1. 引言
黄萎病[1] -[3] 是危害较为严重的维管束病害,其病原菌主要为大丽轮枝菌和黑白轮枝菌。它会对棉花、西红柿、茶叶等多种植物造成不可治愈的伤害,严重影响产量。在植株本身的免疫系统中,当黄萎病病菌的致病基因作用时,特定的植株抗病基因被激活,发挥免疫功能。双方进行作用的对应基因为关联的互作基因对,下文简称为“互作基因”。
目前,较为成熟的基因功能检测技术有基因敲除[4] 、基因转导技术[5] 、基因芯片[6] 等。但这些技术都存在着技术成本昂贵、复杂、重复性差、分析泛围较狭窄等问题。而新兴的生物信息学[7] 能够有效地解决成本昂贵、分析范围狭窄等问题。因此文中使用生物信息技术求取黄萎病的互作基因。
为了根据已知的标记基因对得到更多标记对,本文使用半监督学习对数据集进行挖掘。由于已知的黄萎病抗病基因对数量较少,因此需要先使用典型相关分析增加数据的相关性,即使用典型相关分析和半监督学习在已知非常少量黄萎病互作基因的基础上求解准确率较高的可能互作基因[8] 。
2. 研究方法
2.1. 方法原理简介
在这次研究中,采用典型相关分析法 [9] 对数据进行处理,使具有关联作用的互作基因的相关系数更高,进一步使用半监督学习 [10] 挖掘可能的互作基因。其中:
典型相关分析基本原理是:为了从总体上把握两组变量: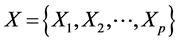 和
和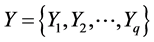 之间的相关关系,分别在两组变量中提取有代表性的两个综合变量
之间的相关关系,分别在两组变量中提取有代表性的两个综合变量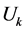 和
和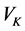 (分别为两个变量组中各变量的线性组合),在X,Y两组变量中,分别构建若干有代表性的变量组成有代表性的综合变量,通过研究这两组综合变量之间的相关关系,来代替这两组变量间的相关关系,这些综合指标称为典型变量,利用这两个综合变量之间的相关关系来反映两组指标之间的整体相关性。
(分别为两个变量组中各变量的线性组合),在X,Y两组变量中,分别构建若干有代表性的变量组成有代表性的综合变量,通过研究这两组综合变量之间的相关关系,来代替这两组变量间的相关关系,这些综合指标称为典型变量,利用这两个综合变量之间的相关关系来反映两组指标之间的整体相关性。
具体的求解过程不在这里赘述,有兴趣的可以参考文献8,实验需要的是在保证变量U,V的相关系数最大,即
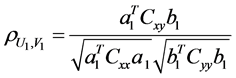 (1)
(1)
最大的前提下,得到典型系数a、b、特征系数λ。
半监督学习是机器学习的一中,在机器学习中,如果只使用有监督学习只关注少量的已标记数据,那么得到的学习模型不具有很好的泛化能力,同时会造成大量未标记数据样本的浪费。如果只使用无监督学习只关注大量的为标记数据,那么会忽略极具有价值已标记数据。因此,研究如何综合利用少量已标记数据和大量为标记数据来提高学习性能的半监督学习称为当前机器学习和模式识别的重要研究领域之一。这种学习方法符合现有大多数需要机器学习的情况。
2.2. 研究流程
文中根据主要的工作原理,制定了具体的研究方法,其具体流程如下所示:
1) 使用BLAST (Basic Logical Alignment Search Tool) [11] ,对采集自生物数据库的DNA,蛋白质等序列进行对比,得到序列相似性参数。
2) 对数据进行离群处理、标准化后作为两组变量X,Y的初始值。
3) 为了扩大变量间的相关性,增大准确率,使用典型相关分析对变量X,Y进行初始标记,简述过程如下:
进行典型相关分析,得到参数a、b、λ,假设有m个不同的特征值,那么存在m个映射,有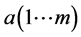 ,
,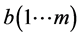 ,
,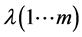 。
。
如图1中, 可以看作是已标记的一组数据对其他数据如
可以看作是已标记的一组数据对其他数据如 进行标记。首先,使用公式2分别计算各基因的相似值,
进行标记。首先,使用公式2分别计算各基因的相似值,
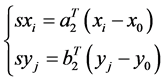 (2)
(2)
然后使用公式3计算基因对的相似度。
 (3)
(3)
得到置信度 ,若置信度极高,可进行标记。
,若置信度极高,可进行标记。
得到置信度的结果如图2所示,其中左图表示每个基因对所对应的置信度,右图显示所有置信度值得分布区域,从中可以发现存在置信度非常高的少量基因对,它们可以作为初始标记的首选。大多数基因对的置信度在0.35~0.5之间,这些基因对具有一定的联系,但相关性不足以标记为关联基因对。
之后取值最大的r个基因对标记为1,得到r + 1个已标记数据,有效地扩大了已标记数据的个数。分别设置r为100、500、1000、5000,比较不同的置信度对结果的影响。
4) 对扩展后的数据进行半监督学习,过程如下:
选择半监督算法,基于此次数据的特性,选择的是基于流型假设,够降维的半监督算法,这次实验使用的算法为Laplacian [12] 算法,对数据进行降维,然后生成拉普拉斯图,得到每个点的邻居。对每个点的邻居进行分析,使用K近邻算法[13] 对未标记数据进行标记。得到所有正例,即标记出的互作基因。
3. 实验
3.1. 简介
实验采用的数据有两大集合,集合一为植物抗病基因集合包括265个数据,集合二是黄萎病致病基因集合包括65个数据。它采自主要源于生物数据库NCBI、PDB及其关联数据库。在已知的少量基因对中,选取互作基因对(gi|283764861 [14] , gi|375968911 [15] )为标记基因,使用文中提出的方法对其他基因
对进行标记,即对基因对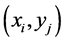 (其中,i = 1···265,j = 1···65,即共有265 × 65 = 17,225个基因对),通过实验标记其是否为互作基因。并通过比较预测的基因对已知的基因对的覆盖率检验方法的正确性,并得到最佳实验方案。
(其中,i = 1···265,j = 1···65,即共有265 × 65 = 17,225个基因对),通过实验标记其是否为互作基因。并通过比较预测的基因对已知的基因对的覆盖率检验方法的正确性,并得到最佳实验方案。
3.2. 实验结果
采取文中2.2节所描述的方案对实验数据进行互作基因的预测,其中,第三步初始标记后得到的标记结果如图3所示,图中r表示初始标记的个数。
第四步进行最终标记得到的互作基因结果图如图4所示,图中的四个子图分别对应图3中的进行r个初始标记后进行最终半监督学习得到的结果。
3.3. 结果分析
由上节的结果图可知:数据具有聚集性,即某些行或某些列数据密集,这样的基因具有普遍关联性,在抗病过程中起重要作用,如植物基因数据集中的第27个基因gi|214011438 [16] 、病菌中的第1个基因gi|333352894等基因具有普遍关联性。结果与现有研究符合,应该加大对它们的研究力度。
此外,数据具有独立性,即某些数据在其所在行列中只有自身,这种数据表示这对基因有一对一的关系,如基因对(gi|510708 complete genome111 [17] , VDAG_05753T0),具有其独特的功能。
对标记的结果进行统计分析,比较各种标记分案下最终结果对已知的少量基因对的覆盖率,结果如表1所示。

Table 1. The coverage rate of result
表1. 结果覆盖率
由覆盖率结果可知,使用文中的方法预测黄萎病抗病基因对是可行的,预测结果覆盖已知的基因对的准确率较高,预测出的互作基因结果具有很高的研究参考价值。
综上可知,使用CAA + SSL的半监督学习方法可以在已知十分少量的互作基因对的情况下,以较高的准确率预测更多的基因对数据,挖掘结果具有可参考性。
4. 结束语
通过实验可以得到高准确率的基因对,为生物实验指明方向,减小研究的范围,有利于提高研究速度,早日攻克黄萎病。此外,此论文所使用的方法同样适用于其他在已知极少量标记数据的基础上求解其他基因对的情况。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金61203265,河南省重点项目122102110106。