1. 引言
森林是陆地生态系统中最大的碳库,其碳汇功能对全球变化和碳循环起着关键性的作用。城市森林作为森林的一个子系统,不仅能够通过调节城市的光、热、气、水、土等生态因子来改善城市的生态环境,而且可以直接吸收城市中排放的碳和通过减缓热岛效应等方式减少城市中碳的排放,在低碳生态城市建设中占有重要的地位[1] 。另外,城市森林的蒸腾作用能够直接或间接的消耗城市中的热辐射,也可以遮挡来自太阳的直接辐射、路面、墙面等的热辐射反射,降低周围的温度,发挥城市森林的热环境效果,进而减缓城市热环境 [2] 。同时,为了全面推荐我国城市走生产发展、生活富裕、生态良好发展道路,为了创造良好的人居环境,弘扬城市绿色文明,提升城市品味,促进人与自然和谐,构建“国家森林城市”是重要的发展道路 [3] 。定量评价昆明市主城区城市森林建设有助于更好的分析评估昆明市生态环境建设。
2. 数据与方法
2.1. 研究区概况
本文选取云南省昆明市主城区为研究区域。昆明市属于北纬低纬度亚热带、高原山地季风气候。因为受印度洋西南暖湿气流的影响,日照时间长、霜期短、年平均气温15℃左右,历史上最高气温31.2℃,最低气温−7.8℃,最热时月平均气温19℃,最冷时月平均气温8℃。由于湿度、温度适宜,日照时间长,霜期短,无霜期240天以上,年平均日照2200小时左右,所以草木四季常青,鲜花常年不谢。昆明春季天气温暖,气候干燥少雨,水分蒸发旺盛,日夜温差变化大。夏天雨量集中,多大雨、暴雨,且无酷暑。秋季气温凉爽,降雨量较少,温度下降快,气候干燥,平均气温比春季低2℃左右,平均降水量比夏季减少一半多,但多于冬、春两季。冬季无严寒,日照充足,天气晴朗,降雨量少。昆明是典型的温带气候特征,城区温度在0℃~29℃之间,年温差在全国最小,这样的气候特征在全球罕有,是著名的“春城”、“花城”[4] 。
2.2. 研究方法
2.2.1. 植被覆盖度的估算
Landsat TM数据和Landsat-8数据主要来自Global Land Cover Facility (http://glcf.umd.edu/data/),其他部分数据来自地理空间数据云(http://www.gscloud.cn)。选择2003、2005和2009年3景TM数据及2013、2014年2景Landsat 8数据产品,空间分辨率除热红外波段外,其余波段为30 × 30 m。在应用ENVI图像处理软件进行头文件的读取、几何校正、大气校正和裁剪等预处理之后,利用红光波段和近红外波段进行研究工作。
遥感影像数据通过绿色植物叶子光谱响应的差异及动态变化来反映绿色植被的信息。因为植被叶子的叶绿素含量、水分含量、组织结构、叶层构造等的不同,导致植物反射光谱特征的不同。叶绿素在红光波段范围内(TM数据光谱范围为0.63 μm~0.69 μm,Landsat-8数据光谱范围为0.63 μm~0.68 μm)强烈地吸收该波段的入射辐射。近红外波段(TM数据波谱范围为0.76 μm~0.90 μm,Landsat-8数据波谱范围为1.56 μm~1.66 μm)对植被差异及植物长势反应敏感,标志着植物光合作用是否正常进行,是叶子健康状况最敏感的标志。归一化植被指数(NDVI)就表示了植被对这两个波段响应的差异,是反映土地植被覆盖状况的一种遥感指标,广泛应用于植被活动研究中。被定义为近红外波段和红光波段之差和这两个波段之和的比值 [5] 。其计算公式为(1):
 (1)
(1)
式中NDVI是归一化植被指数,NIR和R分别是近红外波段和可见光红光波段,对于TM数据而言,近红外波段和红光波段分别为第4和第3波段。对应Landsat 8数据而言,近红外波段和红光波段分别为第5和第3波段。NDVI的取值范围为[−1,1],其中负值表示地面覆盖为水体或者人工建筑等,可见光反射高;0表示有岩石或者裸土等;正值,表示有植被覆盖,且随着覆盖的增大而增大。一般认为NDVI小于0.05时表示植被已很稀少 [6] 。
NDVI尽管能够直观地表达区域的植被变化情况,但在生态评价等方面是一个间接变量。植被覆盖度是最直接可用的和利于区域之间数量比较的植被因素。植被覆盖度可以定义为单位面积上的植被覆盖面积 [7] 。本研究采用像元二分模型估算昆明市主城区植被覆盖度。混合像元普遍存在与遥感影像中,特别在比较复杂的地物分布区域。像元分解模型认为,图像中的每个像元是由多个组成成分构成,每个组成成分对传感器观测到的信息都有影响,因此建立像元分解模型估算植被覆盖度。像元二分模型是最常见的混合像元分解模型之一,这种模型假设遥感图像中每一个像元可以表达为由绿色植被和无植被覆盖即裸土两部分组成,这种估算方法不依赖于实测的植被覆盖数据,因而在实际工作中应用广泛。像元二分模型估算植被覆盖度时多根据植被覆盖度和NDVI之间显著的线性关系来提取植被覆盖度信息,这时植被覆盖度Fv的估算公式为(2) [8] :
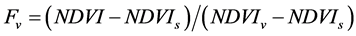 (2)
(2)
式中Fv为植被覆盖度;NDVI为各像元的归一化植被指数;NDVIv和NDVIs分别表示地表覆盖类型为纯植被和纯裸土的NDVI值。NDVI > 0.7表示森林覆盖,0.05 < NDVI < 0.06表示裸土覆盖。所以,可以将NDVIv确定为0.70,NDVIs确定为0.05 [9] 。
2.2.2. 城市森林建设定量评价
通过ArcGIS统计功能,对昆明市主城区主要道路铁路、湖泊河流以及城市森林植被覆盖率进行统计分析,定量评价道路铁路、湖泊河流以及城市森林植被覆盖率是否符合“国家森林城市”评价指标。
1) 城市森林覆盖率定量评价
根据“国家城市森林”评价指标规定,南方城市森林覆盖率需达到35%以上才符合城市森林建设的标准。城市森林覆盖率指在城市的绿化覆盖面积占城市面积的百分比 [10] 。绿化覆盖面积是指城市中乔木、灌木、草坪等所有植被的垂直投影面积。由于缺少植被垂直投影面积数据,由于本论文缺乏植被覆盖精分类的数据,无法区别乔木、灌木,草坪的类别,也无法获得其冠面面积的大小,另外,遥感图像中每个像元是30 m × 30 m范围内地物的综合反映,所以无法精确求出覆盖面积,然而,植被覆盖度是植被(叶、茎、枝)在地面的垂直投影面积所占统计面积的百分比。其值的大小代表每个像元内植被所占的比例,即30 m × 30 m内植被的垂直投影面积为30 m × 30 m × Fv,Fv是植被覆盖度。那么整个统计区域的绿化覆盖率可以近似以公式(3)计算得到。
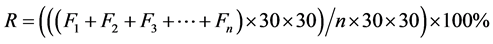 (3)
(3)
其中,R为植被覆盖率, 为每个植被覆盖度像元的值,n为像元个数。化简公式为(4)。
为每个植被覆盖度像元的值,n为像元个数。化简公式为(4)。
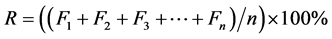 (4)
(4)
2) 道路绿化定量评价
根据“国家城市森林”评价指标规定,公路和铁路等道路绿化率需达80%以上。同时依据《昆明市城镇绿化条例》规定 [11] :铁路、轨道交通两侧绿化宽度各为15~30 m。本论文建立昆明市主城区一级道路、二级道路、三级道路和铁路的缓冲区,由于一级道路、二级道路、三级道路、铁路的宽度各不相同,但是却都是以线要素储存,根据《公路工程标准》规定 [10] ,一级道路车道数为4,行车道宽2 × 7 m;二级道路车道数为2,行车道宽为7 m;三级道路车道数为2,行车道宽度为6 m。所以本论文一级道路以14 m为半径建立缓冲区,二级道路以7 m为半径建立缓冲区,三级道路以6 m为半径建立缓冲区,道路绿化率计算方法同公式(4)。
3) 湖泊、河流等水体沿岸绿化定量评价
根据“国家城市森林”评价指标规定,江、河、湖、海等水体沿岸绿化率达80%以上。同时依据《昆明市城镇绿化条例》第十三条规定 [11] :滇池主要入湖河道两侧绿化宽度各为30~100米。本论文湖泊、河流宽度权重建立缓冲区,以规定最大值100 m为标准建立昆明市主城区湖泊(湖泊为面要素)等湖泊的环形缓冲区,以规定最小值30 m为半径建立河流(河流为线要素)的缓冲区。湖泊河流等水岸绿化率计算方法同公式(4)。
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 植被覆盖度分布特征
采用等间距分割法将地表覆盖度分为5级见表1 [12] 。根据分级标准对植被覆盖度图像进行等级划分,并赋予相应的颜色:白色表示极低覆盖度,黄色代表低覆盖度,绿色代表中度覆盖度,蓝色代表高覆盖度,紫色代表极高覆盖度。得到5期植被覆盖度分级图见图1。
从图1可以看出,2003年五华区、盘龙区以及四周等建设用地呈现白色,为极低植被覆盖区域,滇池东西两岸呈现黄色与绿色,为低覆盖和中度覆盖,西山区北部、官渡区北部以绿色和蓝色分布为主,为中度覆盖和高覆盖;2005年五华区、盘龙区以及四周仍以极低覆盖为主,滇池东西两岸以绿色、蓝色分布为主,为中度覆盖和高覆盖,滇池西岸,出现少量紫色,有极高覆盖区域。官渡区东北方向出现大量的蓝色和绿色,以中度覆盖和高度覆盖为主。西山区西北方向以绿色、蓝色分布为主,为中度覆盖和高覆盖,且出现紫色区域,为极高覆盖;2009年,除五华区、盘龙区及其四周以极低覆盖为主以外,西

Table 1. The classification of vegetation coverage
表1. 植被覆盖度分级
山区、官渡区和滇池东西两岸均以中度覆盖为主,在西山区、滇池东西两岸以及官渡区东北角出现高覆盖区域;2013年,极低覆盖除分布在五华区、盘龙区以外,在西山区和官渡区也出现了较多的极低覆盖,但是,西山区西北角和官渡区东北角以大量的高植被覆盖为主,滇池东岸有少量的中、低植被覆盖区域,西岸以高植被覆盖分布;2014年,西山区西北角和官渡区东北角仍以高植被覆盖分布,滇池西岸以中、高植被覆盖为主,其余部分以极低植被覆盖为主。另外,整体对比2003年~2014年植被覆盖等级分布图可知,2013年和2014年官渡区出现了大量的白色区域,根据赵雷 [13] 等人研究结果显示,昆明市官渡区城乡用地发展方向主要两个方向:一是主要向西南方向扩展,逐渐延伸到星海半岛、福保半岛以及宝丰半岛三个半岛片区,以居住、旅游、休闲等为主,东南方向与新城区呈贡相接。二是东北方向,是新机场和大板桥工业布局地区,其土地需求量将发幅度增加,其研究情况与本文2013年、2014年官渡区白色增加区域基本相符。
3.2. 不同行政区植被覆盖度等级分布
本论文利用ArcGIS数据处理软件对各个植被覆盖度等级面积进行统计。由于植被覆盖度重分类后其属性表中COUNT字段表示各植被覆盖度等级的像元个数,而且我们使用的数据空间分辨率为30 m × 30 m,所以对COUNT字段进行30 × 30计算,即可得到各等级植被覆盖度面积,并通过面积制表功能统计不同行政区各等级植被覆盖所占比例,统计结果见图2。
由图2可知:2003年,五华区和盘龙区极低植被覆盖比例均高于80%,且盘龙区极低覆盖所占比例高于五华区,西山区和官渡区极低植被覆盖所占比例高于40%;低植被覆盖比例从高到低依次排序为:西山区 > 官渡区 > 五华区 > 盘龙区;中度植被覆盖比例官渡区最高,西山区其次,盘龙区最低;西山区和官渡区高植被覆盖比例为9.6%,五华区和盘龙区高植被覆盖比例低于1%,西山区极高覆盖比例为2.1%,官渡区极高覆盖比例为0.7%,而五华区和盘龙区低于1%。2005年2月极低覆盖比例在五华区和盘龙区在80%,在西山区和官渡区比例高于40%;低植被覆盖、高植被覆盖和极高植被覆盖比例,在官渡区、西山区均高于盘龙区和五华区,植被覆盖情况大致和2003年情况一致。2009年,在极低植被覆盖中,五华区覆盖比例低于80%,盘龙区覆盖比例为85%,西山区和官渡区仍高于40%;在低植被覆盖中,五华区覆盖比例为21.9%,盘龙区覆盖比例为13.5%,西山区和官渡区覆盖比例达30%以上,在整体覆盖比例情况较2005年有所改善。在高植被覆盖和极高植被覆盖中,官渡区覆盖比例高于西山区,五华区和盘龙区几乎为0%。2013年,五华区和盘龙区极低植被覆盖比例高达90%以上,西山区和官渡区达到60%以上。五华区和盘龙区随着植被覆盖度等级的增加,所占比例越来越小,到极高植被覆盖时几乎为0%。西山区低植被覆盖、中度植被覆盖、高植被覆盖以及极高植被覆盖比例均高于盘龙区。2014年,五华区、盘龙区极低覆盖比例仍高于90%,西山区高于60%,官渡区高达70%以上;低植被覆盖在西山区分布最多,为15.8%,官渡区其次,为10.6%,五华区和盘龙区两行政区总和为6%左右;高植被覆盖和极高植被覆盖在官渡区和西山区分布总和约为10%,五华区和官渡区分布极少。
整体对比2003年4月~2014年2月间昆明市主城区植被覆盖情况可知:五华区和官渡区极低覆盖类型的比例每年高达80%以上,植被覆盖面积较少,大部分植被覆盖以低植被覆盖较多,中植被覆盖以上分布较少;西山区和官渡区极低覆盖类型的比例每年高达40%以上,到2013年和2014年甚至高达60%以上,低植被覆盖比例约10%~31%左右,2009年高达30%,2013年和2014年低至10%,这可能是由于昆明市主城区城市扩大的原因所致,西山区和官渡区在城乡建设中有大量的建筑物、道路等城市用地出现。
3.3. 城市森林定量评价
本论文通过ArcGIS区域分析功能统计5期城市森林、道路、铁路、河流以及湖泊等各指标植被覆盖度像元个数和像元值总和,统计见表2。
由表2可知:依据“国家森林城市评价指标”规定:南方城市森林覆盖率达到35%以上;公路、铁路等道路绿化率达80%以上;江、河、湖、海等水体沿岸绿化率达80%以上。2003年~2014年间,昆明市城市森林覆盖率均在35%以上,符合“国家森林城市”评价指标。道路、铁路绿化率在2013年之后达到80%以上,2003年~2009年未达到80%,铁路绿化率大于道路绿化率。河流绿化率在2003年~2014年间均达到80%以上,然而,湖泊绿化率在2003年~2009年间,没有达到80%以上,2013年~2014年达到了指标。从表2还可以看出,在2003年~2009年间,河流、道路绿化植被没有达到要求,2013年~2014年,各项城市森林建设指标均达到了“国家森林城市”评价指标的要求,说明昆明市主城区在道路、铁路、河流、湖泊和城市森林等指标达到了“国家森林城市”建设的评价指标,昆明市加强了道路、河流的绿化建设,同时在湖泊绿化建设中也加大了力度。而城市森林指标覆盖指标逐渐降低,到2014年2月

Figure 2. The vegetation coverage area of different administrative region
图2. 不同行政区植被覆盖度面积变化

Table 2. The standard of urban forest construction
表2. 各项城市森林建设指标
达到了标准边缘,这可能是由于近几年昆明市城乡建设中,大量土地需求导致部分草地、农田转变为城市用地,工业用地等。
4. 结论与讨论
昆明市主城区2003年~2014年西山区和官渡区有大量的植被覆盖,植被覆盖度等级较高,五华区和盘龙区植被覆盖较少,植被覆盖度等级较低。
以2003年、2005年、2009年TM遥感影像、2013年、2014年Landsat 8遥感影像数据为数据源,提取2003年~2014年归一化植被指数(NDVI),并通过像元二分法估算昆明市主城区植被覆盖度,通过对植被覆盖度的分级处理,分析不同行政区昆明市主城区植被覆盖等级变化趋势以及不同行政区植被覆盖等级分布。定量评价昆明市主城区城市森林建设情况。结果表明:2003年~2014年昆明市主城区西山区和官渡区有林地覆盖区域NDVI值相对较高,五华区和盘龙区城市用地覆盖NDVI值较低,水体NDVI值最低。西山区和官渡区植被覆盖度等级分布比五华区和盘龙区高。道路、铁路、湖泊、河流等指标基本达到“国家森林城市”评价指标的标准。
基金项目
云南省教育厅科学研究基金项目(2014J098)。