1. 引言
目前,玉米是中国第二大粮食作物,其年产量占世界总量的1/5以上。从2005年以来,中国玉米的国际市场占有率总体上趋于快速下降(李蔚青,2010) [1] 。出口量从2005年的861万吨急剧下降到2011年的不足14万吨。并且,在此过程中下降速度呈现较大的波动性。从短期来看,中国玉米出口量的下降趋势不可逆转。那么,如何让中国玉米平稳地退出国际市场,从而降低(负的)出口增长率的波动水平,无疑具有重要的现实意义。很明显,一国出口中的总体波动水平主要取决于出口企业对出口目的地的自由选择、出口国国内供需、国际竞争者和进口国供需等因素。第一个因素导致的出口波动,属于市场失灵中的协调失灵(coordination failure)。因此,政府可以通过优化出口市场结构或者出口地理集中度在一定程度上降低出口波动水平。出口地理集中度(geographic concentration)是衡量出口市场多元化程度的一个重要指标,其测量方法有很多(Samen, 2010) [2] 。其中,Hirschman指标在国内外的文献中较为常用1。一般认为,地理集中度过高会导致出口收入的不稳定。这种观点已经成为各国政策制定者推行出口市场多元化战略的依据(Adams & Behrman, 1982) [3] 。可是,基于不同国家和不同产品的经验分析所得到的结论并不一致(刘靖、毛雪峰、辛贤,2006;Love,1987;Piya et al., 2010) [4] -[6] 。
那么,出口地理集中度到底是越高越好还是越低越好?或者说,从降低出口波动风险的角度,是否存在最优的地理集中度?国内外学者对此研究较少,相关研究大多集中于出口市场结构的优化。比如,国内学者往往建议“开拓新市场”,但是如何开拓以及安排各出口市场的出口比例,并没有给出具有可操作性的解决途径(程国强,2004;魏浩、马野青,2006) [7] [8] 。在国外学者中,Hirsch和Lev(1971) [9] 较早将Markowitz的理论与出口市场多元化联系起来,但是他们的研究仅仅检验并支持了“出口市场多元化有助于提高出口收入稳定性”的结论。随后,Board et al. (1987 & 1991) [10] [11] 、Kennedy(1998) [12] 、Jang和Chen(2008) [13] 使用马科维茨模型(Markowitz model),分别研究了西班牙、爱尔兰和台湾地区旅游业客源国市场的有效组合(efficient mix)。但是这些研究或者在出口波动风险的衡量方面,或者在出口波动类型的鉴别方面存在不足。
如果以稳定商品出口为目标,地理集中度的优化问题至少应考虑每个出口市场的波动风险。Markowitz (1952 & 1959) [14] [15] 的均值–方差方法为此问题提供了一条解决思路。Markowitz的均值–方差方法已经问世了半个多世纪,经过不断发展,被广泛应用于各种真实资产和金融资产的选择。然而,该方法却一直没有被应用于商品出口市场的多元化问题。为了稳定地退出国际市场,本文试图为中国的政策制定者优化玉米出口地理集中度提供理论依据和备选方案。具体而言,将中国玉米的出口市场细分为4个市场,同时考虑到中国玉米在各市场的出口增长率之间的差异以及波动特点,使用以稳定出口数量增长率为目标的出口市场组合模型(蔡一鸣,2014) [16] 计算中国玉米出口市场的有效边界和有效组合,以及对应于不同预期出口增长率的出口地理集中度。政策制定者对最优地理集中度的选择,取决于其对待风险的态度。
本文余下部分安排如下:第二部分分析中国玉米出口市场的四个主要特征,这些特征表明了降低其出口风险的可能性和必要性;第三部分介绍一个替代方差概念的新指标相对方差,以及以相对方差为基础的出口市场组合模型;第四部分,使用出口市场组合模型计算中国玉米出口市场的有效组合以及最优地理集中度;最后部分是全文结论。
2. 中国玉米出口贸易的特征
从2001到2005年,中国玉米在国际市场上的占有率尽管有较大波动,但是没有出现较明显的变化趋势,出口数量也至少维持在230万吨以上。从2005到2011年,中国玉米的年均出口增长率为-50%,呈现明显的下降趋势,并且主要出口至韩国、日本、朝鲜和其他国家2。下面,从变化趋势、地理集中度、波动性以及相关性四个角度,分析中国玉米在2005年至2011年期间对上述4个市场的出口贸易特征。
首先,对4个市场的出口数量均呈现快速下降趋势。总体而言,在4个市场上的出口数量的年均增长率都低于−10%,并且存在明显差异。其中,对韩国出口贸易的下降速度最快,出口数量从2005年的590万吨下降到2011年的不足9吨,年均增长速度为−89.4%。对日本和其它国家出口的下降速度也非常快,分别为−81.4%和−77.6%。对朝鲜的出口下降速度最慢,为−10.7%。
其次,出口市场的地理集中度总体上趋于上升。具体而言,根据Hirschman指标计算的地理集中度在2008年以前比较稳定,随后趋于上升。该指标最低时为2003年的0.83,2011年达到最高为0.999 (见表1)。在出口市场结构方面,2007年以前中国玉米的出口市场主要集中在韩国和其他国家两个市场,这两个市场的出口份额之和最少时也高达84%。2008年以后,主要出口市场转移至朝鲜。
其三,在4个市场上的出口增长率均具有明显的波动性。尽管在4个市场上的年均出口增长率均为负数,但是年度增长率均有正有负,并且具有极大的波动性(见表2)。以韩国市场为例,增长率最高时为749%,最低时为负的99.9%。4个市场上出口增长率的不确定性,导致了中国玉米总出口数量的增长率也出现了较大的波动,最高时达到60%,而最低时为−95%。因此,降低中国玉米出口所面临的波动风险具有重要的现实意义。
最后,在4个市场上的出口增长率之间具有不完全正相关性。在2005至2011年期间,中国玉米对4个市场的出口增长率之间的相关关系具有较大的差异性(见表3)。其中,对朝鲜和其他国家的出口增长率之间的相关系数最大为0.927,对日本和其它国家的出口增长率之间的相关系数最小为−0.13。这意味着通过有效的出口市场多元化可以降低中国玉米在出口中面临的非系统性风险但不能完全消除它。
3. 相对方差与出口市场组合模型
无论根据何种方法计算一国的出口地理集中度,都需要确定该国对各市场的出口份额。如果以出口波动风险最小化为目标,那么确定出口份额的过程类似于投资者寻求最优证券组合以最小化收益率的波动风险。因此,马科维茨的均值–方差方法具有明显的借鉴意义。事实上,“不确定性”和“不完全正相关性”是应用马科维茨方法的两个必要条件。不确定性意味着存在降低风险的必要性,而不完全正相

Table 1. The export share in 4 markets of China’s corn: 2005-2011
表1. 中国玉米对4个市场的出口份额:2005~2011年
资料来源:中国海关统计各年数据。注:2011年,中国对韩国和日本的玉米出口数量太少,四舍五入后才显示为0。

Table 2. The growth rates of export volume among 4 markets of China’s corn: 2005-2011
表2. 中国玉米对4个市场的出口数量增长率:2005~2011年
资料来源:中国海关统计各年数据。注:由于2008年对韩国的出口数量为0,因此2009年不计算其增长率。表3中计算相关系数时,以年均增长率替代。

Table 3. The correlation coefficients between the export growth rates among 4 markets of China’s corn
表3. 中国玉米对4个市场出口增长率之间的相关系数
资料来源:根据中国海关统计2005至2011年的数据计算得到。
关性意味着通过分散化操作可以降低风险。很明显,中国玉米在4个市场上的出口贸易符合这两个条件。如果完全采用马科维茨的方法,以方差衡量出口波动风险并构建出口市场组合模型,存在以下问题:方差概念一般被认为不适合用于比较不同水平的数列的波动程度(贾军俊、何晓群、金勇进,2000) [17] 。而一国对各出口市场的出口量(出口收入或出口数量)或出口增长率的均值并不相同,并且往往存在显著差异3。如果不同数列的均值之间存在差异,只有剔除均值的影响,才能更准确地比较不同数列之间的波动程度。为了克服这个问题,蔡一鸣(2014)提出了一个衡量波动风险的新指标即相对方差,并在此基础上构建了出口市场组合模型。
3.1. 相对方差及其性质
与方差不同,作为用相对数表示的另一类离散趋势指标,标准差系数(等于标准差除以均值)消除了不同数列平均水平的高低对离散程度测度值的影响,反映了数列中各数据之间离差的相对水平。与标准差系数的功能类似,可以定义了一个新的指标——相对方差如下:
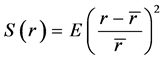 ,其中,
,其中,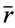 为数列
为数列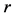 的均值,且
的均值,且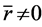 。
。
相对方差度量的不再是数列中各数据相对于均值的绝对偏离的平均水平,而是相对于均值的相对偏离的平均水平。在数值上,相对方差等于标准差系数的平方,因此避免了均值为负值时使用标准差系数衡量离散程度的复杂情况。并且,相对方差越大反映各数据之间的相对差异越大,相对方差越小则反映相对差异越小。
进一步地,根据相对方差的定义,可以得到如下推论(可用归纳法求证):
推论1:令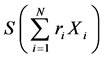 和
和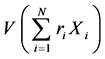 分别为多数列加权之和的相对方差和方差,其中
分别为多数列加权之和的相对方差和方差,其中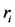 为分布数列
为分布数列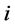 ,
,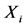 为权数,如果
为权数,如果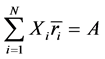 为常数,则有
为常数,则有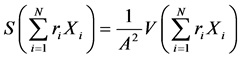 。
。
根据相对方差的上述性质,同时考虑到中国玉米对各出口市场平均出口增长率之间的差异较大,相对方差比方差更适合衡量中国玉米的出口波动风险。其原因在于,相对方差衡量的是出口增长率相对于均值的离散程度,消除了均值的影响,从而使各出口市场的波动风险具有可比性。
3.2. 出口市场组合模型
如前文所述,中国玉米在4个市场上的出口数量总体上都趋于快速下降,因此在各市场上所面临的风险主要来自出口增长率的波动。如果借鉴马科维茨模型的方法,可以选择出口增长率作为预期“收益”变量,并以出口增长率的相对方差衡量波动风险。根据推论1,为了最小化预期出口增长率的波动水平,出口国的目标函数及其约束条件为:
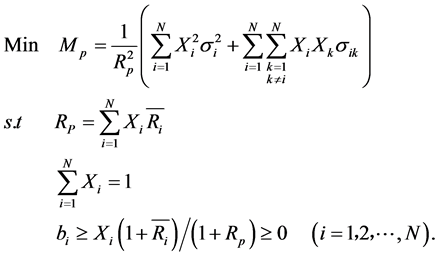
其中,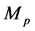 表示在
表示在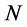 个出口市场上基于相对方差的组合风险,也即对
个出口市场上基于相对方差的组合风险,也即对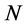 个市场出口增长率的加权之和的相对方差。
个市场出口增长率的加权之和的相对方差。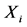 表示不考虑预期出口增量时出口国对第
表示不考虑预期出口增量时出口国对第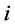 个市场的出口份额。
个市场的出口份额。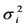 表示出口国对第
表示出口国对第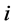 个出口市场出口增长率的方差,
个出口市场出口增长率的方差,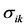 表示对第
表示对第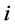 个出口市场与第
个出口市场与第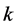 个出口市场出口增长率的协方差。
个出口市场出口增长率的协方差。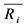 表示对第
表示对第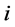 个出口市场的平均出口增长率,
个出口市场的平均出口增长率,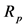 表示
表示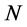 个出口市场组合的预期出口增长率。
个出口市场组合的预期出口增长率。
由于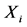 没有考虑预期出口增量,因此出口国对第
没有考虑预期出口增量,因此出口国对第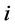 个市场的出口份额需要另外计算。令A代表出口国对所有出口市场的预期出口数量,B代表其中的预期出口增量,则预期出口增长率为
个市场的出口份额需要另外计算。令A代表出口国对所有出口市场的预期出口数量,B代表其中的预期出口增量,则预期出口增长率为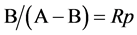 。同时,出口国对第i个市场的预期出口为
。同时,出口国对第i个市场的预期出口为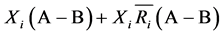 。因此,出口国对第
。因此,出口国对第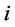 个市场的出口份额为
个市场的出口份额为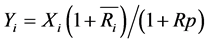 。类似于在证券投资场合对卖空的限制,我们假设这个出口份额为非负数,即不考虑出口国作为贸易中间商的情形。而
。类似于在证券投资场合对卖空的限制,我们假设这个出口份额为非负数,即不考虑出口国作为贸易中间商的情形。而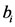 则代表出口国对第
则代表出口国对第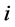 个市场出口份额的潜在最大值。
个市场出口份额的潜在最大值。
4. 中国玉米出口市场的有效组合与最优地理集中度
本小节仅考虑中国玉米在前文所述的4个市场上的有效组合和地理集中度。并且,我们选择的样本区间为2005年至2011年,在此期间,中国玉米的出口数量开始呈现出明显的下降趋势。为了使中国玉米出口市场的有效组合更具有现实意义,我们对中国玉米在4个市场上的出口份额分别设定上限和下限。所有市场的出口份额下限为0。对4个市场的出口数量虽有波动,但均呈现明显的下降趋势,因此我们将4个市场的上限设为样本区间内最高市场份额的1倍。求解出口市场组合模型的软件为EXCEL中的规划求解工具。
4.1. 有效边界与有效组合
图1显示的是中国玉米出口市场的有效边界。从总体上,有效边界的形状表明要获得更高的预期出口增长率,必须承担更高的波动风险。有效边界上的每一个点都表明在既定的预期出口增长率下的出口波动风险是最小的,并且这些点代表了不同的有效市场组合(见表4)。
A点所代表的市场组合的预期出口数量增长率为−10.7%,组合相对方差为425.977,二者在所有有效组合中均为最高。在该组合中,朝鲜所占的市场份额最多为99.8%,达到其市场份额的上限。原因在于,其平均出口增长率等于组合市场的预期出口增长率。H点所代表的市场组合的预期出口数量增长率为−80%,组合相对方差为2.636,二者在所有有效组合中均为最低。在该组合中,日本和其他国家的市场份额均达到上限。原因在于,一方面这两个市场的平均出口增长率均接近组合市场的预期出口增长率,同时二者出口增长率的方差均较小(见表5)。另外,在本文选取的8个有效市场组合中,对于日本、朝鲜和其他国家而言,出口份额的上限和下限均出现在不同的市场组合中,这意味着对这3个市场的出口份额在选择不同的市场组合时,面临着较大的调整。
4.2. 最优地理集中度及其含义
根据表4中的8个有效市场组合,可以利用Hirschman指标计算对应于不同预期出口增长率的地理集中度。比较有效市场组合和样本区间中的地理集中度(见表1),最高的地理集中度出现在样本区间中的2011年,而最低的地理集中度则出现在G点所代表的有效组合中。对于有效边界上的G点而言,其地理集中度最低,同时该点所对应的市场组合风险低于A、B、C、D、E和F点,却高于H点4。地理集中度越高越好还是越低越好呢?事实上,地理集中度与市场风险之间不存在简单的线性关系。原因在于,地理集中度的计算仅仅考虑各出口市场的出口份额,而不考虑各出口市场的波动风险。因此,即使出口国的出口主要集中于少数市场从而地理集中度较高,如果这些市场的波动风险较小,那么组合风险也会较低。反之,即使出口国的出口市场较多从而地理集中度较低,如果这些市场的波动风险都较高且正相关程度也较高,那么组合风险也会较高。这大概是已有的经验研究相互矛盾的主要原因。或者说,从出口
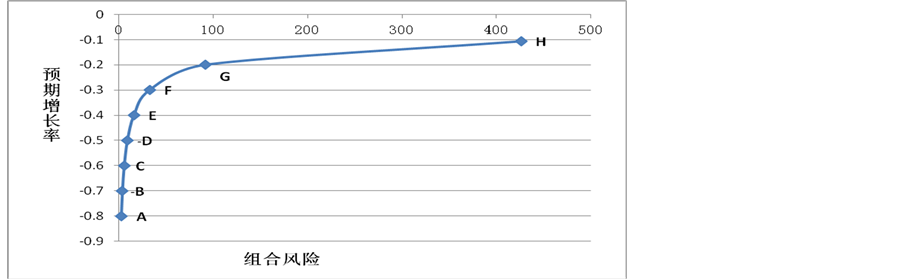
Figure 1. The efficient frontier of China’s corn export markets
图1. 中国玉米出口市场的有效边界

Table 4. The efficient mix and geography concentration of China’s corn export markets
表4. 中国玉米出口市场的有效组合及地理集中度
注:表中的市场份额经过四舍五入,加总后约等于1。

Table 5. The variance and covariance of the export growth rates among 4 markets of China’s corn
表5. 中国玉米在4个市场上出口增长率的方差和协方差
波动风险的角度,一个给定的地理集中度数值并没有揭示太多的信息,只有当它与具体的出口市场及其份额结合在一起时才更有意义。
进一步地,与证券投资者类似,出口国政策制定者对最优市场组合从而最优地理集中度的选择,取决于其对待风险的态度。比如,如果中国的政策制定者属于极端的风险厌恶型,则会选择有效边界上H点所对应的市场组合,从而最优的地理集中度为0.666。如果中国的政策制定者属于极端的风险喜好型,则会选择有效边界上A点所对应的市场组合,从而最优的地理集中度为0.998。不论是0.666还是0.998或是其他的数值,政策制定者所选择的最优地理集中度必须与特定的出口市场联系起来才有意义。
5. 结论
一国出口中的总体波动水平部分来源于出口企业对出口地的自由选择。因此,出口波动在一定程度上属于市场失灵中的协调失灵,需要政府采取必要的干预措施。自2005年以来,中国玉米在韩国、日本、朝鲜和其他国家的出口数量总体上都趋于快速下降,因此在上述市场上所面临的风险主要来自(负的)出口增长率的波动。如果以稳定地退出国际市场为目标,马科维茨的均值–方差方法可以为中国玉米出口地理集中度的优化提供一条解决思路。考虑到各出口市场上的平均出口增长率之间存在显著差异,相对方差比方差更适合衡量出口波动风险。根据以稳定出口增长率为目标的出口市场组合模型,可以计算出中国玉米出口市场的有效组合,并可以进一步计算出对应于不同预期出口增长率的地理集中度。地理集中度与市场风险之间不存在简单的线性关系。而最优地理集中度的选择,取决于政策制定者的风险偏好。
基金项目
广东省哲学社会科学“十二五”规划2012年度学科共建项目,GD12XLJ02。

NOTES
1Hirschman指标的计算公式为,其中为总出口量,为对第个出口市场的出口量。该指标的数值越高表明出口市场越集中。很明显,对出口市场分类标准的不同会影响该指标数值的大小。
22005年以后,中国玉米在韩国、日本和朝鲜以外的出口目的地变化较大,且出口量比较分散,因此本文将其合并为一个“市场”。
3以中国玉米出口为例,在2005年至2011年期间,对韩国的出口增速为−89.4%,而对朝鲜的出口增速则为−10.7%,差异非常明显。
4 G点并不是唯一的反常点。在G点和H点之间,还有很多地理集中度较低而风险却较高的点(表4中没有列出)。