1. 引言
磷是水体生态系统中各种生物所必须的营养盐之一,也是水体发生富营养化的主要元素之一[1] ,其在沉积物–水界面的分配、迁移及循环直接影响水体的初级生产力[2] 。河口区作为独特的生态系统,面对日益严重的环境问题,沉积物对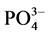 -P吸附解吸行为对上覆水体甚至整个生态系统中营养盐地球化学循环的影响已受到广泛的关注[3] 。
-P吸附解吸行为对上覆水体甚至整个生态系统中营养盐地球化学循环的影响已受到广泛的关注[3] 。
沉积物对磷的吸附能力受到沉积物中原有的磷浓度、溶解氧、氧化还原电位、pH、温度以及Fe、Ca、Al等元素形成的离子沉积物及底层水中的含量的影响[4] [5] 。刘敏等研究了长江河口潮滩表层沉积物对磷酸盐的吸附特征,表明沉积物的吸磷过程主要发生在0~10 h[3] 。Lopez等对西班牙Balerric海岛滨岸沉积物的磷吸附特征以及与沉积物组分之间的相关关系进行了探讨,研究结果表明,沉积物对磷的吸附容量与沉积物中铁铝含量成正相关关系,沉积物对磷的吸附受沉积物中碳含量控制[6] 。石晓勇等在黄河口悬浮物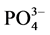 -P的吸附和解吸研究中发现,随温度升高,悬浮物对
-P的吸附和解吸研究中发现,随温度升高,悬浮物对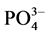 -P的吸附呈线性增加[7] 。
-P的吸附呈线性增加[7] 。
近年来,针对沉积物对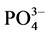 -P的吸附行为的报道有很多,但大多集中在内陆淡水湖泊和水库。本文通过对青岛市李村河河口区感潮河段的3个典型采样点的表层沉积物样品进行
-P的吸附行为的报道有很多,但大多集中在内陆淡水湖泊和水库。本文通过对青岛市李村河河口区感潮河段的3个典型采样点的表层沉积物样品进行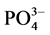 -P吸附动力学和热力学的实验研究,并着重探讨了温度、盐度对
-P吸附动力学和热力学的实验研究,并着重探讨了温度、盐度对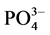 -P吸附动力学过程的影响。
-P吸附动力学过程的影响。
2. 材料与方法
2.1. 样品采集与预处理
在李村河河口感潮区A (36˚09'22.66''N, 120˚21'35.10''E)、B (36˚09'11.87''N, 120˚21'56.65''E)、C (36˚09'03.39''N, 120˚22'29.35''E),共计3个采样点。采样点位置如图1。
采样时间为2010年9月12日,在退潮期间进入河床,采集三点表层1 cm沉积物并装入密封的聚乙
烯塑料袋中。样品运回实验室后,沉积物样品在5000 r∙min−1下离心10 min去除间隙水并于室温下风干,充分研磨混匀后过80目筛备用。
在平潮期于A点用采水器采集海水,装入聚乙烯塑A点用采水器采集海水,装入聚乙烯塑料桶中,滴加饱和氯化汞溶液固定,运回实验室用0.45 µm聚醋酸纤维膜过滤后,装入聚乙烯塑料瓶中备用。
上覆水主要营养盐浓度及化学性质见表1,沉积物中各形态磷的含量及粒径分布见表2。
2.2. 吸附动力学实验方案
在现场采集水样中加入 KH2PO4标准溶液,使水样中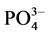 -P的浓度约为6 mg∙L−1。称取2 g沉积物样品250 ml锥形瓶中,加入含有高浓度
-P的浓度约为6 mg∙L−1。称取2 g沉积物样品250 ml锥形瓶中,加入含有高浓度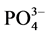 -P的上覆水200 ml,在温度为25℃、振荡频率为150次∙min−1下恒温振荡1 h、2 h、4 h、6 h、8 h、12 h、18 h、24 h后,将混合液均量倒入50 ml离心管中,在3000 r∙min−1下离心10 min。取上清液,并用0.45 µm的聚醋酸纤维膜过滤,然后采用磷钼蓝分光光度法(GB17378.4-2007)测其
-P的上覆水200 ml,在温度为25℃、振荡频率为150次∙min−1下恒温振荡1 h、2 h、4 h、6 h、8 h、12 h、18 h、24 h后,将混合液均量倒入50 ml离心管中,在3000 r∙min−1下离心10 min。取上清液,并用0.45 µm的聚醋酸纤维膜过滤,然后采用磷钼蓝分光光度法(GB17378.4-2007)测其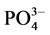 -P的含量。采用式(1)计算得到沉积物对
-P的含量。采用式(1)计算得到沉积物对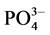 -P的吸附量。建立吸附量Q与时间t的关系曲线,得到吸附动力学曲线,从而得到
-P的吸附量。建立吸附量Q与时间t的关系曲线,得到吸附动力学曲线,从而得到 -P的吸附平衡时间以及
-P的吸附平衡时间以及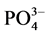 -P吸附速率。
-P吸附速率。
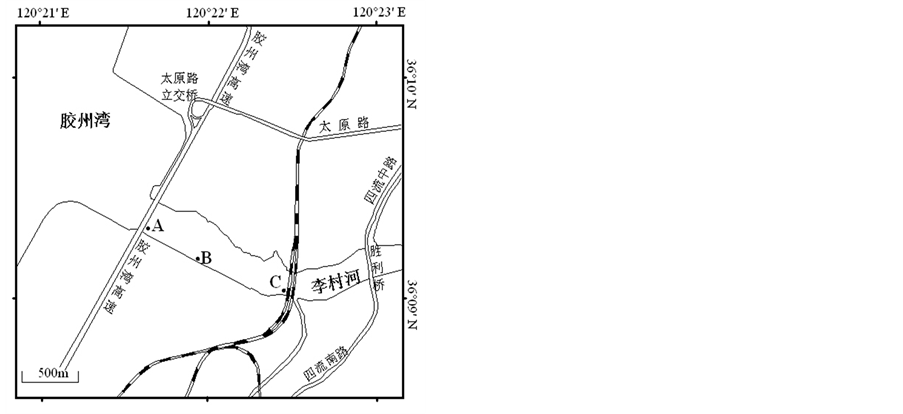
Figure 1. Sampling sites of surface sediments
图1. 表层沉积物采样点位置示意图[8]

Table 1. The chemical characteristics and nutrient concentration of the sea-water sample
表1. 上覆水主要化学性质及营养盐浓度[9]

Table 2. The characteristics of the studied sediment samples and P fraction analysis
表2. 沉积物各形态磷含量及粒径分布表[9]
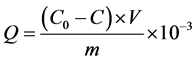 (1)
(1)
式中,Q为沉积物中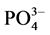 -P的吸附量(mg∙g−1);C0为上覆水中
-P的吸附量(mg∙g−1);C0为上覆水中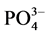 -P的初始浓度(mg/L);C为吸附动力学试验后为上覆水中
-P的初始浓度(mg/L);C为吸附动力学试验后为上覆水中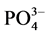 -P的浓度(mg/L);V为上覆水的体积(ml);m为沉积物样品的质量(g)。
-P的浓度(mg/L);V为上覆水的体积(ml);m为沉积物样品的质量(g)。
以A点沉积物为例,采用单因子变量法探讨不同盐度、温度对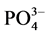 -P吸附动力学的影响,上覆水采用人工海水,其它步骤同上。通过动力学曲线,分析盐度、温度对
-P吸附动力学的影响,上覆水采用人工海水,其它步骤同上。通过动力学曲线,分析盐度、温度对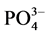 -P吸附动力学的影响。
-P吸附动力学的影响。
以上实验均在相同实验条件下重复3次,相对误差 < 3%。
2.3. 吸附热力学实验方案
称取2 g颗粒物样品于250 ml锥形瓶中,分别加入含有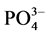 -P浓度为1、3、6、9、12、18、24 mg∙L−1的人工海水。在水温为25℃、振荡频率为150次∙min−1下恒温振荡8小时。恒温静置稳定12 h后,将混合液均量倒入50 ml离心管中,在3000 r∙min−1下离心10 min,将上清液用0.45 µm的聚醋酸纤维膜过滤,测其
-P浓度为1、3、6、9、12、18、24 mg∙L−1的人工海水。在水温为25℃、振荡频率为150次∙min−1下恒温振荡8小时。恒温静置稳定12 h后,将混合液均量倒入50 ml离心管中,在3000 r∙min−1下离心10 min,将上清液用0.45 µm的聚醋酸纤维膜过滤,测其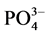 -P含量,采用式(1)计算沉积物对
-P含量,采用式(1)计算沉积物对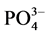 -P的吸附量Q。建立吸附量Q与
-P的吸附量Q。建立吸附量Q与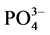 -P的平衡浓度C关系,得到
-P的平衡浓度C关系,得到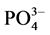 -P的等温吸附曲线。
-P的等温吸附曲线。
以上实验均在相同实验条件下重复3次,相对误差 < 3%。
3. 结果与讨论
3.1. 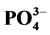 -P吸附动力学曲线
-P吸附动力学曲线
1) 吸附速率与平衡时间
通过实验得到李村河口不同站位(A、B、C)沉积物对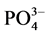 -P的吸附动力学曲线(见图2)。
-P的吸附动力学曲线(见图2)。
从图中可以看出,不同采样点沉积物对上覆水中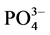 -P的吸附动力学曲线的形状基本一致,均是初期的吸附速率较快,然后吸附速率逐渐降低,在吸附8 h左右反应基本达到平衡。0~1 h为快速吸附阶段,此阶段吸附速率在0.224~0.407 mg∙g−1∙h−1之间;1~12 h为缓慢吸附阶段,吸附速率在0.007~0.174 mg∙g−1∙h−1之间,12 h之后为平衡阶段。
-P的吸附动力学曲线的形状基本一致,均是初期的吸附速率较快,然后吸附速率逐渐降低,在吸附8 h左右反应基本达到平衡。0~1 h为快速吸附阶段,此阶段吸附速率在0.224~0.407 mg∙g−1∙h−1之间;1~12 h为缓慢吸附阶段,吸附速率在0.007~0.174 mg∙g−1∙h−1之间,12 h之后为平衡阶段。
2) 吸附动力学曲线拟合
沉积物对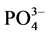 -P吸附的动力学曲线可用以下方程来描述[3] :
-P吸附的动力学曲线可用以下方程来描述[3] :
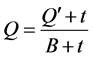 (2)
(2)
式中,Q为t时刻单位质量的颗粒物对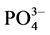 -P的吸附量(mg∙g−1);
-P的吸附量(mg∙g−1);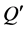 为吸附平衡后颗粒物对
为吸附平衡后颗粒物对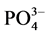 -P的吸附量(mg∙g−1);t为时间(h);B为经验常数。
-P的吸附量(mg∙g−1);t为时间(h);B为经验常数。
根据实验结果的拟合,可以得到颗粒物对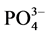 -P吸附的动力学参数(见表3)。
-P吸附的动力学参数(见表3)。
3.2. 不同因子对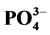 -P吸附的影响
-P吸附的影响
1) 盐度
盐度为0、10‰、20‰、30‰和35‰时,通过实验得到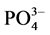 -P吸附动力曲线(见图3)。如图所示,在一定的盐度下,颗粒物对
-P吸附动力曲线(见图3)。如图所示,在一定的盐度下,颗粒物对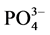 -P的吸附速率逐渐降低。随着上覆水中盐度的增加,
-P的吸附速率逐渐降低。随着上覆水中盐度的增加,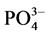 -P的平衡吸附量整体亦呈降低趋势。当盐度为0、10‰、20‰、30‰和35‰时,颗粒物对
-P的平衡吸附量整体亦呈降低趋势。当盐度为0、10‰、20‰、30‰和35‰时,颗粒物对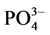 -P的平衡吸附量分别为0.345 mg∙g−1、0.328 mg∙g−1、0.330 mg∙g−1、0.316 mg∙g−1和0.282 mg∙g−1。分析其原因,主要是由于盐度升高,水相中离子强度增大,Cl−、
-P的平衡吸附量分别为0.345 mg∙g−1、0.328 mg∙g−1、0.330 mg∙g−1、0.316 mg∙g−1和0.282 mg∙g−1。分析其原因,主要是由于盐度升高,水相中离子强度增大,Cl−、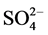 、OH−等阴离子与
、OH−等阴离子与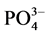 -P竞争颗粒物表面的活性点位,从而降低了
-P竞争颗粒物表面的活性点位,从而降低了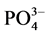 -P的吸附量[10] 。当盐度增加到10‰~20‰时,吸附量出现了波动现象,这可能和颗粒物中的
-P的吸附量[10] 。当盐度增加到10‰~20‰时,吸附量出现了波动现象,这可能和颗粒物中的

Figure 2. 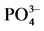 -P adsorption kinetics curve
-P adsorption kinetics curve
图2. 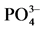 -P吸附动力学曲线
-P吸附动力学曲线

Table 3. Parameters of 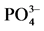 -P adsorption kinetics
-P adsorption kinetics
表3. 颗粒物对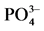 -P吸附的动力学参数表
-P吸附的动力学参数表
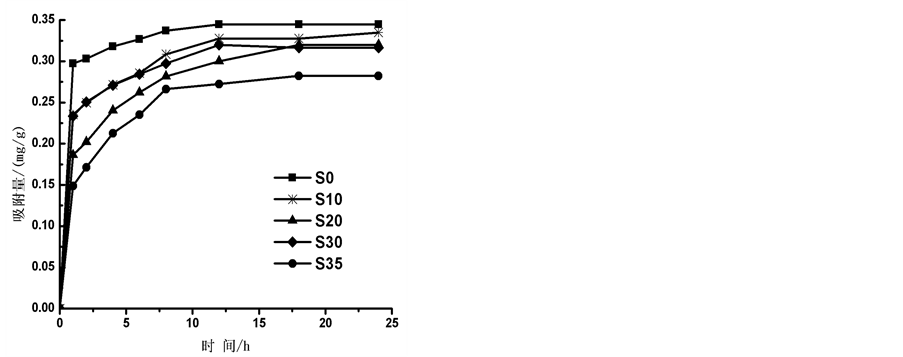
Figure 3. Impact of salinity on 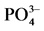 -P kinetics
-P kinetics
图3. 盐度对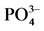 -P吸附动力学的影响
-P吸附动力学的影响
活性铁、活性铝、有机质等与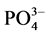 -P形成絮凝体有关[11] 。随着盐度继续增大,絮凝体表面的吸附电位达到饱和,故而盐度增加到35‰时的吸附量又开始呈现下降趋势。
-P形成絮凝体有关[11] 。随着盐度继续增大,絮凝体表面的吸附电位达到饱和,故而盐度增加到35‰时的吸附量又开始呈现下降趋势。
2) 温度
在10℃、20℃和30℃条件下,通过实验得到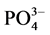 -P的吸附动力曲线(见图4)。从图中可以看出,随着温度的升高,
-P的吸附动力曲线(见图4)。从图中可以看出,随着温度的升高,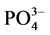 -P吸附速率和吸附量均显著提高。在0~1 h阶段,10℃、20℃、30℃下的吸附速率分别为0.147、0.282和0.406 mg∙g−1∙h−1,平衡吸附量分别达到0.386、0.431和0.504 mg∙g−1。分析其原因,主要是由于温度的升高可显著提高颗粒物–水界面上离子交换强度和速率,从而提高沉积物对
-P吸附速率和吸附量均显著提高。在0~1 h阶段,10℃、20℃、30℃下的吸附速率分别为0.147、0.282和0.406 mg∙g−1∙h−1,平衡吸附量分别达到0.386、0.431和0.504 mg∙g−1。分析其原因,主要是由于温度的升高可显著提高颗粒物–水界面上离子交换强度和速率,从而提高沉积物对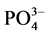 -P的吸附量。另外,
-P的吸附量。另外,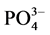 -P的吸附是一个吸热过程[7] ,温度提高有利于反应平衡向颗粒物吸附
-P的吸附是一个吸热过程[7] ,温度提高有利于反应平衡向颗粒物吸附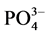 -P的方向进行。
-P的方向进行。
3.3. 吸附等温线
通过等温吸附平衡实验,测得李村河口不同站位(A、B、C)沉积物对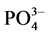 -P的吸附等温曲线(如图5)。
-P的吸附等温曲线(如图5)。
根据实验结果,本文采用Langmiuir型吸附等温方程对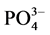 -P吸附等温曲线进行拟合,结果显示3个站位的曲线拟合度R2均在0.98以上,可很好的描述
-P吸附等温曲线进行拟合,结果显示3个站位的曲线拟合度R2均在0.98以上,可很好的描述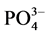 -P在颗粒物表面的吸附特征。
-P在颗粒物表面的吸附特征。
Langmiuir型吸附等温方程[12] 为:
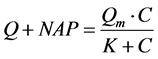 (3)
(3)
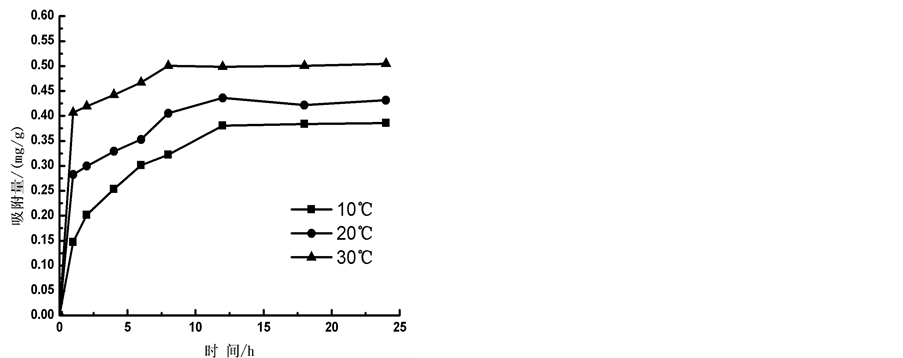
Figure 4. Impact of temperature on  -P kinetics
-P kinetics
图4. 温度对 -P吸附动力学的影响
-P吸附动力学的影响
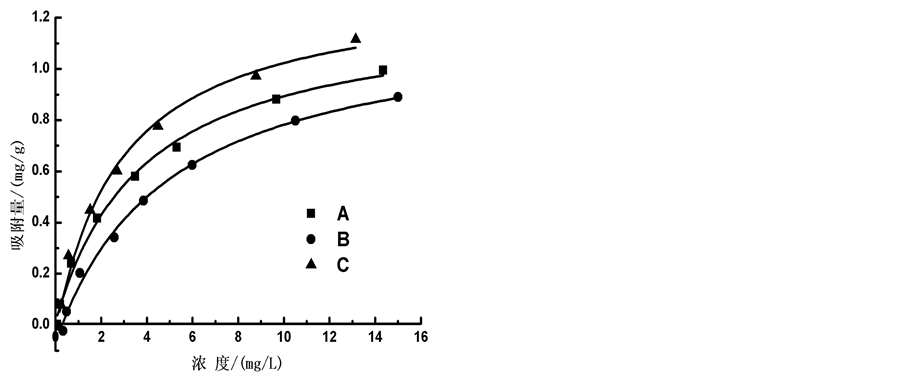
Figure 5.  -P adsorption isothermal curve
-P adsorption isothermal curve
图5.  -P吸附等温曲线
-P吸附等温曲线
式中:Q-吸附平衡后颗粒物对 -P的吸附量,单位mg∙g−1;Qm-颗粒物对
-P的吸附量,单位mg∙g−1;Qm-颗粒物对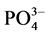 -P的吸附容量,单位mg∙g−1;C-吸附平衡后水相中
-P的吸附容量,单位mg∙g−1;C-吸附平衡后水相中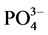 -P的浓度,单位mg∙L−1;K-吸附平衡常数,单位mg∙L−1;NAP-颗粒物中吸附
-P的浓度,单位mg∙L−1;K-吸附平衡常数,单位mg∙L−1;NAP-颗粒物中吸附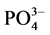 -P的本底值,单位mg∙g−1。
-P的本底值,单位mg∙g−1。
通过拟合的Langmiuir吸附等温方程,从而可计算A、B、C 3个站位沉积物的吸附容量Qm,分别为1.22、1.27和1.36 mg∙g−1,3点的吸附容量大小顺序依次为:C点 > B点 > A点;
颗粒物表面吸附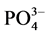 -P的本底值NAP在0.0108~0.0306 mg∙g−1之间,其中B点最大,A点最低,与
-P的本底值NAP在0.0108~0.0306 mg∙g−1之间,其中B点最大,A点最低,与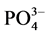 -P释放的动力学曲线所得的结果相对应。当达到吸附平衡并且颗粒物对
-P释放的动力学曲线所得的结果相对应。当达到吸附平衡并且颗粒物对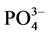 -P的吸附量恰好等于本底值NAP时,水相中
-P的吸附量恰好等于本底值NAP时,水相中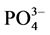 -P的浓度即为临界浓度。通过拟合方程计算得到A、B、C三点的临界浓度分别为0.034、0.289和0.067 mg∙L−1。当水相中的
-P的浓度即为临界浓度。通过拟合方程计算得到A、B、C三点的临界浓度分别为0.034、0.289和0.067 mg∙L−1。当水相中的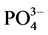 -P含量高于临界浓度时,颗粒物吸附水相中的
-P含量高于临界浓度时,颗粒物吸附水相中的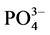 -P,表现为P
-P,表现为P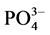 -P的“汇”;当水相中
-P的“汇”;当水相中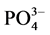 -P浓度低于临界浓度时,颗粒物向水相中释放
-P浓度低于临界浓度时,颗粒物向水相中释放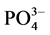 -P,表现为
-P,表现为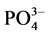 -P的“源”。
-P的“源”。
4. 结论
1) 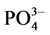 -P的吸附动力学过程可分为3个阶段:0~1 h快速吸附阶段,1~12 h缓慢释放阶段,12 h之后进入平衡阶段。
-P的吸附动力学过程可分为3个阶段:0~1 h快速吸附阶段,1~12 h缓慢释放阶段,12 h之后进入平衡阶段。
2) 盐度升高对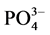 -P的吸附整体呈现抑制作用,但是吸附量在盐度为10‰~20‰区间出现了轻微的波动。
-P的吸附整体呈现抑制作用,但是吸附量在盐度为10‰~20‰区间出现了轻微的波动。
3) 温度升高对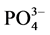 -P的吸附有促进作用。温度升高加快了体系的反应速率,使体系更快的达到平衡。
-P的吸附有促进作用。温度升高加快了体系的反应速率,使体系更快的达到平衡。
4) 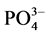 -P吸附等温曲线符合Langmuir等温吸附方程,拟合度达到显著水平。三个取样点的
-P吸附等温曲线符合Langmuir等温吸附方程,拟合度达到显著水平。三个取样点的 -P的吸附–解吸临界浓度分别为:0.034、0.289和0.067 mg∙L−1。
-P的吸附–解吸临界浓度分别为:0.034、0.289和0.067 mg∙L−1。