1. 研究意义与目的
生计的稳定与可持续性是经济发展的基础。通过研究生计资本对生计策略的选择,以及生计策略对生计资本的影响,有利于梳理渔民利用资源探求可持续发展的思路,并有利于相关扶助政策的设计及实施。以山东长岛为例,由于长岛兼具发展渔业的优势和发展旅游业的潜力,渔民生计策略呈现出由渔业、海洋养殖业向旅游业发展趋势。通过建立升级资本评价指标体系,在对山东长岛渔民生计资本进行评估的基础上,分析生计资本与生计策略间的关系,对生计资本如何影响生计策略进行定量分析,并评价山东长岛渔民发展旅游对于可持续性生计发展的影响,并为相关政策的设计及实施提供建议。
同时,研究思路与过程可为其他地区可持续生计思考提供参考。
2. 国内外对于生计可持续性的研究进展
2.1. 可持续生计内涵
可持续生计往往与贫困问题紧密相关。随着对贫困问题属性理解的加深,20世纪80年代至90年代初期,可持续生计方法应运而生。这一研究思想,发端于20世纪80年代中期Chambers的研究工作,其除了对收入的贫困研究之外,还对引起贫困深层次的原因进行了辩证思考,比如生计发展的限制因素,发展能力和机会的贫困等。随着研究的深入,Chambers和Conway (1992) [1] 对可持续生计思想进行了明确阐述,即:生计是谋生的方式,该谋生方式建立在能力、资产(包括储备物、资源、要求权和享有权)和活动基础之上。只有当一种生计能够应对、并在压力和打击下得到恢复;能够在当前和未来保持乃至加强其能力和资产,同时又不损坏自然资源基础,这种生计才是可持续性的。
具体来说,所谓“可持续生计”(Sustainable Livelihoods,SL)是指个人或家庭为改善长远的生活状况所拥有和获得的谋生的能力、资产和有收入的活动 [1] 。这一概念最早见诸于20世纪80年代末世界环境和发展委员会的报告。1992年,联合国环境和发展大会(UNCED)将“可持续生计”概念引入行动议程,主张把稳定的生计作为消除贫困的主要目标。1995年,哥本哈根社会发展世界峰会(WSSD)和北京第四届世界妇女大会(FWCW)则进一步强调了可持续生计对于减贫政策和发展计划的重要意义。
2.2. 可持续生计相关研究方法综述
由于对生计所涵盖内容有不同理解,因而也形成多种可持续生计分析方法,主要有联合国开发计划署(UN-DP)、关怀国际(CARE)和英国国际发展署(DFID)分别提出的可持续生计分析框架。目前,应用最广泛的是DFID在《可持续生计指南》中提出的可持续生计分析框架(即SL框架,靳小怡等,2011) [2] ,以及和UNDP (联合国开发计划署)建立的分析框架。
DFID关于可持续生计框架的研究主要包括影响人们生计的多种因素以及这些因素之间的多元化关系,在这一研究框架中,人作为基本的中心,不断完善其教育质量与所掌握的技术信息等,能够有效推动生计的发展,进而创造出有利于个体安全发展与生产的社会环境。
UNDP关于可持续生计框架的研究主要强调整体性的效果,旨在不断分析外界社会环境以及如何通过环境来推动个体自身能力的发展。在这一研究框架中,投入产出、过程成果等均作为影响生计安全的因素被纳入到框架中。
2.3. 可持续生计相关研究进展
近年来,国内外诸多学者对可持续生计理论及方法,在多个领域进行了运用与推广。
具体来说,Zoomers, A (2001) [3] 在其著作中分析了可持续生计理论在拉丁美洲的应用现状。认为可持续生计研究方法是一项综合的多元分析方法,能够有效的应用于地区的持续发展中,这种持续发展不仅仅包括社会经济的发展,还包括环境的发展、资源的利用、人类的健康等多个方面。Leo J. De Haan (2005) [4] 从全球化、本土化与可持续生计的角度研究了第三世界国家的新发展,他认为生计是一个动态和多因素相互作用的过程,并提出全球化的管理在推动生计可持续发展过程中发挥着重要的作用。Balgis Osman Elasha等(2005) [5] 以苏丹为例,提出了可持续生计方法用于评估气候变化的方式,认为将可持续生计应用于对气候变化的研究,能够较好的分析气候走向,避免气候对人类社会产生的不利影响。他们的这一研究将可持续生计的应用范畴向更加广阔的范围内作出了推广,提出了可持续生计研究方法的多元化应用方式。BobAlexander等(2006) [6] 提出了可持续生计对灾害预防与管理的有效性分析,他们以印尼海啸为例,分析政府应构建旨在降低可持续的脆弱性的可持续生计分析框架,并将这一框架很好的应用于风向管理方面,以更好的理解生计策略的潜在意义以及生计策略具体的外在表现。他们通过对资源的攻击状况进行初步评估,设计出了一个针对如何有效降低生计策略的脆弱性的分析模型,将影响生计策略的多种因素纳入到模型中,以推动这一模型的综合发展与应用。Teresa C. H. Tao和Geoffrey Wall (2008) [7] 从可持续生计策略的角度分析了如何有效推动可持续生计的发展,他们将旅游业纳入到推动可持续生计发展的研究框架中来,认为可持续的旅游业一方面可以被纳入到社区或者社会发展体系中,作为可持续发展的一种必要补充,另一方面,旅游业本身作为一种损耗较低的产业,能够从多方面推动可持续生计的发展,这里主要包括其对经济的带动及对天然自然资源的多产出应用。
3. 主要研究内容,研究方法与技术路线
3.1. 研究内容
本次研究主要依据DFID提出的SL模型,以山东长岛为例,从人力资本、社会资本、自然资本、物质资本、金融资本五个角度对渔民可持续生计资本进行评估,同时基于资本评估基础,分析可持续生计资本与生计策略的关系,一方面,研究可持续生计资本在渔民制定生计策略过程中的作用,另一方面,研究不同生计策略对可持续资本的影响,具体到本次研究案例(山东长岛),即研究渔民从传统海洋养殖业向旅游业转型过程中对于生计可持续性的影响。
3.2. 研究方法与模型
访谈法:在搜集渔民生计资本状况信息、生计策略过程中,采用访谈法,通过实地与当地旅游参与户与未参与户交谈并记录其具体情况,和采访当地村支部,以获得第一手的资料与数据。
SL模型:依据SL模型,从人力资本、社会资本、自然资本、物质资本、金融资本五个角度选取评估可持续生计资本的指标,设计指标体系,并以此为基础设计问卷进行调研。本次调研中,笔者选取长岛县具有代表性的荻沟村与黑石嘴村进行调研,并在两地共选取26户居民对于生计资本、生计策略等各方面信息进行详细访谈。其中,8户居民以传统海洋养殖业作为主要生计方式,15户居民经历了从传统海洋养殖业向其他生计方式(以旅游业为主)的转型,3户居民自定居起一直从事旅游业。样本虽然选取数量较小,但具有代表性,可以反映长岛居民的基本生计策略情况,生计资本拥有状况具有代表性。
AHP层次分析法:AHP层次分析法是美国Pittburgh大学Satty教授早在20世纪70年代就提出的一种多准则决策方法。AHP能够对专家给出的定性比较结果进行定量的分析,从数学分析的角度上给出各方案的排序权重,可为决策者提供依据。根据专家对指标赋予权重,建立可持续生计资本实力综合评价体系,对于山东长岛渔民的生计资本状况进行评估。
二项Logistic回归模型:二项Logistic回归模型属于概率型非线性回归,它是研究二分类观察结果与一些影响因素之间关系的一种多变量分析方法。二项Logistic回归分析不直接分析被解释变量Y的取值与解释变量 间的关系,而是利用多元线性回归模型对Y = 1的概率P进行建模。在本文中,利用二项Logistic模型分析生计策略与可持续生计资本间的关系。
间的关系,而是利用多元线性回归模型对Y = 1的概率P进行建模。在本文中,利用二项Logistic模型分析生计策略与可持续生计资本间的关系。
3.3. 技术路线图
4. 现有研究进展
4.1. 研究区概况及数据基本情况
长岛县位于山东省烟台市,以海岛风情闻名。长岛休闲渔业旅游项目从上世纪九十年代末开始至今,年接待游客超过万人,且年增长率在2位数以上。随着海洋旅游的逐步兴起和升温,休闲渔业旅游也随之迅速发展壮大。长岛地处黄渤海交汇处,海洋生物资源丰富,旅游大环境适宜,年旅游接待量超过150万人次以上,极大地吸引了全国各地的游客。
我们选取了长岛县黑石嘴与荻沟两地作为调研地点。黑石嘴村位于山东省长岛县南长山镇北端,西与妈祖庙隔海相望,南接仙境源、峰山、林海景区,北接月牙湾、九丈崖景区、望福礁民俗风情公园,距离长岛港约3公里,全村拥有23户“渔家乐”业户,其中A级示范户2个,600余张床位,年接待游客60,000余人次,25%的村民参与了旅游相关工作,旅游收入占全村总收入的40%。荻沟村地理位置类似,距离码头较近,但由于发展旅游较晚等原因,发展范围较小,年接待量在1.6万作用。两地均拥有较好的旅游资源并经历了从传统依靠渔业和养殖的生产生活方式向参与旅游业等生计方式转型的过程。
在2014年的研究中,笔者已对于长岛县黑石嘴村与荻沟村居民可持续生计资本信息与生计策略基本信息进行了搜集,对26户居民进行了详细访谈。
4.2. 可持续生计资本基本信息
4.2.1. 资本评价体系建立
以往研究中,笔者针对于人力资本、自然资本、物质资本、金融资本和社会资本设计指标体系具体包括:
人力资本方面:选取家庭劳动力、劳动力受教育程度、劳动力掌握技能三个指标,对于劳动力的数量及质量进行了调查。自然资本方面,选取人均拥有渔船数量、人均拥有养殖规模两个指标;物质资本方面,选取住房类型、住房面积、生活资料、生产资料四个指标;金融资本方面,选取获得银行/信用社贷款情况,获得现金援助的情况,家庭现金收入与储蓄三个指标;社会资本方面,选取参与社会活动和组织、以家庭村干部数量等为内涵的社会地位两个指标。将各题选项量化,以数据形式呈现调研结果,得到原始数据。
由于各项指标原始数据量纲不同,为建立评价体系,利用SPSS19.0对于原始数据进行标准化处理后,每个指标得到对应的位于0~1的赋值,即为指标值。越接近于1表示资本条件越优秀,资本越丰富;越接近于0表示资本越缺乏。
将基本信息定量化后,运用AHP层次分析法,获取指标相对重要性。此次AHP调查采用面对面专家打分法进行,选取烟台市长岛县县政府、长岛县规划局、黑石嘴村村委会、荻沟村村委会等地,选择对渔民生计问题较为了解的专家,共回收有效问卷14份,根据问卷收集的原始数据构建两两判断矩阵,并应用AHP分析法进行数据处理,得到指标的相对影响权重值。各类资本下的指标值分别乘以对应的权重值并相加后得到五类指标的资产数值。具体评估结果如表1所示。

Table 1. Evaluation results of livelihood assets
表1. 生计资本评估结果
首先,根据权重可判断出,劳动力受教育程度在人力资本(0.402)中所占权重最高,人均拥有养殖规模(0.613)在自然资本所占权重最高,生产资料(0.398)在物质资本中所占权重最高,家庭现金收入与储蓄(0.590)在金融资本中所占权重最高,社会地位(0.626)在社会资本中所占权重最高,以上指标都是影响长岛渔民生计的重要因素。
同时,根据资产数值,长岛居民物质资本最为丰富,金融资本稍显缺乏。
4.2.2. 生计资本对生计策略选择的影响
根据以往的调研情况可知,长岛居民可选择生计策略主要分为以传统海洋养殖业为主和不以传统海洋养殖业为主(在本次研究中,该类居民一般从事旅游业,也有少部分居民依赖于其他行业)。基于上文研究情况,通过二元Logistic回归模型对生计资本与生计策略间的关系进行研究。
1) 二元Logistic回归模型
二元Logistic回归分析不直接分析被解释变量Y的取值与解释变量 间的关系,而是利用多元线性回归模型对Y = 1的概率P进行建模 [8] 。
间的关系,而是利用多元线性回归模型对Y = 1的概率P进行建模 [8] 。
 (1)
(1)
式(1)存在两个不足:第一,由于概率P的取值范围在0~1之间,而一般线性回归模型要求被解释变量取值在−∞~+∞之间,因此要对概率P作合理的转换,使转换后的取值范围与一般线性回归模型相吻合。第二,式(2)中的P与解释变量X间的关系是线性的,但实际应用中,这个概率P与X间的关系是非线性的。
基于上述两方面的考虑,对P进行以下两步转换处理:
第一,将P转换成Ω:
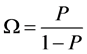 (2)
(2)
式(2)中,称Ω为发生比,是事件发生的概率与不发生的概率之比。Ω是P的单调增函数,这样保证了P与Ω增长(或下降)的一致性。Ω的取值范围在(0, +∞)之间。
第二,将Ω转换成LnΩ
 (3)
(3)
式(3)中,称LnΩ为LogitP。经过这一转换后,LogitP与Ω从而与P之间仍呈增长(或下降)的一致性关系,其取值区间为(−∞, +∞),已与线性回归模型中被解释变量的取值范围相吻合。
称上述两步转换过程为Logit变换,经LogitP变换后,就可以利用一般线性回归模型建立被解释变量取值1的概率与解释变量) 之间的依存模型,即:
之间的依存模型,即:
 (4)
(4)
式(4)就是logistic回归模型,其中b0为回归常数,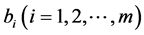 为回归系数。模型中logitP与解释变量之间是线性关系,同时,P与解释变量间的关系如下。在(4)式中用
为回归系数。模型中logitP与解释变量之间是线性关系,同时,P与解释变量间的关系如下。在(4)式中用 代替logitP,则有:
代替logitP,则有:
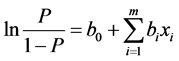 (5)
(5)
于是有:
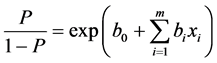 (6)
(6)
最后可得:
 (7)
(7)
式(7)是典型的增长函数,很好地体现了概率P与解释变量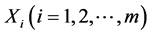 之间的非线性关系。logistic回归模型采用极大似然估计法对模型的参数进行估计,参数被估计出来并通过各种统计检验后,需要对模型参数的含义给予合理的解释。从形式上看,logistic回归模型与一般线性回归模型相同,因此,可以用解释一般线性回归模型中回归系数含义的方法来理解和解释logistic回归模型中回归系数的含义,即当其他解释变量保持不变时,解释变量xi每增加一个单位,将引起logitP增加(或减少) bi个单位。然而在模型的实际应用中,人们关心的是解释变量Xi的变化会引起Ω多大的变化。
之间的非线性关系。logistic回归模型采用极大似然估计法对模型的参数进行估计,参数被估计出来并通过各种统计检验后,需要对模型参数的含义给予合理的解释。从形式上看,logistic回归模型与一般线性回归模型相同,因此,可以用解释一般线性回归模型中回归系数含义的方法来理解和解释logistic回归模型中回归系数的含义,即当其他解释变量保持不变时,解释变量xi每增加一个单位,将引起logitP增加(或减少) bi个单位。然而在模型的实际应用中,人们关心的是解释变量Xi的变化会引起Ω多大的变化。
由(4)式可得发生比Ω与解释变量 的函数:
的函数:
 (8)
(8)
假定其他变量不变,只考虑某一特定自变量Xj增加一个单位对Ω的影响时,可将此时新的Ω设定为Ωj。
 (9)
(9)
(9)式说明,当其他变量不变时,某一特定自变量Xj变动一个单位时,会引起发生比扩大或缩小Ωexp (bj),具体变化方向取决于Xj回归的正负性。
2) 计算结果分析
生计策略是人们在综合考虑自己所拥有的资源后进行选择的结果,因此,生计策略是一个多元变量,受到人力资本、社会资本等五项资本的影响。在问卷调查的过程中,将生计策略归为两类:以传统海洋养殖业为主与其余。并将受访渔民对于生计策略的选择与其所拥有的生计资本加以对应。为分析生计资本对生计决策的影响,将人力资本、自然资本、物质资本、金融资本、社会资本作为自变量,生计策略作为因变量(将以传统海洋养殖业为主赋值为1,其余赋值为0),利用SPSS19.0进行多元二项Logistic回归分析。自变量选取方法采用逐步进入(Forward:LR),变量进入标准为P < 0.1,回归分析结果如表2所示。
根据回归系数的符号可以判断出各项资本对于生计策略的影响方向,总体来说,人力资本与自然资本较为丰富的居民倾向于选择传统海洋养殖业,物质资本、社会资本、金融资本、较为丰富的居民倾向于选择旅游业或者其他非传统海洋养殖业。根据回归系数的绝对值可以判断出各项资本对于生计策略的影响力大小。
4.2.3. 生计策略选择对生计资本可持续性的影响
在4.2.2中,我们运用二元Logistic模型分析了资本如何影响决策。与此对应的,我们在以往的调研中,选取生计策略以旅游业为主的居民,针对其从事旅游业前后资本的变化情况,以旅游业为主的生计策略为例,对生计策略如何影响生计资本进行了定性研究。

Table 2. The effect of livelihood assets on livelihood strategies
表2. 生计资本对生计策略选择的影响
总体来说,研究区村民参与旅游的方式主要为渔家乐,即食宿一体的经营模式,大多为利用本身所拥有的房屋,加以改造后投入运营,主要为个体经营模式。根据调查数据,开设时间较短、规模较小的渔家乐,旅游相关带来的年收入平均在5万元左右,而开设时间较长,规模较大,并且有着固定客源的渔家乐收入可以达到10万元以上。由于规模不等,总体收入有一定差距,但收费模式基本相同,按照一人一天200元收取。
根据长岛县人民政府公布的数据1,从门票收入与旅游人次来看,长岛旅游业不断发展,收入人次持续提高。具体变化趋势图1所示,具体数据如表3所示。
从2009年到2013年长岛市三产占比来看,第三产业GDP占比不断提升,具体变化趋势如图2所示,具体数据如表4所示。
从宏观数据来看,旅游业占比不断提升,且带动了整体经济的发展。从调研数据上来看,除增加经济收入,提升金融资本外,根据问卷,以旅游业发展为主要生计策略的居民,大部分旅游相关培训、其他技能有所提高(人力资本质量提升);由于部分育苗场被关闭发展成了旅游景点,自然资本有所下降;物质资本有所提升,主要体现在生活资本的大量增多,包括房屋的扩建、用于接送客人的交通工具的购买、每个房间电视机、空调的配备以及洗衣机的大量购买;同时,由于与外界联络的增多,居民社会资本有些许的提升。
与此同时,旅游业的发展带动了如运输业、零售业等行业的发展,也造成了养殖业从业人员的转移与流失。
由于信息搜集难度较大,样本数量较小,生计策略对于生计资本的影响仍处于定性评价阶段。通过进一步收集信息,可通过比较采用某生计策略前后资产数值的变化对生计策略的影响进行定量评估。
为进行定量评估,笔者选取自2000年政府出台鼓励政策以来最早从事渔家乐的10户居民,对其14年来的生计资本状况进行了对比分析,得分如表5所示。
资本数值总体提升,表明向旅游业的转型符合长岛渔民可持续生计的要求,可作为今后发展的重要方向。
5. 实现参与旅游业村民生计可持续的对策及建议
可持续生计的重要目标是任何发展和改进都是长远持续性的,要实现参与旅游业村民生计的可持续性就必须把村民的生活质量同社会的长远发展目标相结合,使其不但短期内生存质量能得到保证,而且还能具备长期持续发展的能力。通过对影响参与旅游业村民实现长远生计的因素进行分析,笔者提出如下实现村民长远生计的对策。
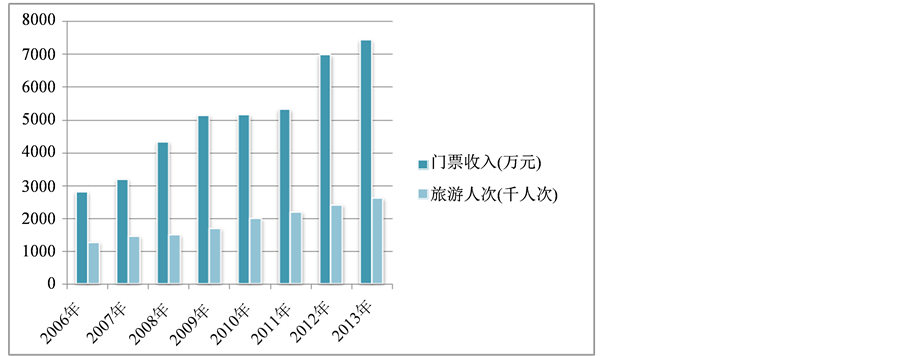
Figure 1. The ticket incomes and the number of travelers of Changdao from 2006 to 2013
图1. 2006~2013年长岛旅游门票收入与旅游人次变化情况

Figure 2. The change of industrial organization in Changdao from 2009 to 2013
图2. 2009~2013年长岛产业结构变化情况

Table 3. The ticket incomes and the number of travelers of Changdao from 2006 to 2013
表3. 2006~2013年长岛旅游门票收入与旅游人次变化具体数据

Table 4. The change of industrial organization in Changdao from 2009 to 2013
表4. 2009~2013年长岛产业结构变化情况

Table 5. The comparison between livelihood assets in 2000 and in 2014
表5. 2010年与2014年生计资本对比
5.1. 村民的应对策略
首先,提高旅游经营水平和服务能力:村民提高创新意识,有参与培训和获取新技能的意愿,提高旅游经营服务能力、经营理念,与时俱进,充分利用各项资源,打造属于自己的特色品牌。不止步于简单的旅游观光,更可以结合人文特色,开发人文旅游项目,如反映渔民文化的民俗表演等,使参与性更强,趣味性更强。
其次,加强合作关系,建立合作组织:加强从事旅游经营不同环节的村民之间的合作,并建立合作组织,形成完整的经营网络,并通过组织与诸如旅游公司等进行协商,有效维护自身权益,并通过建立组织的方式,汇聚力量,有效利用旅游资源,减少旅游业脆弱性带来的风险。
第三,多种生计组合策略:通过多种生计组合策略分散风险,包括传统渔业和非渔业生产生活方式的选择,村民可根据自身资源,合理选择组合方案,既能在旅游旺季时兼顾到旅游方面的发展,又能在淡季时有收入保障。针对自身物质资源、人力资源、金融资源、政策优惠等多方面资本,合理选择旅游业为主,或者旅游业与传统渔业、养殖业,或者旅游业与其他职业的组合。
5.2. 政府的应对策略
政府做任何决策都应该将参与旅游业牧民的生活质量同社会的长远发展目标相结合,使其不但短期内生存质量能得到保证,而且还能具备长期持续发展的能力。
首先,设立对村民的系统培训:针对村民发展情况,对旅游经营所需技能、安全知识等进行系统培训,提高村民经营能力,发展所需技能,为村民提供学习机会。
其次,系统规划,打造特色品牌:打造属于长岛的特色旅游品牌,挖掘各地特色,从各方面多层次展现长岛魅力,发挥长岛旅游潜力。比如结合9月1日《国务院关于促进旅游业改革发展的若干意见》指出的“旅游业发展应与新型工业化、信息化、城镇化和农业现代化结合。”意见,旅游业的跨界融合不仅是行业发展趋势,更是政策鼓励的方向。同时土地供应进一步向旅游业发展倾斜,旅游产业用地的获得将更具备可操作性。比如长岛国际旅游度假村的建设,借助政策力量,开辟新的天地。
第三,完善交通,实现便利:从交通和供水等方面进一步完善公共设施建设,提供居住质量,从而增加吸引力。
第四,大力开发冬季旅游:研究区发展主要为夏季旅游,冬季旅游基本空白。政府应该积极开发冬季旅游,减小季节性带来的风险。
第五,健全相关制度,营造良好社会环境:政府应该针对旅游管理各方面建立完善的管理制度,明确各环节谁负责,怎样处理,避免因法制建设漏洞带来的不安定因素。同时,营造良好的社会环境,使旅游者安心消费,保障旅游业顺利、安全的开展。
第六,加强完善社会保障体系,分散风险:充分发挥政府的服务功能,将社会保障法制建设提高到重要的位置,充分考虑村民对社会保障的现实需求,从经济和社会保障两个方面帮助村民抵御风险。
NOTES
1http://www.changdao.gov.cn/cn/index.jsp长岛县人民政府网站