1. 引言
地下水相对于地表水是优质可靠的供水水源,黄泛平原井灌区,年平均降水入渗系数为0.25 [1] ,按照地下水多年平均采补平衡的原则,仅靠开采每亩土地上的降雨地下水入渗补给量也不能满足正常产量下的作物需水,需要袭夺地下水侧向径流量、非农业土地面积下的浅层地下水、河流、沟渠渗漏量或者增加引用地表灌溉用水量。地下水超采形成大面积下降漏斗,导致各种地质灾害,并加剧了地下水污染。由于生产力的迅速发展和环境污染的日趋严重,迫使含水层补给的理论和方法取得突破性进展[2] 。黄泛平原引黄灌区除了具有浅层地下水条件,还可以引黄河客水灌溉,同时利用纵横交错的沟渠渗漏补给地下水。但是在引黄灌区的末端,引黄水量和时间均受到上游限制和影响,如何在有限的引黄时间里扩大引黄水的渗漏补给量,是面临的挑战。
针对山东省大部分平原井灌区,特别是黄泛平原漏斗区存在的灌溉农业水供需矛盾尖锐、浅层地下水超采并导致大面积地下水漏斗区地面沉降等灾害问题[3] ,提出了明沟–地下滤水管–竖井高效生态的地下水回灌系统,并在处于黄泛平原内的临清市进行回灌试验研究。为了分析回灌效果,本文结合田间实验,利用Hydrus-2D模型对明沟–地下滤水管–竖井[4] 含水层补给系统进行数值模拟与分析,为黄泛平原漏斗区的地下水补给提供科学依据。
HYDRUS是由J.Simunek,T.Vogel和M.Th.van Genuchten等开发的基于Windows接口的变饱和带多孔介质内二维或三维水、热、溶质流动有限元模拟分析模型,包括Hydrus-1D/2D/3D等版本。国内外学者对土壤水分运动做了大量的模拟工作并用Hydrus软件进行了分析。马欢等利用Hydrus-1D模拟了华北平原引黄灌区田间条件下土壤水分动态过程,得出模型对土壤含水率的模拟精度较高[5] 。Cote等利用Hydrus-2D模型分析了地下滴灌条件下的土壤水分运动及溶质运移,强调Hydrus2D能够很好地展示所模拟系统的工作原理,并且通过分析输出结果为系统设计和管理的完善提供依据[6] 。
2. 研究区概况
2.1. 地理位置
临清市位于鲁西北平原,隶属山东省聊城市。车庄沟为鲁北平原中小河道,属海河流域漳卫运河水系,位于临清市西南部陈公堤以东的大沙河河槽洼地,原是黄河故道,经历代群众排水疏浚而成一条南北向的排涝沟,全长28 km,流域面积222.7 km2,其中临清市境内长25 km,流域面积199.7 km2。本项目的研究区选在临清市八岔路镇万庄村的一块农田中,车庄沟支流流经该农田。
2.2. 水文地质概况
2.2.1. 浅层地下水含水层分布
根据当地80年代的水文地质调查图集及以往地下水普查及钻井资料可知:地下水类型主要为松散层类孔隙水。上层为淡水,下层为咸水。其中,最具有供水意义的是上层(浅层潜水–微承压水),即浅层地下水,厚度约为60 m。物探和岩土勘探结果表明,60 m深度内的岩性可分为上、中、下三部分,上部,埋深区间0~15 m为亚砂土、粘土互层,其中8~15 m局部有粘性土分布,构成包气带和水位变动带;中部15~35 m是储存浅层潜水–微承压水的主要部位,主要由粉细砂、细砂、中粗砂组成,含水层顶板埋藏深度为15~20 m,含水砂层厚度为20~25 m,因其厚度大、颗粒粗、含水性好,分布稳定,成为本区最主要的供水含水层;下部35~60 m总的特点是亚砂土夹粉细砂,间有细砂层,形成了一个较为稳定的含水层。
2.2.2. 地下水补给排分析
浅层地下水的补给、径流、排泄决定于含水层的厚度、岩性成分和埋藏条件,同时又与水文、气象、地形地貌等有着密切的联系。另外,人类活动又使地下水补给、径流、排泄条件发生变化。从目前条件来看,浅层地下水以垂向运动为主,水平方向上的循环交替微弱。
目前条件下,该区浅层地下水主要以大气降水、引黄灌溉及渠道侧渗补给为主。灌溉回渗补给是本区浅层地下水资源的重要补给项量,根据灌溉水源分为引黄灌溉回渗和地下水灌溉回渗。区内的河渠,包括尚潘渠、友谊渠均是引水和排洪渠道[7] ,在引水及汛期补给地下水,干枯期间与地下水无联系。
地下水径流主要受控于不均匀的开采强度、地表水文和地形地貌因素。地下水径流方向基本上与地形倾斜方向一致,由西南向东北缓慢流动,水力坡度2/10000~4/10000。
浅层地下水的排泄方式主要是人工开采和水面蒸发。随着浅层地下水的大量开采利用,人工开采占浅层地下水排泄量的比重越来越大,是本区主要排泄量之一。通过水量平衡计算可知地下水和黄河水为临清市的主要供水水源,而且地下水超采量为5024万m3,临清市区及周边已形成约30 km2的地下水降落漏斗,由观测资料可知,从70年代平均地下水埋深从4 m下降到现在的10 m左右,严重影响了当地社会生产和生态环境。蒸发量的大小与水面蒸发强度成正比,与地下水位埋深成反比,因而伴随着地下水位埋深的增大,潜水蒸发量衰减。
2.3. 土壤入渗特性
为查明研究区土壤的渗透性,选取研究区农田两处作为试验点,进行野外双环渗水试验,即向表层土中进行注水,当一定的水量完全渗漏所需时间基本稳定时,利用达西定律的原理求出渗透系数。分析结果见图1。
通过野外双环渗透试验可知,两处试验点的渗透速度都基本稳定于2.8 m/d,说明了研究区不同位置处于相对均质的同一水文地质边界内。根据临清市勘探资料可知,0~20 m的地层,渗透系数为0.2~2.4 m/d,与试验结
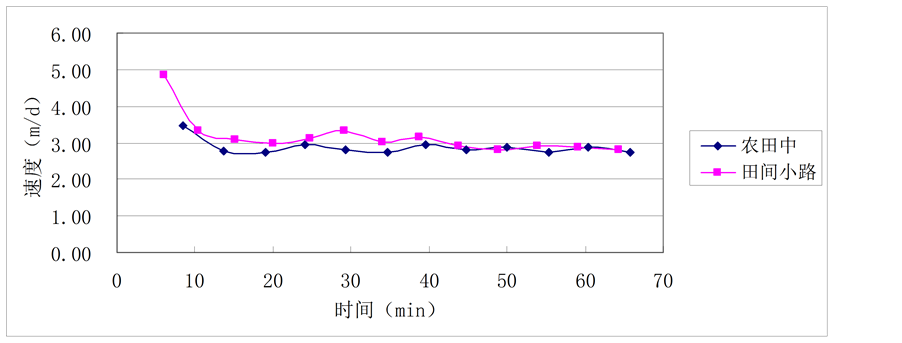
Figure 1. The changing curve of infiltration rate with time
图1. 渗透速度随时间变化曲线
果基本一致。
3. 明沟–地下滤水管–竖井补给系统数值模拟
3.1. 水文地质数学模型
HYDRUS-2D软件中的HYDRUS模型包含了模型应用的数学模型。非饱和带多孔介质中水分流动采用了Richards方程[8] (Richards, 1931):
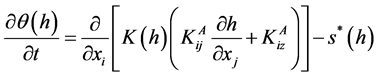 (1)
(1)
在Richard方程(1)中,θ、h、K分别为土壤体积含水量、负压水头项及非饱和水力传导度;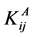 为无因子各向异性张量;K(h)为压力水头下的导水率;xi为空间坐标系;t为时间项;s*为源汇项,代表了因为植物吸水引起的体积含水量的减少,本文模拟中不涉及到植物吸水影响。
为无因子各向异性张量;K(h)为压力水头下的导水率;xi为空间坐标系;t为时间项;s*为源汇项,代表了因为植物吸水引起的体积含水量的减少,本文模拟中不涉及到植物吸水影响。
HYDRUS-2D采用van Genuchten模型[9] 描述非饱和土壤水力特性,参数选择基于下式而定。
 (2)
(2)
式中,q(h)为土壤物理特征曲线;θr土壤残余含水率;θs为土壤饱和含水率;h为压力水头;Ks为饱和导水率;α,n,m和l为经验常数。
3.2. 水文地质概念模型及参数选取
3.2.1. 研究区概念模型
通过对研究区的水文地质状况的分析和总结,结合当地地下水开采的利用现状,以及该区包气带的渗透性、饱和度以及含水率等,将研究区概化为均质、各向同性介质的二维非稳定流模拟问题。明沟–地下滤水管–竖井系统的设计平面图如图2,计算的概念模型如图3(a),图3(b)所示,分别为仅明沟和仅地下滤水管两种模拟情景下的概念模型图,模拟区域长300 m,垂向深16 m,其中研究区内明沟长度取200 m,沟底宽度取4 m,地下滤水管长为200 m,直径为0.3 m。

Figure 2. The design plan of open canal-underground perforated pipe-shaft system
图2. 研究区明沟–地下滤水管–竖井系统设计平面图

 (a) 明沟(open canal) (b) 地下滤水管(perforated pipe)
(a) 明沟(open canal) (b) 地下滤水管(perforated pipe)
Figure 3. Conceptual model diagram of open canal-underground perforated pipe-shaft system
图3. 研究区明沟–地下滤水管–竖井系统概念模型图
3.2.2. 研究区边界条件概化
针对车庄沟平原漏斗区浅层地下水超采严重,长期地下水埋深超过六米,采补不均衡的问题以及周边有一定的引黄和引河补给的条件,相机利用沟渠引蓄客水、当地多余的雨洪地表水,利用促渗工程,将地表水转化成地下水,储存在含水层中,以供今后农业灌溉用水。
通过对研究区的水流特征以及项目的布局状况,在模型计算中,地下滤水管和明沟底部(图3中的粗线区)处理为定水头边界,为3 m,模型不考虑地面的降雨入渗和蒸发,因此上边界设为隔水边界,两侧及底部边界均设为隔水边界。模型的初始水头分布如图4所示。
3.2.3. 两种情景下网格剖分及观测点布置
情景一:明沟渗漏补给的模拟
网格剖分采用非均匀剖分,明沟渗漏模拟网格剖分如图5所示,明沟区域进行网格加密,在整个模拟区域剖分713个三角形单元格,模拟区内选择1个观测点,位于明沟下方初始水面处,如图5所示。

Figure 4. The distribution of initial head in model area
图4. 模拟区初始水头分布
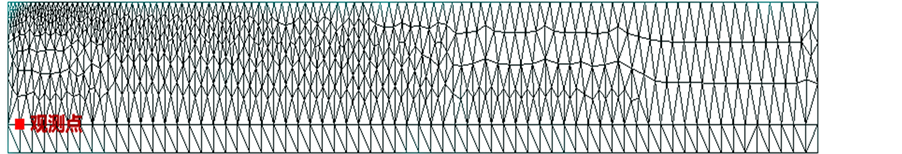
Figure 5. Mesh generation of the open canal simulation
图5. 明沟渗漏模拟网格剖分

Figure 6. Mesh generation of the underground perforated pipe simulation
图6. 地下滤水管渗漏模拟网格剖分
情景二:地下滤水管渗漏补给的模拟
网格剖分采用非均匀剖分,明沟渗漏模拟网格剖分如图6所示,地下滤水管区域进行网格加密,在整个模拟区域剖分745个三角形单元格,模拟区内选择2个观测点,分别位于滤水管下方的初始地下水面处和两滤水管中间处下方初始水面处,如图6所示。
3.2.4. 模拟参数的选择
对于两种情境下的模拟,由于处于同一区域,参数的选择是一致的。整个模拟期为7天,将其划分为70个模拟时段,每一个模拟时段为0.1天。对于时间步长来说,时间步长越小,计算结果越精确,本次模型模拟中时间离散参数见表1。
通过物探和岩土勘探综合分析结果可知,该区域土壤属于粉土,渗透性较好,且不存在连续的弱透水层,因此总体上不会对回灌效果产生太大影响。饱和渗透系数为2.8 m/d,均质各向同性,模型选择van-Genuchten模型来确定土壤水分特性曲线,VG模型中各参数经拟合后取值如表2所示。
3.3. 模型模拟结果分析
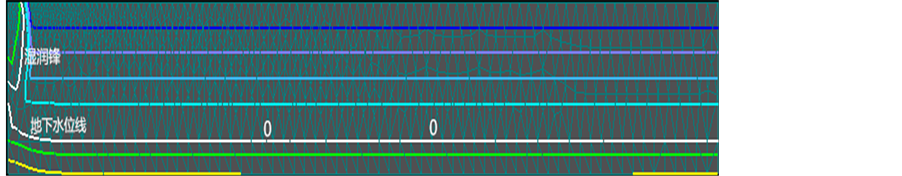
情景一:图7、图8分别为选取的各个时段的水头等值线图和观测点水头变化曲线图,从图中可以看出回灌过程中土壤饱和–非饱和渗流变化情况及补给的效果。补给一旦开始,水分下渗形成的湿润锋就沿着明沟底部逐渐向饱和带移动。在最初约0.3天内,地下水位是不变的,只有湿润锋下移,当湿润峰与地下水的毛管上升水相遇后,引起地下水位的缓慢抬升,0.3~0.7天地下水位线抬升了3.6 m。0.8天后明沟底部下渗水的湿润锋
表1. 时间离散参数
表2. 土壤水分特性的VG模型参数

 (a) 0.7 d
(a) 0.7 d
 (b) 7 d
(b) 7 d
Figure 7. The changing curve of head contour with time (0.7 d, 7 d) in scenario one
图7. 情景一水头等值线随时间(0.7 d, 7 d)变化图
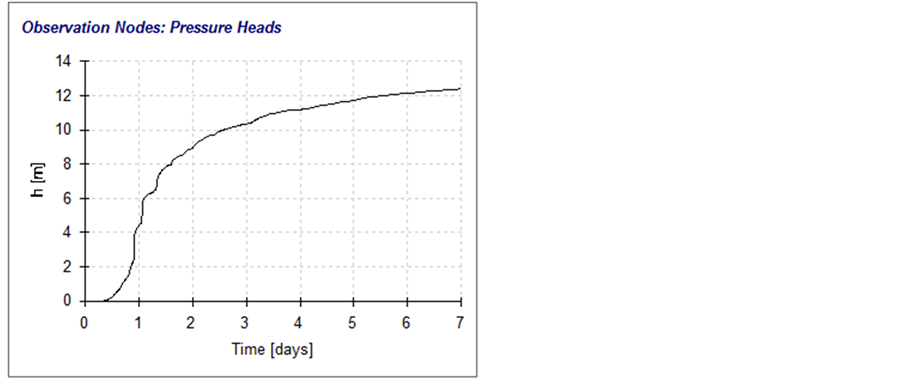
Figure 8. The changing curve of observation point in scenario one
图8. 情景一观测点水头变化曲线
与地下水位线汇合,形成一个连续的饱和带即水丘,地下水位开始大幅抬升,随着回灌补给的进行,到第7天时,明沟底部已达到完全饱和,且地下水位线上升至明沟的底部,之后水分不断侧向扩散。整个模拟期内,明沟底部的地下水位上升了约13 m。根据Mass Balance的分析数据可知,在整个模拟期内,总补给量经计算为18,026 m3。
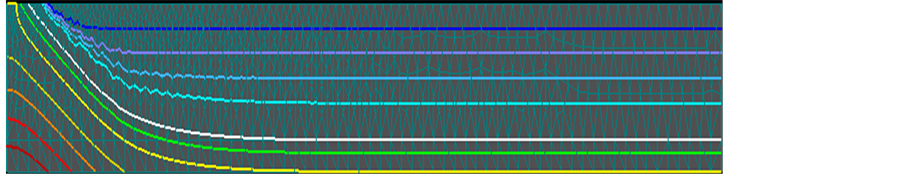
情景二:图9、图10分别为地下滤水管渗漏补给过程中的各个时段的水头等值线图和观测点的水头变化曲线图,从图中可以看出,在最初约1天内,滤水管底部地下水位是不变的,只有湿润锋的下移,当湿润峰与地下水的毛管上升水相遇后,引起地下水位的缓慢抬升,1~1.6天之间滤水管底部水位上升了3 m。1.7天后滤水管底部下渗水的湿润锋与地下水位线汇合,形成连续的饱和带即水丘,地下水位开始大幅抬升,到第7天,滤水管底部已达到完全饱和,之后水分主要是侧向进行扩散。整个模拟期内,滤水管底部水位上升了8.5 m,两根滤水管之间的地下水位上升了2.3 m。根据Mass Balance的分析数据可知,在整个模拟期内,总补给量经计算为56,224 m3。
4. 渗漏总量计算与验证
根据叠加计算,明沟和滤水管总的渗漏量为74,520 m3。实际工程中,引水时间为7天,在每根滤水管的入口处安装了电磁流量计,在整个模拟期内对水量进行实时监测,通过监测数据可知,一根滤水管7天的入渗量

 (a) 1.6 d
(a) 1.6 d
 (b) 7 d
(b) 7 d
Figure 9. The changing curve of head contour with time (1.6 d, 7 d) in scenario two
图9. 情景二水头等值线随时间(1.6 d, 7 d)变化图

Figure 10. The changing curve of observation point in scenario two
图10. 情景二观测点水头变化曲线
为21,975 m3,总入渗量为65,925 m3,与模拟结果叠加后的入渗量基本相符。由于实际运行过程中,滤水管可能发生堵塞现象,因此入渗量要小于数值模拟的结果。
5. 结论
本文针对由临清市井渠结合灌区地下水漏斗问题,利用Hydrus-2D模型对提出的明沟–地下滤水管–竖井含水层补给系统进行数值模拟与分析,模拟结果表明:
1) 水分下渗入渗形成的湿润峰沿着明沟和滤水管的底部逐渐向饱和带移动,湿润锋和地下水的毛管上升水相遇后,地下水位线开始缓慢抬升,湿润锋与地下水位线汇合后,形成连续的饱和带,地下水位开始大幅上升,情景二中增加地下滤水管后,滤水管底部地下水位抬升了8.5 m,两根滤水管之间的水位抬升了2.3 m,因此在实际工程中增加地下滤水管之后可以有效的抬升整个研究区的地下水位;
2) 随着回灌补给的进行,水分的入渗量逐渐增大,情景一中明沟在7天时间的入渗量是18,026 m3,情景二中三根滤水管的入渗量为56,224 m3,3根滤水管的入渗量占总入渗量的75.7%,模拟结果叠加后与实际工程中监测的入渗水量基本相符。因此通过布置地下滤水管可以有效的增加地下水的补给量。
基金项目
山东省重大水利科研与技术推广专项资金资助(项目编号:SDSLKY201310)。