1. 引言
粉尘爆炸研究及事故预防是过程工业面临的重大课题之一,深入认识粉尘爆炸行为、准确预测爆炸特性参数对于粉尘爆炸的防控至关重要[1] 。目前,大多数粉尘爆炸特性研究主要依托于Siwek 20 L和ISO 1 m3球形装置,研究内容主要集中于不同条件下的粉尘爆炸敏感度(爆炸下限浓度、极限氧浓度等)和猛烈度参数(最大爆炸压力、最大压力上升速率及燃烧持续时间等) [2] -[7] ,而对粉尘云形成过程的研究相对较少。因此,当前实验研究结果大多以名义粉尘浓度(即分散粉尘质量除以球体固定容积)为基础展开讨论,即通常假设测试装置内粉尘云分散完全均匀、整个球体内无沉降现象和局部浓度差异[1] [8] [9] ;考虑到粉尘云均匀性很大程度上会影响粉尘云的实际浓度,因此,该假设造成的误差在一定程度上会影响测试参数的准确性,尤其是爆炸下限[9] 。此外,研究还表明,标准测试条件并不能系统地测定最具代表性或者最安全的爆炸特性参数,例如,Siwek 20 L球内60 ms的标准点火延迟时间对大多数粉尘(尤其是纳米粉尘)并不适合[10] [11] 。因此,评估点火时刻粉尘云的分散效率对深入认识粉尘爆炸行为及完善粉尘爆炸测试标准意义重大。
先前研究通常采用PRL (Pittsburgh Research Laboratory)光学粉尘探针[12] [13] 考察实验装置内粉尘云的分散效率,其主要通过检测入射光线的衰减程度以定义实际粉尘云浓度。Hertzberg [14] 和Cashdollar [15] 使用该方法分别考察了8 L、PRL 20 L和Fike 1 m3爆炸装置内粉尘云分散均匀性。Kalejaiye [9] 系统深入地考察了Siwek 20 L爆炸球内粉尘分散效率,并与PRL 20 L和Fike 1 m3爆炸装置内测得结果进行了对比,正如Bourgue定律[16] 所预测的,实验透光率在半对数坐标下都表现出线性下降的规律,但其透光率–时间曲线并未能如实反映粉尘云的沉降过程,且该方法只能在装置内进行定点测量,无法识别粉尘云的运动过程,具有一定的局限性。此外,对Siwek 20 L球内粉尘云形成过程的3D CFD模拟结果[17] [18] 也表明,由于分散过程中存在大量湍流涡结构,装置内粉尘云分散并不均匀。该结果有助于全面理解粉尘云形成过程。然而,由于数值模拟结果的准确性很大程度上取决于边界条件的设置,模型的验证需要可靠的实验数据。
基于以上背景,本文建立了喷粉过程可视化实验装置,以镁粉为实验介质对Siwek 20 L爆炸测试装置内的喷粉过程进行了实验研究,利用高速摄像技术对粉尘云形成过程进行实时记录,同时基于图像处理技术和灰度图像序列获得透光率–时间曲线,继而对粉尘云形成过程中实际粉尘云浓度变化进行分析,研究表明本方法透光率的变化过程与粉尘实际浓度变化具有一致性,从而为标准测试装置内粉尘云形成过程的研究提供新的手段。
2. 可视化实验装置及原理
2.1. 可视化测试装置
Siwek 20 L球形爆炸测试系统是国际标准ISO 6184-1、欧盟标准EN 14034、美国材料试验学会标准ASTME1226和中国标准GB/T 16425共同推荐的用于测试粉尘爆炸特性的标准装置。实验过程中通常采用高压空气射流形成悬浮粉尘云。为深入了解粉尘云形成过程及其分布均匀性,本文建立了Siwek 20 L可视化装置,即将装置原有不锈钢球体替换为透明的耐压有机玻璃球。需要指出的是,Siwek 20 L可视化装置未安装点火系统,以便于观察粉尘云的形成过程,其装置实物图见图1。
该测试系统包括可视化Siwek 20 L装置、控制系统和高速摄像系统三部分,其结构简图如图2所示。装置本体为20 L耐压透明有机玻璃球,分为上下两个半球,通过密封环密封便于拆卸清洗。球体底部通过机械两相阀与容积为0.6 L的储粉罐相连。控制系统用于控制储粉罐进气、喷粉、高速摄像机采样等一系列动作的自动化运行。高速摄像系统则由高速摄像机和光源系统组成,分别位于球体赤道面两侧,高速摄像机的采样速率为400 fps,图片分辨率为1280 × 1024像素,记录范围包含整个有机玻璃球。
实验采用标准燕尾槽分布器并按照标准粉尘分散程序执行。实验时,球体预先抽真空至−0.06 MPa,并将预称质量的镁粉装入储粉罐内;打开光源和高速摄像机等待采样;随后,运行自动控制系统,高速摄像机和粉尘分散系统同时被触发,储粉罐被加压至2.00 MPa后,气动机械两向阀迅速开启,粉尘试样在高压气体的驱动下经两相阀快速分散至球体内形成常压粉尘云,气–粉两相流的发展过程则由高速摄像机实时同步记录。值得注意的是,为消除日光对实验结果的影响,整个实验过程均在暗室环境下进行。

Figure 1. The transparent Siwek 20 L test chamber
图1. Siwek 20 L可视化装置实物图

Figure 2. Schematic diagram of the visualization experimental system
图2. 可视化冷态测试系统简图
2.2. 图像处理
2.2.1. 透光率与粉尘浓度的关系
本文的可视化测量方法主要基于光强衰减原理对粉尘云浓度变化进行检测,当一定波长的平行光束穿过粉尘云时,入射光线会因粉尘颗粒对光的散射和吸收作用发生衰减,且粉尘云浓度越高,入射光线衰减越严重。因此,透过粉尘云的入射光分率(简称“透光率”,T)可以用于测定粉尘云浓度(c) [9] [15] 。透光率与粉尘云浓度间的关系由Bouguer定律 [16] 给出,其表达式如下:
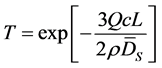 (1)
(1)
其中,Q为消光系数或效率[-],c为通过光束路径的平均粉尘浓度[g/m3],L为固定光程长度[m],ρ为粉尘颗粒密度[g/cm3],Ds为颗粒表面平均直径[μm]。消光系数Q是无量纲参数,包含由散射和吸收引起的光损失。方程式(1)表明,透光率大小取决于粉尘浓度和颗粒粒径。对于粉尘分散过程,其局部浓度与透光率的关系可表述为如下形式:
 (2)
(2)
由此可知,c与lnT呈正比关系,且透光率越高,粉尘浓度越低。
基于上述理论,PRL光学粉尘探针已广泛应用于粉尘爆炸测试装置,成为测量粉尘均匀性的主要手段。然而,该方法只能在装置内进行定点测量,且无法识别粉尘云的运动过程,具有一定的局限性。为此,本文建立了喷粉过程的可视化装置,整个球体内粉尘云的形成及发展过程由高速摄像系统进行实时记录,并通过图像处理技术对图像灰度和透光率进行了关联。
2.2.2. 图像灰度与透光率
灰度(Grayscale)是指黑白图像中点的明暗程度,通常用百分比表示,范围一般从0% (纯白)到100% (纯黑),故黑白图像也称灰度图像。数字图像由像素矩阵组成,其数据阵列记录了图像中每一点的像素值,对于灰度图像而言,图像数据则代表各点的颜色强度值。图3为高速摄像机记录的粉尘云分散过程的帧图片,经过像素矩阵提取后,可以得到灰度值的像素矩阵。

Figure 3. The designated calculation area selected in the present paper
图3. 像素矩阵的提取与计算区域选取
本文采用的可视化实验系统的工作原理与光学粉尘探针类似,粉尘颗粒的存在会吸收和散射入射光,高速摄像机镜头接收入射光强度的减弱,导致其采样图像灰度的增加。图像灰度值与透光率之间的对应关系如图4所示。且满足下述关系:
 (3)
(3)
其边界条件为:
c = 0时,T = 100%,G = 0%
 时,T = 0%,G = 100%
时,T = 0%,G = 100%
喷粉过程开始前,由于装置内无粉尘颗粒存在,入射光源未被散射或吸收,因而能够完全被相机镜头接收,即透光率值为100%,此外,由于入射光线未被遮挡,图像亮度达到最大值,即采样图像灰度值为最小值0% (纯白)。正如前文所述,粉尘云浓度的增加通常会降低入射光线的透光率、增加采样图像的灰度值,因此,当粉尘云浓度足够高时,入射光线无法透过粉尘云抵达相机镜头,采样图像的灰度值达到最大(100%,纯黑),相应地,其透光率也达到0%。
因此,对于图4所示的像素矩阵,其平均透光率可通过下式计算:
算术平均值:
 (4)
(4)
均方根值:
 (5)
(5)
其中,m和n分别为像素矩阵中像素点的行、列数。
3. 图像采集与处理
3.1. 粉尘云形成过程可视化描述
基于上述可视化Siwek 20 L测试系统,镁粉粉尘云的运动过程和均匀性可由高速摄像系统同时记录。实验样品选用市售雾化球形金属镁粉,纯度为99.9%,其粒径分布由带数字图像化技术的Leitz金相显微镜测得,结果由表1给出。图5给出了浓度为500 g/m3的镁粉分散状态随时间变化的灰度图像。其中,镁粉粉尘云随空气射流流动的方向由虚线箭头表示。

Figure 4. The corresponding relation between transmission data and grayscale value
图4. 透光率与图像灰度值之间的相关性

Figure 5. Selected frames of dust dispersion process for magnesium dust with nominal concentration of 500 g/m3
图5. 镁粉分散状态随时间变化的序列灰度图像(C = 500 g/m3)

Table 1. The particle size distribution of tested magnesium dust
表1. 实验镁粉的粒径分布
结果表明,Siwek 20 L装置内镁粉分散过程中粉尘云湍动剧烈、流动复杂且均匀性较差。从图中可以看出,镁粉粉尘云大多以块状粉尘颗粒束组成。分散初期粉尘云浓度随粉尘颗粒的持续注入而迅速增加,大量粉尘颗粒在高速气流作用下沿球壁面快速汇聚于顶部,气流的对冲作用致使颗粒束向分布器垂直方向运动并沿壁面下落,粉尘云在球体内形成涡流。然而,由于后续喷射气流速度减弱,扬尘诱导湍流强度逐渐衰减,尤其是在两向阀关闭之后(t = 60 ms),粉尘云中部分颗粒逐渐开始沉降,粉尘云浓度逐渐下降。
此外,值得指出的是在150~300 ms范围内,粉尘云浓度显著增加且更加均匀,这主要是由于喷粉结束后大颗粒逐渐沉降,粉尘云中颗粒分布大多为分散性较好的细颗粒部分,其在回旋气流作用下由底部运动至中间区域形成了较为均匀的粉尘云。然而由于湍流的严重衰减,其浓度随后迅速下降。
3.2. 喷粉过程中粉尘云浓度变化规律
3.2.1. 典型的透光率–时间曲线
选取镁粉试样在质量浓度500 g/m3下的连续高速记录图像进行分析,图6给出了选定像素矩阵(50 × 50像素,见图3)的平均透光率随扬尘时间的变化规律。由图可知,采用算术平均值和均方根值计算的透光率结果差异较小,透光率T随扬尘时间的增加,由其初始值100%迅速下降达到最小值并在40~70 ms内保持相对稳定但随时间波动剧烈;此后,随着扬尘时间的进一步增加,透光率则逐渐增加。
3.2.2. 粉尘云实际浓度变化
根据Bougure定律 [9] 可知,粉尘云浓度与透光率成正比关系,其变化规律具有一致性,即透光率越低,粉尘云浓度越高。因此,图6中给出的透光率–时间曲线同时也反映了粉尘云实际浓度随时间的变化关系。由图可知,粉尘云浓度在0~40 ms内迅速增加,并在40~70 ms内保持相对稳定,当扬尘时间大于100 ms时,粉尘云浓度衰减较为显著。
究其原因,在扬尘过程开始前(t < 0 ms),装置内无粉尘颗粒存在,入射光线因未被吸收或散射而不发生衰减,整个采样区域的透光率值恒定为100%。扬尘过程开始后,透光率在0~40 ms内的迅速下降主要归因于粉尘颗粒的不断增加,大量粉尘颗粒在高压气流的作用下持续注入球体内部,粉尘浓度的不断增加大削弱了入射光线的透过性,其强度的大幅衰减致使采样图像的灰度显著增加,因此透光率迅速下降;40 ms以后扬尘过程基本完成,由于湍流强度较高以及大量粉尘颗粒的持续喷射,粉尘云达到相对稳定的高浓度悬浮状态,因此透光率在40~70 ms内达到最小值并保持相对恒定;当扬尘时间超过70 ms后,由于玻璃球内湍流强度不断衰减,大量粉尘(尤其是大颗粒粉尘)在自身重力作用下不断沉降,粉尘浓度持续降低,因而透光率呈现出不断增加的趋势。
需要指出的是,透光率在0~7.5 ms内与其初始值保持一致并未发生明显衰减,这主要归因于实验用燕尾槽分布器的分散模式 [18] 。扬尘过程开始后,大量粉尘颗粒在高压气流的作用下高速撞击分布器上板面,经下板面反弹后沿壁面运动至球体顶部汇聚,最后分散至整个球体。而图中采样位置处于球心附近位置,在0~7.5 ms内颗粒并未运动至该位置,因此透光率并未出现衰减。
此外,图5中虚线给出了透光率随时间变化的趋势线,据此可以将喷粉过程划分为三个连续阶段:即粉尘颗粒快速喷射阶段、粉尘云稳定阶段和粉尘云沉降阶段。鉴于粉尘爆炸特性受粉尘云浓度影响显著,因此,较为准确的粉尘爆炸特性测试应在粉尘云稳定阶段进行点火。由此可知,Siwek 20 L装置设置的60 ms标准点火延迟时间是适合的。
3.3. 可视化方法与PRL光学粉尘探针法的对比分析
图7分别利用PRL光学粉尘探针法和喷粉过程可视化图像法测得的典型透光率–时间曲线。图7(a)为Kalejaiye et al. [9] 利用粉尘探针法测得的25 g/m3沥青粉的透光率–时间曲线,与可视化图像法测得结果(镁粉粉尘浓度200 g/m3,见图7(b))进行对比分析发现,在扬尘初期阶段,两种测量方法对粉尘云浓度

Figure 6. Typical transmission-time traces in the designated calculation area
图6. 透光率随时间的变化曲线

Figure 7. Comparative analysis of the transmission-time trace obtained from (a) the PRL optical dust probe and (b) the visualization methods
图7. PRL光学粉尘探针法(a)和喷粉过程可视化图像法(b)测得的透光率–时间曲线
增加而导致的透光率下降都表现出较高的灵敏性,虽然图像法获得的透光率–时间曲线与PRL光学粉尘探针法测得的曲线较为类似,但亦存在诸多不同点。
图7(a)中结果表明,采用PRL光学粉尘探针测得的透光率大约在10 ms处取得最小值,随后迅速增加并保持相对稳定,研究者将该尖峰归因于PRL光学粉尘探针视窗处高速喷射的初始块状粉尘簇 [9] ;值得注意的是,即使在较低粉尘浓度下(沥青粉尘,25 g/m3),透光率的最小值仍接近于0。
需要指出的是,扬尘过程超过30 ms后,各位置处的透光率值基本保持稳定。然而,考虑到适当的湍流强度是维持粉尘悬浮的必要条件,扬尘完成后粉尘云湍流强度随时间急剧衰减、颗粒不断沉降(尤其是大粒径颗粒),粉尘云浓度逐渐降低,继而反映为透光率的增加。因此,PRL光学粉尘探针法测得的透光率–时间曲线并不能完全真实反映喷粉过程中粉尘云浓度变化的实际过程,尤其是粉尘云沉降过程。
此外,粉尘云浓度是粉尘爆炸特性的重要影响因素之一 [6] [8] ,图7(b)表明粉尘云浓度在40~70 ms范围内达到其最大值,该结果说明国际标准ISO 6184-1、欧盟标准EN 14034、美国材料试验学会标准ASTME1226和中国标准GB/T 16425共同推荐的60 ms标准点火延迟时间具有合理性。因此,采用图像法对Siwek 20 L装置内粉尘云分散过程的表征结果优于PRL光学探针法的结果,能更准确反映出粉尘爆炸测试装置内粉尘云浓度的实际变化规律。
4. 结论
本文着重于开发表征粉尘分散过程的可视化研究方法。该方法旨在可视化Siwek 20 L测试系统基础上,利用高速摄像机全面记录粉尘爆炸装置内粉尘云的运动状态,并采用图像处理技术提取透光率–时间曲线,对分散过程中粉尘云浓度变化进行分析。研究为粉尘云均匀性分析提供了新的方法,为粉尘分散过程数值模拟提供了实验依据,对粉尘爆炸测试的标准化具有重要意义。
1) 基于可视化Siwek 20 L测试系统,可以直观地观察并记录粉尘云的形成过程(包括粉尘云的运动状态和时空均匀性)。
2) 对于金属镁粉,其分散过程中粉尘云湍动剧烈、流动复杂且均匀性较差。粉尘云分散后期阶段,由于湍流强度的急剧衰减,粉尘云沉降现象加剧。
3) 基于图像处理技术获得的透光率–时间曲线呈现出先迅速下降并趋稳,后逐渐上升的变化规律。粉尘云浓度越高,入射光线透过性越差,采样图像的灰度值越大,即粉尘云的透光率也越低。
4) 相较于PRL光学粉尘探针法,本文开发的图像法所获结果能更真实地反映粉尘云浓度的实际变化规律。