1. 引言
流动性风险对资产定价的作用是近年来学术界研究的重点。Chordia等人(2000, 2001) [1] [2] 首先提出股票的流动性风险应分为系统流动性风险和个股特质流动性风险,并且实证检验了系统流动性风险对个股特质流动性风险存在显著影响。后续文献研究对股票系统流动性风险进行了多种定义,且验证了系统流动性风险与股票收益率的正相关关系,见Jones (2002) [3] 、Pastor等(2003) [4] 和Bekaert等(2007) [5] 。Acharya和Pedersen (2005) [6] 则提出一个包含以下三项系统流动性风险的资产定价模型:个股收益率对市场流动性的敏感度、个股流动性对全市场流动性的敏感度、个股流动性对市场收益率的敏感度。他们发现个股收益率与个股非流动性、市场BETA和以上三个代表着系统流动性风险的敏感度因子均呈正相关。国内也有相关研究,宋逢明和谭慧(2005) [7] 采用2001至2003年间的A股数据实证研究,证明了我国的订单驱动型市场也像外国报价驱动型市场一样有着系统流动性风险。罗登跃等人(2005) [8] 和麦元勋(2006) [9] 利用Acharya和Pedersen (2005) [6] 提出的模型分析了中国市场,他们均发现我国市场存在系统性流动风险溢价,且溢价主要来源于个股收益率对市场流动性的敏感性和个股流动性对市场收益率的敏感性。尹海员和李忠民(2011) [10] 研究发现中国沪市系统流动性因素不能完全涵盖个股流动性水平,但未对个股特质流动性进行具体研究。
以上文献重点研究系统流动性风险在资产定价中的作用。传统观点认为通过充分分散投资个股特质流动性风险可以被完全对冲,因此不影响个股资产收益率及价格。虽然部分已有研究已经发现了系统流动性风险并不能涵盖所有个股流动性风险水平,但并未就个股特质流动性进行深入探讨。直到Brown等人(2010) [11] 特别关注了个股特质流动性风险的影响,研究发现投资者选择变现资产时会权衡当前的市场冲击强度和未来的不确定性,+依据所持有资产的特质流动性水平进行决策。风险厌恶的投资者为了避免不可预知的风险,首先选择卖出特质流动性风险高的股票并要求更高的收益率补偿。Akbas等人(2011) [12] 进而实证研究了特质流动性风险与资产收益率的关系,采用Amihud (2002) [13] 提出的个股“非流动性指标”,建立“市场模型”构造了特质流动性波动率指标,并利用美国AMEX和NYSE市场1964年至2010年的数据进行实证研究,结果表明美国市场的股票特质流动性风险在横截面上与收益率呈显著稳健的正相关关系。
前沿研究正在突破传统观点的局限,关注个股特质流动性风险这一影响资产定价和投资策略的重要因素。实际投资中,一方面由于个人投资者无法持有充分分散的资产组合,因而组合内的个股特质流动性风险难以完全对冲;另一方面即使是持有充分分散投资的机构投资者,例如共同基金经理人,也会因为突然的大量赎回而面临优先考虑流动性需求的投资决策。在短期市场急剧冲击和变现压力下,个股特质流动性及其风险对资产收益及投资策略的影响尤为凸显。
目前尚未见对中国市场的相关研究,因此本文借鉴最新成果实证研究中国A股市场的特质流动性风险水平及其在资产定价中的作用。本文采用Akbas等人(2011) [12] 的“市场模型”构造中国A股市场特质流动性波动率因子,考察在A股市场中该因子的独立性;并通过资产组合对比分析和Fama-Macbeth回归,研究股票特质流动性波动率在横截面上与收益率之间的关系。此外,现有文献仅限于在横截面上的相关关系研究,本文还将研究它们在时间序列上的关系,进一步考察特质流动性风险因子对资产定价的贡献。
2. 研究方法与数据来源
2.1. 指标定义与研究方法
首先定义个股流动性、个股特质流动性、以及特质流动性波动率风险指标。Amihud (2002) [13] 提出“非流动性”指标来衡量股票流动性,该指标为个股日收益率的绝对值与其日成交额的比值,表达式如下:
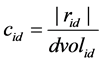 (1)
(1)
其中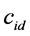 、
、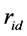 和
和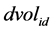 分别表示第
分别表示第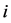 只股票在第
只股票在第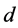 日的“非流动性”、日收益率(包括分红)和成交额。个股非流动性指标越小代表其流动性越高。
日的“非流动性”、日收益率(包括分红)和成交额。个股非流动性指标越小代表其流动性越高。
度量月度个股流动性时取月内个股所有交易日的非流动性指标做算术平均:
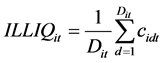 (2)
(2)
其中,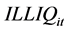 代表第
代表第 只股票第
只股票第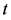 月的月度“非流动性”,
月的月度“非流动性”,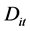 是第
是第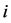 只股票第
只股票第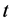 月的交易日总数。
月的交易日总数。
Akbas等人(2011) [12] 进而提出了流动性“市场模型”,该模型利用时间序列回归将个股日流动性分解为系统性流动性和特质流动性。其中,决定个股系统性流动性的是整个市场的流动性和超额收益,而不受这两个因素影响的残差项就是个股当日的特质流动性,模型如下:
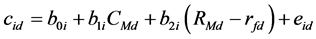 (3)
(3)
其中,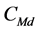 是
是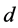 日市场所有股票的平均“非流动性”,
日市场所有股票的平均“非流动性”,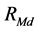 为当日市场收益率,
为当日市场收益率,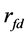 为市场无风险收益率,残差项
为市场无风险收益率,残差项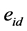 即为股票
即为股票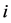 在第
在第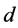 日的特质流动性水平。
日的特质流动性水平。
对日度特质流动性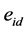 按照月度求标准差产生个股的月度特质流动性波动率。横向比较个股时发现流动性绝对值较大的股票更可能有较大的标准差,这样的波动率就不再是特质流动性简单的波动率,而是受到了流动性水平的影响。为了消除这一影响,我们借鉴变异系数的计算方法定义特质流动性波动率为特质流动性标准差除以个股月度流动性绝对值,具体方法如下,
按照月度求标准差产生个股的月度特质流动性波动率。横向比较个股时发现流动性绝对值较大的股票更可能有较大的标准差,这样的波动率就不再是特质流动性简单的波动率,而是受到了流动性水平的影响。为了消除这一影响,我们借鉴变异系数的计算方法定义特质流动性波动率为特质流动性标准差除以个股月度流动性绝对值,具体方法如下,
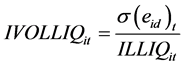 (4)
(4)
其中,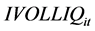 为第
为第 只股票第
只股票第 月的特质流动性波动率,作为个股特质流动性风险的代理变量。
月的特质流动性波动率,作为个股特质流动性风险的代理变量。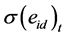 是月内日特质流动性的标准差。
是月内日特质流动性的标准差。
本文将采用以上指标,通过横截面和时间序列回归研究中国A股市场个股特质流动性风险对资产定价的作用。实证研究过程首先对中国A股市场相关变量进行描述性统计分析,充分观察中国股市的个股特质流动性风险特征。接下来检验不同特质流动性波动率水平的资产组合之间是否存在显著的收益率差异,并通过Fama-Macbeth截面回归检验特质流动性波动率在同一时期的横截面上与资产收益率的相关关系。最后应用时间序列回归分析,在经典Fama-French三因子模型中引入特质流动性风险因子构建调整四因子定价模型,并将回归参数结果与经典模型进行对比分析,考察个股特质流动性波动率对模型定价效率的改进作用。
2.2. 数据来源
本文选取2006年1月1日到
2013 年 12 月 31 日
上证A股和深证A股所有股票为研究样本。样本包含2597只股票96个月的交易数据,共计3,621,089个日观测值和166,882个月观测值。数据全部来自国泰安CSMAR数据库,其中股票收益率是考虑红利再投资的日收益率或月收益率,无风险收益率采用国债基准收益率,市场收益率采用考虑红利再投资的沪深300日收益率或月收益率。另外考虑到月内回归的准确性,剔除了月度交易日在10天及以下的股票。本文采用统计软件SAS 9.3进行数据处理和分析。
3. 描述性统计与变量相关性分析
3.1. 特质流动性波动率描述性统计
采用“市场模型”(3)式回归获取2597只A股股票的月度个股特质流动性波动率及其变化率,以便充分观察A股市场特质流动性特征,变量描述性统计见表1。
表1可见,特质流动性波动率的平均值0.64,t值577.84,样本股票特质流动性波动率显著不为零;峰度6.77,偏度1.66,说明其相对于正态分布而言更向均值集中且右偏。观察特质流动性波动率的变化率均值为0; 值为1.50,无法拒绝其均值为0的假设。这说明样本期的96个月内,特质流动性波动率围绕同一个均值运动,并没有发现波动率均值有显著变化趋势。
值为1.50,无法拒绝其均值为0的假设。这说明样本期的96个月内,特质流动性波动率围绕同一个均值运动,并没有发现波动率均值有显著变化趋势。
由于本文定义的特质流动性波动率来自于回归方程的残差项,如果系统流动性是个股流动性的唯一决定因素,本文所定义的特质流动性将成为一个完全随机的残差项,而其与资产定价的关系研究也将没有意义。为了排除这一可能,本文检验特质流动性波动率及其变化率的1到5阶自相关系数。表2结果可知特质流动性波动率有着较为显著的自相关,且自相关系数随着阶数增长而逐渐下降,这说明同一股票有着相对稳定的特质流动性波动率。而特质流动性波动率的变化率存在显著的一阶自相关,可见特质流动性波动率并非完全随机,而是反映股票流动性特质的变量。
3.2. 控制变量相关性分析
实证过程引入非流动性指标、规模因子、账面市值比、盈余价格比、换手率和动量因子作为控制变量和影响因子。描述性统计见表3,其中收益率是月度百分比增长率,平均值2.49%,这是由于沪深300指数自2006年1月4日的开盘价926.56点上涨到2013年12月30日的收盘价2299.46点,共上涨了149.01%。规模因子是将原始以亿元为单位的总市值数据进行对数化处理后的结果。

Table 1. Descriptive statistics of idiosyncratic volatility of liquidity
表1. 特质流动性波动率的统计性描述

Table 2. Self-correlation of idiosyncratic volatility of liquidity
表2. 特质流动性波动率自相关系数表
控制变量相关系数见表4。特质流动性波动率与其他控制变量的相关系数普遍较低,这说明本文所构造的特质流动性波动率是一个相对独立的因子,包含着其他因子所不能刻画的特征。而且非流动性指标与特质流动性波动率的相关性仅为−0.01 (Pearson)和−0.10 (Spearman),可见本文对特质流动性波动率的定义消除了个股流动性水平的影响。另外,非流动性指标与规模因子的相关系数为−0.57 (Pearson)和−0.65 (Spearman),具有非常显著的负相关性,符合规模越大的公司其流动性越好的假设。而与之相比,换手率和规模因子的相关系数只有0.14 (Pearson)和0.17 (Spearman),可见换手率不能完整表达流动性的特征,而非流动性指标作为流动性的代理变量则更为恰当。
4. 横截面分析
4.1. 资产组合分析
组合分析过程按月度特质流动性波动率从小到大对股票进行排序,采用等数量或等市值分组方法划定资产组合,考察平均收益率的组间差别。这一检验的思路是:如果特质流动性波动率在横截面内对资产收益率没有影响,则按特质流动性波动率分组的资产组合组间平均收益率应该不存在显著差别。反之,若组间存在显著的收益率差别,则可验证该变量对收益率存在影响。以下将分别通过单变量和双变量两种分组方式进行检验。
首先按特质流动性波动率单变量排序分为五组,考察各组加权平均超额收益率。结果如表5所示,特质流动性波动率大的资产组合具有更高的收益率。等数量分组中,特质流动性波动率最高与最低组别的月均收益率差为5.79%,t值为9.79,非常显著。等市值分组比较结果同样非常显著,且数据显示依照

Table 3. Descriptive statistics of control variables
表3. 控制变量的描述性统计表

Table 4. Pearson (left-down) and Spearman (right-up) correlations
表4. Pearson (左下半区)及Spearman (右上半区)相关系数表
等市值分组,第1组和第5组可构造一个零头寸投资组合,该组合的月均超额收益率套利空间为5.23%。我们还可以发现,相同特质流动性波动率的前提下按数量等分的组别和按市值等分的组别的收益率和包含的股票数量都很接近。这也符合前文特质流动性波动率与市值的相关性很小发现。因此,在接下来其他的分组方法中,我们没有继续采用等市值分组,而是仅费用等数量分组进行研究。
接下来在分别控制规模因子和账面市值比前提下,构建双变量交叉等数量分组考察其组间平均收益率差,结果见表6。两种分组比较结果显示,通过买入最高特质流动性波动率的资产的同时卖出最低特质流动性波动率的资产,投资者可以获得3.77%至7.14%,及3.00%至7.95%不等的月均超额收益率,而且这些超额收益的t值都较大,组间存在显著收益差。这说明在分别控制规模因子和账面市值比的前提下,特质流动性波动率依然与超额收益正相关。
进一步观察,随着规模因子增大同一特质流动性波动率水平组内收益率均呈现了先升后降的趋势,造成这种现象的直接原因可能是由于2006年到2013年期间上证综指经历了从1183点到6124点又下行至1664点的剧烈波动行情,具有高市值的权重股扮演着领涨或领跌的角色。而随着账面市值比增大,组间收益率差从7.95%单调下降到3.00%,可见账面市值比的提高降低了特质流动性波动率对收益率的影响作用。
4.2. Fama-Macbeth回归
以上资产组合比较分析已经显示了特质流动性波动率与分组收益率之间的显著正相关性,接下来检

Table 5. Portfolios based on single-variable
表5. 单变量投资组合统计表

Table 6. Portfolios based on double-variables
表6. 双变量交叉分组资产组合统计表
验特质流动性波动率与截面收益率之间的关系,采用Fama-Macbeth (简记为FM)截面回归模型:
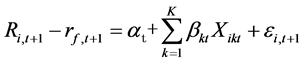 (5)
(5)
其中, 是第
是第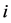 只股票第
只股票第 月的收益率,
月的收益率,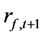 是第
是第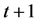 月的无风险收益率;
月的无风险收益率;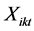 是第
是第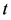 月第
月第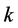 个影响因子指标;
个影响因子指标;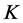 为影响因子总数;
为影响因子总数;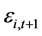 表示回归残差。
表示回归残差。
将特质流动性波动率、非流动性指标、换手率、规模、账面市值比、收益市值比及动量因子等影响因子分批加入FM模型回归,比较特质流动性波动率的系数及显著性变化,观察回归模型的平均调整 ,判断特质流动性波动率是否显著地影响股票横截面收益率。通过这一检验可分析特质流动性波动率与横截面收益率相关性的显著性和稳健性。回归结果见表7。
,判断特质流动性波动率是否显著地影响股票横截面收益率。通过这一检验可分析特质流动性波动率与横截面收益率相关性的显著性和稳健性。回归结果见表7。
表7中模型1是包含规模因子加账面市值比的经典因子模型,其回归调整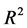 为0.041,模型2在此基础上添加了特质流动性波动率因子,其调整
为0.041,模型2在此基础上添加了特质流动性波动率因子,其调整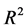 提高为0.085。模型3则考虑了6个经典控制变量,调整
提高为0.085。模型3则考虑了6个经典控制变量,调整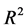 为0.129,模型4再次引入特质流动性波动率因子,调整
为0.129,模型4再次引入特质流动性波动率因子,调整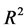 提高为0.164。以上两组比较可见,在添加了特质流动性波动率因子后,模型对横截面收益的解释力均有所提高,特质流动性波动率因子系数相对较高且显著。而添加该因子前后其他因子的系数及显著程度变化不大,说明新添加的因子与原有因子相关性不高,相对独立。结果显示特质流动性波动率因子包含着其他因子没有包含的定价信息,在横截面上对资产收益率具有一定的解释作用。
提高为0.164。以上两组比较可见,在添加了特质流动性波动率因子后,模型对横截面收益的解释力均有所提高,特质流动性波动率因子系数相对较高且显著。而添加该因子前后其他因子的系数及显著程度变化不大,说明新添加的因子与原有因子相关性不高,相对独立。结果显示特质流动性波动率因子包含着其他因子没有包含的定价信息,在横截面上对资产收益率具有一定的解释作用。
5. 时间序列回归
时间序列回归分析通过分别采用Fama-French (FF)经典三因子模型和引入了特质流动性风险因子的调整四因子模型回归,比较回归结果,考察热质流动性风险因子在资产定价中的作用。Fama-French经典三因子模型和加入特质流动性风险因子的调整四因子模型分别为:
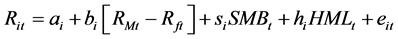 (6)
(6)
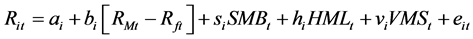 (7)
(7)
其中, 为第
为第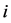 个资产组合在
个资产组合在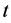 月的市值加权超额收益率,
月的市值加权超额收益率,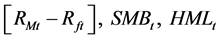 是Fama-French三因子模型所采用的市场超额收益率,公司规模因子和账面市值比因子。
是Fama-French三因子模型所采用的市场超额收益率,公司规模因子和账面市值比因子。

Table 7. Result of Fama-Macbeth regression
表7. Fama-Macbeth横截面回归结果
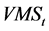 是本文构造的特质流动性风险因子,因子构造参照Carhart (1997) [14] 对动量因子的处理方法,具体如下。分月度将所有股票分别按照市值和特质流动性波动率排列分组,按市值50%-50%分为两组,同时按特质流动性波动率30%-40%-30%分为三组,交叉共6个资产组合。挑选大市值最高特质流动性波动率组、大市值最低特质流动性波动率组、小市值最高特质流动性波动率组合、和小市值最低特质流动性波动率组这四个组合,分别计算四个资产组合的市值加权平均收益率(记为
是本文构造的特质流动性风险因子,因子构造参照Carhart (1997) [14] 对动量因子的处理方法,具体如下。分月度将所有股票分别按照市值和特质流动性波动率排列分组,按市值50%-50%分为两组,同时按特质流动性波动率30%-40%-30%分为三组,交叉共6个资产组合。挑选大市值最高特质流动性波动率组、大市值最低特质流动性波动率组、小市值最高特质流动性波动率组合、和小市值最低特质流动性波动率组这四个组合,分别计算四个资产组合的市值加权平均收益率(记为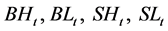 )。定义第
)。定义第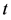 月特质流动性风险因子
月特质流动性风险因子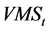 为:
为:
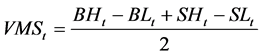 (8)
(8)
回归过程将样本数据根据市值和账面市值比交叉等分25组,分别应用上述三因子和四因子模型进行回归,并对回归结果进行以下两个方面比较分析。一方面比较两个模型的组内回归截距,截距项代表不能用模型中的风险因子解释的收益率,截距项越接近于零则模型的解释力越强。如果特质流动性风险因子能够改善模型定价效率,则调整四因子模型截距项无法拒绝其为零的个数应该有所增多,否则则不能显示新引入的风险因子的作用。另一方面比较CAPM、FF三因子模型、调整四因子模型回归的组间平均截距和平均调整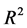 ,从整体分析特质流动性风险因子对模型定价效率的改进作用。
,从整体分析特质流动性风险因子对模型定价效率的改进作用。
比较表8和表9,FF三因子模型和调整四因子模型分组回归截距可见,置信度90%时,三因子回归结果有5个截距项无法拒绝其等于零的假设;四因子回归结果有9个截距项无法拒绝其等于零的假设,数量增加了80%。当置信度设定为95%时,该数字为从7增加至9,增加了28.6%。两种置信度下模型在加入特质流动性风险因子后,其无法拒绝为零的截距项数量都大幅增加,说明特质流动性波动率因子的引入显著增强了模型对股票资产收益率的解释效率。
表10可见,比较CAPM和FF三因子模型平均调整 ,从0.724提高到0.925,变化幅度比较大。而四因子模型又将
,从0.724提高到0.925,变化幅度比较大。而四因子模型又将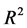 提高到0.940,但相对三因子模型的改进幅度较小。另外比较三个模型的平均截距项,分别为3.705、1.791和1.648,也显示了逐级降低的趋势。从调整
提高到0.940,但相对三因子模型的改进幅度较小。另外比较三个模型的平均截距项,分别为3.705、1.791和1.648,也显示了逐级降低的趋势。从调整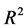 和截距项的变化都可以看出,特质流动性风险因子对模型的定价效率和解释力有进一步改进作用,但相对于规模因子和账面市值比因子而言,改进作用相对较小。
和截距项的变化都可以看出,特质流动性风险因子对模型的定价效率和解释力有进一步改进作用,但相对于规模因子和账面市值比因子而言,改进作用相对较小。
另外,表10结果显示特质流动性波动率因子的系数0.137,意味着在时间序列上特质流动性波动率
表8. FF三因子模型的回归截距

Table 9. Result of the adjusted four-factor model
表9. 调整四因子模型的回归截距
注:**表示95%置信度下显著不为零,*表示90%置信度下显著不为零。
表10. 三种模型回归结果
较高的股票具有较高的收益率水平。这一结果表明特质流动性风险并没有因为充分分散投资而被完全对冲,仍然影响着个股收益率水平。实际投资过程中,当理性风险厌恶的投资者面对市场冲击及变现需求时,他们并非总是首先变现那些特质流动性高的资产,因为这样将造成其剩余资产的特质流动性降低,从而面对将来可能更大的流动性成本,因此投资者会综合评估而选择变现资产。同时,由于特质流动性风险越高的股票,其将来的流动性风险水平越是难以预计,因此在受到市场冲击和急需变现的压力时投资人更有可能选择这样的股票提前出售,从而避免将来其流动性急剧恶化。这些特质流动性风险较高的股票,在选择对其变现时往往已经处于流动性较差的状态,为了弥补提前变现造成的损失投资者将要求更高的收益率。
6. 结论
本文实证研究发现,中国A股市场股票在样本期内具有相对稳定的特质流动性风险水平。本文所定义的特质流动性波动率作为特质流动性风险的代理变量,是一个相对独立的变量,与其他风险因子的相关性普遍较低。资产组合比较显示个股特质流动性异常收益显著,且与构造投资组合的权重无关。进一步结果显示A股市场横截面范围内特质流动性波动率与收益率呈显著的正相关关系。即使加入规模因子、账面市值比因子等其他控制变量,以上特质流动性波动率与收益率之间的正相关关系依旧稳定。在经典模型中加入个股特质流动性波动率变量,模型的解释力有所提高。时间序列研究表明,特质流动性风险因子可增强模型的定价效率,且特质流动性风险水平越高,资产收益率越高。但相对于规模因子和账面市值比因子而言,特质流动性风险因子的定价作用较小。我们可以得出结论,无论在横截面内还是在时间序列内,中国A股市场都存在着显著的特质流动性风险溢价。
本文研究所显示的特质流动性风险与资产收益率相关关系,对受到市场急剧冲击并需要在短期内迅速变现的投资策略具有启示作用。绝大部分市场投资人并非持有完全分散化的资产组合,这样的资产配置中个股的特质流动性风险更是难以对冲分散,因此影响着个股收益率水平。后续研究可在特质流动性及其风险指标的选择、实证模型及方法改进、不同区域及不同类型的市场特征对比等方面展开,进一步探讨特质流动性风险的定价作用。