1. 引言
当今,我国已成为世界上的汽车产销大国。随着国民经济的不断发展,汽车保有量也是逐年攀升,随之而来的环境问题、能源问题以及噪声等问题不断恶化。节能减排成为我国汽车工业发展的大势所趋,也是响应创建“环境友好型、资源节约型”社会号召的一项关键举措。
调查研究表明[1] [2] ,现代汽车发动机的热效率约30%左右,其余的能量则以发动机冷却、汽车尾气以及摩擦损耗等形式耗散了,通过尾气带走的热量高占30%~45%。如果能够充分回收利用这一废热能量,将有助于提高车辆的动力性能和燃油经济性,更能够节约石油资源,减少温室气体排放,具有良好的环保效益。
世界范围内对车用尾气余热温差发电技术的研究已全面展开,各主要汽车公司均开展了相应的技术开发[3] -[7] 。宝马和通用汽车等公司已经成功尝试利用温差发电装置回收尾气废热,以起到部分替代车载发电机的作用。美国能源部(DOE)近几年通过相关的产业化研究项目,以资助通用汽车等公司开展温差发电技术回收汽车尾气的研究。
本文开发了一套模块化的汽车尾气温差发电装置,并与实验车进行了集成安装。在实际的道路测试过程中,该发电装置的峰值功率可达300 W,可在一定程度上满足汽车正常行驶中的电力需求。
资助信息:本文得到了中国华能集团“千人计划”专项以及北京市科委的资助,感谢北京市工程技术研究中心NO: BG0083的支持。
2. 汽车尾气温差发电装置
2.1. 结构形式
温差发电装置的结构取决于热源特征、散热方式、温度分布情况以及所用的热电片性能和排列方式。汽车尾气温差发电装置即是回收汽车尾气的热量发电,从而起到节约燃油的目的。
基于平板式的结构[8] ,本文所开发的温差发电装置主要包括以下几个部分:热端吸热气箱、冷端散热系统、热电片组以及紧固结构,如图1所示,由两个吸热气箱及三个冷却水箱相互层叠而成。两个气箱的进出口分别通过一个三通连接为一个整体,冷却水箱的进出口则分别通过一个四通连接为一个整体。吸热气箱和冷水水箱之间夹装热电片组,共四层热电片组。
工作时,来流尾气经三通后一分为二进入上下两个气箱,出口再经一个三通汇聚成一股排出,而来流冷却水则经过四通后一分为三,分别接入上、中、下三个冷却水箱,出口也是汇成一股返回。尾气与冷却水属逆流形式,有利于整个系统的热量传输以及沿程热电片温度的均匀化。
2.2. 安装位置
沿尾气流动方向,尾气温度总体呈下降趋势,能量品质沿流动方向逐渐降低。同时,考虑到以下两个因素:1) 温差发电装置的安装不影响三元催化器的催化效果;2) 所采用的热电片能够长时间运行,不会因为局部温度过高而造成热电片的损坏。因此,本次方案将装置安装在三元催化器和消声器之间,这
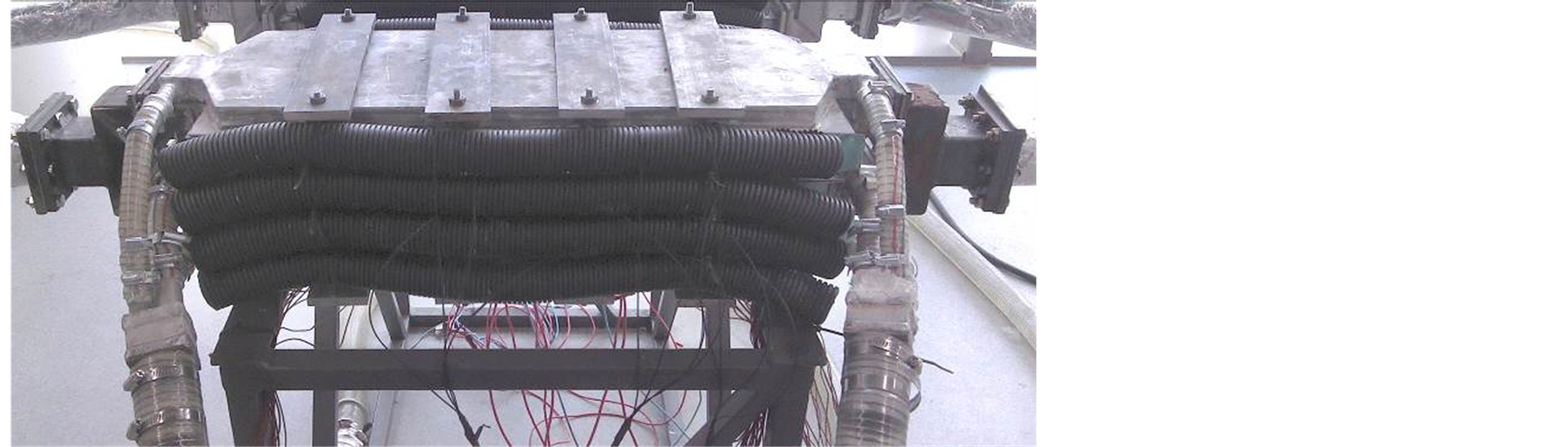
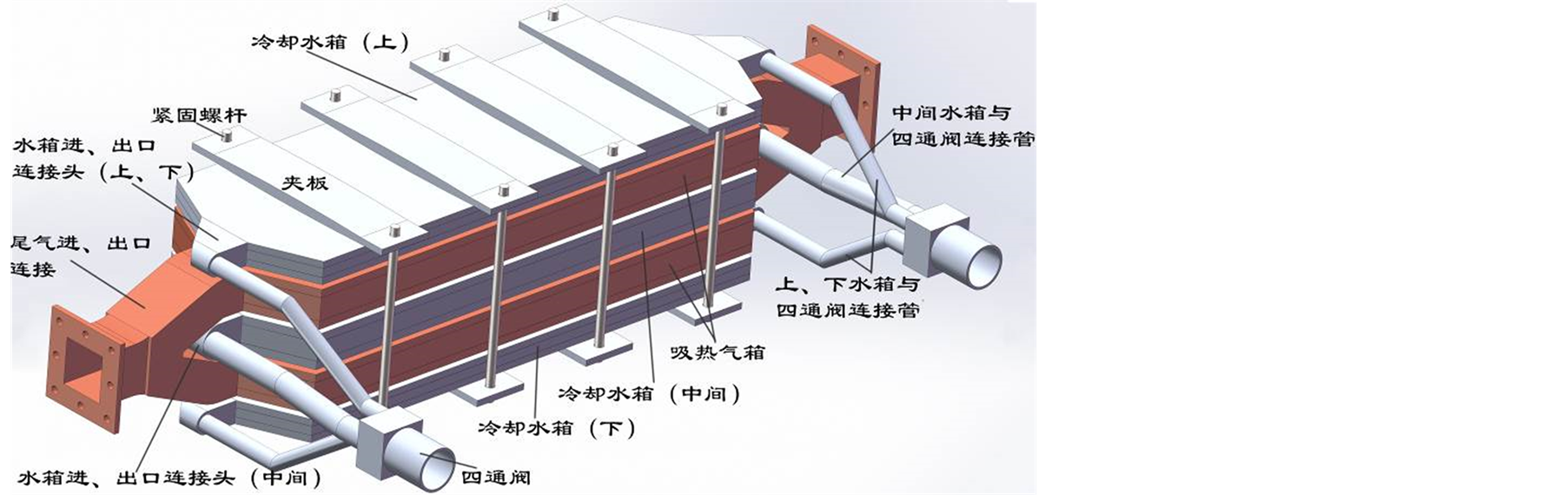

Figure 1. This is to illustrate figures of ATEH structure as follows: (a) design; (b) ATEH unit
图1. 汽车尾气温差发电装置结构图
一段区域,尾气的温度约200℃~600℃,经换热后满足热电片的运行要求,且可充分利用尾气的热量。
3. 实车测试系统
3.1. 实验车
实验采用北京福田牌汽油动力皮卡汽车,型号为萨普V系列2.0 L排量,其发动机型号为4Q20 M,该发动机在2000~4500 rpm时可产生95 kw的功率,如图2所示。
3.2. 集成安装
将温差发电装置与皮卡车集成,需要用到的主要部件包括:
1) 车用冷却系统总成:用于发电装置的冷端散热;
2) DC/DC转换模块:将发电装置输出电能稳压至车用12 V电压;
3) 热电偶:监测关键位置处的温度;
4) 行驶记录仪:通过发动机ECU端口实时记录发动机工况数据及油耗,并进行行驶路线的记录;
5) 储能电池:存储发电装置的输出电能。
具体的集成安装主要分以下几个步骤:
第一步:将原车排气系统拆除,安装新的排气系统,并进行保温处理;
第二步:在后货箱内,预先量测位置,布置新的排气系统;
第三步:将货箱地板开孔,用保温排气管将尾气引进货厢内,将温差发电单元按照要求安装在车后货箱内;
第四步:安装冷端散热系统,从而完成主要部件的安装;
第五步:在三元催化进出口、烟气进出口、冷却水入口等位置布设热电偶,同时,在发电装置进出口处的热电片冷热端布设了热电偶。在车辆行驶过程中,对这些位置处的温度进行监测。
第六步:在驾驶室内布置DC/DC转换装置,以及储能电池。将发电单元的输出端引至DC/DC转换模块,进而与储能电池连接。接着,将这套供电系统与车载电源系统进行集成,并解脱汽车自身的发电装置;
第七步:在驾驶室内安装行驶记录仪,采集车辆发动机ECU控制单元的数据,主要是监测和记录车
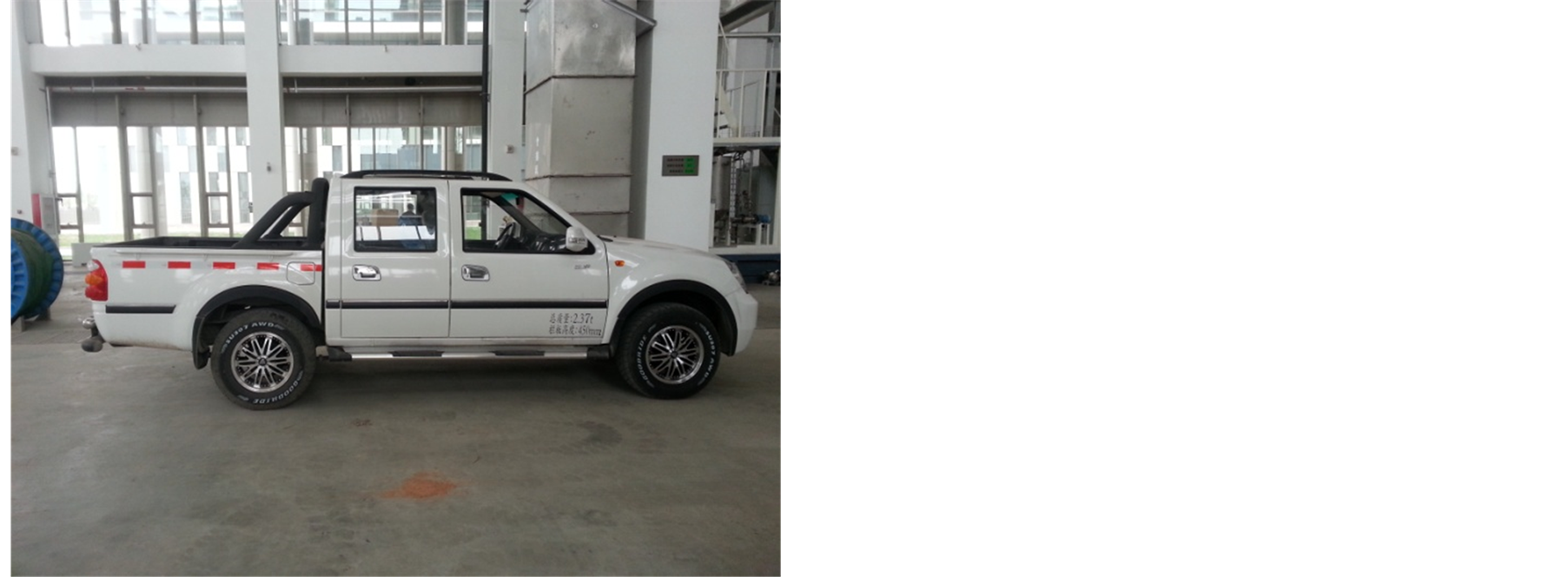

Figure 2. This picture shows a pickup truck for our experiments
图2. 实验皮卡车
辆的行驶路线、距离、速度以及油耗等。
经过上述七步后,便完成了发电单元与车辆的集成安装,以及实验所需测试仪器的安装。完成后的实验车如图3所示。
4. 测试条件及过程
测试路线为北京六环外环(约200 km),总测试里程为1000 km。
测试时,停用原车的发电机后,通过温差发电装置模块及储能单元为汽车提供电能。
车用冷却系统总成为发电装置提供冷却水。宽电压输入DC/DC转换器对温差发电装置的输出电能进行稳压转换(转换效率为90% ± 3%),并进行温差发电装置电流、电压、输出功率的记录,然后输出至储能系统,再利用48 V-12 VDC/DC转换模块将储能系统的电压转换为车辆用电设备的电压,从而替代原车发电系统。热电偶布置于发动机三元催化器前后及发电装置烟气进出口位置,监测当地的温度值。
5. 结果及分析
实验过程中,记录了温差发电装置的输出电压和电流,计算其输出功率。
图4给出了温差发电装置典型的输出功率曲线。图中,Va表示汽车的运行速度,单位是米/秒(m/s),Vr表示当前时间段内汽车的平均运行速度,单位是米/秒(m/s),n表示发动机的转速,单位是转/分钟(r/min)。
据图可知,温差发电装置的输出功率随时间而变化,这是由于汽车的路况运行状态在发生变化,装置的峰值功率可达300 W。
进一步对各参数进行分析,发现对输出功率影响最大的是发动机的转速。因为发动机的转速增大时,汽车的燃油消耗增多,相应的尾气流量和温度都会有所提升,温差发电装置的吸热量增多,输出功率相应增大。
6. 总结
本文开发了一套平板式模块化的汽车尾气温差发电装置,并与一辆实验皮卡车进行了集成安装。在实际的道路测试过程中,该发电模块的峰值功率可达300 W,可在一定程度上满足汽车正常行驶中的电力需求,从而减少汽车行驶过程中的燃油消耗,起到节能减排的作用。
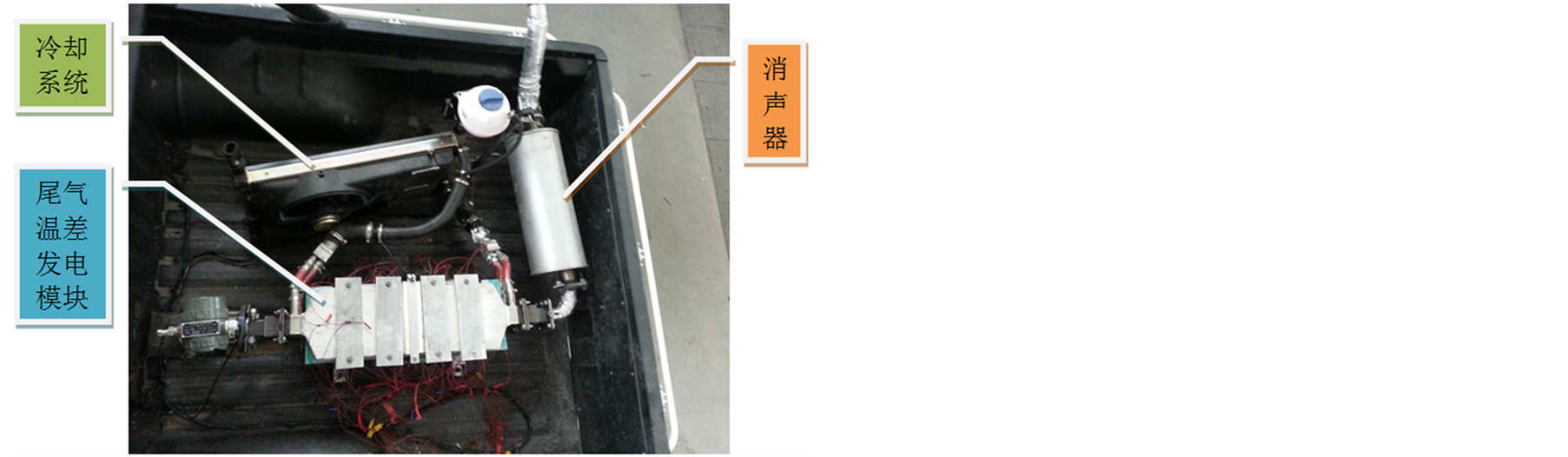
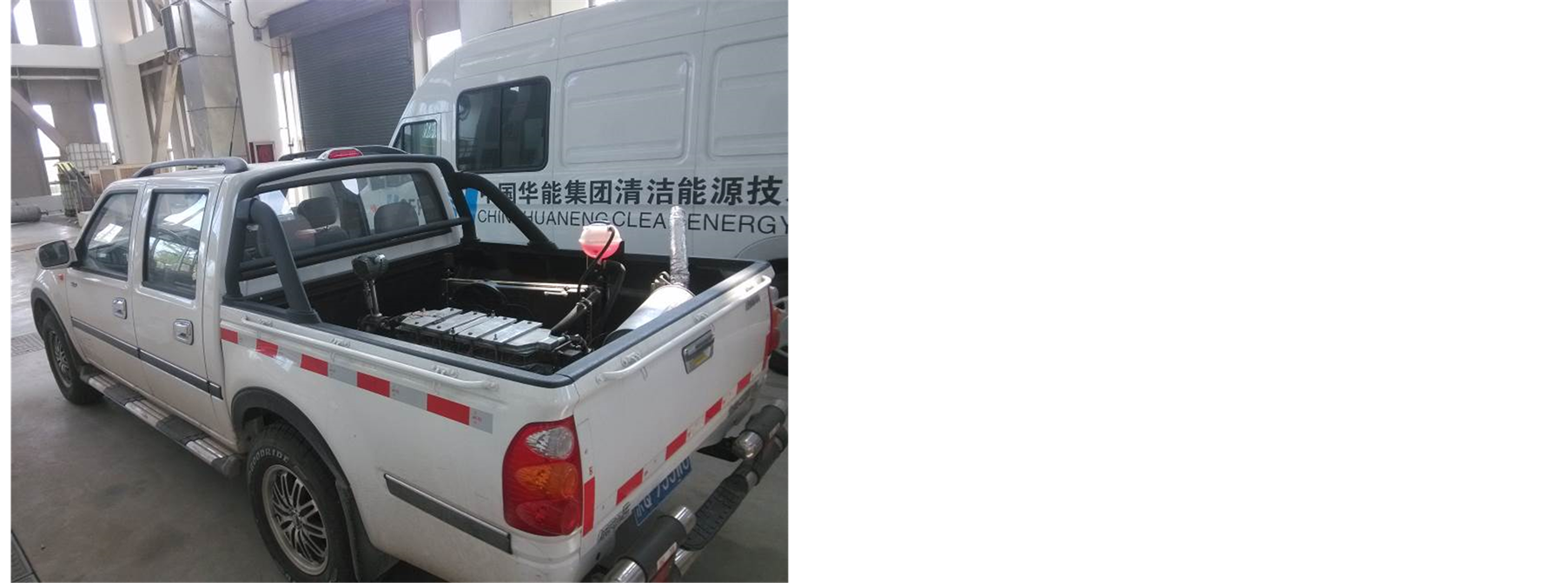


(a) 局部图 (b) 整体图
Figure 3. ATEH is shown for the automobile test system in the laboratory pictures at below: (a) zoom-in; (b) overview
图3. 实车测试系统
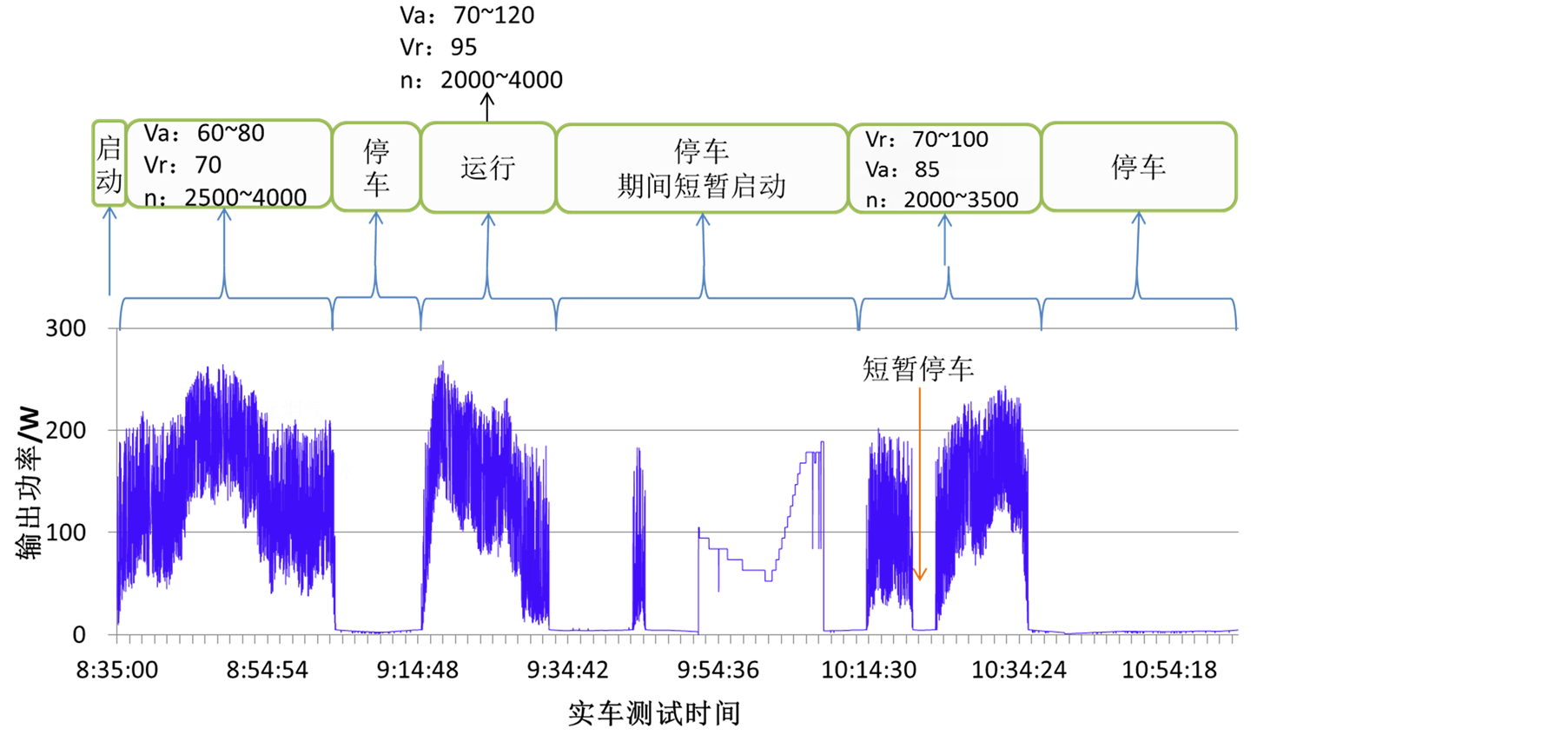
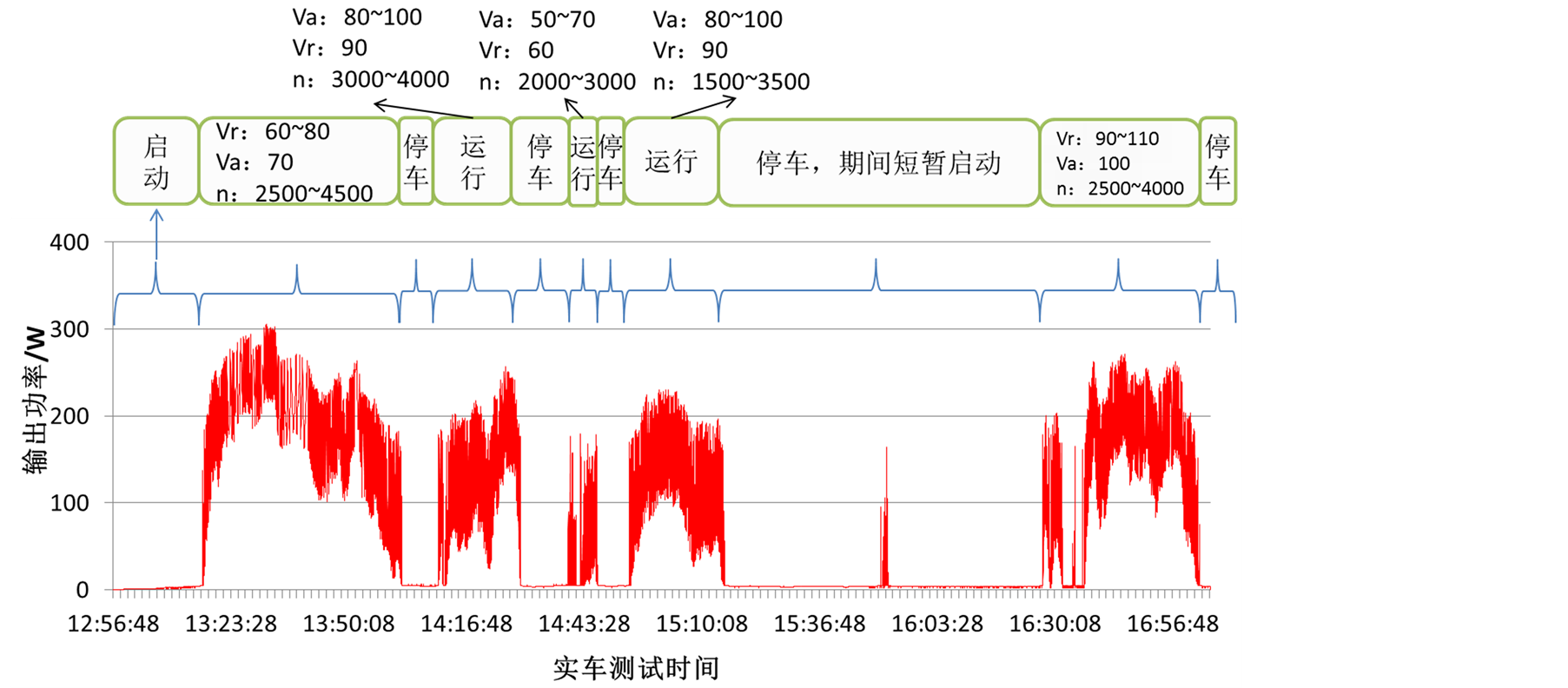
Figure 4. Output power curves during automobile testing as follows: (1) road condition-1; (2) road condition-2
图4. 实车测试的输出功率曲线
致 谢
本文得到了中国华能集团“千人计划”专项以及北京市科委的资助,感谢北京市工程技术研究中心 NO: BG0083的支持。

NOTES
*通讯作者。