1. 引言
随着社会发展和人们生活水平的提高,高脂血症的发病与日俱增,血脂异常的流行已经成为21世纪全球性卫生问题一大挑战。我国监测数据显示,近50年来,我国不论在城市还是在农村,心脑血管疾病的发病率和死亡率均呈上升的趋势,占总死亡人数的45%左右,而死亡人数中至少一半同高脂血症有关[1] 。有研究已经证实高脂血症是心脑血管疾病的重要危险因素之一[2] 。我国大量流行病学研究表明,除了血脂异常增加冠心病发病的作用强度与西方人群相同外,我国人群特有的高总胆固醇水平还增加了缺血性脑卒中的发病风险[3] 。脑卒中死亡率在农村地区已超过城市[4] 。因此,加强我国农村居民高脂血症防控刻不容缓。
一些膳食因素与高脂血症密切相关,如油脂类摄入与高脂血症患病呈正相关。随着我国经济和社会的高速发展,居民的生活水平得到了极大的改善,人们的生活方式、饮食习惯都发生了很大的改变。不合理的膳食不仅是心脑血管疾病发病的重要危险因素,在延缓疾病进展和促进康复中也起到重要作用[5] 。云南作为一个少数民族聚居地省份,又是国家烟草的主要生产和消费地,喜好吸烟和饮酒等生活习惯都增加了患心脑血管疾病的危险性;同时易门县地处云南省中西部,山川秀美,物产丰富,68.5%的森林覆盖率为易门带来了丰富的野生菌资源,有“中国野生菌之乡”之称,为省烤烟、野生菌和豆鼓产品加工基地县,当地居民喜好吃油炸蘑菇和农家特色油炸豆鼓等食品,心脑血管疾病已经成为当地居民健康的主要疾病。本研究拟对当地农村居民的高脂血症现状进行调查,分析当地村民饮食习惯和高脂血症之间的关系,探求当地居民高脂血症膳食危险因素,为高脂血症防治提供科学依据。
2. 对象与方法
2.1. 对象
以云南省易门县18周岁以上常住人口为研究对象,采用多阶段随机抽样的方法随机抽取易门县的2个乡镇,从每个乡镇中随机抽取2~3个行政村,再从选取的行政村中随机抽取18周岁以上的常住人口进行调查。样本含量的计算公式: (N为调查例数,其中Zα为显著检验的的统计量,α = 0.05时
(N为调查例数,其中Zα为显著检验的的统计量,α = 0.05时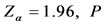 为预期的现患率,
为预期的现患率, )。
)。
2.2. 方法
2.2.1. 研究对象抽样
采用多阶段随机抽样的方法:第一阶段,将易门四乡三镇分为7个一级抽样单位,从中随机抽选2个一级抽样单位(龙泉镇和浦贝乡)入样;第二阶段,将易门龙泉镇和浦贝乡2个一级抽样单位分为18个二级抽样单位(行政村),从每个一级抽样单位随机分别抽取2~3个二级抽样单位(行政村)入样;第三阶段,从抽取的4~6个二级抽样单位(行政村)中共随机抽取615名18周岁以上常住居民为研究对象。
2.2.2. 问卷调查
采用询问法进行调查,调查员经统一培训。调查内容包括一般情况和食物频率两部分。一般情况包括年龄、高脂血症病史和父母高脂血症病史等。食物频率回顾问卷询问调查对象过去1年内油脂类、谷类、薯类、畜禽肉类、鱼虾类、奶类、豆类及制品、蛋类、坚果、蔬菜、水果等16大类85种食物的食用频率及每次食用量。
计算基本公式为:食物摄入量(g/日) = [摄入量(g)/次 × 摄入频率(次)/年]/365 d根据每个调查对象平均每日摄入各类食物的量,然后计算出平均每标准人每日摄入各类食物的量,按照中国疾病预防控制中心营养与食品安全所《中国食物成分表》[6] 计算每标准人日能量和营养素,依据中国营养学会2002年出版的《中国居民膳食营养素参考摄入量(RNls)》[7] 进行评价。
2.2.3. 实验室血脂测定
采取村民清晨空腹静脉血。血清TC测定:COD-CE-PAP法,TC试剂盒(批号:0211011);血清TG测定:GPO-PAP法,TG试剂盒(批号:0311021);血清HDL-C测定:直接法,HDL-C试剂盒(批号:0311021);血清LDL-C测定:直接法,LDL-C试剂盒(批号:CH0101102);生化复合校准品(批号:1210131);生化质控物(批号:0111011)。用BECKMAN COULTER AU480全自动生化分析仪(美国贝克曼库尔克公司)进行测定。
血脂异常纳入标准[8] :血清胆固醇(TC) ≥ 5.70 mmol/L和/或甘油三脂(TG) ≥ 1.70 mmol/L和/或高密度脂蛋白(HDL-C) < 1.04 mmol/L和/或低密度脂蛋白(LDL-C) > 3.37 mmol/L。
2.3. 数据处理
用Epidata3.1软件建立数据库,所有调查表经过严格复核后,采用双录入的方法录入数据。以统计分析软件SPSS 17.0进行数据分析,各因素与高脂血症关系采用非条件多因素Logistic回归进行分析。
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 一般膳食摄入情况
把膳食调查中易门农村居民主要食物消费的85种食物归为16类,每类食物人均摄入量见表1所示,各类食物平均摄入量与2002年中国居民营养与健康状况调查报告 [9] 中的数据相比,谷类、畜禽肉类、油脂类、奶类、蔬菜和水果的摄入高于全国农村人均和全国人均水平,但薯类、豆类及制品的摄入量均低于全国农村人均和全国人均水平,蛋类的摄入量低于全国人均水平;易门县农村居民的膳食结构中主要是以谷类为主,其次是蔬菜,再者是水果、畜禽肉等,与《中国居民膳食指南和平衡膳食宝塔》比较,其中畜禽肉和油脂类的摄入量超过参考摄入量;薯类、豆类及制品、奶类、蛋类、鱼虾类和蔬菜类食物摄入量欠缺,谷类和水果的摄入量与参考摄入量接近。总体而言易门农村居民膳食结构欠平衡,可能与

Table 1. The average intake of dietary of the surveyed population (g/standard man/d)
表1. 调查人群的膳食平均摄入量(g/标准人/日)
注:a易门人均与全国农村人均水平的比较,P < 0.05;b易门人均与全国人均水平的比较,P < 0.05。
该地独特的饮食习惯有关。
3.2. 高脂血症患病情况
经实验室测定,调查的615名村民中有479人血脂异常,患病率为77.9%,其中,男性有244人,患病率为85.3%;女性有235人,患病率为71.4%,见下表2。经x2检验得出,男女间的高脂血症患病率之间的差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001),表现为男性高脂血症患病率高于女性。不同年龄组间的高脂血症患病率差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。
3.3. 主要非膳食因素与高血脂的关系
采用逐步回归(前进法)分析了几类与高脂血症有显著关联的非膳食因素,最终进入方程的变量有:性别、年龄、婚姻状况和饮酒4个变量(表3)。在后面的分析中以此模型为基础来研究膳食因素与高脂血症发病的关系。
由表3可知,男性患高脂血症的风险高于女性,其危险度是女性的2.40倍,饮酒与高脂血症呈正相关,年龄及婚姻状况与患高脂血症无关联。
3.4.主要膳食种类与高血脂的关系
将多因素分析有显著关联的各膳食种类代入控制了性别、年龄、婚姻状况和饮酒的Logistic回归模型,进行逐步分析(前进法),以观察控制了主要非膳食因素后膳食种类与高脂血症的关系。
由表4可知,最终进入方程的影响高脂血症的主要膳食因素变量(P < 0.05)为:薯类、豆类及制品、鱼虾类和油脂类摄入量4个变量,其中薯类、豆类及制品和鱼虾类食物与高脂血症患病呈负相关,油脂

Table 2. The prevalence of the subjects with hyperlipoidemia
表2. 调查人群高血脂症患病率情况

Table 3. The non-dietary factors logistic regression analysis of hyperlipoidemia in rural residents in Yimen County
表3. 易门县农村居民高脂血症非膳食因素logistic回归分析

Table 4. The dietary factors logistic regression analysis of hyperlipoidemia in rural residents in Yimen County
表4. 易门县农村居民高脂血症的膳食影响因素logistic回归分析
类与高脂血症患病呈正相关。
4. 结论
本研究结果显示,云南省易门县农村居民的膳食摄入存在膳食结构不合理问题,离健康饮食的标准还有很大差距,油脂类摄入量与高脂血症患病呈正相关,这与本地居民喜好吃油炸蘑菇和农家特色油炸豆鼓等食品有关,因此指导村民合理膳食对于预防和控制高脂血症具有重要意义。
5. 讨论
本次调查结果显示,云南省易门县农村居民高脂血症发生率为77.9%,高于云南省农村居民的高脂血症患病率(14.6%) [10] ,也高于全国高脂血症患病率(18.6%)。易门县农村居民高脂血症患病率均高于全国成人水平和云南省成人水平,究其原因由于社会的发展,人们物质生活水平的提高,饮食结构和生活节奏发生了巨大变化,当地许多人认为生活水平提高了,在日常饮食中逐步加大了肉类、动物油等食物的比重,以为这样会让身体吸收更多的营养、更健康。殊不知,长期大量食用此类食物,会导致体内高胆固醇和甘油三酯含量升高,形成高脂血症,为冠心病和动脉粥样硬化等心脑血管疾病埋下了隐患。因此,针对易门县农村居民膳食存在的问题,当地卫生部门应对本地居民进行有针对性的健康教育活动,使居民充分认识到高脂血症引起心脑血管疾病的发展态势及不合理膳食对人体危害性的重视,引导居民对膳食结构进行调整,逐步改变以动物性食物为主的膳食结构,调整为以植物性食物为主的传统型膳食结构,增加蔬菜、水果、薯类、豆类及制品和鱼虾类食物摄入,降低油脂摄入,提高膳食质量,参加适当的体力活动和体育锻炼、保持健康的心理状态等,同时引导当地居民摒弃吸烟和饮酒等不良生活习惯和行为方式,对心脑血管疾病积极开展“早发现、早诊断、早治疗”的防治工作;除此之外,政府应加大对技术革新的扶持力度,改变本地企业蘑菇和农家豆鼓等食物的加工方式,以控制高脂血症引起的心脑血管疾病发病率,保障农村居民的健康。最终在日常生活中,使易门本地农村居民养成良好的饮食习惯,控制高脂肪、高胆固醇食物的摄入量,从而达到降低心脑血管疾病发病率和死亡率的目的。
基金项目
国家自然基金(31260372)。