1. 引言
土壤侵蚀引起的土壤养分流失、土壤质量退化及水土流失等问题一直是我国科学研究的重点[1] -[5] 。我国南方红壤地区水热资源丰富,降水丰沛且多暴雨,垦殖指数最高,为土壤侵蚀提供了良好的基础与动力,使得该区域成为水土流失最为严重的地区[6] 。而降雨和地形因素则是该区土壤侵蚀退化的最主要影响因子[7] ,分析降雨对水土保持治理、土壤侵蚀具有重要的参考价值[8] 。国内外采用天然降雨与人工模拟降雨相结合的研究手段,对土壤侵蚀及退化规律开展了大量研究,重点分析了黄土坡面产流与产沙的关系,并得到许多经验方程和水文模型[9] [10] 。但红壤结构状况和物质组成与黄土性质迥然不同,土壤结构特征及其对坡面水文过程的影响也存在显著差异,再加上在降雨–径流–泥沙–入渗的水文过程中表层土壤容易受到植被、地形、降雨等外界条件影响[11] ,直接参考或引用其规律、模型,一定程度上影响了红壤水土流失的治理效果。本文以湖南省长沙市浏阳河流域第四纪红色粘土为研究对象,通过室内人工模拟降雨,从降雨强度对湖南低山丘陵区红壤坡面水文过程的影响进行研究,分析不同降雨强度对坡面水文过程的影响,为红壤坡面水文过程的研究提供科学参考。
2. 材料与方法
2.1. 试验设计
本研究采用自制侧喷式降雨器模拟天然降雨,降雨高度为6.5 m,为保证降雨强度的均匀性和天然降雨的相似性,雨水先喷打在直径5 mm过滤网上然后降落,使雨滴达到终点速度。试验土槽为自制钢制土槽,规格为2 m × 0.3 m × 0.3 m,底部有直径5 mm小孔。根据研究区红壤的特点,试验设计红壤坡度为15˚,并设计5个降雨强度(55 mm∙h−1、70 mm∙h−1、85 mm∙h−1、100 mm∙h−1、120 mm∙h−1),降雨均匀度在85%以上,降雨时间为60 min,每个试验重复2次,取平均值进行计算和分析。
2.2. 试验材料
供试土壤采自湖南省浏阳河流域长沙段,属第四纪红粘土母质发育的红壤,其基本物理性状见表1。质地较粘重,吸水性强,但田间持水性不高,富含铁、铝氧化物,呈酸性。试验用土过10 mm筛,自然风干至初始含水量为15%,土壤样品原有自然结构被破坏,属于被扰动土壤。
2.3. 试验材料
首先在土槽底部装填大约3 cm厚的沙子,上铺透水纱布来模拟天然透水层,然后以5 cm为间隔分层装填27 cm的试验土壤。
每场试验均在降雨10 min后揭开遮雨布并记录降雨时间,降雨历时均为60 min。坡面开始产流后,记录开始产流时间,并采集径流泥沙样品,每次采样时间为1 min。试验结束后,测量每一个径流泥沙样的重量,用烘干法测出坡面径流含沙量,并用排除法计算相应径流量。
降雨结束后,以5 cm分层采集土样,共计162处,测定土壤含水量,以分析土壤入渗水分分布状况。
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 降雨强度对坡面产流时间的影响
在坡度相同的条件下,随着降雨强度的不同,开始产流时间存在着差异(见表2)。研究表明,雨强在55 mm∙h−1~85 mm∙h−1之间,产流时间大约在30 min左右,雨强增加到100 mm∙h−1和120 mm∙h−1时,产流所需时间突然急剧减小至9 min左右,说明85 mm∙h−1到100 mm∙h−1雨强之间产流形成机制及影响产流形成的主要因素发生了极速转变,同时考虑到试验时间长、环境气温、设备或人工操作等因素会对土壤层物理环境及性质产生影响,也会使得实验结果出现一定误差。在100 mm∙h−1与120 mm∙h−1大雨强影响下,地表土壤受降雨打击力明显,地表土壤容易结皮,从而影响下渗,缩短产流开始时间。除85 mm∙h−1外,地表开始产流时间与降雨强度的关系表现为开始产流时间随降雨强度增大逐渐缩短,这也与之前的研究结果相一致[12] [13] 。研究表明土壤层产流形成过程主要是由降雨强度决定的,降雨强度越大,单位时间内坡面所承受的降雨量就越大,土壤表层达到田间持水量的时间缩短,所以产流所需要的时间必然缩短。此外雨强越大,降雨产生的动能越大,则坡面就越容易产生结皮,在一定程度上影响到坡度的开始产流时间。
3.2. 降雨强度对坡面产沙强度的影响
产沙强度是随着降雨强度的增加而增大的,不同降雨强度下表现规律又略有不同,这与郑粉莉等[12] 研究发现红壤坡面土壤侵蚀量随雨强的增大明显增大的结果相一致(见图1)。分析表明,55 mm∙h−1降雨强度下地表便开始产沙,产沙在降雨30 min后出现,产沙时间较晚且强度不大,仅在50 min后略有上升,平均产沙强度在0.49 g∙min−1左右;70 mm∙h−1与85 mm∙h−1雨强的产沙强度随降雨时间变化规律基本一致,均是产流初期较小且增长缓慢,之后突然增大以波状趋于平稳;100 mm∙h−1雨强的平均产沙强度较大为 6.90 g∙min−1,且在降雨后期产沙强度呈减小的规律表现明显;而120 mm∙h−1的产沙强度最大,最大值达到33.6 g∙min−1,平均产沙强度为17.91 g∙min−1。100 mm∙h−1与120 mm∙h−1雨强下产沙强度大,且其产沙规律随降雨时间与其他雨强略有不同,主要表现在产沙强度随降雨时间迅速达到最大值后又逐渐减小。其原因可能是大雨强下,雨水对地表打击力大,使得表层土壤土粒松散,松散的土粒在地表产流冲刷下流失,产沙强度越来越大形成产沙高峰;同时大雨强对地表的打击作用加强,使得地表致密层厚度变大,土壤结构抗侵蚀能力加大,表层土壤大面积被冲刷侵蚀而产生细沟,导致土层高度低于产流出口高度,泥沙受重力影响淤积在槽口处不能流出,所以产沙强度逐渐减小。

Table 1. Basic physical properties of red soil from Changsha section of Liuyang river
表1. 浏阳河流域长沙段红壤基本物理性状

Table 2. The time of starting flow in different rainfall intensity under the condition of rainfall
表2. 降雨条件下不同降雨强度的开始产流时间(单位:min)
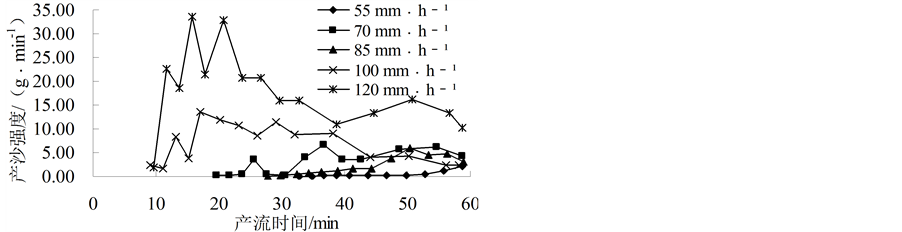
Figure 1. The runoff rate in different rainfall intensity
图1. 不同降雨强度下产沙强度的变化
3.3. 降雨强度对坡面产流强度与入渗强度的影响
根据坡面降雨产流过程,定时采集径流样,并计算出产流强度H (mm∙min−1)和坡面平均入渗率ia (mm∙min−1) [14] ,结果见图2。在降雨初期,由于土壤初始含水率较低,雨水以入渗为主;降雨一段时间后,各降雨强度试验才逐渐出现地表产流;随降雨强度的增大,地表产流强度均呈现增加趋势,相应地入渗强度逐渐减小,但在雨强为85 mm∙h−1时出现特殊情况,相同时间内的产流强度均小于70 mm∙h−1,说明可能存在临界降雨强度现象。
不同降雨强度下,地表入渗强度随产流时间一般呈指数下降趋势,相应地产流强度随产流时间呈对数上升趋势,这一规律与张会茹等[13] 研究发现的径流率和入渗率与降雨历时的关系相一致。各降雨强度的产流强度对数关系系数随降雨强度基本呈波状变化,规律性不明显;特别在100 mm∙h−1与120 mm∙h−1降雨强度下,产流强度对数关系系数明显减小,相关系数更小。这是由于100 mm∙h−1和120 mm∙h−1降雨强度下产流强度在地表产流后迅速达到一个峰值,然后随降雨时间基本稳定;可能因为降雨强度大,地表土层受降雨强度打击大,地表结皮快,表层土壤迅速达到饱和,雨水下渗稳定,从而导致地表产流过程速度快,强度大,持续性强。随着降雨强度的增大,产流强度超过入渗强度的交叉点逐渐提前,说明降雨强度越大,产流增强的速度越快,雨水越容易以地表产流形式流失。所以,影响产流、入渗强度在降雨过程中变化趋势的最主要因素是降雨强度。
3.4. 降雨强度对坡面水文过程的影响
在试验过程中,土壤蓄水量随土层深度增加存在明显的变化(见图3),上层土壤含水量均有增加,这是由于本试验土壤初始含水率是15%,而土壤初始含水率越高受降雨强度的影响越小,初始含水率达到31%之上时,降雨对其含水量变化毫无影响[15] 。在不同降雨强度下,土层深度0~15 cm范围内蓄水增量基本相等,约在8.50~9.80 mm之间,但在15~30 cm深度范围内随深度变化越来越明显,除85 mm∙h−1降雨强度外,土壤蓄水量均随深度增加而减少,这是因为表层土层透水性相对底部较好,产生的壤中流在槽底的阻挡下顺已设置的壤中流出口流出,所以土层在一定深度范围内达到田间持水量,而超过这个深度范围后,土壤含水量就会越来越小。

Figure 3. Impoundage on every layer in different rainfall intensity
图3. 不同降雨强度土壤蓄水量随深度的变化
此外,由图还可以看出,有土壤蓄水量值在最底层出现突然变小现象,这是因为有壤中流试验槽底层铺有3 cm

Table 3. R, Iρ, Wρ in different rainfall intensity
表3. 不同降雨强度的R、Iρ、Wρ
的细沙模拟天然透水层,而实际土壤层只有27 cm,所以计算的底层土壤深度只有2 cm,则蓄水量值较小。
当室内试验土槽表面裸露、平整时,一次降雨的入渗量(Iρ)可认为是降雨量与径流量之差 [16] ,结合计算的土壤蓄水量(Wρ)见表3。可见,径流量R随降雨强度增大逐渐增大;Wρ与Iρ随降雨强度的变化规律基本相似,均随降雨强度的增大先增大后减小,在降雨强度100 mm∙h−1出现拐点,蓄水比例逐渐减小。Wρ相对于Iρ较小,这是因为取样时间大约需要2 h,而在取样过程中入渗不会间断,又红壤吸水性强,但蓄水能力差,部分入渗量在取样过程中在槽底流失,则实际土壤含水率应比所测值大。
本文通过室内人工模拟降水试验分析降雨强度对红壤土坡面水文过程的影响,由于实验条件的限制以及人工操作等原因,使得实验结果具有一定的局限性,还需要野外实验论证。但本文研究了不同降雨强度下的红壤坡面水文过程,为红壤坡面水文过程模型模拟的确立提供了数据支持和科学依据。
4. 结论
1) 降雨强度是影响坡面产流形成的主要因素,坡面产流时间基本随降雨强度的增大逐渐提前,尤其在雨强为100 mm∙h−1与120 mm∙h−1时迅速提前。
2) 降雨强度是坡面产沙的根本动力,各降雨强度下坡面产沙量均随降雨强度的增大而增大,在100~120 mm∙h−1雨强下,产流后期地表产沙强度随降雨时间逐渐减弱。
3) 随降雨强度增大,坡面产流量、入渗量、地表产流总量与入渗总量均呈增加趋势,而蓄水比例呈现减少趋势;坡面入渗强度随产流时间一般呈指数下降,相应地坡面产流强度随产流时间呈对数上升,但100 mm∙h−1与120 mm∙h−1大雨强时产流强度对数关系的相关性较差。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金(4157011554)、湖南省“十二五”重点学科建设项目(地理学)和湖南省高校创新平台开放基金(12KD35)资助。