1. 引言
纵向数据是指一段时间内对每个个体在不同的时间点进行观察记录而得到的数据,与横截面相比,纵向数据的优势主要在于它更加有效的估计了样本内和样本间随时间变化的趋势。纵向数据主要是处理响应变量和协变量的变化关系,同时还要考虑响应变量组内的相关性。Verbeke同Molenberghs [1] ,Raudenbush [2] ,Collins [3] 以及Davidian [4] 等都提出了关于纵向数据的处理方法。常用传统的方法有:线型随机效应混合,广义线性随机效应混合模型等。
在传统的统计中,我们通常要对分布和模型形式作出假定,在这些假定下确定损失函数,并因此得到各种检验,统计量的临界值等判别准则。但是这些都是在对数据分布和模型所做的假设下得到的,如果这些假定不满足,得到的这些准则也没有什么意义了。这些假设无法用确定性方法验证,最多只能用显著性检验来拒绝它,如果不能拒绝也不能说这些假定是正确的。故传统的方法对假定具有很强的依赖性。
在当今大数据的时代,Izenman [5] 说过数据之大,用传统方法无法解决,即使能解决,结果也很糟糕。计算机的发展之快,这就促使了机器学习方法产生。相对传统的方法而言,机器学习方法对数据的分布不需要任何的假定,并用交叉验证的方法来判断模型的好坏。交叉验证就是拿一部分数据作为训练集,得到模型。再用另一部分数据作为测试集来看误差是多少。八折交叉验证就是把数据分成8份,每次拿一份作为测试集,其他的七份作为训练集,重复八次,得到八个误差作为平均。该方法预测的效果很好。本文将用机器学习方法和传统方法做预测对比。
本文使用的误差为标准化均方误差(NMSE, normalized mean squared error),定义为:
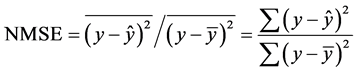
这里的y是指测试集中因变量的值,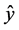 是根据训练集得到的模型对测试集第个因变量的预测,而
是根据训练集得到的模型对测试集第个因变量的预测,而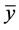 为测试集因变量的均值,即不用模型时对因变量的预测。如果这个误差大于1,则说明模型比不用模型还糟糕。
为测试集因变量的均值,即不用模型时对因变量的预测。如果这个误差大于1,则说明模型比不用模型还糟糕。
2. 数据说明
本文的数据来自网址:http://faculty.washington.edu/heagerty/Books/AnalysisLongitudinal/milk.data数据是由79头奶牛吃三种不同的饲料,在不同的周期下观察每一头牛奶所产牛奶含蛋白质的含量。本文将三个数据整合在一起进行分析。数据的变量有:diet,cow,week,protein。其中diet变量有3个分类:一部分奶牛吃大麦饲料、一部分吃白羽扇豆饲料、一部分吃大麦和白羽扇豆的混合饲料,且每头年的观察周期不一定相同,每头牛至少观察12周。
3. 线性随机效应混合模型对变化训练集的预测
线性随机效应混合模型可视为线性模型和随机效应混合模型的有机结合。该模型将把不同个体的差异作为随机部分加入模型之中以反映个体对其重复测量的影响。线性随机效应混合模型的一般形式[6] :
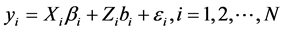
式中,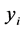 为
为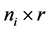 ,
, 为
为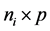 ,
,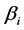 为
为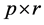 ,
, 为
为 ,
, 为
为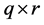 ,
,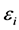 为
为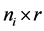 。
。
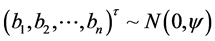
对所有的 ,
,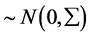
 而且独立于
而且独立于 。通常
。通常 及
及 的第一列为常数,
的第一列为常数, 包含的是
包含的是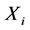 的子集,要估计的是
的子集,要估计的是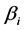 ,
,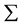 ,
,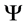 。公式中
。公式中 的为固定部分,
的为固定部分,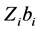 而为效应部分。
而为效应部分。
这里的正态性假定很强,它使得人们可以使用最大似然法来估计参数。由于真实数据的正态性及模型表示的准确性很难验证,因此,对于一个实际数据,一般很难确定一个最优的模型及方法。
对于该数据,经R软件[7] 分析,protein变量作为因变量,其它变量作为自变量,且自变量week和diet即作固定效应部分也是随机效应部分。模型的表达式为:a = lme (protein ~ week + diet, random = ~week + diet|cow, w[-m,])。这里的lme是线性随机效应混合模型的函数,w是数据的名称,m代表测试集的下标。
从每头牛到第5周的观察开始建立训练集,该头牛的其它周观察作为测试集并变化训练集(训练集逐渐变大)做预测。利用线性随机效应混合模型预测并进行八折交叉验证得到的标准均方误差如图1所示。
从图1中,我们能看到一个明显的趋势:随着训练集的变大,标准均方误差越小(预测的效果越好)。训练集很小时,预测的误差十分大。例如以每头牛的前五周数据作为训练集建立线性随机效应混合模型时,预测的均方误差达到27.184230,这个结果比不用模型时去预测还糟糕。当以每头牛的前11周数据作为训练集建立线性随机效应混合模型时,预测的均方误差达到1.802646,虽然这个结果要比前面的好的多,但仍然不如不用模型预测的效果好。也可以说明要减小误差,增大训练集也是一种有效的方法。经过R的运算可知线性随机效应混合模型对数据预测产生的标准均方误差为:

4. 机器学习方法对变化训练集的预测
前面的随机效应混合模型是需要建立在假设上面的,但这里的机器学习方法不需要。但是机器学习习方法的解释能力要比传统的方法更差。Robert [8] 曾在预测精度和模型的可解性上来权衡传统方法和机器学习方法如图2。
从图2中可知:传统模型的可解性要比机器学习方法强,但预测能力却远远不如机器学习方法。所以对于不同的目的(预测或推断),选择的模型也不一样。下面我们先简单的介绍下机器学习方法,再用机器学习方法来对该数据进行预测。
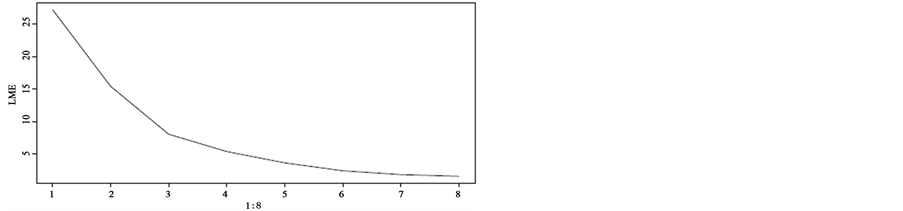
Figure 1. Normalized mean square error of linear random effects mixed model with the prediction of the changing training set
图1. 线性随机效应混合模型对变化训练集的预测标准均方误差图
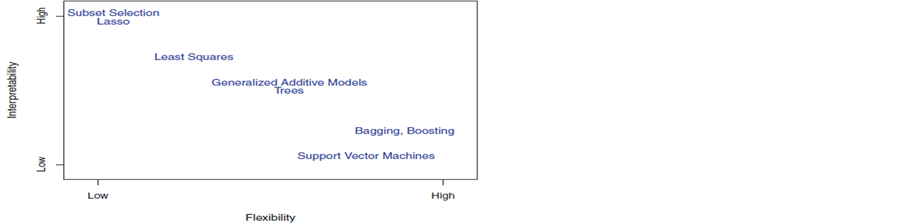
Figure 2. The trade-off between prediction accuracy and model interpretability in machine learning method and traditional method
图2. 机器学习方法和传统方法在预测精度和模型可解性上的权衡
决策树的构造过程是:在任何节点,每个数量自变量都自行选择一个把在该节点的观测值中因变量水平分得最开的分割点,如果有分类变量,则选一个把因变量水平最能够分开的一个取值。然后各个自变量互相竞争(包括可能的分类自变量)看哪个变量能够把该节点观测值中因变量各个水平分得最开(即各个水平百分比“差别”最大,有各种关于“差别”的度量)。选中的变量成为该节点的拆分变量。于是决策树就根据拆分变量的分割点分叉,把观测值就分成两部分,也就是两个新节点。在每个新节点,自变量内部和互相的竞争又重新开始,再产生一个新的拆分变量。如此进行下去,或者到规定的步数、或者节点已经只剩一个水平时截止决策树就完成了。
随机森林是决策树的组合方法。2001年,Breiman [9] 在研究单棵决策树组合问题时取得重要的进展,它把单棵树进行组合形成了随机森林。随机森林的工作原理[9] 为:(1) 从所有(n个)观测值中抽取n个观测值作为自助法样本。即有放回的抽取和原始数据同样样本量的样本。然后根据这个新样本建造一个(分类)决策树,在构造树的过程中不用所有的变量当候选拆分变量,而是随机的挑选部分变量来竞争拆分变量。这样,不仅仅是每棵树所用的数据是随机抽取的。而且每个节点的拆分变量的选择也是随机的;(2) 不断的重复(1),直到建成的决策树等于指定的数目为止;(3) 如果来了新的数据,每棵树给出一个预测值,然后所有的树用简单多数投票来决定其因变量的预测值。
基于模型的bagging方法,其工作原理可参考文献[10] 。Bagging (bootstrap aggregating),可以译为“自助整合法”,它利用了自助法(bootstrap)放回抽样。它对训练样本做许多次(比如k次)放回抽样,每次抽取样本量相同的观测值,由于是放回抽样,因此就有了k个不同的样本。然后,对每个样本生成一棵决策树。这样,每棵树都对一个新的观测值产生一个预测。如果目的是分类,那么由这些树的分类结果的“投票”。
支持向量机方法是一种线性和非线性的数据分析的新分类方法。近年来它的理论研究和算法实现方面都取得了突破性进展,成为解决“维数灾难”和“过学习”等传统问题的有力手段。由于介绍此方法需占很大的篇幅,故对此方法详细的介绍可参考文献[11] 。
神经网络模型是对自然的神经网络的模仿,它可以有效地解决很复杂的有大量互相相关变量的回归和分类问题。神经网络的原理就是把上层节点的值加权平均送到下层节点,最终到输出层节点,然后根据误差大小反馈回前面的层,再重新加权平均,反复的训练,直至误差在允许的范围之内。下面的公式可以说明具有一个隐藏层的一般神经网络的加权过程。具体细节可参考文献[12] 。
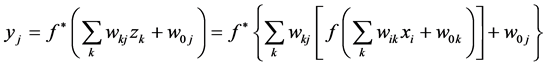
式中,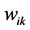 是自变量
是自变量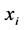 在隐藏层第k个节点的权重,
在隐藏层第k个节点的权重,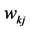 是隐藏层第k个节点对于第j个因变量的权重,
是隐藏层第k个节点对于第j个因变量的权重,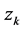 是隐藏层第k个节点的值,这里
是隐藏层第k个节点的值,这里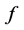 和
和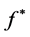 是激活函数。
是激活函数。
由于机器学习方法对序号没用,故我们把变量cow删除。采用循环的方式用机器学习方法和线性模型建模并变化训练集来做交叉验证。所得的标准均方误差图如图3。
从图3中明显可以看出线性模型的预测不如机器学习方法,这和传统模型需要依赖与假设检验有很大的关系。但当以每头牛的前12周数据作为训练集建立模型时,预测效果和机器学习方法很接近,标准均方误差是1.29。线性模型对此数据的预测随着训练集的增大表现的越好。而无论哪种机器学习方法对此数据的预测都表现的差不多,且具有稳健性(几乎不随训练集的变化而变化)。
以下是经过R分析运算各种模型对数据预测产生的标准均方误差值和标准均方误差图,如图4所示。

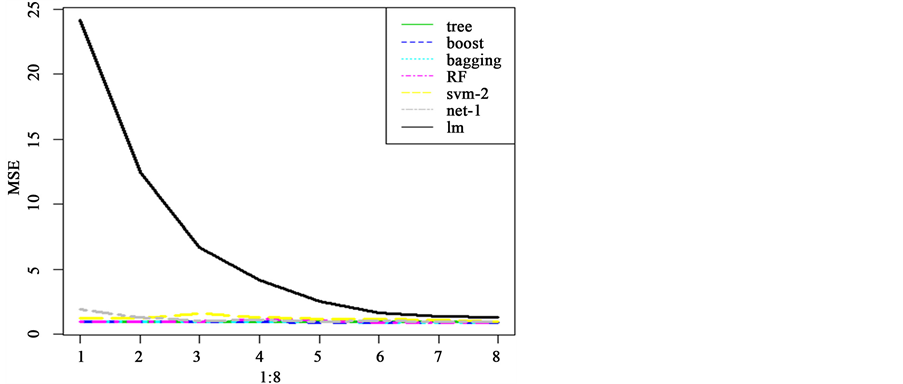
Figure 3. The normalized mean square error which is predicted by machine learning method and the linear model
图3. 机器学习方法和线性模型预测的标准均方误差图
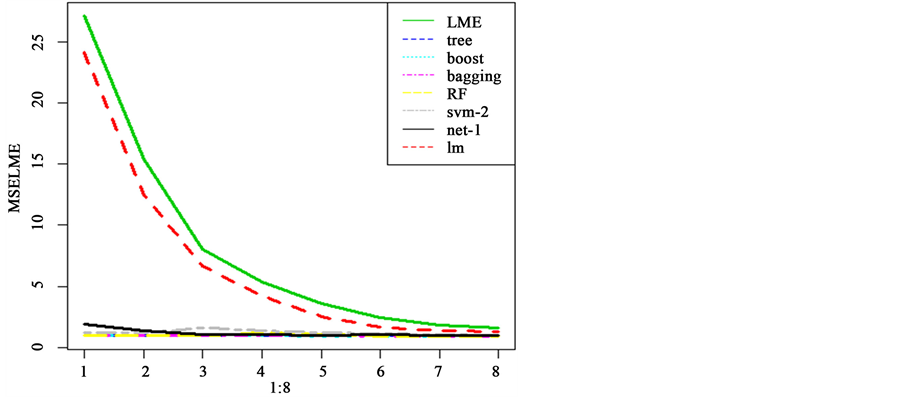
Figure 4. The normalized mean square error by all models
图4. 所有模型的标准均方误差图
无论是从上面的值还是下面的图表,都可以看出机器学习方法对该数据的预测要远远好于传统的方法。
5. 总结
本文数据的分析结果可以知道:不依赖于任何假设的机器学习方法在此数据上的预测效果要远远比传统的依赖于假设检验的线性模型和线性随机效应混合模型好。这是因为机器方法摆脱了假设分布–用明确的模型来拟合–假设检验–p值的经典统计过程。这种基于算法或程序的模型预测效果一般很好。但如果数据的目的是用于推断,则传统的方法可能会更具有解释性。具体数据具体分析,或许对于某个数据传统的方法要比机器学习方法好。所以在实际中必须根据数据的特点来选择最优的模型。
致谢
本论文的思想来源于吴喜之教授,他是个十分具有爱心的教授,经常无私地帮助身边需要帮助的人。这篇文章的难处主要是R软件的编程能力,从编程到程序的优化,老师给了我很多指导,有了您的指导,才有我各方面的进步,由衷感谢吴老师。同时感谢王涛老师对我学习生活各方面的督促和帮助。感谢国家自然基金的资助。