[3] ,如表1所示。
身管结构形式以钢壳体包封为例,轨道材料选用T3铜,轨道与钢壳之间选用G10材料作为绝缘支撑,上下轨道两侧选用陶瓷绝缘支撑[4] 。身管截面简图如图1所示。

Table 1. Material parameters
表1. 材料参数

Figure 1. Body tube section
图1. 身管截面图
身管结构采用连续支撑形式,G10绝缘材料除了绝缘外对发射轨道起到连续支撑作用。电磁轨道发射装置发射时受到轨道内在的电磁斥力,轨道有向外扩张的作用力[5] 。但是电枢在轨道中运行时,要依靠与上下轨道的紧密接触才能达到导通电流,产生推力的效果。这就要求电磁轨道发射装置的上下轨道不能发生明显的位移,保证轨道与电枢的有效接触面积和基础接触压力。而这些条件的满足就依靠材料的自身特性,G10材料自身能够承受足够大的压力形变量很小,并具有良好的电绝缘性能。故在电磁轨道发射装置的设计中被经常用到。
对于电磁轨道发射装置的研究而言,不仅材料的绝缘性能要完全满足身管设计和发射的需要,还要看内膛材料是否具备一定的抗烧蚀性能。陶瓷的应用解决了这一问题。陶瓷具有很好的高温性能,陶瓷与G10的应用解决了电磁轨道发射装置身管设计中的绝缘与耐烧蚀问题。
轨道材料的使用要充分考虑材料的导电和抗烧蚀性能。轨道的导电性能直接影响轨道发射装置的发射效率,提高材料的导电性能就可降低电流在轨道上的损耗。抗烧蚀性能可以提高电磁轨道发射装置的使用寿命。
壳体设计应该满足电磁轨道发射装置发射时的受力要求,壳体材料要有足够的刚度和强度来满足在发射过程中轨道受力时的扩张量,理论计算轨道发射装置上下轨道之间的扩张量不超过0.5 mm,在这样的条件下才能满足电枢发射时轨道与电枢的有效接触力和接触面积。
3. 力学仿真边界条件
身管设计要满足使用要求,就必须根据使用要求对身管的力学性能进行仿真计算。在对身管的刚度和强度进行校核计算之前,先要对轨道所受的电磁力进行仿真计算[6] 。轨道电磁受力的仿真,以50 mm口径电磁轨道发射装置设计为例进行分析计算。根据发射时电枢要达到的速度和电源输出能量要求,对轨道所受电磁扩张力进行仿真分析。根据ansoft软件建模计算轨道发射装置轨道电磁力仿真曲线如图2所示。
由仿真波形图可以看出,随时间变化时单位长度上的轨道受力情况。根据轨道的长度,就可计算出整个轨道上所受的电磁扩张力的峰值。整个轨道上的受力情况就可作为壳体设计和身管内材料强度和刚度校核的依据。在身管的力学仿真计算中,轨道所受的电磁扩张力就可作为ansys有限元分析计算的边界条件。
4. 身管的力学仿真计算
4.1. ansys仿真
在电磁轨道发射装置研究的初期阶段,为了测试研究轨道发射装置的各种力学及电学特性,轨道发射装置的发射身管设计有不同的形式,有开放式轨道加绝缘支撑上下通过螺杆固定,有采用上下钢壳螺栓固定,内部采用轨道和绝缘支撑结构,还有轨道和绝缘材料采用碳纤维缠绕结构。
文章主要研究上下钢壳固定,内部采用轨道和绝缘支撑结构的力学仿真模型。在电磁发射装置的力学仿真计算中,材料自身的力学性能和身管模型的简化很重要[7] 。表1已经列出电磁发射所用材料的基本力学性能。在ansys计算时,假定轨道和绝缘支撑刚度满足电磁扩张力的抗压要求,仿真计算壳体的刚度和强度。轨道发射装置身管结构装配模型如图3(a)所示,总长4000 mm。根据计算要求、模型轴向
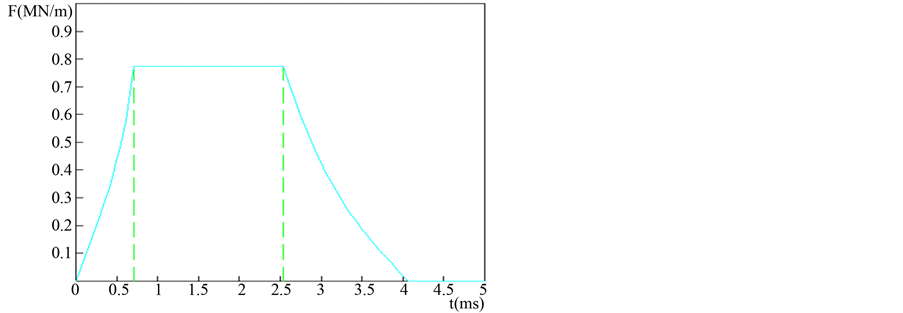
Figure 2. Rail electromagnetic force simulation waveform figure
图2. 轨道电磁受力仿真波形图
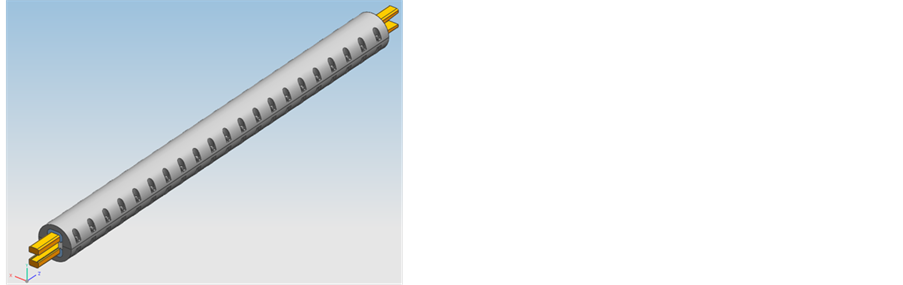
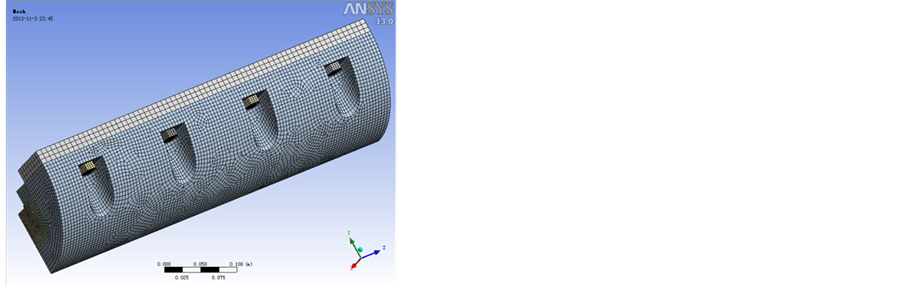

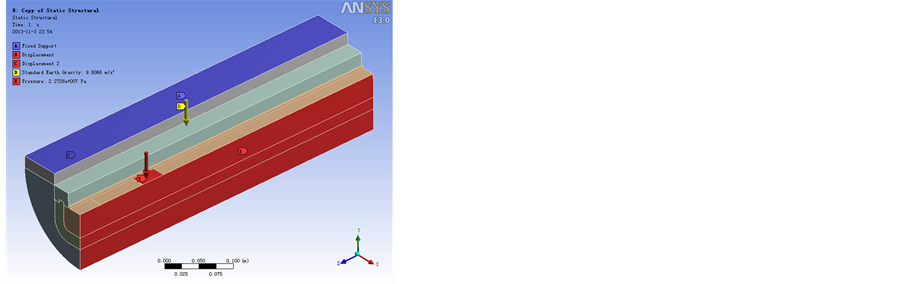
(a) 装配模型 (b) 简化模型单元网格 (c) A工况边界条件 (d) B工况边界条件
Figure 3. Calculation model
图3. 计算模型
重复性与对称性的特点,截取端头500 mm长对称模型为研究对象,仅考虑身管与螺栓结构,单元网格划分如图3(b)示。对称面施加对称约束条件,截面固定,身管水平对称面建立接触关系。将作用于轨道表面的压力载荷等效至身管表面,分两种作用位置分别计算:
A工况:载荷作用于身管端头,如图3(c)所示;
B工况:载荷作用于两相邻螺栓中间,如图3(d)所示。
4.2. 仿真结果及分析
分别对上述两种工况模型进行计算,得到的计算结果如表2及图4~图11所示。由计算结果可知:
1) A工况的变形比应力较B工况大;
2) 无论A工况还是B工况,最大变形均不超过0.1 mm;
3) 无论A工况还是B工况,身管与螺栓的最大等效应力均远低于材料屈服极限。
通过仿真计算,身管仿真计算模型刚度、强度及螺栓满足轨道发射装置发射时对身管变形量的要求,按50 mm口径计算结果,身管的上下扩张量小于0.1 mm,满足轨间变形量不大于0.5 mm的使用要求,初步判断设计模型满足电磁发射使用时的强度和刚度要求。
5. 试验验证
仿真计算设计的轨道发射装置身管通过在靶场的试验验证,在验证过程中,通过5发的发射后,消

Table 2. Two kinds of working condition of calculation results summary
表2. 两种工况计算结果汇总
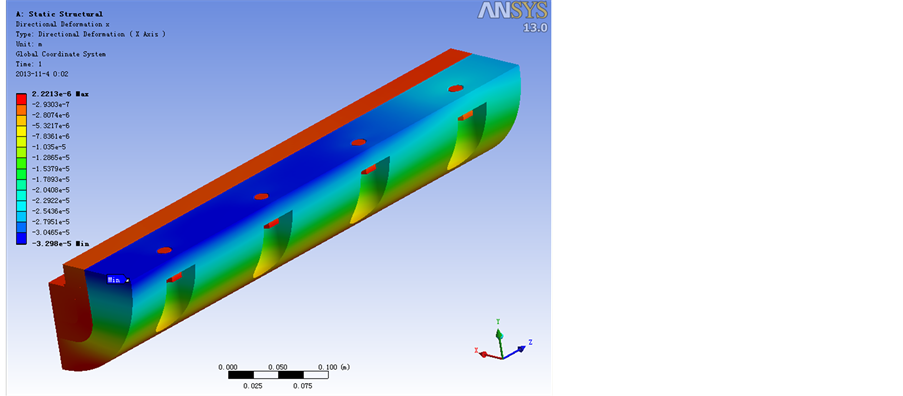
Figure 4. A working condition of the body tube deformation figure (or so)
图4. A工况身管变形图(左右)

Figure 5. A working condition of the body tube deformation diagram (high and low)
图5. A工况身管变形图(高低)
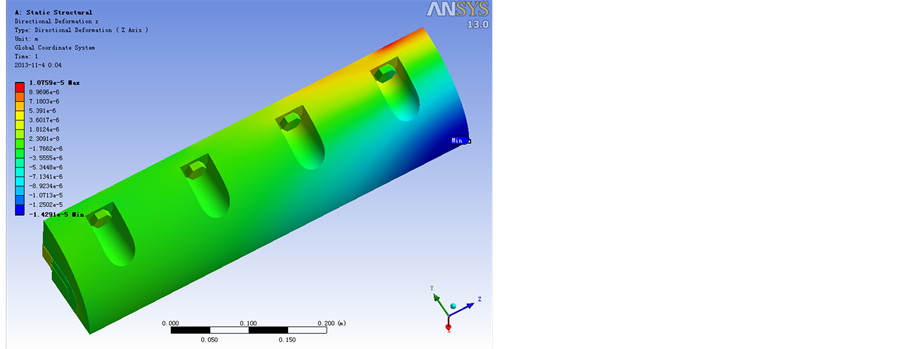
Figure 6. A working condition of the body tube deformation diagram (front and back)
图6. A工况身管变形图(前后)
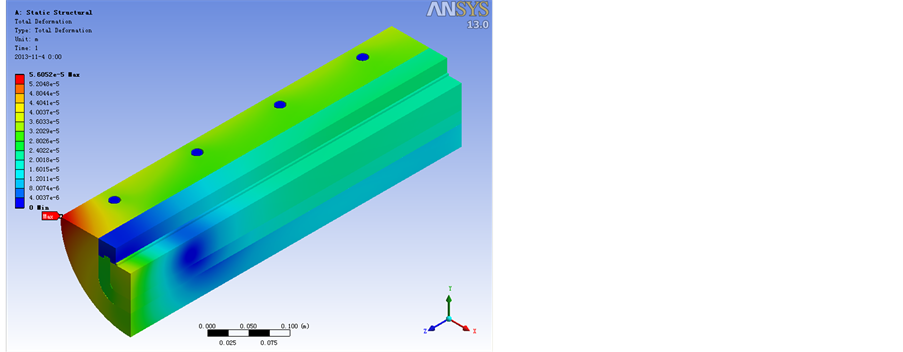
Figure 7. A working condition of the body tube deformation figure
图7. A工况身管合变形图

Figure 8. A working condition of the bolt deformation figure (or so)
图8. A工况螺栓变形图(左右)

Figure 9. A working condition of the bolt deformation figure (high and low)
图9. A工况螺栓变形图(高低)
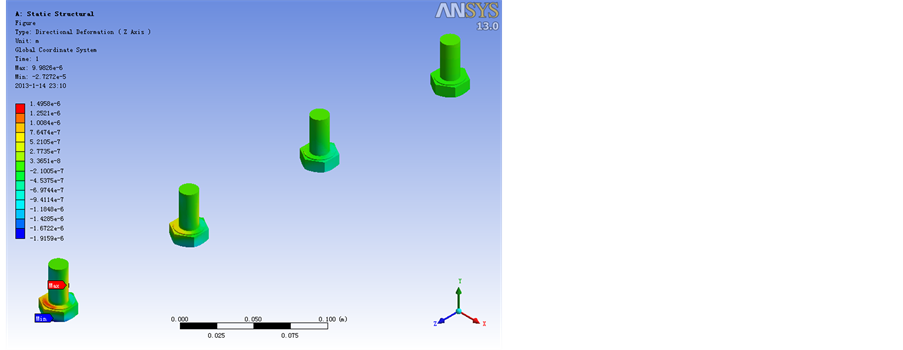
Figure 10. A working condition of the bolt deformation figure (front and back)
图10. A工况螺栓变形图(前后)
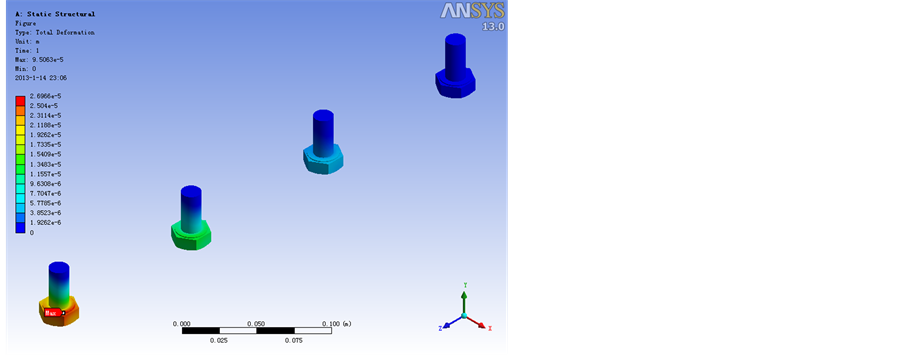
Figure 11. A working condition of the bolt deformation figure
图11. A工况螺栓合变形图
除了结构装配过程中内应力和材料间的间隙。对身管内膛尺寸进行测量,确定内膛的实际尺寸。在后续的发射试验中,对发射装置内膛的轨道之间尺寸进行测量,得到的数据显示轨道之间的间距变化在0.1 mm以内。
经过试验验证,力学仿真结果是正确的,身管的合变形量满足电磁发射的要求。该电磁发射身管的设计没有考虑电磁发射过程中的共振及轨道的变化机理[8] ,只简单从实际使用受力的角度考虑材料的力学性能和材料受力下的形变量要求进行设计和仿真计算。
6. 结束语
文章主要介绍了电磁轨道设计中所用到的材料和实际应用研究中对身管刚度和强度的仿真计算时的结构模型的简化,钢壳体身管设计的力学仿真计算。在轨道发射装置研究中,钢壳体轨道发射装置只是轨道发射装置研究的一个阶段,对于实际使用对轨道发射装置发射速度的要求,钢壳体的强度和刚度将远远不能满足电磁轨道发射装置的发射要求,随着材料技术的不断发展,将会有新的身管面世,轨道发射装置的身管外形结构也将发生巨大变化。但是身管设计中,最基本的力学仿真计算还是必须要做的工作。文章主要讲了现阶段研究过程中的身管设计中的仿真计算,随着科技的发展,力学仿真将更趋于逼真化,将更接近于应用的实际状况。