摘要:
海浪波周期是波浪能资源开发、舰船航行安全等重点关注的要素之一,也是目前海浪研究的瓶颈。由于资料稀缺的限制,针对海浪波周期的研究可谓凤毛麟角。本文以CCMP风场驱动目前国际先进的第三代海浪数值模式WW3 (WAVEWATCH-III),模拟得到首份覆盖整个中国海、长时间序列、高时空分辨率、高精度的海浪场数据,首次实现了中国海海浪波周期季节特征的精细化研究,期望可以为“海之梦”、“中国梦”尽绵薄之力。研究结果表明中国海的海浪波周期存在较大的季节性、区域性差异,且与季风存在密切的关系:1) 中国海的波周期在1月和10月整体大于4月和7月。渤海的波周期在各个季节都小于其余海域。1月、4月和10月,海浪波周期的大值区主要分布在25˚N以南,而7月主要分布于15˚N以北。2) 从年平均海浪波周期的分布特征来看,南中国海大部分海域、东海大部分海域以及菲律宾以东近海的年平均波周期明显大于其余海域,高值中心分布于南海北部海域。3) 在季风期间(包含冬季风和夏季风),季风影响明显的区域波周期较小,而其余海域的波周期则偏高。
Abstract:
The wave period is close to the development of wave energy resource, navigation, ocean engineering, prevents and reduces sea wave calamity, and so on. In this study, the first China Sea wave data were obtained, using WW3 wave model forced by CCMP (Cross-Calibrated, Multi-Platform) wind field. Then the seasonal characteristics of the China Sea wave period were analyzed. Results showed that, 1) Wave period in January and October was greater than that in April and July. Wave period in the Bohai Sea was smaller than that in other waters all year round. In January, April and October, large area of wave period was mainly located in the south of 25˚N, while in the north of 15˚N in July. 2) From annual average wave period, values in the South China Sea, East Sea, and east of Philippine was greater than that in other waters. 3) During the period of monsoon, wave period in the area affected by the monsoon was larger than in the area not affected by the monsoon.
1. 引言
海浪波周期是航海、波浪能开发、防灾减灾、海洋工程中较为关注的要素之一。在波浪能资源的评估中,波浪能的大小与波高的平方和波周期的乘积成正比(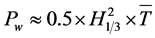 ,
,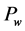 为波浪能流密度,
为波浪能流密度,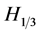 为有效波高,
为有效波高,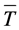 为平均周期),可见波周期在波浪能中占有非常重要的地位[1] -[3] 。海浪波周期同样也是航海极为关注的要素,当舰艇的摇摆周期和海浪波周期相近时,容易发生共振现象,会对舰艇自身的安全造成威胁。
为平均周期),可见波周期在波浪能中占有非常重要的地位[1] -[3] 。海浪波周期同样也是航海极为关注的要素,当舰艇的摇摆周期和海浪波周期相近时,容易发生共振现象,会对舰艇自身的安全造成威胁。
前人在海浪方面做了很多工作和很大贡献,但多是针对波高、波向展开的分析,由于海浪波周期数据非常稀缺,针对海浪波周期的研究可谓凤毛麟角。郑崇伟等[4] 曾利用ERA-40海浪再分析数据,统计了南海的风浪、涌浪、混合浪波周期的分布特征,但由于该数据的分辨率相对较低(1.5˚ × 1.5˚),只能提供大致的参考,不能很好的满足实际应用中的需求。
本文基于目前国际先进的第三代海浪数值模式WW3 (WAVEWATCH-III),以具有高分辨率、长时间序列的CCMP (Cross-Calibrated, Multi-Platform)风场为驱动场,模拟得到首份覆盖整个中国海、长时间序列、高时空分辨率、高精度的海浪场数据,首次实现了中国海海浪波周期季节特征的精细化研究,为航海、防灾减灾、波浪能开发等提供科学指导,为“海之梦”、“中国梦”尽绵薄之力。
2. 数据和方法
2.1. 数据来源
本文基于目前国际先进的第三代海浪数值模式WW3 (WAVEWATCH-III),以具有高分辨率、长时间序列的CCMP (Cross-Calibrated, Multi-Platform)风场[5] [6] 为驱动场,模拟得到首份覆盖整个中国海、长时间序列、高时空分辨率、高精度的海浪场数据。由于海浪具有“失忆”的特点,为了消除边界效应,在海浪数据的模拟过程中,本文在所需要的范围基础上将范围扩大,最后从中截取所需要的范围。模拟海浪数据的具体信息如下,空间范围:3.875˚S~41.125˚N,95.125˚E~135.125˚E;空间分辨率:0.25˚ × 0.25˚,时间序列:1988年01月01日00:00时~2011年12月31日18:00时;时间分辨率:3小时。
2.2. 数据的有效性检验
目前,我国乃至整个全球的海洋观测资料都可谓凤毛麟角,本文尝试着利用来自日本、韩国等周边国家的海浪观测数据,用于验证模拟海浪数据的有效性,也期望这种方法可以为丰富我国海洋数据库提供参考。经与浮标观测数据、T/P (全称TOPEX/Poseidon)高度计反演的数据对比发现该数据具有较高可信度[7] -[10] ,以往的研究也表明WW3模式对中国海的海浪具有较强的模拟能力[11] ,本文在此简要列举部分验证结果,见图1~3。
通过定性对比模拟值与观测值的曲线发现,二者具有很好的一致性。此外,本文还计算了相关系数(CC)、偏差(Bias)、均方根误差(RMSE)以及平均绝对误差(MAE),定量地分析模拟海浪数据的精度,结果表明模拟数据具有较高精度。
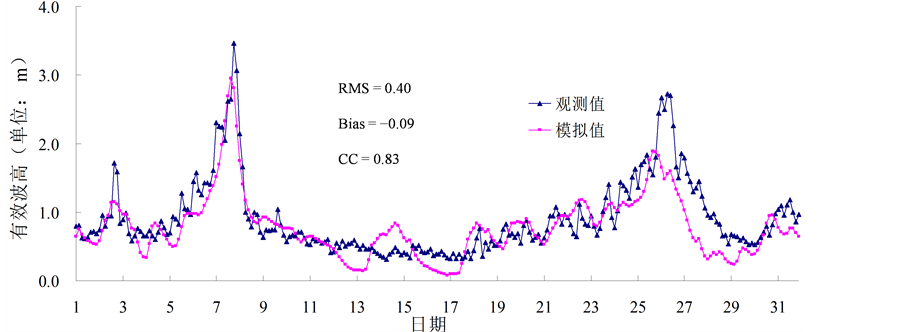
Figure 1. Simulation SWH and observation SWH in Japan “SATA Cape” during October 2009
图1. 2009年10月日本佐多岬观测站的观测有效波高与本文的模拟有效波高
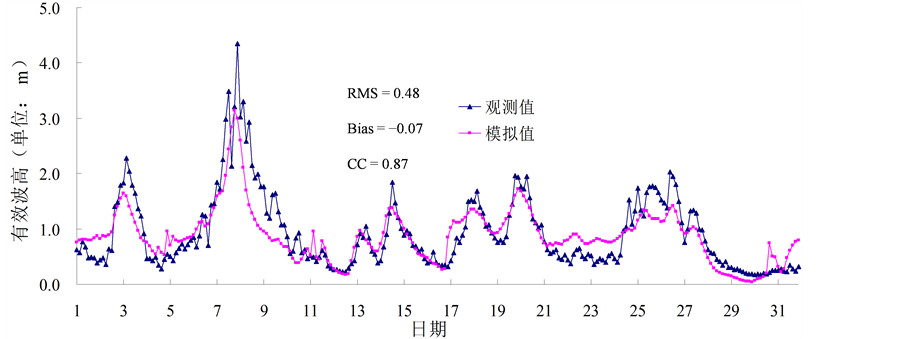
Figure 2. Simulation SWH and observation SWH in Japan “Fukue Island” during October 2009
图2. 2009年10月日本福江岛观测站的观测有效波高与本文的模拟有效波高
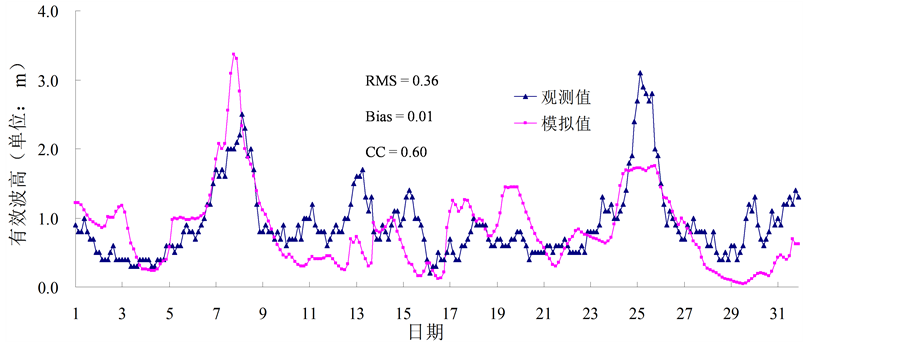
Figure 3. Simulation SWH and observation SWH in Korea “Cheju Island” during October 2009
图3. 2009年10月韩国济州岛观测站的观测有效波高与本文的模拟有效波高
3. 波周期的季节特征
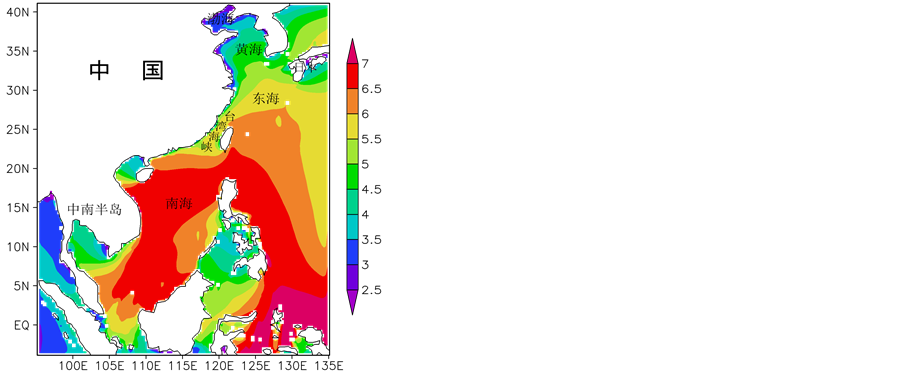
利用模拟得到的近24年、逐3小时的模拟海浪数据,分析了0.25˚ × 0.25˚每个网格点上海浪波周期的季节特征,以及年平均海浪波周期的分布特征,见图4、图5。中国海的波周期在1月和10月整体大于4月和7月。渤海的波周期在各个季节都小于其余海域,1月和10月,南中国海为大值区,基本都在6.5 s以上。7月,波周期的大值区分布于琉球群岛附近海域。
1月(代表冬季),波周期的分布特征表现出较大的区域性差异,南中国海的波周期明显高于其余海域,东海次之,黄渤海明显偏低。该季节波周期大值区集中分布于南中国海、菲律宾东部近海,基本都在6.0 s以上,离岸很大一部分海域在6.5 s以上,其中高值中心分布于菲律宾以南的赤道附近海域。南海北部近海、东海的波周期次之,在5.0~6.5 s之间。黄海的波周期主要在3.5~5.0 s。渤海属于低值中心,在3.5 s以内。泰国湾、北部湾的周期也偏低,在3.5~5.0 s之间。
4月(代表春季),波周期明显低于1月,区域性差异也没有1月明显,该季节各个海域的波周期较为接近,相对大值区分布于长江口——九州岛以南的大范围海域,在5.0~6.0 s之间;黄海中南部的离岸为4.5~5.0 s,黄海中南部的近岸、黄海北部为4.0~4.5 s;渤海仍然是低值中心,在3.5 s以内,这应该是由于渤海海域狭小,海浪尚未充分成长天气过程已经结束所造成的。
7月(代表夏季),与其余季节的波周期分布存在较大差异,其余季节的大值区主要分布在25˚N以南,而7月波周期的大值区则明显北抬,主要分布于15˚N以北,基本在5.5 s以上。黄渤海在这个季节的波周期也明显大于其余季节,仅部分近岸的波周期在3.5 s以内。南海中南部海域、北部湾、泰国湾的波周期都集中分布在3.5~4.5 s之间。
10月(代表秋季),该季节的波周期分布特征与1月非常相似,这应该是由于10月冷空气也逐渐盛行所致。
从海浪波周期的年分布特征来看,南中国海大部分海域、东海大部分海域以及菲律宾以东近海的年平均波周期明显大于其余海域,基本在5.5 s以上,高值中心分布于南海北部海域,年平均波周期可达6.0 s以上。黄海大范围海域的波周期在4.0~5.0 s之间,渤海在4.0 s以内。北部湾和泰国湾的波周期在3.5~4.5 s之间。
整体来看,在季风期间(包含冬季风和夏季风),季风影响明显的区域波周期较小,而其余海域的波周期则偏高,这应该是由于季风影响区域的风浪成分更大,其余海域则涌浪成分更大,涌浪的波周期往往大于风浪的波周期。
 (a)
(a)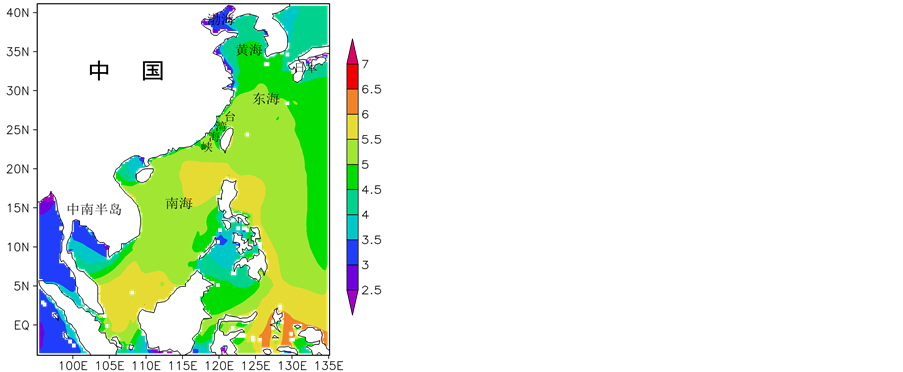 (b)
(b)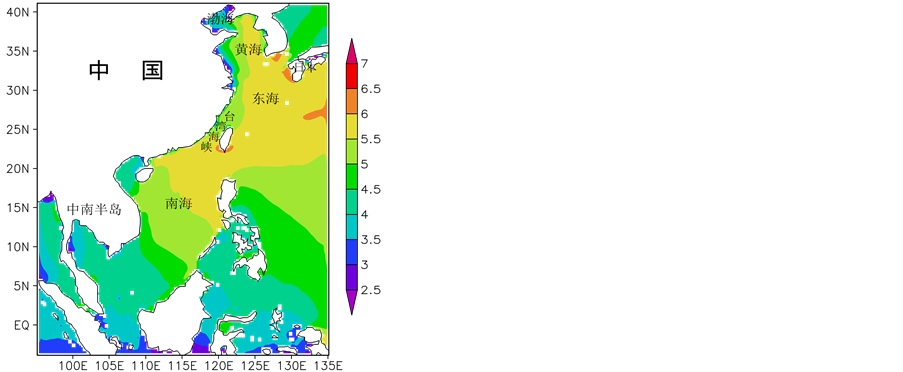 (c)
(c)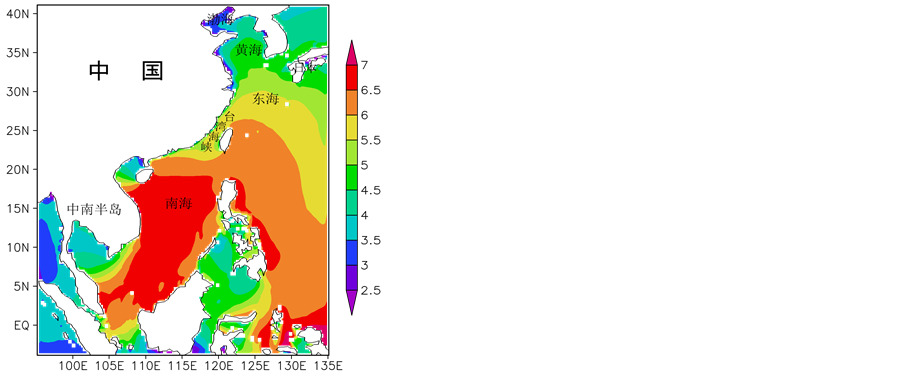 (d)
(d)
Figure 4. Wave period in January (a), April (b), July (c) and October (d) in the China Sea, unit: s
图4. (a)~(d):中国海1、4、7、10月海浪波周期的分布特征,单位:s
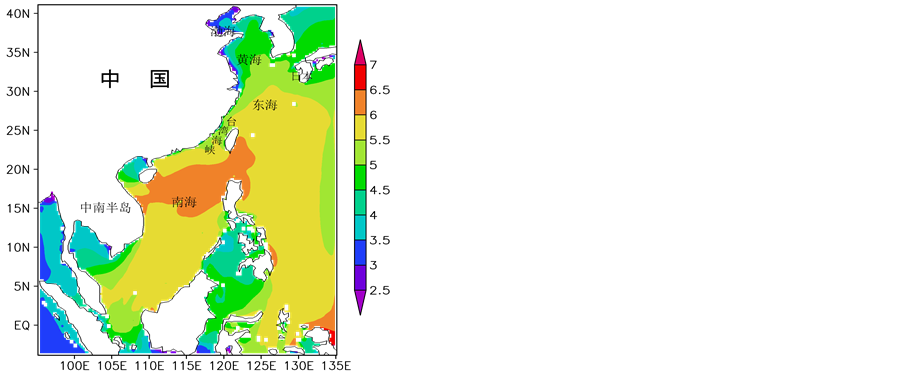
Figure 5. Annual average wave period in the China Sea, unit: s
图5. 中国海年平均波周期的分布特征,单位:s
4. 小结与讨论
本文以CCMP风场驱动目前国际先进的第三代海浪数值模式WW3,模拟得到首份覆盖整个中国海、长时间序列、高时空分辨率、高精度的海浪场数据,首次实现了中国海海浪波周期季节特征的精细化研究。结果表明:
1) 中国海的波周期在1月和10月整体大于4月和7月。渤海的波周期在各个季节都小于其余海域。1月、4月和10月,海浪波周期的大值区主要分布在25˚N以南,而7月波周期的大值区则明显北抬,主要分布于15˚N以北。
2) 从海浪波周期的年分布特征来看,南中国海大部分海域、东海大部分海域以及菲律宾以东近海的年平均波周期明显大于其余海域,基本在5.5 s以上,高值中心分布于南海北部海域,年平均波周期可达6.0 s以上。黄海大范围海域的波周期在4.0~5.0 s之间,渤海在4.0 s以内。北部湾和泰国湾的波周期在3.5~4.5 s之间。
3) 在季风期间(包含冬季风和夏季风),季风影响明显的区域波周期较小,而其余海域的波周期则偏高,这应该是由于季风影响区域的风浪成分更大,其余海域则涌浪成分更大,涌浪的波周期往往大于风浪的波周期。

NOTES
*通讯作者。